Take the test
Zaichenko Anna Vladimirovna - Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Head of the Department of Clinical Pharmacology, Institute for Advanced Training of Pharmacy Specialists of the National Pharmaceutical University, Kharkov Bryukhanova Tatyana Aleksandrovna - Assistant of the Department of Clinical Pharmacology of the Institute for Advanced Training of Pharmacy Specialists of the National Pharmaceutical University, Kharkov
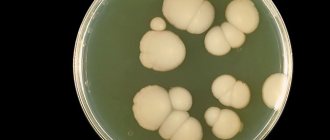
Effective treatment of fungal infections (mycoses) remains one of the most pressing and not fully resolved problems of modern healthcare. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), every third person on the planet suffers from mycoses, and 90% of people have encountered a fungal disease at least once in their lives. The incidence of these diseases is steadily increasing: every 10 years the number of patients increases 2.5 times (Klimko N.N., 2007).
Fungal skin lesions in the general structure of dermatological nosologies occupy 2nd place after pyoderma (Mikhailets N.V., 2010; Mikhailets N.V., Svyatenko T.V., 2010). The frequency of onychomycosis is about 50% of all fungal skin diseases. (Kolyadenko V.G., Zaplavskaya E.A., 1999). Every tenth visit to a dermatologist is related to these diseases. In Ukraine, over the past 10 years, the incidence of mycosis of the feet has increased 2.3 times. In some social groups (military personnel, athletes, miners), mycosis of the feet is detected with a frequency of 20–50%, among liquidators of the Chernobyl accident - 42.7% (Boiko S.Yu., 2002).
The leading role in the occurrence of mycoses belongs to dermatophytes (up to 94%). Of these, 75–85% are Trichophyton rubrum, 10–20% are Trichophyton mentagrophytes var. interdogotale and up to 3% - others (Boiko S.Yu., 1999; Glukhenkiy B.T. et al., 1999). These include the genera Trichophyton (Tr.), Microspomm, Epidermophyton (Ep.). Much less often the causative agents of fungal skin diseases are yeast and non-dermatophyte molds. Yeast fungi - saprophytes of the skin and its appendages - are detected in 69% of healthy people. Therefore, as a rule, yeasts are secondary pathogens that do not play an important etiological role (Roberts DT, 1997).
Among the main reasons causing such a wide spread of diseases in this group are:
- irrational use of antibacterial drugs;
- wide distribution of nosologies requiring the use of immunosuppressive drugs, cytostatics, glucocorticosteroids;
- an increase in the number of patients with impaired immune status;
- severe somatic disorders (for example, diabetes mellitus, etc.);
- the spread of resistant strains of pathogenic and opportunistic fungi, the development of deep mycoses, the causative agents of which are opportunistic fungi;
- difficult economic situation and low level of health education of the population.
Treatment of fungal diseases requires an integrated approach, which includes both topical and systemic therapy. Combination therapy is used to increase the effectiveness of systemic drugs, reduce the duration of therapy, and prevent relapses of the disease. Combination therapy is currently considered the most effective method of treating fungal diseases (Kutasevich Ya.F., 2000).
Today, antimycotics are one of the most numerous groups of dermatological drugs. The following groups of antifungal drugs used in the treatment of fungal diseases of the skin and its appendages are distinguished:
- antibiotics - grisans (griseofulvin), polyenes (amphotericin B, nystatin, natamycin);
- azoles - imidazoles (bifonazole, ketoconazole, clotrimazole, miconazole, etc.), triazoles (itraconazole, fluconazole, etc.);
- allylamines (naftifine, terbinafine);
- morpholine derivatives (amorolfine);
- oxypyridone derivatives (ciclopirox);
- detergents and antiseptics (iodophors, undecylenic acid, salts of quaternary ammonium bases, etc.) (Zaichenko A.V. et al., 2012).
The most significant problem that significantly limits the use of azole antimycotics is the increase in the number of resistant strains of fungi. Resistance to terbinafine, which has a different chemical structure, develops much more slowly, and at the moment most fungal strains are susceptible to it (Roberts DT, 1997).
One of the most promising groups of antimycotic drugs is drugs from the allylamine group. The most well studied and has many years of experience in use is a representative of the allylamine group - terbinafine (the drug Exifin®).
Terbinafine, discovered in 1983, belongs to the antifungal drugs from the allylamine group. It is a derivative of naftifine, from which it differs by the replacement of the phenyl ring with tert-butyl acetylene in the side chain of the molecule. This replacement provides 10–100 times higher activity of terbinafine in vitro compared to naftifine and, as a consequence, greater clinical effectiveness of the drug (Terehova Yu.B. et al., 2010).
The effectiveness of terbinafine is due to its mechanism of action, which differs from other antifungal drugs. The antifungal effect of most antimycotics is based on the effect on the cytoplasmic membranes of fungal cells by blocking the synthesis of their main component, ergosterol. Terbinafine begins to act at an earlier stage: by inhibiting squalene epoxidase in the cell membrane of the fungus, it disrupts the early stage of ergosterol synthesis. Thus, the mechanism of action of terbinafine on fungal cells is two-component: the drug has fungistatic and fungicidal properties. The fungistatic effect is due to the suppression of ergosterol synthesis, as a result of which the integrity of the cytoplasmic membrane of the fungal cell is disrupted, and the cell itself loses its ability to grow and develop. The fungicidal effect of the drug is due to the accumulation of squalene in the cell (due to inhibition of the enzyme squalene epoxidase). Squalene, accumulating in the fungal cell, extracts lipid components from the cell membrane. Lipid granules accumulating inside the cell, gradually increasing in volume, rupture the cytoplasmic membranes, thus realizing the fungicidal effect of the drug. When taken orally, terbinafine is effective against pathogens of dermatomycosis (Trichophyton, for example T. rubrum, T. mentagrophetes, T. verrusonum, T. violaceum, as well as Microsporum canis, Epidermophyton floccosum). When applied topically, terbinafine is also effective against yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida (mainly Candida albicans), as well as against Pityrosporum orbiculare (Malassezia furtur), the causative agent of pityriasis versicolor. The drug exhibits a fungicidal effect even in very low concentrations. One of the most important properties is that the minimum inhibitory and minimum fungicidal concentrations are almost the same.
The high effectiveness of Exifin® is due to the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of terbinafine. When administered orally, the active substance quickly diffuses through the dermal layer of the skin and accumulates in the lipophilic stratum corneum. Terbinafine is also excreted with sebum, resulting in its high concentrations in the hair follicles and hair. In experimental studies, it was shown that terbinafine has a more pronounced tropism for fungal epoxidases than for animals, does not affect the metabolism of sex hormones, and has high epidermo- and onychotropism. During the first few weeks after starting to take the drug orally, the active substance accumulates in the skin and nail plates in concentrations that provide a fungicidal effect. Stable concentrations of the drug are achieved after 10–14 days. When administered topically, less than 5% of the dose is absorbed, indicating minimal systemic effect. Terbinafine is metabolized in the liver to form pharmacologically inactive metabolites. At least 7 different isoenzymes of the cytochrome P450 (CYP) system are involved in the metabolism of terbinafine. The presence of 7 alternative pathways of terbinafine metabolism makes it possible to almost completely eliminate the possibility of pharmacogenetically determined ineffectiveness of the drug. The presence of several metabolic pathways sets terbinafine apart from other antimycotics, most of which have only one (less often several) metabolic pathways. Given the multifunctional nature of terbinafine as a substrate for the CYP system, it can be assumed that potential drug interactions when prescribing terbinafine will be negligible. This is another significant advantage of Exifin®, since antimycotics belong to one of the groups of drugs that have the largest number of unwanted drug interactions. The drug is excreted primarily in the urine, mainly in the form of inactive metabolites, and does not accumulate in the body. Thus, in patients with impaired liver and kidney function, the effectiveness of terbinafine does not decrease, but increases, which requires recalculation (reduction) of the dose (Gafarov M.M. et al., 2003; Koshkin S.V. et al., 2003; Fayzulina E.V. et al., 2003).
The effectiveness of the drug Exifin® is confirmed by many years of experience in clinical use for the treatment of mycoses in adults and children, as well as numerous publications on the results of the clinical use of Exifin® for the treatment of patients with mycoses of the feet and onychomycosis, as well as patients with concomitant pathology. Studies of the drug Exifin® () were carried out in dermatological dispensaries in Donetsk (City Clinical Dermatovenerological Dispensary No. 1) and Kyiv (Dermatovenerological Dispensary No. 2) (Bytsan O., 2002).
At the Dermatovenerologic Dispensary No. 1 of Donetsk, 63 patients with onychomycosis were treated with Exifin. The age of the patients ranged from 4 to 73 years. The duration of the disease is from 5 months to 40 years. The diagnosis was confirmed microscopically in all patients, and culturally in 46 (growth of Trichophyton rubrum was obtained). Damage to the nail plates of the feet was noted in 48 patients, hands - in 9, feet and hands - in 6. Adults received Exifin® 250 mg daily, children weighing up to 20 kg - 62.5 mg, 20-40 kg - 125 mg , more than 40 kg - 250 mg. The duration of treatment was 2–4 months. The results of the study indicate that Exifin® is a highly effective drug in the treatment of patients with onychomycosis caused by Trichophyton rubrum. The drug has a good safety profile, and its relatively low cost allows it to be used in patients of various segments of the population. All patients tolerated Exifin therapy well (Kutsenko I.V., 2002).
In the dermatological clinic No. 2 in Kyiv, 42 patients (22 men and 20 women) aged 18–53 years were under observation. In 18 patients (10 men and 8 women), mycosis of the feet without nail damage was determined. In 24 patients (12 men and 12 women), lesions of the skin of the feet were combined with onychomycosis. The diagnosis of mycosis in all patients was confirmed by microscopic and cultural studies. The duration of the disease is from 1 year to 19 years. Patients with only skin lesions were prescribed Exifin® 250 mg once daily orally for 16 days; detachment according to Arievich - 2 times a week; soap rinses and soda baths - daily for 10 days; treatment of lesions with 1% Exifin® cream - 1 time per day for 3 weeks. In patients with onychomycosis, systemic treatment was extended to 3 months. The nail plates were softened with a paste containing 50% urea, followed by their removal with special drills. After removal of the nail plate, the nail bed was treated with 1% Exifin® cream 2 times a day throughout the course of treatment with a systemic antimycotic.
In the group of patients without concomitant onychomycosis, clinical and mycological cure occurred in 18 patients (100% of cases). During the entire observation period, no relapses of the disease were detected. In 23 patients with lesions of the nail plates, clinical and mycological cure was noted (95.8%). The effectiveness of complex treatment of mycosis of the feet and onychomycosis was 95.5%, which is significantly higher than the results of monotherapy with systemic antimycotic drugs. No side effects were noted during treatment in any patient (Boiko S.Yu., 2002).
The results of the above-described clinical studies indicate the high effectiveness and safety of the use of terbinafine in the form of Exifin® in the treatment of mycoses (including chronic, as well as combined onycho- and dermatomycosis). Along with proven therapeutic efficacy and safety, the affordability of this drug creates an additional consumer advantage for the patient.
Thus, the drug Exifin® (terbinafine, Dr. Reddy`s Laboratories Ltd) is a highly effective drug for the treatment of fungal infections (dermato- and onychomycosis), as well as a combination of these diseases. Data on the successful experience of clinical use of Exifin® are reflected in numerous scientific publications. The drug has a good safety profile, the experience of clinical use is characterized by a minimal number of side effects. The pharmacodynamic features of Exifin® (epidermo- and onychotropicity) ensure the high effectiveness of the drug in the treatment of various types of mycoses. The pharmacokinetic characteristics of the drug (achieving a stable concentration after 10–14 days and a prolonged half-life) are optimal for the treatment of mycoses, since they allow shorter courses of therapy while maintaining the required concentration of the drug in the affected tissues. Alternative pathways of terbinafine metabolism practically eliminate the possibility of genetically determined ineffectiveness of the drug in patients with hereditary characteristics of the cytochrome P450 enzymatic system. This benefit also minimizes the risk of unwanted drug interactions. Its good tolerability, the availability of topical and oral dosage forms, and ease of use allow us to consider this drug one of the most promising in the treatment of mycoses.
Summarizing the above, it is obvious that the drug Exifin® is a well-studied, highly effective, safe and economically accessible remedy for the treatment of various types of mycoses - this gives the pharmacist and pharmacist good reason to confidently use it as a reliable tool for the pharmaceutical care of visitors to their pharmacy (algorithm).
What kind of disease is nail fungus?
Nail fungus or onychomycosis is a common disease that has an infectious form. It develops due to the active activity of microorganisms, of which there are about 50 species.
But for simplicity, they are divided into three groups:
- Dermatomycetes;
- Mold;
- Yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida.
The most common are dermatomycetes; up to 90% of cases of nail fungus are associated with types of microorganisms included in this group.
How to choose the right remedy against mycosis
To select antifungal agents, it is necessary to carry out a diagnosis, during which the prevalence, duration of the disease, and the pathogen that caused the disease will be identified. It is necessary to promptly contact a specialist who, taking into account the location of the disease, the patient’s age, and his sensitivity to the drug, will prescribe the active substance for therapy.
Causes of the disease
The causes and conditions for the development of this disease may be:
- Failure to comply with basic rules of personal hygiene;
- Contact with an infected person, as a rule, through any common objects (combs, towels, slippers, manicure and pedicure tools);
- Weak immunity, for example, while taking antibiotics;
- Various diabetic diseases;
- Age over 60 years - according to statistics, nail fungus most often occurs in people of this age;
- Impaired blood supply to the extremities, for example, varicose veins;
- The presence of fungal formations on the skin and inside the body.
In addition to the above, the following factors contribute to the development of nail fungus:
- Serious mechanical damage to the nail plate and finger injuries;
- Long-term exposure to adverse chemical factors;
- Increased sweating, wet and cold extremities with VSD;
- Flat feet, synthetic and tight shoes, that is, everything that leads to a small distance between the toes;
- Humid and warm climatic conditions of the area;
- Professional costs: manicurists and pedicurists, dermatovenerologists are more at risk of developing nail fungus;
- Frequent visits to public places, especially with wooden floors and high humidity in the premises (gyms, baths and saunas).
However, do not panic; just because you go to the gym often or if you are approaching sixty years of age does not mean that you will definitely have nail fungus.
Types and characteristics of fungal diseases of the nail plates on the feet and hands
A disease of the nail plates on the hands and feet caused by fungal pathogens is called onychomycosis.
Most often, older people suffer from this disease. The disease varies in the depth of penetration of the infection into the nail plate and the area of spread.
- Distal - nail damage is observed at the edge of the plate. The color changes: it can be grayish, yellowish or brown. The diseased area gradually grows in size. The surface becomes rough, delaminates, and crumbles.
- Lateral - develops on the sides of the nail, can involve both one and both sides of the plate.
- White superficial onychomycosis is characterized by multiple whitish spots on the surface of the nails. The top layer is destroyed, and the resulting scales completely destroy the nail.
- Proximal - the cuticle is affected, the inflammatory process begins. A white spot forms at the skin ridge itself, growing over the entire nail. The shine disappears, the color of the plate becomes cloudy, it crumbles and collapses.
- Total – the entire nail plate is destroyed.
Important! The same patient may experience several forms of damage to the nail plates.
Nail plates are affected by various fungal pathogens, including:
- dermatophyte fungi;
- yeast-like fungi;
- mold fungi.
In total, there are more than 50 subspecies of microorganisms that cause fungal nail infections.
Symptoms of the disease
Like any disease, nail fungus has symptoms even in its early stages.
You should worry and visit a doctor if:
- Constantly feel itching of your fingers, especially their tips;
- Redness and other changes in skin color around and under the nails;
- Ingrown, peeling, deformation and brittleness of nails;
- Changing the color of your nails.
In later stages, symptoms become more severe:
- More painful itching;
- Severe burning sensation;
- The nail crumbles or, conversely, thickens (depending on the type of fungus);
- Inflammation;
- Wet limbs;
- Dysbacteriosis;
- General weakness and drowsiness.
If you notice any symptoms of nail fungus, you should immediately contact a dermatologist for diagnosis. If the presence of fungus is confirmed, the dermatologist will determine its type and prescribe appropriate treatment.
What to use for diabetes?
When you have diabetes, a lot of problems accumulate in the body, and any treatment, especially fungal diseases, should be carried out differently from everyone else. Many drugs for the treatment of such pathologies may be contraindicated for diabetics.
There are very important rules for diabetic patients , not only in terms of treating fungal diseases, but also all others.
- You need to be treated immediately when the first symptoms appear, even if you have to take prohibited drugs, then in a much smaller dose and for a much shorter time.
- Treatment can only be done under the supervision of a doctor; self-medication is strictly prohibited.
- The best way out is to treat the fungal infection at the earliest stage with local remedies, so you certainly won’t harm yourself.
Preparatory procedures
Before using antifungal medications on nails, it is recommended to identify the type of fungus.
There are many types of fungus, which only an experienced doctor can identify. Taking this kind of ointment on your own is highly undesirable.
Before use you must:
- Wash your feet thoroughly with laundry soap;
- Take a bath with soda, salt or any other disinfectant;
- Treat your nails with a special nail file from the pharmacy;
- Rinse and dry your feet again;
- Apply the product according to the instructions.
Below we will talk about the most common means of combating nail fungus.
What to use?
Attention! The fungus is very difficult to treat, so you need to treat it with all means at once: just one thing will not help you.
- There should be no breaks in the fight against fungal infections of the plates.
- It is not recommended to do mechanical correction on diseased nails - this will only provoke the spread of the disease further.
- Do not treat nail fungus yourself; only a doctor can identify the causative agent and select the appropriate set of medications for you.
- It would be completely useful to use folk recipes along with medication treatments: take medications that stimulate the human immune system in the fight against infection. These can be infusions of echinacea, lemongrass, viburnum, rose hips, and black currant.
- Use all medications strictly according to the instructions and as prescribed by your doctor.
- Nails must be kept clean and dry to prevent the development of foreign microorganisms.
All manicure and pedicure products must be strictly individual and carefully treated with antiseptic solutions after use.
Therapeutic antifungal varnishes
Nail fungus, unfortunately, is a fairly common disease.
While the body is strong, there is nothing to fear, but as soon as the immune system weakens, harmful microorganisms begin their attack.
Mycosis completely changes a person’s usual way of life.
Some drugs are addictive.
Therefore, medicine does not stand still and is developing new methods to combat this difficult disease.
One of these innovative products is all kinds of antifungal nail polishes.
The advantages of antifungal varnishes lie in the specifics of their application:
- The liquid consistency allows it to spread evenly and fill even the smallest cracks and penetrate deeply, destroying harmful spores;
- When it dries, a hard, impenetrable surface is formed , which lasts for a very long time even under strong external influences;
- The hard film does not allow the fungus to spread , plus it prevents the penetration of oxygen, which is why the fungus stops multiplying;
- Correctly selected varnish will get rid of fungus in 2-3 days.
Antifungal varnishes have some disadvantages:
- Typically high price;
- Often should not be used by pregnant women, children and adolescents;
- Most often they are effective only in the early stages of the disease;
- If the skin is also affected, varnishes are useless;
- Burning sensation upon application and contact with skin;
- Individual intolerance is possible.
When using antifungal varnish, you should always act according to the instructions for the product. Some varnishes need to be applied 1-2 times a week, but the treatment lasts up to six months. Others are applied several times a day. Therefore, it is important not to skip this procedure in order to get rid of the hated fungus.
Top budget antifungal varnishes
Below are the most popular cheap antimycotic varnishes:
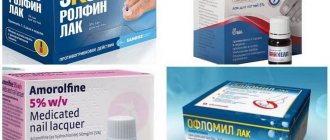
- Demicten is one of the effective remedies for nail fungus. Its cost is about 360 rubles . Apply every day until signs of the disease disappear, and then apply a thin layer for another 3 months for prevention. The volume of varnish will be enough for several months. Moreover, the product has no contraindications other than individual intolerance. It can be used by adults and children. The disadvantages include an uncomfortable shoulder blade;
- Stop fungus - a varnish for eliminating fungal infections is produced by the company Domix Green. Its active component, terbinafine hydrochloride, works to eliminate the fungal infection that is localized deep in the nail. Blocks the spread of fungal and bacterial infections. Cost 170 rubles ;
- Wartner Nailexpert is good not only as a treatment, but also as a prevention. Costs about 260 rubles . This product improves the appearance of the nail, reduces fragility, accelerates regeneration, and success in the fight against fungus will be noticeable within 2-3 weeks. However, Nailexpert is contraindicated under 18 years of age and in the presence of skin lesions in the treatment area, and the application technique must be followed impeccably;
- Belvedere - this varnish is often classified as a means of prevention; the price is very pleasing and is about 120 rubles . Contains vitamins, minerals, plant ceramides, which reduce splitting, fight brittleness and strengthen the nail plate. There are no age restrictions;
- Oflomil is a more expensive drug, but has a powerful fungistatic and fungicidal effect. Costs about 700 rubles . Forms a protective film on the nail plate, accelerates regeneration and penetrates deep into the affected tissues, dries quickly, and the effect of a single use lasts about two weeks, which saves both time and money. Contraindicated in children under 5 years of age, women during pregnancy and lactation, and also prohibited in combination with other antifungal drugs.
Lamisil, Batrafen, and Lotseryl are also considered good antifungal varnishes. In many respects, of course, they are better. 1,500 rubles and more for them
What else do you need to know about this kind of lesions on the human body?
Fungi are very resilient and very difficult to fight. Some dermatophytes manage to retain their vitality for up to 2 years, even when deprived of a comfortable habitat. They will simply wait for an opportunity to “catch on” to a viable organism and bloom wildly on it.
Those who decide to start fighting onychomycosis can expect various kinds of pitfalls on the path to full recovery.
Fungal infections are very resistant to hostile environmental conditions and manage to develop immunity to many medications.
Therefore, if you have begun the fight against this infection, do not give it up halfway, be sure to bring the matter to the end: until a brand new, fresh nail appears. Otherwise, the next time you decide to use the same product, you will notice that there is no result! And not at all because the product is bad. It’s just that while you were peacefully resting from treatment, the fungi were preparing for war and developed immunity to the remedy that you had already used.
Important! Only systematic use of medications, preferably in combination, and ideally under the supervision of a specialist, can save you from problems with nails.
Antifungal serums and solutions (drops)
Most doctors are inclined to believe that it is best to treat the fungus topically. Such antimycotics allow you to fight the fungus directly in the affected area.
Various antifungal serums and solutions can also help in the fight against nail fungus. These drugs can be used both independently and in complex treatment of onychomycosis.
Their principle of action includes both fungicidal and fungistatic effects, which allows not only to fight affected areas, but also to protect healthy ones.
The advantages of antifungal serums and solutions include the following:
- Application is accompanied by a burning sensation, like all antifungal drugs, but it soon disappears;
- The harmful effects on the body are minimal: no more than 5% of the medicinal components can enter the blood;
- Uniform distribution over the affected area;
- Deep penetration;
- Neutralization of unpleasant odors;
The following clearly stand out among the shortcomings:
- A doctor's prescription is required, despite the fact that they are available without a prescription: for different types of fungus, as a rule, different serums and solutions are needed;
- It is necessary to apply up to three times a day, which is very inconvenient for busy people;
- Since the structure is liquid, there is a risk of contact with the skin, which can cause discomfort;
- Optimal effectiveness is achieved only in the early stages of the disease.
Antifungal solutions and serums should also be used according to the instructions, after preparing the feet and nails.
Typically, solutions and serums are applied 2-3 times a day until the nail part and the skin around it are completely moisturized. Often solutions are sold with a pipette, they are called drops , then it is easier to maintain the dosage.
Features of drug therapy
Onychomycosis is not just a fungal infection of the nails; very often the main cause of such an unpleasant disorder can be serious diseases:
- diabetes;
- immunodeficiency, both congenital and acquired;
- psoriasis.
The peculiarity of the treatment of onychomycosis includes a complex effect on the infected organism:
- It is recommended to use the tablets together inside the body with the accompanying use of external agents and traditional medicine methods.
- The use of local antifungal agents: ointments, gels, varnishes.
- Traditional methods of treatment: various types of baths, nail treatment.
- Daily removal of part of the lesion from the nail plate.
Only through daily struggle is it possible to cope with such an unpleasant disease.
Antifungal sprays
Antifungal sprays are very popular due to their effectiveness and ease of use. Many types of antifungal agents can no longer be found in solution, but in the form of a spray - please.
A wide range allows you to choose a spray for each case of illness. However, in order not to make a mistake with your choice, you should first contact a dermatologist so that when forming a treatment regimen, you can take into account all the associated factors and select the optimal spray right away.
Among the obvious advantages of antifungal sprays it is worth noting:
- Avoid direct contact during application;
- Impeccable treatment of the affected nail area: gets into even the most microscopic cracks;
- Maintaining the exact dosage;
- Deodorizing and drying affected areas;
- Elimination of unwanted greasy stains on both skin and clothing;
- The use of sprays does not disrupt the functioning of the dermis.
It is worth mentioning their minor, but still disadvantages:
- As correctly, should not be used during pregnancy, lactation and children under 12 years of age;
- Side effects often include itching, burning, and allergic reactions;
- It is required in large quantities, since when spraying it is necessary to cover both the affected nail and the skin around it.
It is also worth following the rules for treating the skin before applying the spray. Spray on the affected areas and on the surface around it.
When using antifungal sprays, monitor for irritation and inflammatory reactions - this is a signal to immediately stop treatment and change the drug. If there is no effect after a week of use, this indicates that additional diagnostics and a change in treatment regimen are required.
There are many different types of antifungal sprays available these days.
Top budget antifungal sprays
Below are cheap antifungal sprays that have earned their popularity due to their effectiveness:
- Bifosin is the most inexpensive spray. It can be found in pharmacies for about 130 rubles . A very effective remedy that should be used once a day, before bed. It can help get rid of mycosis in 3-4 weeks. Bifosin is used once a day, preferably before bedtime;
- Terbix is an effective remedy for fungus. Its price rarely reaches 200 rubles . It is able to fight a wide range of fungi. Moreover, treatment usually lasts no more than a month. Terbix spray should be used 1 or 2 times a day, depending on contraindications. The disadvantages include a large list of contraindications, such as renal and liver failure, alcoholism, metabolic diseases, occlusive vascular diseases of the extremities;
- Lamitel is a spray that is also very inexpensive, about 150 rubles . Well suited for patients prone to relapses of fungal diseases. The dosage depends on the severity of the disease, so consultation with a specialist is required. Usually, treatment of the affected areas is prescribed 1-2 times a day;
- Thermikon is a product that will be an excellent preventative solution. This spray costs about 300 rubles . Effectively protects the skin and nail plate from fungal infections. By using it in treatment, you can stop the spread of infection. The downside is its characteristic ethyl smell and a fairly large list of contraindications.
Bifosyn Terbix Lamitel Thermikon
Systemic therapy for onychomycosis
Reference. If onychomycosis is in an advanced stage, when the fungus has spread to several nails or has gone deeper, the nails have become deformed, it is necessary to proceed to systemic treatment of the disease.
There are only 8 systemic antifungal drugs, the most commonly used are Griseofulvin, Terbinafine, Ketoconazole, Itraconazole and Fluconazole for internal use.
The antifungal drug griseofulvin has been used to treat nail fungus for more than 30 years. It only acts on dermatophytes.
It is very important that the doctor prescribes treatment. Since only in laboratory conditions is it possible to identify the causative agents of lesions of the nail plates and act on them.
Below is a table that clearly demonstrates what types of pathogens this or that drug effectively fights.
| Drug name | Dermatophytes | Candida | Molds |
| "Griseofulvin" | + | – | – |
| "Terbinafine" | + | – | ? |
| "Ketoconazole" | + | + | – |
| "Itraconazole" | + | + | + |
| "Fluconazole" | + | + | – |
That is, depending on the identified pathogen, an effective drug is prescribed.
When lesions of the nail plate are localized on the toes, longer treatment is required than on the hands.
Drugs such as Griseofulvin and Ketoconazole have a lot of side effects and are unsafe for such long-term use.
Another factor that people pay attention to when prescribing therapy is how quickly the nail plate grows. In other words, if healthy nails on the hands are renewed within 4-6 months, then on the feet this process will take 12-18.
Important! Drugs such as Terbinafine and Itraconazole can accumulate there and linger for a long time. Thus, by taking these medications, it is possible to reduce the course of therapy altogether.
Drugs to combat onychomycosis are prescribed according to 4 regimens:
- The standard regimen is when the drug is taken on a daily basis throughout the entire treatment period until a new nail plate grows.
- The shortened scheme differs in that the treatment period ends before a healthy nail grows. According to this regimen, Itraconazole and Terbinafine are used in normal or increased doses. After stopping treatment, their active substances remain in the nails for a long time and the treatment continues on its own.
- An intermittent regimen is characterized by taking an increased or usual dose of medication in several short courses. The interval between courses is equal to the duration of the course (course week/break week). This scheme is also suitable for those who can accumulate Itraconazole and Terbinafine.
- Pulse therapy is characterized by taking increased doses of the drug in short courses with breaks exceeding the duration of the course. For treatment in this case, Itraconazole or Fluconazole is used.
Ointments and creams for nail fungus
The most popular means of combating fungus are ointments and creams.
This unshakable reputation comes with the following benefits:
- Wide spectrum of action;
- Affordable price;
- Convenience and ease of application;
- Versatility: suitable for both nail fungus and skin fungus;
- Impact accuracy;
- Instant results.
Plus, if you choose a cream, it is an undeniable comfort, as it does not leave greasy stains on clothes.
However, ointments with creams also have some disadvantages:
- Consultation with a specialist is required, since ointment and cream are selected depending on the type of fungus; appearance cannot accurately indicate the type of fungus;
- It is important to prevent addiction, and only a good specialist will identify this in time;
- Creams are effective only in the initial stages, and in the later stages of the disease, effectiveness occurs only with complex treatment.
Like any antifungal remedy, ointments and creams require careful preparation of surfaces and strict adherence to the instructions and frequency of application.
Top budget antifungal creams and ointments
List of the most effective and cheapest creams and ointments for nail fungus:
- Ketoconazole is an ointment that is considered one of the best in the fight against fungus. Costs about 130 rubles . This ointment not only destroys the fungus, but also helps restore and strengthen the nail plate. Prescribed for adults and children weighing over 30 kg;
- Candide is also available in cream form. It will cost about 300 rubles . An effective remedy that can rid a patient of fungus in 2-3 weeks. There are no age restrictions, I also use it for children under one year old.
- Terbinafine - the components of this product act on the membranes of fungi, which is why they die. Effectively fights not only the consequences, but also the cause, that is, the causative agent of a fungal infection. Cream and ointment cost approximately 100 rubles . However, it has a fairly large list of contraindications, including the age of children under 3 years and up to 20 kg, as well as the lactation period;
- Terbizil is a cream that is slightly more expensive than those indicated. On average it costs about 280 rubles . It destroys fungal lesions, creating an invisible protective layer on the nail. At the same time, it also eliminates the unpleasant effects of fungus in the form of odor. Taken by adults and children over 12 years old 1-2 times a day for 1-2 weeks;
- Clotrimazole - the drug inhibits the growth of pathogenic organisms, kills the fungus and prevents it from spreading to other nails and skin. Ointment can be found for about 50 rubles , cream – 150 rubles . Clotrimazole will not help in advanced cases, it has a specific odor, and side effects include itching and burning. Under the age of 5 years, the ointment should be used under the strict supervision of a specialist;
- Bifosin is a cream that is also quite effective against fungus. It penetrates the affected tissue quite quickly and begins its action. The average price is about 100 rubles . It is worth keeping in mind that most often its effectiveness was manifested in the earliest stages of the fungus and during prevention. Use during pregnancy and children under one year of age is undesirable, only if necessary and with the prescription of a specialist;
- Kanizon is an inexpensive cream that is designed to fight mold fungi and dermatophytes for only 80 rubles . The composition also contains clotrimazole, which promotes rapid healing. It has no contraindications; the only possible side effect is an allergic reaction. However, use in pregnant children with extreme caution. Before use, consultation is required to determine the type of fungus;
- Nogtimycin is a cream that should be applied under the patch. A very inexpensive and effective product. Cost 110 rubles . The only inconvenience is that the preparatory procedures take 30-40 minutes before use. There are no age restrictions;
- Fundizol - helps eliminate manifestations of mycosis of the skin and nail plates, it is used to remove ingrown toenails, has an antiseptic and deodorizing effect. Cost from 90 rubles .
There are still many different creams and ointments for fungus. These are the most common names, as they have proven their effectiveness more than once.
In order not to go through cream or ointment one after another, you need to contact a dermatologist and carry out a diagnosis. A thorough study will allow you to choose the optimal ointment for treatment.
Introduction
People who are diagnosed with mycosis know firsthand that the treatment of this unpleasant disease is very long and requires an integrated approach.
And if at the initial stage of the disease you can get by with external means, such as ointments, sprays, gels, then an advanced disease requires treatment from the inside. When asked which tablets to use against foot fungus, dermatologists answer: it all depends on the type of pathogen, the general health of the patient and the area of the lesion.
Oral antifungals
Nowadays, fungal diseases, unfortunately, are becoming more and more common. When all of the above remedies fail to eliminate the disease, doctors prescribe tablets against the fungus.
Such treatment has a much greater impact on the body; the range of contraindications and side effects can be much greater. Therefore, such treatment should be chosen exclusively in conjunction with a doctor.
Top budget antifungal oral drugs
The most popular cheap oral drugs for fungus are:
- Terbinafine - these tablets are considered the most effective. They cost about 190 rubles . This medicine has a cumulative property, so it can defeat the fungus in a couple of weeks. There are some contraindications, including use in children under three years of age and in women during lactation;
- Fluconazole is an inexpensive antifungal agent that has a wide spectrum of action. They cost about 40 rubles , it is worth considering that this is the price for one capsule. Can handle even advanced cases. However, treatment takes from 6 to 12 months. There is a list of contraindications, for example, it should not be taken by children under 4 years of age, women during lactation, and pregnant women only in extreme cases. The dosage depends on the degree of the disease and the patient’s weight;
- Ketoconazole - a pack of tablets costs about 160 rubles . They have an active fungicidal and fungistatic effect. May cause intestinal disorders and headaches. Contraindicated for persons with acute and chronic liver diseases, pregnant women, and women during lactation. The dosage regimen depends on the doctor’s instructions and, as a rule, also depends on the person’s weight;
- Nystatin is a very inexpensive tablet, the price of which is about 130 rubles . It combines well with tetracycline. But this is an antibiotic, so it is prescribed only by the attending physician;
- Griseofulvin is a drug that is more expensive than the above. Costs about 230 rubles . It completely stops the growth of parasitic organisms. It is prescribed 8 tablets per day until the first negative test for fungi. Then every other day for 2 weeks, then 2 times a week for 2 weeks. As a rule, treatment lasts up to 8 months. In children, the dosage is prescribed per 1 kg of weight. Use is prohibited during pregnancy and children under 2 years of age.
Treatment of mycosis of the scalp
The most common fungal infection of the scalp is microsporia. In addition, there are forms of the disease such as trichophytosis and favus. External therapy for these diseases is ineffective. It is used only as an addition to systemic medications. Hair shaving is not currently used. Additionally, drugs for the systemic treatment of mycosis capitis are necessarily used:
- griseofulvin;
- terbinafine;
- itraconazole;
- fluconazole.
Cheap antifungal drugs for pregnant women
The most difficult thing is to choose a drug to treat fungus in pregnant women. This is due to the risks of absorption of the drug into the blood and thereby affecting the fetus.
During pregnancy, it is strictly forbidden to take systemic antifungal agents. Even if the drug’s instructions do not directly state that it should not be taken during pregnancy, you should consult your doctor.
The safest anti-fungal drugs for pregnant women:
- Clotrisal - there is no direct data on the possible penetration of clotrimazole into the placenta. Therefore, use is possible, but with strict doctor’s prescription, the average cost is 80 rubles ;
- Miconazole - it is allowed to apply cream and make lotions with the solution on the affected areas of the nail. The course should not exceed 6 weeks. Average cost 130 rubles ;
- Zinc ointment - during pregnancy, you can get rid of fungus using this ointment. It must be applied 4-5 times a day. Average cost 30 rubles ;
- Sulfur-tar ointment is a combined preparation with antiparasitic action. Birch tar has a disinfectant and anti-inflammatory effect. Average price 30 rubles ;
- Fungazol - approved for use from the second trimester of pregnancy, it should be used with caution, it can cause an allergic reaction. Average cost 130 rubles ;
- Demicten is an antifungal varnish, unlike its closest analogue, Loceril, and is not contraindicated during pregnancy. Average cost 360 rubles ;
- Mikoseptin - approved for use from the second trimester of pregnancy, has a natural base. Average cost 300 rubles ;
- Belvedere - used for prevention, but use with caution during pregnancy, average cost 120 rubles .
There are very few medicinal ointments, creams and varnishes that can be used during pregnancy. Therefore, they often turn to folk remedies.
Thus, propolis solution, garlic, salt and peppermint lotions, tangerine oil, grapefruit extract, Kalanchoe or milkweed pulp, baths with herbs such as verbena, calendula, horsetail, oak bark can help in the fight against nail fungus during pregnancy. .
The maximum effect can be achieved by alternating techniques and following the treatment regimen continuously.
Classification
In addition to classification by mechanism of action, antimycotic drugs are distinguished according to the following criteria:
- By origin: natural, synthetic.
- Indications for use: local, systemic.
- By route of administration: orally, parenterally (intramuscularly or intravenously), externally.
- By chemical structure: polyenes (Amphotericin B and its lipid complex, Nystatin), azoles (Fluconazole, Voriconazole, Itraconazole, Ketoconazole), glucan synthesis inhibitors - echinocandins (Caspofungin), fluoropyridimines (Flucytosine), morpholine derivatives (Amorolfine), allylamines (Terbinafine, Naftifine), grisans (Griseofulvin).
Currently, there are more than 100 names and 20 dosage forms of drugs on the pharmaceutical market. Of these, the most widely used group is azole antimycotics. Representatives of this group are characterized by a fungistatic effect.
Nystatin is most often used to treat superficial forms of mycoses. Promising antifungal agents awaiting widespread use include the following: Voriconazole, Posaconazole, Ravuconazole, Ambizom, Niotran.
Inexpensive folk recipes to combat nail fungus
When choosing a means of combating fungus, you can turn to folk recipes. Folk remedies allow you to save money and still get the desired result.
Essential oils
Essential oils can help fight fungus:
- cinnamon;
- tea tree;
- oregano;
- carnations;
- sage
Such oils usually cost no more than 100 rubles per bottle, it all depends on the oil manufacturer.
They have an anti-inflammatory, bactericidal and cleansing effect.
Essential oils in the treatment of fungus can be used in the form of compresses and special baths.
Baths with essential oils are a very pleasant procedure that does not take much time:
- Add 10 drops of essential oil to warm water, put your feet or hands in it and keep it there for 20 minutes;
- After completing the procedure, the legs or arms are wrapped in a towel and held for several minutes.
Compress with essential oil:
- For a compress, mix several parts of oil and water;
- Soak a cotton swab with this mixture;
- Then apply to the affected area for 60 minutes;
- This method is also quite effective in fighting fungus.
Propolis
The effectiveness of this method is due to the fact that propolis is very effective in the fight against fungi and gets rid of pathogenic flora in a short time. Therefore, propolis can also help with onychomycosis.
Propolis tincture costs only about 50 rubles .
With propolis tincture you can make so-called lotions.
Typically, propolis lotions for nail fungus are made like this:
- Prepare your feet by washing them thoroughly and steaming your nails; nails that are too long are cut off or filed. This is necessary for better penetration of the drug;
- Then wipe the skin around the affected nail with a tampon soaked in the tincture so that it is protected from the spread of infection;
- A tampon with propolis tincture is applied to the affected nail and secured with a plaster and bandage;
- You need to keep the tampon in place for a day;
- Then the affected nail is filed down as far as possible and the procedure is repeated;
- This procedure must be done until a healthy nail appears.
Celandine
Pharmaceutical celandine is a proven remedy against fungal infections.
Celandine oil costs no more than 100 rubles , but this product gives a positive result much faster than many modern ointments.
Use of alcohol tincture:
- Prepare an alcohol tincture by mixing 250 ml of 70% alcohol and 30 drops of celandine oil;
- Leave for a day in a dark place;
- This solution must be applied very carefully, trying not to get on the skin;
- To apply layers, you can use a brush or cotton swabs;
- Before applying the product, your feet should be steamed well in a bath (about 10-15 minutes);
- Dry and clean the skin or nails of dead particles;
- Only after this should the medicinal solution be applied;
- The result will be noticeable within 10-14 days.
Iodine
This method of using iodine is based on the fact that the fungus has a protein structure, and iodine is able to destroy it. That is, applying iodine to an infected surface helps destroy the structure of the fungus from the inside.
The cost of a bottle of iodine starts from 10 rubles .
Tar soap
With this method, all the steps are very simple:
- Tar soap is used for washing hands and feet daily and preferably several times a day;
- Nowadays, birch tar is often added to shower gels, which will make therapeutic water procedures much more comfortable.
The cost of soap is from 40 rubles .
Vinegar
Vinegar creates a special acidic environment that prevents spores from growing on the surface of the skin. Moreover, the fungus, left without access to nutrients and minerals, simply dies over time.
Healing baths:
- Before carrying out them, it is important to remove dead skin particles and affected areas of the nail plate, as well as wash off the varnish coating;
- To prepare a bath, you will need ordinary table vinegar 9%, as well as a small amount of hot water so that its level is ankle-deep, with a temperature of about +50°C;
- Keep your feet in this solution for about 15 minutes;
- Then wipe dry with a towel.
You can also make lotions from apple bite and iodine:
- To prepare this remedy, you need to mix vinegar and iodine in equal proportions;
- It is necessary to wipe the affected area several times a day until the disease completely leaves you;
- After wiping, it is advisable to put on cotton socks.
The average cost of table vinegar is 20 rubles , apple vinegar - 30 rubles .
Tea tree oil
On many forums on the Internet you can find reviews about the positive effects of tea tree oil in the fight against fungal nail damage.
Tea tree oil is an essential oil with a pleasant smell and thick consistency. This is a truly powerful remedy in the fight against microbes of various natures: it has a bactericidal, anti-inflammatory and symptomatic (relieves itching and burning) agent.
This product is for external use only. It is absolutely forbidden to swallow it!
Reference. In an advanced state of the disease, tea tree oil can only be used in conjunction with medications prescribed for therapy by a doctor.
A single use of it is unlikely to cope with a neglected problem. The oil can be used in several ways:
- rub into the damaged plates, having previously prepared it for the procedure in the usual way;
- prepare foot baths with a few drops of the product.
Below you can watch a video about using tea tree oil to get rid of nail fungus:
Analogs of expensive products
Below you will find a table showing cheaper analogues, which are not only cheaper than Western medicines, but also help to effectively get rid of fungus.
| Foreign drug | price, rub. | Domestic analogues | Price, rub. |
| Exoderil (Austria) | 450 rub. -1350 rub. | Fugnoterbin, Mycoderil | 300 rub. — 700 rub. (domestic analogues) |
| Lamisil (Switzerland) | 550 rub. -2200 rub. | Thermikon | 150 rub. — 800 rub . (domestic analogue) |
| Lotseril (France) | 1200 rub. — 2400 rub. | Terbinafine | 150 rub. (analogue made in India) |
| Batrafen (France) | 359 rub. (cream) - 2200 rub. (varnish) | Terbinafine | RUB 150.00 (analogue made in India) |
| Nizoral (Belgium) | RUB 450.00 | Mycozoral, Ketoconazole | RUB 200.00 (domestic analogues) |
| Mikospor (Germany) | RUB 550.00 | Bifosin | 100.00 rub. (domestic analogue) |
General rules for the use of tablets and capsules
All medications must be taken according to the regimen prescribed by the doctor. A regimen with an equal number of hours between doses should be followed. If an appointment is missed, it must be taken immediately, but not if the next appointment is already close.
You cannot double the dose of the drug . Most instructions indicate the order of taking the drug in relation to meals. If this is not indicated, the drug is taken on an empty stomach. This means taking the medicine after meals 2 hours and 1 hour before meals.
It is better to take medications with regular boiled water; do not drink alcohol while taking antifungal medications. The drugs must be taken according to a clear schedule, which is established by the doctor based on the clinical picture of the disease.
Prevention of nail fungus
Any disease is easier to prevent than to treat. Nail fungus is no exception.
Therefore, below are tips for preventing the appearance of nail fungus:
- Always keep your feet clean and dry;
- Wash them with soap and water daily and dry them thoroughly;
- Wear a clean pair of socks every day;
- Wear several pairs of shoes so that you can periodically change pairs and the shoes have time to air out;
- Use breathable shoes, shoes made from natural materials;
- Shoes should be comfortable and spacious;
- Keep manicure tools clean;
- If you are predisposed to fungal diseases, do not use nail polish at all or apply an anti-fungal polish underneath;
- Trim your nails in a timely manner: it should be at the level of your toes;
- When contacting manicure and pedicure salons, pay attention to how they process instruments and whether they do this in principle;
- If you are prescribed treatment, complete the full course prescribed by your doctor;
- Try not to walk barefoot, especially in bathhouses, saunas, locker rooms, gyms, on carpet and wood floors, especially in areas of high humidity. Always wear special shoes in such areas;
- Throw away your old shoes if you have been treated for toe fungus.
What to do in case of extensive lesions of the plates?
Let’s start with the fact that you definitely shouldn’t “rip out” your nails.
Now a new method of nail treatment has appeared - hardware treatment. This device is similar to a dental drill. The top layer of the damaged plate is gradually ground down to its normal state. It should be noted that the procedure itself is absolutely painless. But only a doctor can determine the number of such sessions per course of treatment.
Attention! It makes sense to completely remove the nail plate only if more than half of it is affected.
Along the way, you can use preparations for external use: gels, creams, varnishes. And drugs for internal use - in the form of capsules and tablets. So, in total, you will quickly rid yourself of this problem.
And finally, I would like to note that it is always easier to prevent any health problem than to deal with it for a long time and painfully. When it comes to fungi, this statement is right on point! How to protect yourself from these pests.
As a matter of principle, try not to visit places where you can “catch” the fungus - swimming pools, public baths, saunas, public beaches. And if you have been there, then use means of preventing infection:
- "Zalain";
- "Atifin";
- "Tebikur";
- "Lamitel";
- "Candide";
- "Exoderil";
- "Mikospor".
- Use only individual nail care tools and personal items: slippers, shoes, socks.
- The stockings, socks, and tights themselves should contain as little synthetics as possible, and ideally be made from natural fabrics. Such things absorb moisture, do not leave your nails in a damp environment and prevent infections from spreading and developing.
- Be sure to wipe yourself dry after water procedures.
- If there are microcracks on the surface of your feet and hands, immediately treat them with antiseptic solutions.
And most importantly: treat any problem that arises immediately, as soon as you notice it, under the supervision of a doctor.
New aspects in the problem of choosing a modern antimycotic
About the article
3517
0
Regular issues of "RMZh" No. 18 dated September 27, 2004 p. 1047
Category: Dermatology
Authors: Novoselov V.S. , Novoselov A.V.
For quotation:
Novoselov V.S., Novoselov A.V. New aspects in the problem of choosing a modern antimycotic. RMJ. 2004;18:1047.
Every fourth person in the world suffers from mycoses. Due to their exceptional properties, mushrooms accompany humans everywhere, and therefore the problem of mycoses is always relevant. According to the literature, this pathology accounts for up to 42% of all dermatoses, among which onychomas and goats, in particular, are one of the most common fungal diseases. Therefore, there is a constant search for new, most effective methods of treating it. We try to combine certain means to achieve the goal in order to avoid possible problems associated with the adaptive “tricks” of fungi, in turn, striving at any cost neutralize our efforts. Unfortunately, among those who protect human health, there are often specialists who do not always know how to use the weapons they possess. In this regard, mushrooms adapt to our means of struggle and complicate life not only for the victim, but also for those who are trying to help him. Another reason that ensures the success of the mushroom’s extensive campaign against humans is the amazing quality of the latter, known as long-suffering. A person is able to endure the inconvenience associated with the presence of a fungus in his body for years, decades! How many people can one person infect if he has devoted a third of his life to cultivating microorganisms on himself?! And it is not surprising that often efforts to treat and prevent onychomyas in goats become useless. And what funds are invested in prevention, diagnosis and treatment - there is no need to say. Also, an obvious problem that arises for a person is the fact of the duration of treatment for onychomycosis, which is largely due to his “inhuman” patience. A person is ready to endure, as long as it does not affect his position in society. And this is already a pitfall of the same civilization, which makes life easier for a healthy person, but complicates it for a sick person. To confirm the relevance of this problem, it is enough to turn to statistics. So, just over the last 10 years, the incidence of onychomycosis has more than doubled! Taking glucocorticoids, immunosuppressants, HIV infection, primary immunodeficiencies or graft-versus-host reaction, etc. At a high incidence of mycoses (>40% ) in these patients indicate Raznatovsky K.I. et al. (“Difficult patient in mycology”, 2004). The fungal process in them has a chronic progressive course, a high frequency of relapses, pronounced contagiousness and insufficient effectiveness of the standard antimycotic regimens used. The authors point out that the main background concomitant pathological processes that contribute to the development of refractory pathological conditions that are torpid to antimycotic therapy are endocrinopathies, immunodeficiency states, various skin diseases, peripheral circulatory disorders and hematopoietic disorders (long-term neutropenia). In these patients, in addition to the progressive course of mycosis, there is a generalization of the process, frequent lesions of the skin appendages, follicular and infiltrative-suppurative forms of the disease, laboratory tests reveal several types of fungi. The principles of therapy for immunocompromised patients suffering from dermatomycosis require careful modification of treatment, taking into account the verification of detected fungi . The bioavailability of the antimycotic, the possibility of using an increased dose of the drug, its good tolerability over long periods of treatment, and its interaction with other medications, including antifungal drugs (combination of treatment) must be taken into account. Particular attention should be paid to the prevention of possible relapses of the mycotic process. The method of radical control of fungal diseases, in particular dermatophytosis, is the cure of patients suffering from them, since this leads to a break in the epidemiological chain of transmission of infection from a sick person to a healthy person and into the environment, which helps to reduce incidence of mycoses in general. Finding effective means of treating patients with various mycoses is one of the pressing problems of modern mycology. It is well known that systemic antimycotics, included in a complex of therapeutic measures, triple the cure rate compared to treatment with external antifungal agents only. One of the generally recognized effective systemic antifungals is the allylamine compound - terbinafine hydrochloride. Compared with other antifungal drugs (azoles, morpholines), terbinafine acts at the level of the squalene epoxidase cycle at the earliest stages of sterol metabolism. On the one hand, by inhibiting squalene epoxidase, it inhibits the formation of the main component of the cell wall of fungi, ergosterol, and on the other hand, it promotes the accumulation of squalenes. Fungal squalene epoxidase is 10,000 times more sensitive than a similar human enzyme. This explains the selectivity of terbinafine and its high specificity for target cells of fungal origin. In turn, the drug has no effect on the synthesis of human steroidogenic structures (enzymes, cholesterol, vitamins, hormones), formed with the help of the enzyme 14-a-dimethylase. The object of the targeted action of antimycotics, for example, the azole group, is precisely this enzyme, not only in fungi, but also in humans. Terbinafine can be prescribed to somatically aggravated patients who are forced to take various medications for health reasons. Since squalene epoxidase is not a P-450 enzyme, terbinafine has little interaction with medications metabolized by this enzyme system. It should be noted the high synergism of terbinafine and azole compounds on the formation of er gosterol, which is the main component of the cell wall of fungi. This circumstance makes it possible to combine azole drugs with terbinafine in order to suppress the resistance of fungi during mono-antimycotic therapy. For example, 90% of fungal strains resistant to fluconazole were sensitive to the combination of terbinafine and fluconazole. Their resistance, apparently, was associated with excessive production of 14-a-dimethylase and, therefore, its incomplete destruction. Based on the type of action on the pathogen, terbinafine, as an antimycotic, has fungistatic and fungicidal properties. Fungal cells, losing the ability to grow and develop, can only survive due to disruption of the cytoplasmic membranes due to the lack of ergosterol in them - this determines the fungistatic effect of the drug. The fungicidal property of terbinafine is based on the accumulation of squalenes, which further aggravate the condition of the cell membranes of fungi, since, like a kind of sponge, lipid components are extracted from them. On the one hand, the wall of the fungus is destroyed, on the other, the volume of lipid granules increases. Due to the intracellular accumulation of lipid structures, the previously altered cytoplasmic membrane is ruptured, which leads to the death of the fungal cell. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of terbinafine depends on the accumulation of squalenes more than on ergosterol deficiency, since a decrease in the number of viable cells from 10 to 0.1% correlates with an increase in the level of squalene from 0 to 0.1 μg/g. It is undeniable that The fungicidal effect of terbinafine prevails over the fungistatic one. Therefore, the therapeutic effect is achieved with a lower concentration of the drug than is required to completely inhibit the formation of ergosterol. This may explain the significant difference in the results of treatment with terbinafine and griseofulvin (the latter has an exclusively fungistatic effect on dermatophytes). Clinicians know that when using terbinafine orally, there is no need to create special conditions for taking the drug, since terbinafine is well absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, and this process is not affected by the acidity of gastric juice, the nature of the food, or its saturation with lipids. This condition is important when using some other systemic antimycotics known in the country and is specifically stipulated in the annotations attached to these drugs. The therapeutic concentration of terbinafine in the patient’s body is very stable. It does not depend on age, gender, other demographic indicators and the use of other medications, since terbinafine practically does not interact with them and does not affect their metabolism. Terbinafine is detected in the blood within two hours after taking the drug. The half-life of absorption is 0.8 hours, distribution is 4.6 hours. It is noted that in the blood terbinafine is 99% bound to proteins and, to a lesser extent, to blood cells. When taken at a dose of 250 mg/day. the peak blood concentration is stable and is 0.9 mg/ml; dose 500 mg/day – creates 1.7–2.0 mcg/ml. Plasma concentrations of terbinafine become stable after 1–4 weeks of continuous administration of the drug at a dose of 250 mg per day. Due to the lipophilicity of the drug and its connection with chylomicrons, the distribution of terbinafine in the body occurs through the lymphatic route, which is especially noted by researchers. Through the lymphatic vessels, terbinafine directly reaches infiltrative-suppurative and abscessing foci of skin lesions, accompanied by lymphadenitis and lymphangitis. This route of distribution of the systemic antimycotic in the patient’s body, combined with its pronounced antibacterial properties and anti-inflammatory effect, contributes to the accelerated resolution of complicated forms of dermatophytosis. Thus, terbinafine accumulates most actively in tissues rich in keratin and/or lipids, in abscessed lesions, in adipose tissue, dermis, hair follicles, stratum corneum, nails and hair. Compared to tissues, the accumulation of terbinafine in the nails is somewhat slower and is due, firstly, to the greater (10 times) thickness of the nail compared to the stratum corneum of the skin, and secondly, to its lower enrichment in lipids, a third of them, through its entry through the vessels of the nail beds and matrices. Proof of this is the rapid saturation of the nails with terbinafine in the normotrophic type of lesion (thickness 0.3–0.4 mm). In this case, the root part, saturated with terbinafine, is layered on the ventral part of the nail, impregnated with terbinafine, coming from the vessels of the nail bed [N.S. Potekaev et al., 2003]. The high effectiveness of treatment with terbinafine for normotrophic nails (within 6–8 weeks), in particular on the hands, is explained by both the accelerated growth of the nail plates on the upper extremities and the rapid entry of the drug into the affected nail structures. For the hypertrophic type of nail plate lesions, others are needed therapeutic approaches, since subungual hyperkeratosis thickens the nail by 20–30 times, which complicates the access of terbinafine to fungi. The drug, diffusing from the nail bed, impregnates and sanitizes only a thin part of the subungual formations directly adjacent to the nail bed. The main role is played by terbinafine, which enters the root part of the nail from the matrix, where its high concentration is created when the drug is taken permanently. The root part of the nail plate, saturated with terbinafine, moves towards its distal edge during the process of growth. If you do not clean the affected nail structures, including subungual hyperkeratosis, then the slowly growing nail, as a rule, turns out to be deformed. To heal such a nail, 12–16 or more weeks of constant use of the drug are required. When taken daily at a dose of 250 mg/day. Terbinafine is detected in the nail plate after a week, reaching a level of 0.3–0.55 mcg/g after 2–4 weeks, and 0.78 mcg/g after 12 weeks. The maximum concentration of terbinafine in the nails is detected 18 weeks after the start of antifungal therapy. Entering the body, terbinafine is gradually detected in the nail plates, where it accumulates during 6-week and 12-week courses of therapy, after which it cleared from the nails within 30 and 36 weeks, respectively. The minimum inhibitory concentration of terbinafine for T. rubrum is only 0.0001–0.0005 μg/ml (unlike most dermatophytes, which require a dose of 0.003 to 0.05 μg/ml). In the experiment Preventive treatment of healthy (before infection) parts of the nails with terbinafine prevents the adhesion of T. interdigitalis and T. rubrum, their growth, the formation of germ tubes, and damage to arthroconidia on the surface of the nail. The minimum concentration of the drug to prevent invasion by fungi is 0.002 mg/l. In addition to the above varieties of dermatophytes, Terbinafine suppresses the activity of mold fungi of the genera Aspergillus, Scitalidum, Scopufariopsis, Sporotrichum. The required minimum inhibitory concentration in this case is at least 1 mg/ml. Terbinafine is active against yeast fungi of the genus Candida, Criptokokkus and Malassazea. According to Austrian researchers, the MIC for Candida albicans is 1–2 mg/ml, for C. parapsilosis – 0.008 mg/ml, for fungi of the genus Criptokokkus – 0.006–2 mg/ml. The drug was not so active against C. glabrata and C. crusei. The excellent pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of terbinafine compensate for the relatively high MIC against molds and yeast-like fungi. This turns out to be quite sufficient to achieve good results in the treatment of these mycoses. Obviously, the high antifungal effect of the drug depends not only on its adsorption, mechanism of action, pharmacological activity, but also on its metabolism, elimination and interaction with other medications. So 40% of the administered dose of terbinafine is metabolized in the liver, where it breaks down into fifteen mostly inactive metabolites. However, some of them, in particular, carboxybutyl and dimethylcarboxybutylterbinafine, also have antimycotic activity. Biotransformation of terbinafine is carried out by dimethylation of the nitrogen atom, the formation of oxides and oxidation of side chains. The biotransformation of the drug is not affected by gender and age, but it is certain that it slows down with liver and kidney failure. It is interesting that the elimination of terbinafine is three-phase. About 70–80% of the drug is excreted in the urine, the rest is excreted in the feces. Without a doubt, terbinafine is perhaps the most gentle systemic antimycotic, since, obviously, the safe nature of terbinafine follows primarily from its mechanism of action, and, as has been said, above, it, unlike other systemic antimycotics, does not “attack” other “targets”, purposefully acting on squalene epoxidase exclusively in fungal cells. The level of hormones produced by the adrenal glands, ovaries and testes does not change during terbinafine therapy, since it does not interact with enzymes involved in the synthesis of hormones of these endocrine glands. In healthy young male volunteers, after a week of taking this antimycotic at a daily dose of 500 mg, testosterone levels did not differ from the baseline. The advantages of terbinafine include the absence of a negative effect on the function of leukocytes. Even at a concentration 5 times higher than the therapeutic one, it did not affect phagocytosis, metabolic activity of polymorphonuclear neutrophils and chemotaxis. Terbinafine added together with fungal spores to a monolayer of human neutrophils at a concentration of 0.2 μg/ml increased phagocytosis and intracellular killing of fungi by neutrophils. Under the influence of terbinafine therapy, indicators of cell-mediated immunity improve, which is associated with the release of a large amount of antigenic material as a result of the death of fungal structures. In addition, the antibacterial activity of terbinafine is quite comparable to the effect of gentamicin sulfate. This action, coupled with pronounced antifungal activity, increases the effectiveness of treatment of mixed fungal-bacterial severe abscessive dermatophytoses, in which the addition of secondary flora plays an important role. Anti-inflammatory activity of terbinafine is also noted. It is able to reduce the generation of superoxide radicals of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and the peroxide activity of hydroxyl radicals of polyunsaturated fatty acids. Clinically, terbinafine has been observed to suppress ultraviolet UVB erythema due to the suppression of the biological activity of oxidative radicals caused by UVB irradiation. Thus, terbinafine, with high antifungal and antibacterial activity of a wide spectrum of action, also has pronounced anti-inflammatory properties. It was used by clinicians in more than 80 countries in more than 18 million patients with various mycoses aged from 2 to 98 years. In more than 9 million patients, sailing diseases were present. Terbinafine was accompanied by menniya and other medicines in almost half of cases. The treatment of treatment ranged from 1 to 6 months, and the daily and course doses of the drug were significantly varyed. So, based on thorough clinical observations, terbinafines are recommended for the treatment of children from the second year Life, taking into account body weight, respectively 12–20 kg - 62.5 mg, 20–40 kg - 125 mg,> 40 kg - 250 mg is one multiple per day. For the elderly and senile age, healing in taking the drug exists only in the presence of an intercarnet pathology in the form of a violation of the renal bothering function. The case of the use of terbinafine is known, indicating its very sparing properties in relation to the body of the lower person. A 40 -year -old patient with a complication after a translating of the aortic valve in the form of fungal endocardi, caused by Culvularia Lunata, used a terbinfine in those years of 250 mg/day, which led to the patient's gender recovery. It is significant that with such a terbinashy therapy in the patient, the patient did not occur in general adverse reactions and complications. The following side effects are most commonly found from the gastrointestinal tract (4.9%), characterized by a sense of overflowing of the stomach, discomfort, abdominal pain, and dishes of pepsic phenomena, nausea and vomiting. The hepatic OSs are more often manifested by an increase in the level of liver of the liver. They are associated with the fact that the terbinfine is metabolized by the PECHET system of the SUR2 D6. However, since the terbinafine is 99% associated with plasma proteins, and this enzyme takes part in the metabolism of a very insignificant number of pharmacological agents, the drug after extensive studies recognized as the least damaging antimicium tick in relation to the liver (1 case of 14,000). The skin and mucous membranes of mucous membranes and mucous membranes The shells (2.7%) can be represented by skin itching and rashes - from spotted, lichenoid, urticar and acneiors to multiformone exudative erythema. Stevens -Johnson syndrome detected 1: 350,000, and toxic epidermal necrolysis - U1: 700,000 examined, which can be due to the sinimal frequency of the manifestation of these pathologies from the intake of terbinafine. Nevertheless, the clinicians are found to stop taking terbinfine in case of a state of sequenced rashes, as well as exclude it in pains with multiforme exudative erythema, systemic eity matosis and exudative psoriasis. We tend to believe that most complications of teribi nafin are allergic in nature, which can be warned thoroughly collected by an allergological anamnesis, on the meaning of antihistamines and hypoallergenic diet. Psihosomatic disorders (1.3%) are poorly represented, drowsiness, increased fatigue, heads and dizziness. In isolated cases, a briefly rugal violation of taste sensitivity is possible. Crimean is rarely found thrombocytopenia (1: 200,000) of insetropenia (1: 400,000). It is not recommended to prescribe to pregnant women and cropping women (since terbinafine is able to be released with unloading milk), as well as with an kidney. and liver under the stature. In practice, 1 case (1:18 000 000) times the vitation of toxic hepatitis is noted against the background of the intake of terbinafine. Terbinafine favorably differs from other systemic nits, since it interacts much less often. Indeed, terbinafine can be jointly met with antihistamine drugs (terphenin, astemizole). Snowstock/tranquilizers (Diazepine benzo derivatives) - Tolperisone, Triazols, Diazepam, antipsychotics (Pimoside) are successfully combined with terbinafine in the treatment of pain - psychosomatics. Statins (Simvastatin, Lovastatin), Motorics of the gastrointestinal tract (cizapride), antiarrhythmic agents (quinidine) are also very compatible with terbinafine while treating somatically -storage patients, despite the long periods of their local use. Aktivasia cyclosporin. In turn, the activity of Terbin of the final decreases when taking rifampicin and terphenin, one at the fluconazole and H2 antagonists increase the antimicotic activity of terbinafine. Since the mechanism -free changes in blood coagulation with a combined reception of terbinafine and warfarin is not entirely clear, it is advisable to draw a disinematic control of a prothrombin index in this group of patients. The principles of antimicotic treatment. Combination (systemic + local antifungal agent) is carried out with the aim of mutual potentiation of the action of anti -mycotics. The impact on various mushrooms -targets, such as the point of the action of the action of antimicotics preparations, leading the accelerated resolution of clinical manifestations without the summarization of side effects and reduce the therapeutic spleen of the action of antimicotics. In addition, this treats a decrease in the invasive ability of mushrooms and as an investigation - an increase in the resistance of the body. Considering the frequent cases of the resistance of mushrooms to cantimikotics, as well as the frequent micotic infection of patients, in order to intensify the effects of mushrooms at a time, including resistant to one mu. Of the antimycotics used, it is wider to use the capitals of combined (systemic) therapy with anti -fungal agents related to different chemical production and having different mechanisms of action. This is practically justified antimicotic therapy leading to an increase in antifungal activity of the drug, so, as mentioned above, is successfully combined with fluconazole. The advantage of this combination is commonly in the synergism of the drugs used. And this is notable, since in order to overcome the resistance of the Glucris to fluconazole in patients with severe mycoses, an increase in the tutor of the terbinafin by 52% (with its combination with fluconaso scrap) allows you to reduce the combined total dowry of terbinafine with fluconazole [N.S. Potkeev et al., 2003]. The disadvantages of combined treatment with two SIS dark antimycotics (for example, terbinafine + fluconazole) can be both an increase in the risk of unwanted reactions and an increase in the cost of therapy. However, among the systemicantimicotics of terbinafine is the most economical sustling. Intermittent scheme of fluconazole reception (I will immediately introduce 150 mg at a dose of 150 mg), at different hours (terbinafine - UR ROM, Fluconazole - in the evening), Dynamic monthly content the role of the state of biochemical indicators allows you to run the development of unwanted effects, creating a highlyclinic effect on the ongoing therapy. , numerous works dedicated to the adoption of patients suffering from mycosis, all world experience with menienia of terbinafine convincingly testify: most of the concrete fungicidal effect of terbinafine, an increased sensory sensation of fungi, especially dermatophytes - abominated pathogens of fungal diseases of the skin, nails Ivolos, practically the absence of resistance The mushrooms to the system of systemic antimicotics with a gentle character of the act on the body make terbinafin almost the perfect tool for the treatment of patients with nail dermatophytics and in the los.
Content is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Share the article on social networks
Recommend the article to your colleagues