People who experience skin diseases will forever remember the torment - unbearable itching and rashes that can drive them crazy. Appearance also brings many experiences. After all, you don’t want to explain to everyone you meet that microbial eczema is practically harmless to others.
The diagnosis is unpleasant for the patient and occurs with inflammation of the epidermis in the area of the head, body and limbs. Severe itching, pain and the general poor condition of the patient make him hot-tempered and irritable.
Microbial eczema in the photo 6 pieces
Microbial eczema in an adult in the photo
Microbial eczema on the hands
Microbial eczema of the leg in an adult
Microbial eczema on the legs photo
Microbial eczema on the feet
Microbial eczema on the legs photo
Microbial eczema on the hands (see photo) and other areas of the body, a type of disease. It has a secondary flow. It develops on already diseased surfaces where bacterial or fungal infections occur. Inflammatory changes caused by infection are superimposed on the background symptoms that have already appeared.
Interesting to know
Diagnostics is carried out to determine the microorganisms responsible for what is happening. They examine the tank. sowing of separated elements or taking scrapings to identify fungi. The pathogenic flora that causes this type of eczema is added in approximately 25% of cases of the total number of cases.
Bacterial eczema and drug therapy
The use of oral medications is recommended in cases of severe microbial eczema. In this case, antibiotics are required, among which ampicillin, azithromycin, cefazolin, and doxycycline are often prescribed. In cases where the bacterial basis of the disease is supplemented by a fungal infection, antimycotics such as fluconazole are indicated.
A high degree of damage to the skin by microbial eczema is a reason for prescribing systemic corticosteroids and cytostatics. This is one or two of the following drugs: triamcinolone, prednisolone, methotrexate, cyclosporine.
Along with antimicrobial agents, antihistamines are indicated: loratadine, suprastin, diazolin. They are prescribed by a doctor in order to relieve the patient of allergies - a characteristic sign of microbial eczema, when the body reacts to the presence of foreign microorganisms and other irritating factors. A course of intravenous injections of calcium chloride or sodium thiosulfate is recommended.
In all cases of eczema, the doctor prescribes medications, including its microbial type, and uses sedatives to relieve itching, improve the patient’s condition at night, eliminate insomnia and irritability due to constant severe discomfort. These medications include sleeping pills, bromine preparations, as well as herbal infusions and teas: valerian, motherwort, chamomile. In addition to drug therapy, B vitamins and vitamin A are taken to maintain the general condition and improve the quality of the skin.
Causes of microbial eczema
Very often, the culprit of infection, determined during culture, is hemolytic streptococcus. He's not the only one. Infection can be caused by:
- Staphylococcus aureus.
- Klebsiella.
- Neisseria meningitis or gonorrhea.
- Candida fungi, etc.
The limbs are often affected. Since this is an associated infection, it affects areas already affected by chronic manifestations. Microorganisms enter tissues through damaged areas. They multiply quickly, creating inflammation localized in foci. This often occurs around injured wounds that do not heal for a long time: postoperative wounds, fistulas, trophic ulcers and other poorly healing injuries.
note
Microbial eczema on the legs is common and treatment is relatively difficult. It appears due to a disease - varicose veins, lymphostasis or long-lasting fungal infections.
The result of secondary pathology is clearly visible mass rashes. They cause discomfort to the owner. For an effective fight, it is important to find out the etiology. There are moments that are conducive to easy onset of the disease. In patients with microbial eczema, the reasons lie in the following features:
- In disorders of the autonomic and nervous systems.
- Neuroendocrine diseases.
- Congenital strong skin sensitivity.
- Hypovitaminosis.
- Genetic predisposition to allergies.
- Weakness of immunity.
A weakened body with accumulated allergens, which in turn are provocateurs for infections, risks turning the disease into a chronic one. This form threatens with constant unpleasant health problems and long-term treatment.
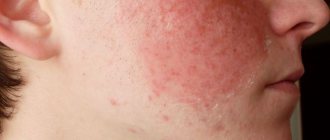
Having no education in the field of medicine, rarely observing such problems, it is difficult to imagine the possible extent of infection and the type of affected skin areas. Next, you can form an objective opinion about microbial eczema on the legs; the photo has a rather unpleasant picture. Severe redness, purulent discharge, dried yellowish-brown crusts, cracks, papules and other unsightly elements create the overall picture.
Therefore, if you find yourself predisposed to allergic manifestations: redness, diathesis and any initial stages of skin lesions, be sure to go to a dermatologist! It is better to prevent a disease than to bring it to a state that is difficult to treat.
Find out more
Causes of the disease
General factors contributing to its appearance are psychovegetative disorders, neuroendocrine diseases, and decreased immunity.
The development of the disease occurs, as a rule, in injured areas of the epidermis: the infection penetrates into abrasions, wounds, cracks, and the process of its spread begins.
The causative agents of microbial eczema are either bacteria (streptococci or staphylococci) or a fungus of the genus Candida. They penetrate the injured epidermis of the hands, and the inflammatory process begins very quickly.
The causative agent of the disease is a fungus of the genus Candida
Symptoms of microbial eczema
By and large, microbial eczema and the causes of the disease create a special type of dermatitis, which has a viral or bacterial development. That is why it can be dangerous for those around, especially small children. When an infection occurs, the incubation period extends from a short period to a long period, numbering several weeks. This disease is officially registered and has an ICD10 code. It needs to be studied at the cellular level. Before this, the dermatologist will collect anamnesis to identify the pathogen.
Interesting to know
If the process is acute, then the development is almost instantaneous. Itchy skin takes on a suspicious red color. Swelling appears and papules form. After some time, the vesicles burst, releasing the secretion, and the skin cracks. After several days, unsightly yellowish crusts form. It is worth starting proper treatment immediately to prevent a chronic form.
When the disease becomes chronic, the symptoms become moderate. The infection is concentrated in the dermis. After a while, you can notice signs of intoxication. The danger of the condition is due to an unfavorable prognosis. It is no longer possible to cure a chronic disease. Symptoms will constantly appear, changing the strength and localization of occurrence. In this case, it is necessary to take a serious approach to prevention in order to stop the development and keep the disease in positive dynamics. To answer the question about microbial eczema and how to treat it, it is necessary to determine the etiology and diagnose the stage of the disease:
- Erythematous stage. The process begins with it and is accompanied by redness of the skin with defined boundaries. The patient is bothered by severe itching.
- Papulovesicular - got its name due to large-scale rashes. Now many blisters filled with serous fluid appear.
- Weeping - begins after the opening of the papules, when exudate oozes.
- Dry - determined by the formation of crusts. Plaques have boundaries, and the infection spreads further, affecting healthy areas.
In addition, the disease has some differences depending on the location. Dermatology divides the disease into types:
- Nummular. The second name is plaque eczema. Redness, plaque-shaped, up to 3 cm in diameter, causes swelling. Most often this type of microbial eczema appears on the hands.
- Varicose. Develops due to varicose veins of the lower extremities. The veins become enlarged, swelling and reddened spots appear on the skin. This area is very itchy and ulcers soon form.
- Post-traumatic. It can be characterized by severe wound healing, for example, postoperative wounds, the formation of blisters with purulent contents and long-term treatment.
- Sycosiform. Occurs in patients with sycosis. Bright red lesions that constantly become wet, releasing exudate. The spread occurs on the face in the area of the chin and lips, in the pubic area and armpits.
- Located in the nipple area. Often occurs during feeding of infants. I am concerned about severe burning, itching and painful cracks. Over time, a rash and purulent discharge may appear.
Pathological flora is diagnosed both clinically and by laboratory tests. This is necessary because the signs of the action of various microorganisms are similar. The doctor will prescribe measures to identify a specific pathogen:
- Scraping
- General blood analysis.
- Examination of a biopsy sample taken from a progressive lesion.
- Consultations with an allergist, endocrinologist and other specialized specialists.
After all the nuances are clarified, the most effective therapy will be prescribed.
Possible causes of the disease
The development of miotic eczema is caused by the entry of various fungal pathogens into the body. There are about 500 species of such fungal pathogens. But most often the following lead to miotic eczema: mold fungi, Candida fungi, pathogens of pityriasis versicolor, pathogens of mycosis of the nails, pathogens of trichosporia nodosum.
For the development of miotic eczema, one entry of the fungus into the body is not enough. For damage to begin, a reaction must occur in the body. This reaction occurs due to various factors. The main factors include:
- Frequent skin injuries.
- Allergy to pathogenic microorganisms.
- Weakened immunity.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Lack of personal hygiene.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system.
- Long-term use of antibiotics.
- Avitaminosis.
- Infection in open wounds.
When several factors are combined, a fungus that enters the body will lead to the development of mycotic eczema.
Treatment of microbial eczema
Any form of allergic manifestations and dermatitis must be supported not only by a course of medication, but also by following a diet and giving up bad habits. It is possible to fight effectively only by coordinating actions with a doctor, with a full study of the etiology. Self-medication is inappropriate in serious cases.
Having diagnosed microbial eczema, treatment is designed to combat the infection, and it is also important to eliminate the factors that provoke the disease. As a rule, treatment is carried out comprehensively, which includes a course of medications and agents used topically to treat diseased areas of the skin surface. Medications are prescribed based on the type of disease. Usually they combine the use of antibiotics and ointments for external use.
Traditional medicine recipes
Traditional medicine recipes, based mainly on herbs and other plants, help get rid of itching and quickly heal the affected skin surface, which is especially important for paratraumatic microbial eczema, which occurs due to a violation of the integrity of the skin.
Here are a few such recipes:
- Multi-component lotion . Seedlings, nettles, birch buds, calendula, St. John's wort, yarrow (all this can be purchased at the pharmacy) - mix 20 g of each ingredient and use to prepare lotions: 1 tbsp. l. mixture pour 1 tbsp. boiling water, strain after 2 hours and apply the lotion to the affected areas for half an hour. The same composition can be taken three times a day, 50 ml.
- A decoction of pine needles and cones . Brew 100 g of dry needles and cones with 1 liter of boiling water, let it brew for 1 hour and then make 15-minute applications on the affected areas of the skin.
- Decoction of walnut leaves . Pour 100 g of fresh leaves into 0.5 liters of cold water, boil for 5 minutes, let cool and brew. Use to wipe affected areas.
- Compress of black elderberry leaves (fresh) . Wash the leaves, lightly beat them with a knife, apply to the affected areas, cover with film and leave for 10-15 minutes.
Pine cones are very rich in vitamin C and B1 and are good for the skin
Treatment of microbial eczema on the hands
To alleviate the condition of the skin of the upper extremities affected by the infection, sedatives and antihistamines are prescribed. They soothe and significantly reduce painful symptoms. For microbial eczema on the hands, a course of vitamins will be added to the treatment, sometimes by injection. This is necessary for faster healing and regeneration of the skin.
In case of complex disease, hormonal ointments are used to quickly relieve acute manifestations. Such ointments are unsafe; they are prescribed for a short time, later replaced with creams with an anti-inflammatory effect.
Treatment of microbial eczema on the legs
The lower extremities are often affected due to problems with the veins and the development of varicose veins. It is caused by streptococci and candida. A rash can also appear when wounds, burns become infected, or if there are lesions with other types of eczema. Typical manifestations: redness, itching, blisters containing exudate. When they burst, they expose erosions.
Microbial eczema on the legs requires the use of antiseptics in treatment. Depending on the etiology, medications are used to combat bacteria or fungi. They are produced in injections, ointments, tablets and prescribed in combination. Recipes that came from the people - compresses, herbal lotions - also work well.
Prevention of microbial eczema
Compliance with hygiene rules and attention to skin lesions is the best prevention. However, having a predisposition to allergic reactions, frequent occurrence of dermatitis and other skin ailments, it is imperative to adhere to a diet and lead a healthy, active life. For a good metabolism, the body must get physical work every day.
The diet should consist of boiled and steamed dishes. Limit your consumption of allergenic foods: honey, eggs, seafood. Sweet carbonated drinks, semi-finished products and sausages are harmful, it is better to avoid them altogether. Use household chemicals and detergents carefully, trying to limit their contact with the skin surface. Follow all the instructions and microbial eczema, the photo of which you will see below, will definitely recede!
Diet and proper nutrition
Diet is an integral component of the treatment complex. In fact, it fully complies with the principles of rational nutrition, except that you will have to give up citrus fruits, as well as spicy and irritating foods (pepper, garlic, onions).
Smoked, canned and pickled foods and alcohol are excluded from the diet. Fluid intake will have to be limited to avoid swelling.
The basis of the diet is dairy products, cereals, meat (boiled only), vegetables and fruits containing a lot of fiber, and greens.