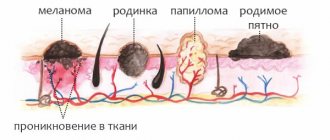
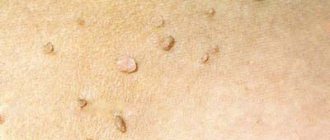
Papilloma, papillomatosis
(
papilloma
; lat. papilla nipple + -oma;
papillomatosis
; papilloma, papillomat[is] + -osis; synonym:
papillary polyp, papillary fibroepithelioma
) - a benign tumor developing from squamous or transitional epithelium, having the appearance of a papillary growth protruding above the surface of the surrounding epithelium. The term papillomatosis refers to a process characterized by the formation of numerous papillomas. Along with benign true tumors, papillomas often include morphologically similar hyperplastic processes of various origins - most often papillary growths of the epithelium and stroma, which have an inflammatory nature.
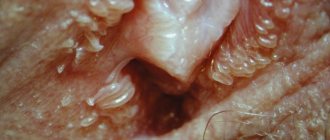
Papillomas are found on the skin, mucous membrane of the mouth, nose, paranasal (paranasal, T.; sinus paranasales) sinuses, pharynx, vocal cords, renal pelvis, ureters and bladder.
Reasons for development
Most often, skin papilloma occurs in older people, on visible areas of the body (face, neck, hands). Factors contributing to the development of the virus may be the following:
- advanced age of a person;
- smoking for many years;
- prolonged insolation (solar radiation);
- exposure to carcinogens;
- skin burns;
- chronic pathologies of the skin;
- old scars.
Depending on the protective systems and physical condition of a person, the above factors can provoke development over several years or decades.
Usually the immune system suppresses the viability of the virus. But in some circumstances she stops fighting him:
- A long-term disease of an infectious or inflammatory nature. A person takes strong medications that not only destroy the main cause of the disease, but also disrupt the natural metabolic and protective functions of the body.
- Prolonged depression, nervous breakdown, and other events of a nervous nature weaken the immune system.
- Prolonged physical activity that adversely affects the general condition.
- Avitaminosis.
- Hormonal disorders, which lead mainly to diabetes, diseases of the endocrine system and metabolic disorders.
- Pregnancy.
- Chronic swelling of the joints.
Mechanism of infection and prevention
Infection with the virus occurs through sexual, domestic and hematogenous routes. A newborn can intercept the disease from the mother as it passes through the birth canal. It is worth noting that women, more often than men, become infected through sexual contact. While among men, the household method of infection is common.
You can become infected with papilloma through minor abrasions and cuts. That is why it is necessary to treat fresh wounds with antiseptic solutions and secure them with adhesive tape!
Papilloma is a benign growth, the occurrence of which can be avoided. To do this, you need to take vitamin and mineral complexes in a timely manner, get rid of bad habits and adhere to a healthy diet. For girls who have not become sexually active, advanced vaccines are recommended: Gardasil and Cervarix. This will help avoid both sexual and domestic infections with papilloma.
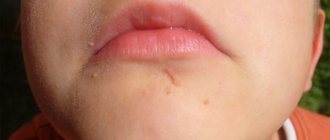
Appearance
Basal cell papilloma is a benign tumor. Outwardly it looks like a rough compaction with a clearly defined border of a flesh-colored or yellow-brown shade.
There are types:
- Pigmented.
- Knotty.
- Superficial.
- Scleroderma-like.
- Ulcerated.
A network of dilated capillaries is often observed around the wart. They are a source of nutrition for papilloma.
Papilloma rarely leads to complications. However, if her body is injured, bleeding may occur. If desired, you can remove the body in the dermatologist's office.
Indications for the procedure for pathology
High-risk infections should be evaluated for malignant changes. The diagnosis is usually made clinically; for intraepithelial neoplasia, histological examination is necessary. Since there is a high tendency for relapse, regular follow-up examinations are necessary.
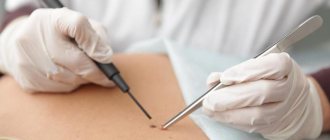
A biopsy is used to rule out or diagnose a specific condition. An important indication for histological examination is suspicion of cancer. The doctor may perform a biopsy if a tumor is suspected in the bones, muscles, fat and connective tissue, skin, breast and liver.
Other diseases can also be detected through biopsy or even treated. Polyps in the gastrointestinal tract can be removed and examined using biopsy forceps. A biopsy is also necessary for those diseases in which the mucous membranes are characteristically altered.
A skin biopsy can be used to multiply connective tissue cells (fibroblasts), whose genetic material is tested for pathological changes such as mutations and chromosomal defects.
For all lesions, it is recommended to repeat the procedure after 4-8 weeks. If there are no relapses, the study is carried out after another 3-6 months. For intraoral and intraurethral lesions, follow-up is performed every 3-6 months up to 1 year. For high-grade anogenital intraepithelial neoplasms, repeat examinations are performed every 6 months for 5 years, then annually.
Preparation of a preparation from a selected tissue sample
Diagnostics
The reason for contacting a dermatologist is the numerous appearance of warts on the body. The specialist will correctly determine by its appearance its type and danger to the patient’s health. The doctor also determines the course of the disease - acute or chronic. To do this, a sequential chain reaction is carried out.
In the direction of a dermatologist, a consultation with an oncologist may be necessary in order to exclude the possibility of oncological development of the compaction.
To accurately determine the type of infected tissue, a biopsy is performed - a small sample of damaged tissue is taken for detailed examination in the laboratory for malignancy. Another diagnostic method is cytological examination.
Is basal cell papilloma dangerous?
Papilloma is a neoplasm that does not progress to the stage of cancer in children. Adults, if growths are detected on the body, should immediately seek help from a doctor. The fact is that often, seborrheic keratosis is found in the structure of the growth, which occurs due to age-related changes. In many cases, this is the main reason for the degeneration of the growth into a malignant tumor.
It is important to know that keratotic papilloma does not go away on its own! It requires high-quality and long-term treatment!
For women, basal cell keratosis papilloma is dangerous for causing cancer of the rectum, uterus and cervix. There is also a high probability of developing cervical erosion. Women who are addicted to alcohol and addicted to smoking are especially at risk of complications. That is why, if growths or their modifications are detected on the body, you need to immediately give up bad habits.
For men, this disease does not pose any particular threat. Often, male representatives are carriers of the papillomavirus. At the same time, the favorite place to localize the growth is the groin area. Which leads to rapid infection of the partner.
Drug treatment
Taking medications includes a course of treatment based on immunostimulating drugs and cytostatics. To suppress the virus, the following is prescribed:
- Isoprinosine – stimulates the immune system, antiviral. Has the form of tablets.
- Bleomycin is an antitumor antibiotic used for external and internal tumors.
- Interferon – antiviral, immunostimulating.
Many drugs have serious contraindications, so a specialist should select medications and adjust the dosage and duration of use.
ethnoscience
The recipes mainly consist of herbal preparations that provide the body with a vitamin complex.
There are also products for external use. You can remove the problem without surgery using one of the following methods:
- Celandine. Freshly picked juice is applied to the sore spot. The substance literally burns out the formation in 1.5-2 weeks. It is very poisonous, and in order to avoid burns, it is recommended to use it no more than once a day, and lubricate the skin around it with a greasy ointment.
- Garlic. A couple of cloves of garlic are pressed with a garlic press and mixed in equal proportions with skin cream (for example, for children). The mixture is applied to the seal for two weeks, and the top is covered with a plaster.
- Kalanchoe. The leaf is cut and the cut is applied to the papilloma, secured with a plaster or bandage.
If the course of treatment has ended, and there are no visible changes for the better, it is still recommended to consult a dermatologist for surgical removal. Also a serious reason to stop treatment is bleeding and pain in the treated area.
Therapeutic measures
It is useless to fight papilloma with medications, since the growth cannot be treated with medication. Typically, such formations are removed using hardware methods.
Types of excisions
- Radio wave removal - exposure to radio waves. The procedure does not leave swelling or redness. All residual traces disappear over time.
- Cryodestruction is the removal of a tumor with liquid nitrogen. Under the influence of low temperatures, papilloma cells freeze and gradually die. For large lesions, multiple procedures may be required.
- Electrocoagulation – burning out the growth with an electric current of a given frequency. With this method, the virus stops spreading, and the likelihood of relapse is reduced to zero. Sometimes minor marks remain.
- Laser therapy – evaporation of papilloma cells with a laser beam. After the procedure, a dry crust appears. After a couple of days it disappears and does not leave a scar.
Modern methods help to quickly and painlessly remove a benign tumor. It is important to consult a doctor in time to prevent the development of oncological degeneration.
What to do after the procedure
After removing the growth, recommendations are given regarding further care of the resulting wound:
- do not touch with your fingers, do not pick,
- avoid contact with water,
- prevent dirt from entering.
Additionally, you need to treat with an antiseptic solution. If you follow simple rules, the wound will quickly heal, leaving no reminder of papilloma.
People's Councils
Many people prefer to get rid of growths using traditional medicine.
- Daily treatment with celandine juice. After the procedure, the papilloma must be covered with a plaster. Apply until it disappears completely.
- Two parts of baby cream are mixed with one part of chopped garlic. The mixture is applied to the neoplasm and covered with a film for three hours. Use daily for at least two weeks.
- Use of aloe. A fresh leaf is cut in half and fixed on the papilloma for 12 hours. Apply until it disappears.
Attention! The effectiveness of folk recipes is not confirmed by anything. Before using any product, you need to get your doctor’s approval and find out about possible contraindications.