How does the virus enter the body?
The content of the article
The main route of infection is sexual. Moreover, regardless of the form of sexual contact - anal, vaginal or oral. A condom reduces the risk of infection, but it is not a panacea.
With a much lower probability, HPV can enter the body through contact and household contact - through touching, hugging, personal hygiene products, manicure tools, etc. Most often, danger awaits in public places - bathhouse, swimming pool, sauna, bus, etc.
The presence of damage and microcracks on the skin favors infection. A vertical route of infection is also possible - from mother to child. The virus can be transmitted to an infant during fetal development or when passing through the birth canal.
Prevention
- spend more time in the fresh air;
- normalize the diet;
- draw up a clear daily schedule, eliminate lack of sleep;
- strengthen the immune system with physical exercise, initially physical exercise is enough;
- consume your daily fluid intake;
- to refuse from bad habits.
We should not forget that if you follow the rules of sexual behavior (do not enter into single relationships, use personal protective equipment), the principles of personal hygiene (refuse to use shared items - towels, washcloths, razors), the risk of HPV infection is significantly reduced.
Reasons for the appearance of formations
The presence of HPV in the body does not guarantee the development of its clinical manifestations - the appearance of growths. It may remain in standby mode for a long time until favorable conditions occur. Activation of the virus is associated primarily with weakened immunity. This condition is provoked by both environmental conditions and the presence of various diseases.
Human papillomavirus
Lifestyle reasons:
- stress and nervous tension;
- disrupted daily routine;
- unbalanced and unhealthy diet;
- presence of bad habits – smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs;
- avitaminosis;
- long-term use of cytostatics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- excessive mental and physical stress;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- hypothermia, overheating.
Causes associated with the presence of diseases:
- acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections, influenza;
- HIV AIDS;
- herpes type 2;
- oncology;
- endocrine system disorders;
- anorexia;
- chronic anemia, etc.
Weak immune resistance can also be inherited.
What are condylomas
Condylomas are transmitted primarily through sexual contact. Infection with the virus occurs during sexual intercourse, sometimes through kissing. A newborn can be infected with HPV during childbirth if his mother has condylomas.
HPV does not appear immediately; it has a long incubation period, sometimes up to several years. The disease is detected when the immune system is weakened or concomitant diseases occur. It could be:
- infection with the herpes virus;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- hormonal disorders;
- infectious diseases;
- bad habits;
- avitaminosis.
Condylomas are divided into pointed and broad. The first ones have a thin stalk, the structure of the tumor is lobular. The cause of their occurrence is a viral infection. Such formations appear in the groin, genitals, and perineum. Tumors often become inflamed, causing discomfort to the patient. Doctors recommend removing them. Wide condylomas with a thick base are formed due to secondary syphilis.
How to distinguish papilloma from condyloma
Knowing the difference between papilloma and condyloma is necessary to determine further actions. While some can remain on the body throughout life and cause only cosmetic discomfort, others carry the risk of malignant degeneration.
| Index | Papilloma | Condyloma |
| Structure | Homogeneous | Heterogeneous, small, papillary |
| Form | Round or oval, located on a soft stem | Arbitrary, located in clusters, in the form of ridges. Characterized by a narrowing from the stem to the end |
| Size | Up to 10 mm. As a result of traumatic exposure, it may increase by 2-15 mm. | Also capable of growing |
| Color | Weak or intense pigmentation | Virtually no different in color from surrounding tissues |
| Localization | Preferably on the skin | On the mucous membranes, mainly of the urogenital area; on skin folds subject to friction from clothing |
| Peculiarities | Causes aesthetic discomfort. Rarely inflamed, usually only due to injury | It often becomes inflamed and infected. Possible ulceration of the body of the growth, pain |
| Main route of infection | Contact and household | Sexual |
| Exciter type | Typically 2, 7 and 28 strains | 6, 11, 16, 18, 39, 54, 56, 73 strains |
| Risk of malignancy | No | Yes |
Treatment of papillomas and condylomas
A person who discovers a tumor on his body (warts, balls, sores) independently decides whether to see a doctor. It is important to consult with a specialist; only a doctor will be able to determine the degree of health risk as a result of the action of the virus that provoked the growth.
Remember, self-medication and attempts to get rid of a wart on your own will not lead to anything good! Attempts at self-removal may result in treatment in an oncology medical facility.
In some cases, foreign inclusions can be treated with medication. For this, the patient is prescribed a course of antifungal and antiviral drugs. In addition, the doctor assesses the state of the patient’s immune system and has the right to prescribe maintenance therapy.
Formations on the mucous membranes of the genital organs can be eliminated by using ointments that contain immunostimulants, or by using vaginal suppositories with interferon.
If the ball is suspected of being oncological, the patient will be sent to undergo tests for tumor markers. In this case, the person will be prescribed cytostatics as medications.
Modern options for getting rid of papillomas and condylomas
The medical service offers the following ways to get rid of skin pathologies:
- Chemical methods. The principle of operation of these methods is based on the use of products with a high acid content.
- Cryocoagulation. The method is based on the effect of low temperatures on skin formations. The result is that liquid nitrogen eliminates thickening. The disadvantage of the method is the high risk of re-formation of the outgrowth.
- Radio wave method.
- Laser treatment. The laser beam can remove some skin thickenings, but not all types of HPV are sensitive to the laser.
- Surgical intervention. Previously, this method was considered the only one that was supposed to remove foreign viral formations. The disadvantages of the technique are cosmetic defects in the form of scars and cicatrices.
Only a doctor can choose the only correct method for removing foreign phenomena. When choosing a virus removal technology, the doctor takes into account factors such as the severity of the disease, the presence of chronic diseases in the patient, the health risk as a result of the formation of a viral thickening, the state of the patient’s immune system, and his tendency to allergic reactions.
How to cure
To date, there is not a single proven treatment for HPV in the world.
The tactics for combating papillomas and condylomas are as follows:
- removal of formation;
- antiviral therapy – to suppress the activity of the virus;
- immunomodulatory therapy – to improve the functioning of the immune system.
To get rid of the growth, various methods are used:
- laser removal;
- cryodestruction;
- radio wave exposure;
- electrocoagulation;
- chemical removal;
- traditional surgery.
The choice of method is made by the doctor depending on the type of formation, its location, size, etc.
A number of other distinctive features
It is not difficult for a specialist to identify the difference between condyloma and papilloma from a photo, while ordinary patients do not always succeed. But in addition to the above, these neoplasms can be distinguished by a number of other factors. An important indicator is density - papillomas are harder to the touch, which cannot be said about condylomas. They also mostly occur in different places. Condylomas, as a rule, are localized exclusively on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, in the genital area or around the anus. As for papillomas, they occur on the mucous membrane in rare cases; they often appear on the surface of the skin.
It is condylomas that are prone to frequent fusion, which leads to the formation of groups; this does not happen with papillomas. And if you remove mucous tumors, the risk that they will reappear exists and is quite higher than with the same procedure in the case of papillomas.
In addition, papillomas do not pose a serious danger to humans. You can calmly decide to remove them or live with them without paying any attention to them. You need to be careful with condylomas, and it is better to get rid of them to avoid the appearance of malignant neoplasms.
In other words, despite the differences, condylomas and papillomas have the same nature of origin.
Laser removal
This is a modern method of excision of formation, which has become widespread.
Its popularity is due to its advantages:
- painlessness;
- low-injury;
- bloodlessness;
- speed of the procedure;
- minimal risk of infection;
- short rehabilitation period;
- no scars.
Thanks to the precision of the laser beam, it is possible to remove growths even in particularly sensitive areas, such as the intimate area, eyelid, etc.
Cryodestruction
This removal method is only used for skin tags. It consists of a short-term effect on the formation of liquid nitrogen. Pathological tissues are destroyed by flash freezing.
Cryodestruction
The advantages of cryodestruction include easy tolerance by the patient, no need for anesthesia and no risk of scar formation. Disadvantages are difficulty in controlling the depth of impact and a longer rehabilitation period.
Are papillomas harmless?
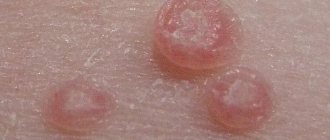
Papillomas are cylindrical growths of skin on thin movable legs, which signal the presence of HPV (human papillomavirus) in the body.
It is difficult to track their appearance, since they may not appear for a long time, similar to herpes, and then appear as if out of nowhere. Most often, first one small papilloma “mother” pops up, which soon brings with it a bunch of “babies”.
Favorite areas for skin growths are the bends of the elbows, armpits, eyelids, and popliteal fossae. However, they are not limited to them: papillomas can successfully grow anywhere.
Many men take this quite calmly and do not try to deal with unpleasant guests. The fair sex is more concerned about papillomas, because it is a cosmetic defect. Let's figure out whether papillomas are so harmless and whether we need to fight them.
What is human papillomavirus
HPV is a virus that causes a benign tumor in the form of papilloma. It is classified as a sexually transmitted disease (STD) along with syphilis, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis and chlamydia.
However, it can also be contracted in everyday life - for example, through close contact with a carrier of the virus through touch or when visiting public places (it penetrates through scratches on the skin).
There is another way of infection - self-infection during shaving or hair removal.
When the virus has already “taken root” in your body, an outbreak of papillomas is provoked by any, even the most insignificant, at first glance, factor - stress, exacerbation of gastrointestinal diseases, a recent cold. As a rule, papillomavirus occurs precisely against the background of weak immunity.
How does HPV manifest?
There are different strains of the papilloma virus. For example, genital warts are papillary skin growths on the genitals and perineum. Depending on the intensity of the lesion, these formations can look different: either as single growths or as a whole cluster, visually similar to a head of cauliflower. The growths cause a lot of discomfort: they itch and even bleed.
It happens that patients come to medical clinics who have been unsuccessfully treated for years for “exacerbations of candidiasis” with “just one pill.” They are quite surprised by the fact that they do not have any thrush, the smear turns out to be “clean”, and itching and irritation are caused by condylomas.
Papillomas and condylomas, like herpes, periodically appear and disappear, since they are only consequences of the virus itself. An exacerbation of the disease occurs during a period of decreased defenses.
Papillomas in the throat
The human papillomavirus does not only appear on the eyelids and other visible parts of the body. Often, papillomatosis occurs in the respiratory tract: the tissue of the nasopharynx can grow to the lungs. These benign formations take over the larynx, bringing a person a lot of unpleasant sensations.
Unlike regular clinics, medical clinics not only accurately diagnose this type of HPV, but also perform quick and painless removal of growths. Local therapists and ENT doctors do not always recognize laryngeal papillomotosis, so they prescribe only ineffective rinses.
Who can get infected with the virus
Fans of tobacco and alcoholic beverages, as well as people leading a chaotic intimate life, have a high risk of infection. Women who have been using birth control pills for a long time are also at risk. At the same time, anyone can be a carrier of HPV - a child, a young man, an old man.
HPV and pregnancy planning
The papilloma virus in women can cause serious consequences. If the mother is its carrier, then the baby passing through the birth canal will become infected with it in almost 100% of cases.
HPV enters the baby's mouth and eyes, and then spreads throughout the body. This is why it is so important to get tested before conceiving and rule out any types of diseases related to STDs.
Determining HPV is an important step in preparing for pregnancy.
If a virus that was previously in a latent form is detected during pregnancy, do not despair: contact qualified doctors at SM-Clinic. They will advise you and tell you what can be done without harming the health of the mother and child.
Diagnosis of human papillomavirus
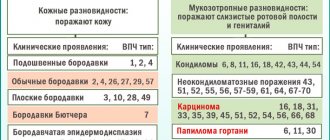
Scientists have identified over a hundred types of HPV. Not all of them are harmless: some subtypes can cause cervical cancer!
- Non-oncogenic papillomaviruses - HPV 1, 2, 3, 5.
- Oncogenic papillomaviruses of low oncogenic risk - HPV 6, 11, 42, 43, 44, 54, 61, 70, 72, 81.
- Oncogenic papillomaviruses of intermediate oncogenic risk - HPV 26, 53, 66.
- Oncogenic papillomaviruses of high oncogenic risk - HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59 and 68.
Due to the asymptomatic course of the disease, many carriers of the virus do not contact specialists in time. The only way to protect yourself from HPV is to get vaccinated, preferably before you become sexually active. However, you can prevent the development of cancer, even if you have not been vaccinated against the virus.
To avoid trouble, you need to visit a gynecologist a couple of times a year and undergo an examination. Thus, precancerous changes in the cervix are detected through a Papanicolaou test (cytology smear). The DNA of the virus is also successfully determined using a blood test using the PCR method.
They have their own laboratories with high-quality reagents - this guarantees high accuracy of HPV test results. Only after blood and smear tests can you determine the types of virus present in your body and remove papillomas.
Remember: small formations on your body indicate poor health. It may be worth visiting a doctor and getting checked for gastrointestinal tract or gynecological diseases.
It is not recommended to tear off skin growths, scratch them, or tie them with thread. This will not solve the problem, but will only worsen it: the virus will become more aggressive and begin to capture new territories.
To remove formations effectively and painlessly, contact the specialists at SM-Clinic. Removal of papillomas in Ryazan is carried out without complications and marks on the skin. At the same time, it is better to observe certain conditions: eat right, avoid stress, walk and sleep at least 6-8 hours a day.
If you notice unpleasant growths on your skin, do not delay diagnosis and treatment: make an appointment with an experienced doctor by calling +7 (4912) 77-67-51. This way you will maintain your health and avoid negative consequences.
Share with friends:
Electrocoagulation
The method is aimed at cauterizing the growth using electric current. With its help, you can remove papillomas and condylomas on any part of the body, including delicate ones. However, for the urogenital area and eyelids, it is better to give preference to methods that are less painful.
Electrocoagulator
The formation is destroyed under the influence of high temperature, due to which the surrounding tissues are also damaged. In addition, patients note poor healing, and sometimes scarring and relapses. The advantages of this type of removal are sterility, bloodlessness, the ability to adjust the current strength and control the depth of exposure.
Why are growths dangerous?
Papillomas and condylomas are conventionally considered safe neoplasms on the skin, but the risk of benign cells degenerating into malignant ones is higher in the second case.
Condylomas are skin manifestations of the action of oncogenic types of the virus. Years of research have revealed a relationship between HPV and cervical cancer. Timely diagnosis with further removal of condylomas helps to significantly reduce the risk of developing cancer in women.
The growths can be located not only on the skin and external genitalia, but also in the vagina and on the cervix. Due to the peculiarities of blood circulation in the genital organs, condyloma receives enough nutrition and can grow rapidly. In gynecology, there are cases where condylomas located on the vaginal wall grew up to 10 cm in diameter.
Folk remedies
On the Internet you can find many recipes and techniques for removing papillomas and condylomas. However, you should not self-medicate. Only a doctor can safely and effectively get rid of the problem. Any attempts to bandage the formation with thread, cauterize it with celandine juice and other popular folk methods can provoke complications.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Condylomas, papillomas and genital warts in women - gynecology at the ON Clinic medical center
For women's health, condylomas and papillomas pose a much more serious threat than for men. This is due to the fact that one of the most common female cancers, cervical cancer, can be caused by certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV), which also contribute to their appearance.
Flat and genital warts in women as a threat to cancer pathology
Human papillomavirus is one of the most common viral diseases on Earth. It has many varieties, each of which manifests itself differently in a woman’s body.
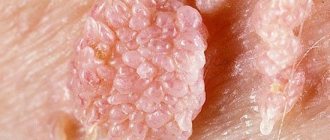
An integral companion of this disease are condylomas - small growths (by their nature they are benign tumors), similar to warts with a thin and soft stalk.
They can be located in various parts of the body: on the neck, in the armpits, in the genital area and even on the tongue.
Condylomas do not metastasize and do not pose a direct threat to human health, but, nevertheless, it is better for a woman facing this problem to play it safe and go for a medical examination.
Genital condylomas are benign neoplasms of viral origin that occur on the skin and mucous membranes of both women and men.
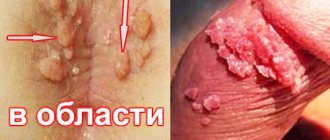
These formations are clusters of small papillae that are flesh-colored or pink. Their consistency is soft. The diameter varies from a few millimeters to several centimeters. Genital warts in women are most often localized in the area of both external and internal genital organs . This:
- vulva;
- clitoris;
- vestibule of the vagina;
- Cervix;
- urethra (urethra);
- crotch;
- anus (back passage).
That is why they are also called genital warts. In addition to the intimate area, condylomas occasionally affect the oral cavity and armpits . If they are not complicated by anything, then their appearance and development are mostly asymptomatic.
Vulvar condyloma most often occurs in young and pregnant women.
Flat condyloma of the cervix is another equally common type of benign formation of the urogenital tract, which is just as dangerous if left untreated. A peculiarity of flat condyloma is that its development and growth are directed not outward, as in genital condyloma, but inward to the epithelium of the mucous membrane of the cervix.
It does not rise above the surface of the skin or mucous membrane - but remains flat, flush with the surface from which it was formed. And this makes it difficult to diagnose during a routine examination. It is formed in the deep layers of the cervical epithelium.
Development from deep layers indicates a chronic form of the virus, its long-standing presence in the body.
Flat condyloma also occurs mainly in young women. In approximately half of the cases, this type occurs with dysplasia, which is assessed as a pre-oncology condition.
Genital condylomas in women and their treatment are of practical interest not only for gynecologists, but also for oncologists. For, unfortunately, it is the genital and flat condylomas that are most likely to degenerate.
Consequences of condyloma in women
Vaginal condyloma or uterine condyloma is dangerous not only because it is an alarming signal for a woman and a reason to be checked for cancer. It brings discomfort to sexual life and complicates personal hygiene procedures.
During sexual intercourse or while taking a shower, you can accidentally damage it and introduce infection through an open wound. Under no circumstances should you try to remove it yourself - this is very dangerous! Treatment of condylomas in women is the prerogative of qualified specialists.
Remember that this is a neoplasm and do not be confused by its tiny size, it can cause a lot of inconvenience and complications in the future.
Symptoms: what to look out for
Symptoms of condyloma in women are, first of all, its characteristic appearance. That is, a cluster of small papillae rising above the surface of the skin.
Other important symptoms of genital warts are the tactility of the neoplasms, their high physical tangibility. It’s not for nothing that they are called pointed: that means they have a sharp, tangible tip. This quality is very important for the initial detection of symptoms by the woman herself.
For example, if it is not located on the surface of the skin, where it is easy to notice, but inside the body (vagina, urethra, cervix). Therefore, the development of the slightest new sensations (unusual discomfort during sexual intercourse, pain, burning and itching) should immediately attract attention.
Treatment of condylomas in women at ON Clinic
Treatment of condylomas in women (as well as warts on the genitals, papillomas on the labia), as in men, is carried out using the most effective methods in modern dermatology and gynecology:
- local cryotherapy and cryodestruction (cauterization with liquid nitrogen);
- cauterization with concentrated acids;
- laser ablation (evaporation);
- surgical excision (removal);
- ozone therapy;
- radiosurgery;
- electrocoagulation;
- Darsonvalization.
It should be understood that treatment of such a disease is always symptomatic. That is, it is possible to eliminate only its clinical manifestations - but not their cause - HPV in women. Therefore, a certain probability of relapse is always present.
In order to reduce the risk of malignancy (malignancy), to which genital warts are prone, as well as to increase the overall resistance of the body, immunotherapy with interferon preparations can be carried out in parallel.
Thanks to modern technologies, defects such as vaginal condyloma or cervical condyloma can be easily removed without pain or surgery .
For these purposes, in medicine we use the Surgitron device.
This device removes condylomas in women through radio wave exposure, which is absolutely safe for human health .
In the course of several short-term procedures, you can get rid of condylomas without feeling any discomfort. Treatment at ON Clinic is carried out by qualified specialists after a detailed examination and study of the medical history.
Why complicate your life, feel pain and discomfort, when there is a reliable and absolutely safe way to remove condyloma in women? International gynecological specialists are always ready to clearly explain to patients what condylomas are and their causes.
In the arsenal of specialized specialists there will always be something to treat condylomas in women. Making an appointment with a gynecologist at ON Clinic is very simple.
You can call the phone number listed for your region or fill out the appointment form on our website.