Is seborrheic dermatitis contagious or not, is it transmitted from person to person?
.
Seborrheic dermatitis, or as this disease is popularly called, seborrhea, is a disease of the scalp and face, namely the scalp, the disease is caused by a fungus. Most people are carriers of the fungus, but the disease does not manifest itself in any way. It is localized in places where the sebaceous glands actively work: the face (nose, cheeks, forehead), back, namely the interscapular area, chest.
Seborrheic dermatitis is an unpleasant disease
How to recognize the disease?
The emergence and spread of fungus can be triggered by many factors: consumption of fatty and concentrated foods, sugar, spices, bad habits, hereditary characteristics of subcutaneous fat, hormonal changes, infections and decreased immunity, stress and chronic fatigue, metabolic disorders, psychological and emotional instability .
With sudden changes for the worse, conditions are created in the human body for the development of a fungus that causes disease. Teenagers are most susceptible to seborrheic dermatitis, since at their age the sebaceous glands work very actively, thereby creating favorable conditions for the development of fungus.
Seborrhea is not difficult to diagnose; it is determined by a number of symptoms:
- excessive peeling of the skin;
- itching and burning;
- the appearance of dandruff;
- if the disease progresses, the scales have a characteristic yellowish color;
- red spots appear on the body and face;
- exacerbation in the autumn-spring periods.
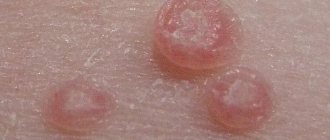
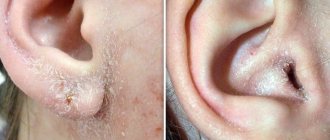
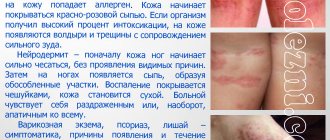
This type of dermatitis manifests itself throughout the body and in the scalp, mainly in places where hair grows on the eyebrows, eyelids, nasolabial folds, in men in the place of the beard and mustache, chest, and can extend into the ears inside and outside.
Often found in the groin, abdomen, armpits, and in women on the mammary glands. Does not apply only to the palms and armpits. Red spots characteristic of seborrhea are accompanied by itching and peeling, sometimes burning, and the appearance of papules that combine into plaques.
These growths have clear boundaries and are covered with yellow, greasy scales.
If the disease progresses, you can notice bright yellow crusts on the skin, the area of which increases noticeably. They are also accompanied by a bacterial infection.
On the scalp, dermatitis looks like ordinary transmitted dandruff, only larger in size, so those infected mistakenly believe that it is dry skin and do not resort to treatment. The main difference between seborrhea and ordinary dandruff is constant itching of the skin and bright red spots at the site of the lesion.
Seborrheic dermatitis begins with itching and flaking
Features of the disease
Since all people are carriers of the fungus, it is impossible to become infected. With the help of immunity, a healthy body prevents the growth of yeast-like fungus. When malfunctions occur in the body, intensive reproduction of blastomycetes begins, they break down subcutaneous fat into other fatty acids, which causes inflammation.
Specialists make a diagnosis based on skin examinations in the laboratory under a microscope to rule out other diseases and determine the type of fungus that caused the rash. The position and activity of hormones can be determined by a blood test.
If problems arise with making a diagnosis, specialists turn to a skin biopsy. It is not difficult for an experienced doctor to diagnose the disease. Even if a person himself was able to determine that he has seborrheic dermatitis, he still needs to go for a consultation with a dermatologist.
Resorting to treatment on your own is risky because you may aggravate the situation and not contribute to the cure. Such symptoms may be similar to other types of dermatitis.
Examination under a microscope allows you to determine the type of pathogen
Is it possible to catch seborrhea?
Many people are tormented by the question, is seborrheic dermatitis contagious? Since the fungus that causes the disease is found on the skin of healthy people, seborrhea is absolutely not contagious.
Various factors, such as infections and bacteria or active sebaceous glands, contribute to the appearance of spots and scales.
This disease is not transmitted from person to person, even through direct contact with the patient’s skin, because everyone has a fungus - this is a normal state of human microflora.
If there are no factors that provoke changes in the human body, namely metabolic disorders or hormonal imbalances and similar prerequisites, the disease will not progress.
Dermatitis is absolutely not contagious, and moreover, it cannot be inherited; only a predisposition to increased activity of the sebaceous glands can be inherited.
Stress contributes to the activity of the disease, so protect yourself from stress, and if someone from your environment is sick, then you should not avoid him.
You simply cannot get sick even if you use the same hygiene and household items. The disease is not transmitted through:
- hugs or handshakes;
- kisses;
- airborne or tactile, etc.
You don’t have to be afraid to come into contact with an infected person. If you adhere to a healthy lifestyle, then such problems will not arise.
Proper nutrition and minimizing stress helps prevent illness or cure if symptoms appear.
Basically, medications treat symptoms, so a relapse is possible in the future; comprehensive measures will be needed to strengthen the immune system and the body as a whole.
Seborrhea is not transmitted through hugs
Treatment of seborrhea
Modern medicine does not offer remedies that cure seborrheic dermatitis, since it is impossible to regulate the functioning of the sebaceous glands with the help of medications. The proposed treatment is symptomatic.
During an exacerbation, doctors prescribe antifungal drugs; the course of treatment lasts one to two weeks. For seborrhea of the scalp, shampoos are prescribed, which can be purchased at the pharmacy; they contain antimycotic components.
Shampoos reduce itching, relieve swelling and inflammation. If the disease is not treated, there is a possibility of complications developing. These include:
- baldness;
- furunculosis;
- the appearance of dandruff in large quantities;
- conjunctivitis;
- otitis.
Dermatologists prescribe treatment depending on the type of seborrhea. There are three types in total.
- The fatty type has two forms: liquid and thick. In the liquid form, a fatty secretion is observed in the area of the wings of the nose and head. Girls under 14 years of age are susceptible to this form of the disease. In the thick form, an infection gets into the sebum, causing acne and pimples to appear; the thick form affects men and boys under 20 years of age.
- The dry type develops in adolescents before puberty. This is due to the fact that the secretion of the sebaceous glands is reduced, which causes the skin to crack and dry out.
- Mixed type of seborrhea affects men. It manifests itself differently in both dry and oily skin. On the cheeks, nose, forehead there is mostly dry and cracked skin with characteristic redness, on the scalp it is oily, but it can be the other way around.
Baldness is one of the consequences of seborrhea
Is there a risk of getting sick and how to avoid it?
Seborrhea of the head is absolutely not contagious; it is treated comprehensively, going through several stages. First you need to adjust your diet and eat foods that contain zinc and vitamins A, B, C, PP. Apply antifungal drugs or antiseptics in the form of shampoos, creams or gels to the scalp. There are also treatment methods from the field of traditional medicine.
When eliminating a disease from the skin of the face, a complex treatment approach is used, reducing the manifestations of symptoms and treating the causes that provoked the active production of sebum.
Redness or suppuration on the face seriously spoils your appearance. Therefore, when self-treating, in order not to aggravate the situation, you should not use cleansers with active ingredients or alcohol-based ones. It is recommended to use antiseptic agents that relieve inflammation and cleanse the skin of bacteria and fungi.
Specialists can also prescribe antibacterial, antihistamine, vitamin and mineral components. Depending on the root cause of the disease, you can resort to other drugs that treat the digestive tract, hormonal levels, etc.
If you are prone to seborrheic dermatitis, you can prevent it in the following ways:
- take care of yourself and maintain personal hygiene;
- do not squeeze pimples;
- do not use cosmetics that dry out the skin;
- men should not wear a beard or mustache;
- proper nutrition;
- rejection of bad habits;
- hardening;
- systematic rest;
- avoiding overwork and stress;
- add plenty of fruits and vegetables to your diet to avoid vitamin deficiencies.
You should not ignore the disease, because failure to treat seborrhea of the scalp leads to premature baldness. There is also no need to be afraid of contacting patients, because seborrheic dermatitis is not contagious.
Solving the problem of skin dermatitis is not difficult; you can get rid of constant itching, cosmetic defects and tightness. If you follow the prevention recommendations, your face will shine with health and beauty.
Source: https://kozhmed.ru/dermatit/seborejnyj-zarazen-ili-net.html
Classification of pathology
Depending on the microbe that caused the skin symptoms, dermatitis may be:
- Gribkov. Most often, skin lesions are caused by the yeast fungus Candida, but this can also be caused by the causative agent of pityriasis versicolor, the fungus Actinomycetes, Trichophyton and others.
- Bacterial. It is caused by streptococci - the causative agents of scarlet fever, impetigo, ecthyma vulgaris, and erysipelas. The causes of such infectious dermatitis can also be staphylococcus - the causative agent of folliculitis, pseudofurunculosis, Ritter's dermatitis, and epidemic pemphigus.
- Parasitic, caused by rickettsia (for typhus), scabies (for scabies).
- Viral dermatitis occurs most often in children. It develops with chickenpox, rubella, enterovirus infection, and measles.
Regardless of the cause of infectious dermatitis, your chances of getting it increase significantly if you:
- hypothermia and overheating;
- microcracks and deeper injuries to the skin;
- diabetes mellitus;
- renal failure;
- immunodeficiency;
- taking glucocorticoid drugs (Prednisolone, Dexamethasone, Solu-Medrol) or cytostatics (Methotrexate, Cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil and others);
- varicose veins.
If the infectious process is accompanied by the release of large quantities of histamine and other substances characteristic of allergic diseases, infectious-allergic dermatitis develops. In this case, spots, nodules or blisters, characteristic of the normal course of the infectious process, become surrounded by redness around the perimeter or are located on an allergy-specific blister, accompanied by itching. This pathology is more difficult to diagnose; an infectious disease specialist can do this.
Are seborrheic dermatitis and its other forms contagious?
Seborrheic dermatitis does not pose a serious danger to the patient, but from an aesthetic point of view, seborrhea looks unpleasant.
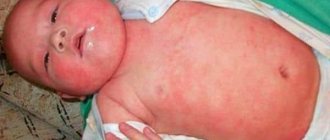
As a rule, it is chronic and appears not only on the scalp, but also on the face. In this case, redness of the skin, rash and the formation of seborrheic crusts are observed.
The rash is characterized by severe itching, so many patients have a completely natural question: is seborrheic dermatitis contagious? In order to find out the routes of infection, it is necessary to know the etiology, development factors and symptoms of the disease.
Mechanisms of development and symptoms of the disease
The main causes of seborrheic dermatitis include:
- individual susceptibility of the body;
- exposure to ultraviolet rays;
- emotional and nervous stress;
- eating disorders;
- unfavorable environmental situation in the patient’s region of residence;
- hereditary predisposition;
- increased sensitivity of the immune system.
It should be noted that any dermatitis has typical symptoms, regardless of the factors that caused its exacerbation.
Classification of dermatitis
The most common are contact (simple), allergic, atopic and seborrheic dermatitis.
CONTACT. This type of disease is caused by aggressive exposure to external irritants (acid, alkali, ultraviolet radiation, etc.). It is NOT SPREAD from person to person.
ALLERGIC. Develops as a result of exposure to an irritant on an organism predisposed to allergies. Like other forms of dermatitis, allergic dermatitis CANNOT BE TRANSMITTED BY CONTACT, and therefore does not pose a danger to other people.
ATOPIC. Atopic dermatitis is an allergic disease and is TRANSMITTED BY INHERITANCE. However, it should be understood that it is not the disease that is transmitted genetically, but the tendency to develop it. Atopic dermatitis does not have an infectious path of development, therefore it is not transmitted through direct contact.
INFECTIOUS. This form of the disease, like others, despite being classified as infectious dermatitis, is safe for healthy people.
The question is that this type of disease is quite often provoked by various infections, which can easily be transmitted from person to person.
In other words, when a healthy person comes into contact with a patient who has been diagnosed with infectious dermatitis, TRANSMISSION OF VIRUSES AND INFECTIONS of the immediate cause of the disease MAY OCCUR.
Can you get seborrheic dermatitis?
Despite the fact that medicine does not stand still, today there is no single factor contributing to the development of the seborrheic form of the disease.
This form of the disease is provoked by endocrine and trophic disorders associated with hypersecretion of the sebaceous gland, which is manifested by rashes in the face and scalp.
The main factors in the appearance of the seborrheic form of the disease are fungal spores pityrosporum. However, for negative symptoms to occur in the head area, first of all, the patient’s immune system must be weakened.
This is the main condition for the development of this disease.
Therefore, we can confidently say that seborrheic dermatitis does not belong to that part of infectious diseases that are transmitted through direct contact between people. In addition, this type of dermatitis is not only NOT INFECTIOUS, but also NOT TRANSMITTED BY INHERITANCE! The offspring inherits only a predisposition to dermatitis, manifested by hypersecretion of the sebaceous glands.
Patients with seborrheic dermatitis who are wondering whether the dermatitis is contagious should know that this disease has NO CONTACT ROUTES OF TRANSMISSION.
It is not able to move from a sick person to a healthy one during a handshake, kiss, etc., so it does not involve isolating the patient from the people around him.
The patient should only adhere to a hypoallergenic diet and strictly follow medical prescriptions.
Prevention of dermatitis
Of no small importance in preventing unpleasant manifestations in the head and face area is the prevention of the development of seborrheic dermatitis. As a rule, there are no special obstacles or difficulties to comply with it.
- The patient must maintain personal hygiene and give up the bad habit of squeezing pimples. If the skin is oily, especially in the scalp area, it is recommended to use drying cosmetics. Men should give up beards and mustaches.
- It is important to follow a diet, consuming large amounts of plant fiber and vitamins. Perform hardening procedures accompanied by an active lifestyle. In addition, it is important to avoid nervous tension in the body, as very often this leads to an exacerbation of the process.
It must be remembered that treatment and timely prevention of the disease should be carried out under the supervision of the attending physician, which allows for a longer remission.
Source: https://AllergiyaNet.ru/zabolevaniya/dermatit/zarazen-li-seborejnyj-dermatit-i-drugie-formy.html
Allergic
Allergic dermatitis is the body’s reaction to a specific allergen: food product, household detergent. Knowing what exactly caused the reaction, you can cope with an outbreak of the disease: it is enough to eliminate the irritant. In the case of food products, everything is simple: the allergen must be removed from the diet and avoided in the future. If the cause was external irritants (aggressive chemicals, alkalis, acids, UV radiation), it will be more difficult to identify, let alone avoid contact. In this case, you will have to seek medical help.
Is seborrheic dermatitis transmitted and is seborrhea contagious? What is important to know
Reading time: 2 min.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by a rash with the formation of crusts on the scalp or torso, where the sebaceous glands are located.
The development of the pathological process is provoked by yeast-like fungi of the Malassezia species; more details about the reasons can be found in this article. Skin papular rash is accompanied by itching, burning and peeling. It can merge into large spots and become covered with yellow, greasy scales.
At the sight of red, flaky skin, many are interested in the question of whether seborrhea is contagious. Also read our material about seborrheic dermatitis.
Mechanism of the disease
Is the fear of “catching” seborrhea in close contact with a sick person justified? To answer this question, you need to familiarize yourself with the reasons for the development of the pathological process.
Yeast-like fungi Malassezia exist in the upper layers of the epidermis and are part of the normal human skin microflora.
To grow and develop, they need fatty acids, which are present in the secretion of human sebaceous glands.
Using sebum as food, they secrete specific decomposition products that provoke irritation and inflammation of the epidermis. This process of fat utilization weakens the skin barrier function and causes an imbalance of microflora.
Active reproduction of Malassezia fungi can be triggered by the following factors:
- neglect of personal hygiene rules;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- frequent severe stress;
- prolonged exposure to the sun or solarium;
- unbalanced diet, causing a lack of vitamins and microelements in the body; impaired sweating processes;
- general exhaustion of the body.
The influence of yeast-like fungi on the human body is closely related to environmental conditions - temperature, humidity, geographical factors. The slightest weakening of the host's immunity leads to the uncontrolled growth of Malassezia, which gives rise to the development of seborrheic dermatitis.
Is seborrhea transmitted from person to person?
It is impossible to become infected with seborrheic dermatitis from a sick person through hugs, handshakes, kisses or other tactile touches. A towel, washcloth, comb, clothing and hats are not carriers of the pathogen.
The disease is also not transmitted by airborne droplets, fecal-oral or vector-borne transmission. The thing is that fungi of the genus Malassezia can be found on the skin of almost all people on the planet.
But for some they live and do not cause any discomfort, while for others, under the influence of internal and external irritants, they begin to actively grow and provoke the appearance of itching, rashes and peeling.
Seborrhea cannot be inherited either through the female or male line. Only a predisposition to intensive production of sebum by the sebaceous glands is inherited and nothing more.
If relatives have had similar skin problems, it is recommended to protect yourself from the causes of the disease.
To this end, you should strengthen your immune system, harden your body, lead a healthy lifestyle and avoid stressful situations.
If a person from your environment gets sick, then you should not isolate him from people or avoid communicating with him. On the contrary, we need to provide him with psychological help so that he is not ashamed of his appearance.
Sometimes patients, out of ignorance, themselves refuse contact with other people for fear of transmitting the disease to others.
It should be explained to them that seborrheic dermatitis is not an infectious disease and is not transmitted by talking, sneezing or coughing.
IMPORTANT TO KNOW : The infectious form of seborrheic dermatitis is also considered safe for healthy people.
Its development is provoked by bacterial pathogens that are quite capable of being transmitted from person to person. However, this does not mean that seborrhea will form after contact.
Even with the probable transmission of viruses or bacteria, a good immune response of the body will not allow them to settle on a new host.
In general, we can conclude that seborrhea occurs under one condition - the presence of excessive secretion of the sebaceous glands.
If there is no breeding ground for the yeast-like fungi Malassezia, then there is nothing to worry about.
In order to prevent the disease, it is necessary to follow the principles of proper nutrition, control sweating, use less cosmetics and observe the rules of personal hygiene.
Source: https://KozhaExpert.ru/seborejnyj-dermatit/zarazna-li-seboreya
Features of the disease
Disease of the scalp is associated with increased sebum secretion and can occur in two types - dry and oily.
- With dry seborrhea, the hair becomes very fragile and brittle, a large amount of dandruff appears on the skin, and unpleasant itching occurs.
- If seborrhea is of the oily type, then the hair always looks untidy and shiny. Dandruff appears in the form of yellow plaques. Hair may begin to fall out, sometimes quite severely.
If no measures are taken, the sebaceous glands will begin to work more and more actively and will constantly affect new areas. Irregular hair washing aggravates the situation . Complications are expressed by red spots and plaques. If you scratch these skin lesions, they may bleed.
Important!
Competent diagnosis is important for an accurate diagnosis. It is best to consult a dermatologist and, if necessary, do a biochemical blood test.
Is seborrhea of the scalp contagious: how is the disease transmitted?
Many in adolescence suffered from oily hair, dandruff and a shiny forehead. These are the initial signs of seborrhea.
Gradually, hormonal levels improve, which means sebum production returns to normal.
However, this disease can make itself felt at absolutely any age.
Is seborrheic dermatitis contagious or not?
The disease is not transmitted through contact. Its main cause is hormonal and autonomic disorders . Fungi that cause seborrhea are opportunistic microflora.
Every person has them, but until these microorganisms begin to grow and multiply, they do not pose any danger to humans.
People with this disease are absolutely safe for others: you can safely use a shared towel and comb.
Causes of occurrence on the scalp
Seborrhea can develop at any age, but most often it is detected during puberty in adolescents. The disease can be caused by:
- situations of stress;
- endocrine system disorders;
- overwork;
- lack of vitamins A and B;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- prolonged exposure to the sun.
During illness, the amount and composition of sebum changes. This leads to a decrease in the functions of the skin and sebaceous glands. The development of the disease in the human body is closely related to environmental conditions - temperature and humidity.
Important!
Approximately 10% of people suffering from seborrhea cannot get rid of this “scourge” for the rest of their lives. Therefore, it is better to warn her. To do this, use only those shampoos that suit your hair type; eat right, take vitamins and strengthen your immune system.
How to recognize seborrheic dermatitis?
The first sign of the disease is peeling and inflammation of the skin, accompanied by itching. When the disease is mild, small white scales appear on the skin . They cause discomfort.
If the patient develops seborrhea, the forehead and skin behind the ears are added to the “affected” areas. Red spots with scales form. If no measures are taken, they will become covered with bloody crusts. The victim begins to experience severe itching.
How is the disease transmitted?
It is impossible to contract a disease from another person through tactile contact. Seborrhea is not transmitted through shared objects or by airborne droplets. So don't be afraid to communicate with people who have been diagnosed with this condition.
This disease cannot be inherited; The only thing that can be passed on to you genetically is a predisposition to excessive sebum production .
If one of your relatives has encountered such problems, then, if possible, protect yourself from the causes of the development of the disease. Try not to be nervous and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Important!
The infectious form of seborrhea is also considered safe for healthy people. Even with accurate transmission of the virus, a good immune response of the body will not allow it to continue living in a new place.
If someone close to you suffers from seborrhea, do not under any circumstances exclude this person from your social circles and do not show in any way that this situation causes you discomfort. On the contrary, explain that you shouldn’t refuse contact with people and be ashamed of your appearance.
Source: https://zdravkozh.com/seboreya/zarazna-ili-net.html
Prevention methods
Specific actions are determined by the type of disease and whether it is contagious or not:
- With the contact type, it is important to exclude contact with the factor that caused the specific reaction. If this cannot be avoided, the surface of the skin is washed with running water, then sent for medical help. Even for healthy people with well-functioning internal organs and strong immunity, it is dangerous to interact with toxic substances for a long time.
- Atopic is most often associated with disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, nervous or endocrine system. Preventive measures are aimed at eliminating the underlying disease. A diet that excludes the consumption of foods with a high allergenic titer will be mandatory.
- Infectious dermatitis is contagious only if the rules of contact with patients are violated. For example, sharing bedding and dishes increases the risk of infection. When in direct contact with an infectious patient, use a mask and gloves. The state of immunity and the presence of vaccinations are also important.
Preventive measures prolong the period of remission and prevent the development of pathology if there is a predisposition.
Is seborrheic dermatitis contagious or not and how is it transmitted?
Seborrheic dermatitis is a harmless disease. It brings other problems, in particular, aesthetic and psychological ones. The rashes appear on the neck, face and scalp and are very noticeable.
People around perceive the external symptoms of seborrheic lesions with caution and often try to reduce contact with patients for fear of becoming infected.
Therefore, both the patient and the people around him are concerned about the question of whether seborrheic dermatitis is contagious or not.
Mechanism of development and symptoms
The disease is chronic and affects areas of the skin and scalp where the sebaceous glands actively work (usually the face and upper body). The exact mechanism of seborrheic type dermatitis has not yet been determined; existing assumptions require proof.
It is believed that the cause is the lipophilic (fat-eating) yeast-like fungus Malassezia, which is found on human skin and is not contagious. According to statistics, these fungi are found in the skin microflora of more than 78% of people. Settled around the sebaceous glands, they use the sebum secreted by the skin as food for their own development.
With normal skin condition and normal functioning of the sebaceous glands, the fungi are kept in an inactive state and do not cause harm to humans. But if the functioning of certain systems is disrupted, the lifestyle is incorrect, as well as some individual characteristics of the body, the fungi are activated, and the immune system ceases to limit their development.
As a result, increased work of the sebaceous gland begins, which is manifested by rashes, peeling, and dandruff (if it is the hairy part). When the microflora is disturbed, the vital activity of fungi is activated. By processing sebum, they release components that irritate the skin.
Internal factors leading to activation of fungi:
- frequent and severe stress;
- disruption of the normal functioning of the nervous and endocrine systems, the digestive tract;
- HIV;
- weakening of the immune system.
External factors:
- hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating);
- folds on the skin due to excess weight;
- increased sebum production (therefore, people with oily skin have a greater risk of developing the disease).
The disease can also develop under the influence of external irritants (acid, alkali from detergents), and alcohol consumption.
The human body can control the growth of fungi. However, due to weakened immune defenses, frequent stressful situations, endocrine disorders, and nervous diseases, this natural ability is lost. Yeast-like fungi begin to grow and multiply.
The symptoms are:
- Peeling of the skin and dandruff.
- Inflammation with itching.
- The rash is pink and noticeably different in color from normal skin. The lesions are usually large and merge with each other. If symptoms appear behind the ears, on the chest or between the shoulder blades, the spots may be separate, round in shape, and small in size.
- Formation of a greasy seborrheic crust, which is easily removed. In severe cases of dermatitis, pus may accumulate under the crust.
Since the patient scratches the itchy areas, dermatitis can be complemented by another infectious disease that penetrates through the scratched wounds.
Is seborrheic dermatitis contagious?
The main question for others is: is this disease transmitted from person to person? In short: no, it is not transferable. Most people have this fungus on their skin in a healthy state, that is, theoretically, almost all of us can get sick anyway.
The cause of dermatitis is abnormalities in the functioning of the immune system and the hormonal system, so the disease is not transmitted through contact from person to person through any transmission route (airborne, through touch, through clothing, sexual contact).
If your own health is in order, you will not become infected even if you touch the affected area of a sick person. If you have any disorders and your skin is prone to excessive oiliness, seborrheic dermatitis may develop, even if you have never seen anyone with this disease.
The only amendment: if the patient has some additional infectious disease, for example, a staphylococcal infection, others can become infected with it through blood from scratched wounds.
Similar but contagious diseases
Many dermatological diseases manifest themselves with symptoms that can easily be confused with seborrheic dermatitis. This is why people fear for their health if they see patients with problem skin (rashes, redness, peeling). An ordinary person cannot recognize at first glance whether a disease is contagious or not.
In terms of symptoms, the following infectious diseases are similar to seborrheic (oily and dry) dermatitis:
- Scabies. The skin becomes covered in rashes, peels, and is very itchy. The rashes look different in appearance - brighter in color, small and frequent.
- Tinea versicolor. Rashes are localized not only where the sebaceous glands are actively working. The rash comes in different shades and can spread over a large area.
- Dermatomycosis. The disease also occurs due to fungi, but is contagious. The rashes are round in shape and large in size, so they can be distinguished visually from the seborrheic type of dermatitis. The disease is highly contagious, so patients diagnosed with infectious dermatomycosis need to observe hygiene measures so as not to spread the infection.
Reasonable prevention measures
To prevent dermatitis, you need to properly and regularly take care of yourself. Rules and recommendations:
- Using products to care for oily skin. Skin prone to excessive sebum production requires special cosmetics. Not every remedy is suitable for it. They should be used on an ongoing basis (if sebum is secreted constantly, regardless of the weather) or during periods of heavy secretion (in summer, winter under warm clothes).
- Dieting. You should avoid foods with a lot of glucose (sweets, confectionery, baked goods), fatty foods, and fried foods. If there are any problems with the gastrointestinal tract, you need to follow a diet appropriate for your illness.
- Regular change of bed and underwear.
- Avoiding stress and moral overload.
- Timely treatment of problems with the immune system, gastrointestinal tract, central nervous system.
- Prevention of obesity, and if you are overweight, regular hygiene and careful care of the areas in the folds.
- If the scalp is oily, choose a suitable shampoo (it is recommended to seek the help of a trichologist or dermatologist) or a short haircut.
All people with oily skin and intensively working sebaceous glands need to adhere to preventive measures. Teenagers are most susceptible to the seborrheic type of skin inflammation. During adolescence, the sebaceous glands function more actively than in a healthy adult. Therefore, it is necessary to increase the number of hygiene procedures.
Source: https://tden.ru/health/seborejnyj-zarazen-ili-net