- Nature of the disease and cause of development
- Classification of formations
- Locations localization
- Which doctor should I contact?
- Diagnostics
- Therapy methods
- Treatment with folk remedies
- What is the forecast
- Prevention
The cutaneous horn is a tumor-like formation consisting of horny skin cells. Appears independently or due to other benign formations or malignant origin. The clinical picture is a single horny element developing on the skin. The cutaneous horn can only be treated by surgical removal.
Description
Cutaneous horn (xanthelasma or xanthoma) - what is it? Cutaneous horn refers to neoplasms that are keratinized growths on the skin. At an early stage, the growth looks like a smooth yellowish or grayish plaque, which, as it grows, forms a cone-shaped bulge and rises above the skin. Typically, xanthoma forms in folds of skin that form wrinkles.
This neoplasm appears as a result of excessive proliferation of epidermal skin cells. Active and dead cells accumulate and subsequently merge into a single formation of a specific shape. This collection of cells grows in length and does not usually affect healthy tissue. In most cases, the neoplasm is 1–3 centimeters in size, but sometimes growth up to tens of centimeters is observed. The largest record cutaneous horn reached a length of 30 centimeters.
Horny keratoma usually forms in older people, and in most cases in women. In men, this neoplasm is rare, and, as a rule, among those working in harmful and dangerous conditions (drivers, stokers, miners, sailors, industrial workers). The International Classification of Diseases classifies this neoplasm in the section “Other specified epidermal thickenings.” The ICD 10 code is L85.
Medical scientists doubt the independence of this pathology; the pathogenesis of horny keratoma has not been fully studied. Modern dermatology considers the term “cutaneous horn” to be a collective term, since it can be the result of many tumor processes, including as a condition of an optional precancer.
Cutaneous horn is dangerous because in 5% of cases it becomes malignant. The neoplasm degenerates into squamous cell carcinoma of the epidermis. Therefore, if such a formation is detected, it is necessary to undergo a histology analysis.
Keratoma keratoma occurs extremely rarely in children. This neoplasm is formed in a child due to various damage to the skin or infections that have entered the skin. One of the reasons for the appearance of such pathology in adolescents is considered to be changes in hormonal levels. Horny keratoma can arise from hormonal imbalance and changes in the body. Such processes occur both in adolescence and old age, or during pregnancy.
How to get rid of warts at home using pharmaceutical products
When a wart appears on a finger, how to get rid of it is the main question; a number of medications are used to solve it. The action of some of them is aimed at eliminating skin growths, others have antiviral properties, suppress the activity of HPV, and increase the body's immune defense.
Hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is an antiseptic that is a colorless liquid with a faint sour odor. Hydrogen peroxide has low effectiveness in removing skin tumors.
Hydrogen peroxide is applied to the papillomas, one drop every 5-6 hours. Manipulation using hydrogen peroxide is performed daily.
Iodine
The drug is applied to skin growths and flat warts using a cotton swab 1–5 times a day. The minimum duration of iodine use is a week.
The product should not be used if you are hypersensitive to it, children or pregnant women.
Ointment for papillomas
Viferon is an ointment for warts on the hands and other parts of the body, which has antiviral activity. The drug contains human recombinant interferon. Viferon also contains tocopherol acetate, which enhances the antiviral effect of interferon.
The product is applied to the growths once a day. Viferon is used from 5 days to a month. Ointment for papillomas can be used by pregnant and breastfeeding women. Viferon is also available in gel form.
Allomedin gel is a medicine for warts containing the peptide allostatin. It is applied to papillomas twice a day for 3 weeks.
Oxolinic ointment for warts is another remedy with an antiviral effect. The active substance of the drug is dioxotetrahydroxytetrahydronaphthalene. This ointment for papillomas is applied to neoplasms 1–3 times a day for a month.
How to treat warts with tablets
Treatment of warts and papillomas with medications includes the use of drugs that enhance immune defense. Isoprinosine is a synthetic purine derivative with an immunostimulating, nonspecific antiviral effect.
How to remove a wart at home with solutions
Verrucacid contains phenol, metacresol, and has a necrotizing effect when applied to neoplasms. The product is used in the presence of papillomas of various locations, including plantar warts. Small growths are treated 3–4 times in a row, waiting for the preparation to dry completely, large ones – 7–10 times. The manipulation is repeated after a week.
SuperClean solution contains sodium, potassium hydroxide, which is an alkaline solution. It is usually applied drop by drop to the papillomatous growth with a plastic applicator for 3 days. It should be borne in mind that this drug does not eliminate the cause of warts on the hands and treatment with it only causes the death of the tissues treated with it.
The Collomac solution contains salicylic acid, which softens skin growths when applied topically. It is used twice a day for a week. The drug should not be used to treat moles.
Removal at home using cryogenic preparations
Cryopharma is a drug for cryodestruction of warts. It is produced in the form of a bottle with dimethyl ether, propane, reaching a temperature of -57°C at the exit from the bottle.
The product is applied to the papilloma using special applicators included in the package. The treated tissues are frozen, and after 10–14 days the skin growths disappear on their own.
ul
Leading clinics in Israel
Assuta
Israel, Tel Aviv
Ikhilov
Israel, Tel Aviv
Hadassah
Israel, Jerusalem
Localization
The localization of the cutaneous horn is very diverse. It can occur on the human body in any part of the skin, less often the mucous membrane. Most often, neoplasms form on areas of the skin that have been worn out, subjected to prolonged friction, compression or moisture, as well as in folds and wrinkles. The most common locations for keratoma corneum are: the area around the eyes, the upper and lower eyelids, the auricle, the neck and the oral mucosa.
A little less frequently, such a formation can form on areas of the head that border the mucous membranes (on the lip or nose) and on open areas of the skin (on the face, forehead, around the red border of the lips, cheek, chin). On the scalp, horny keratoma forms very rarely, usually at the site of a mole. In rare cases, it appears on the chest, back, arms and legs, fingers, feet and other parts of the body. A similar formation in the mouth and on the mucous membrane of the larynx can occur in smokers.
How to remove a wart at home using folk methods
These methods are aimed at eliminating existing skin growths; they do not destroy papillomaviruses present in the body.
Folk remedies for warts can be used only after examination by a doctor, who has ruled out the malignant nature of the tumors.
They should not be applied to mucous membranes or eyelids, otherwise chemical burns will occur.
Removal with celandine
For warts and papillomas, plant juice is used, which is made independently or purchased at a pharmacy.
If this medicine for warts is obtained at home, the herb along with the root is thoroughly washed and dried. The plant is passed through a meat grinder twice, and the resulting pulp is squeezed out using gauze folded in several layers. The juice is poured into a dark glass container and closed with a stopper.
In a week, the fermentation process will begin; it is necessary to open the container for a while every day for 7 days to release accumulated gases. After this time, the juice is ready for use. If a medicine for papillomas is prepared in the form of a tincture, vodka is added to the resulting juice in a 2:1 ratio.
Balm “Mountain Celandine” is a remedy for papillomas and warts, sold in pharmacies. In addition to celandine juice, the drug contains extracts of string, spear-shaped poop, gentian, and golden rhododendron.
Before applying the product, the papilloma must be steamed. When using celandine for warts, the instructions for use recommend treating the skin around the growths with oil and rich cream to prevent damage to healthy areas. Using a match or a small stick, the drug is applied to the surface of the growth every 2-3 days.
How to remove a wart on a finger with tea tree oil
This remedy for warts on the hands and other parts of the body does not have an aggressive effect on healthy tissue. It is necessary that the oil does not contain any additional components.
The product is applied to a small piece of gauze folded in several layers. The latter is attached with a patch to the affected area. The procedure is carried out before bed every day.
Baking soda for home treatment
When papillomas are removed using baking soda, the latter is mixed with warm water until a paste forms. The composition is applied to the neoplasm and left on the skin for several hours after drying. The procedure is repeated twice a day for 2 weeks.
Sometimes castor oil is added to soda instead of water. The resulting composition is applied to the warts overnight and covered with a band-aid. The manipulation is repeated for 14 days.
How to quickly remove a wart at home with vinegar
Wart growths on the skin are removed with table vinegar or apple cider vinegar. The affected area is thoroughly washed with soap and dried.
Cotton wool or a thick cloth is moistened in vinegar, applied to the growth, and fixed with a plaster or bandage. It is recommended to perform the procedure daily, in the evening, leaving the bandage on all night.
How to get rid of pathology using potatoes
If warts appear on the feet or hands, the washed potatoes are crushed using a grater. A compress is made from the resulting pulp, covered with gauze and secured with a bandage.
The procedure is performed at night and repeated for a month.
How to remove a wart using garlic
Rub a cut clove of garlic onto the skin growth several times a day. This plant is also used together with apple cider vinegar.
How to remove warts from a finger with a thread
When treating skin growths at home, some try to remove them with a thread. A loop is made from the latter, put on the papilloma, and tightened tightly. The blood supply to this area is disrupted, the cells cease to receive sufficient amounts of oxygen and nutrients, and necrosis develops—tissue death.
ul
Brief conclusions
Warts on the face are not only an aesthetic problem. They are an indicator of overall health.
No one is protected from the occurrence of a misfortune. The cause of the growth is HPV. The exception is senile warts.
If growths appear, you need to visit a doctor and undergo an examination. Before starting treatment, you should make sure that the condyloma is benign.
Removal of rashes should not be neglected. Over time, they can develop into malignant tumors.
To prevent relapse, you should take comprehensive care of your health. Giving up bad habits will improve your quality of life, block HPV, and maintain your attractiveness.
We advise you to read:
What methods and means to get rid of plantar warts
Causes of warts on the lip and how to get rid of them
Instructions for getting rid of a wart on the heel
What are senile warts and how to deal with them
ul
Causes
Modern medicine has still not fully elucidated the etiology of cutaneous horn. Most often, such neoplasms form in older people. The reason for this is age-related metabolic disorders, which leads to abnormal proliferation of epidermal cells. In the presence of harmful factors, this disease can occur even in infants.
Scientists believe that several processes serve as prerequisites for the development of cutaneous horn:
- acceleration of mitotic division of skin cells;
- acceleration of migration to the surface of skin cells with excess keratin;
- acceleration of physiological death of skin cells;
- accumulation of keratinized skin cells, which leads to growth in length.
Some internal factors are considered to be the causes of keratoma keratoma:
- genetic predisposition;
- obesity;
- hypovitaminosis (lack of vitamins in the body);
- digestive disorders;
- a history of cancer;
- hormonal imbalance;
- disruption of intracellular metabolism in the body;
- alcoholism and drug addiction;
- disorders in the body's immune system;
- nervous overstrain.
Possible external causes of the appearance of a cutaneous horn are:
- excessive insolation (long-term exposure to solar radiation);
- skin infections (for example, cutaneus larva migrans - a rare disease transmitted to humans from cats and dogs);
- damage to the skin;
- viruses (human papillomavirus, feline viral leukemia, etc.);
- failure to maintain personal hygiene;
- aggressive environment (contact with acids and alkalis);
- poor circulation from wearing tight clothes.
In addition, many diseases can cause the formation of horny keratoma:
- warts;
- papillomas;
- keratoacanthoma - a benign tumor of the hair follicles;
- actinic keratoma (keratosis) – benign skin formation;
- leukoplakia – a disease of the mucous membranes that causes keratinization;
- fibroma is a benign tumor of fibrous connective tissue;
- angiokeratoma is a dermatosis characterized by single or multiple benign vascular formations;
- Bowen's disease is a rare type of squamous cell carcinoma;
- fungal diseases;
- seborrhea;
- psoriasis;
- long-term dermatitis and allergic rash of various etiologies;
- lupus erythematosus and tuberculosis (in rare cases).
Many of the above factors serve as a stimulus for the appearance of hyperkeratosis - abnormal growth of the stratum corneum of the epidermis. Cutaneous horn is one of the histological signs of hyperkeratosis. In many cases, this disease is accompanied by other skin pathologies: acanthosis, keratoacanthoma, papillomatosis.
Would you like to receive an estimate for treatment?
*Only upon receipt of data on the patient’s disease, a representative of the clinic will be able to calculate an accurate estimate for treatment.
Precancerous skin diseases
Despite the fact that the malignant process of the skin is visually accessible, however, the stages and variability of its development, as well as the wide variety of benign dermatological pathologies, often do not allow timely recognition of a cancerous tumor.
In connection with the above, the problem of early diagnosis and treatment of a “pre-morbid” disease or pathological condition, that is, precancer, against which the development of a malignant neoplasm is more or less likely, has become of great relevance in dermatology and oncology.
Precancerous skin diseases are multiple or single papules, nodules, growths, spots, foci of hyperkeratosis or irritation of various shapes, colors and sizes, etc. They are benign epithelial formations and pathological conditions of non-tumor origin, but which can transform into malignant tumors.
The cause of malignancy can be:
- various external factors of a nonspecific nature - frequent or constant mechanical irritations or injuries, prolonged contact with chemicals (aniline dyes, petroleum derivatives, coal, arsenic, pesticides), exposure to temperature factors (frostbite and burns), excessive solar radiation, ionizing radiation, weathering;
- endogenous factors (in the body itself) - endocrine disorders, dysfunction of the immune system and some others;
- lack of timely treatment of benign pathology;
- age - among middle-aged and elderly people, transformation into cancer occurs much more often.
Diagnosis and treatment of precancerous skin pathologies are carried out by dermatological or oncological specialists.
Classification and diagnosis
A generally accepted classification of precancerous pathologies of the skin has not yet been developed due to the lack of sufficiently clear theoretical ideas about these pathological conditions. Therefore, the main ones are very conditionally divided into 2 groups:
- Obligate.
- Optional.
Obligate precancerous skin diseases
Obligate pathological conditions are characterized by a high probability of transformation into a malignant formation. These include:
- xeroderma pigmentosum;
- limited precancerous hyperkeratosis of the skin of the red border of the lips;
- Bowen's disease;
- Keir's erythroplasia;
- Paget's disease.
The last three pathologies are currently considered as a special form of skin cancer ( cancer in situ ), which is a local pre-invasive (intraepithelial) malignant process that does not extend beyond the skin. However, traditionally they are still classified as precancerous pathological conditions.
Xeroderma pigmentosum
It is a genetically determined, staged disease characterized by excessive sensitivity to even minor solar radiation. The first symptoms of this pathology with damage to the skin of the face and hands appear already in the first 3 years of a child’s life.
After a short exposure to the sun, limited erythematous spots and small pigmented yellowish-brown spots that resemble freckles appear on exposed areas of the skin. Their number gradually increases, the skin in these places becomes dry and flaky.
Subsequently, atrophic changes develop in their place, areas with telangiectasia and a smooth shiny surface appear. Even later, against this background, ulcerations and cracks appear, growths of a papillomatous and warty nature, transforming into a basal cell or squamous cell form of cancer, melanoma or sarcoma.
Malignancy occurs in 100% of cases. Malignant tumors have a high tendency to disintegrate and metastasize. Most patients die before the age of 15–20 years due to the generalization of the tumor process. However, although the gene for this pathology occurs in approximately 0.28% of people, it is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, and therefore the disease develops in only one in 250 thousand cases.
Treatment of xeroderma pigmentosum is carried out after histological examination. For single growths, it involves electrical excision, laser or cryodestruction; for multiple growths, it involves a course of close-focus radiotherapy.
Limited precancerous hyperkeratosis of the skin of the red border of the lips
Unlike other obligate precancerous diseases, it often affects young and middle-aged people. Of all precancerous lip pathologies, 80% are due to this form of the disease. The lesion is polygonal in shape and sizes from 2 mm to 1.5 cm and is localized mainly on the lower lip directly on the red border.
It is surrounded by a whitish thin ridge, located approximately midway between the corner of the mouth and the center of the lip, soft and painful on palpation. The level of its surface in most patients is slightly lower than the level of the surrounding red border of the lip, which is why the lesion appears sunken. The surface is covered with grayish-brownish, densely spaced scales.
Usually the formation exists for several years in a benign state, but sometimes it transforms into a malignant tumor within the first year and even the first months from the moment of its appearance. The main symptoms that partially help in diagnosing malignancy are:
- the appearance of a compaction at its base;
- the appearance of erosion on its surface;
- strengthening of keratinization processes.
Treatment consists of electroexcision, laser destruction or surgical excision within healthy tissue, followed by histological examination. The decision on further treatment depends on the results of the latter.
Bowen's disease
Occurs with equal frequency among men and women over 40 years of age. Factors that provoke the development of a precancerous condition are ultraviolet rays and some toxic substances (arsenic, tar, tar). Any areas of the skin can be affected, but most often - closed areas (torso, genitals), less often - the face and neck.
Depending on the clinical manifestations, 4 forms of the disease are distinguished:
- papular-squamous;
- papular-cortical;
- atrophic;
- getting wet.
As a rule, the disease manifests itself as single or multiple plaques ranging in size from 1 mm to 10 cm. They tend to grow peripherally and have oval or irregular outlines, slightly rising above the surface of the skin, clear or blurred boundaries, yellow-red, and subsequently yellow-brown coloring Characteristically, there is an atrophic area of tissue or a scar in the central part of the plaque.
Sometimes the elements are covered with uneven crusts or scales, which resemble psoriatic elements. When these crusts or scales are removed, growths in the form of papillae with a smooth or warty surface may be exposed. When palpating the papules, the density of paper or cardboard is determined.
The course of Bowen's disease is long (years). Against this background, papillary (a type of squamous cell) cancer develops.
Erythroplasia Keira
It is a variant of the previous pathology and occurs only in 40–70-year-old men in the area of the glans penis or, less commonly, on the foreskin. In older men, the pathology is characterized by a more malignant course.
The disease manifests itself as single or multiple plaques with pronounced boundaries. The elements have raised edges and regular outlines, a smooth velvety surface of a reddish or bright red color. In case of infection, purulent or crumbly white deposits are possible.
Treatment of Bowen's disease and Keir's erythroplasia consists of electrical excision or cryodestruction of single lesions that are small in size. In other cases, the use of close-focus radiotherapy is recommended.
Paget's disease
It is a focus of erythema, accompanied by local pain, itching, tingling, burning. On its pinkish and slightly pigmented surface, reminiscent of eczema in appearance, epithelial scales, ulcerations and erosions appear.
The lesion has clearly defined boundaries and has a tendency to gradually slowly (over several years) expand and spread to neighboring tissues. Localization - mainly in the area around the nipple, but in 20% - in the face, head, back, thighs and buttocks, perineum and external genitalia, on the skin of the armpits.
The disease occurs after 50-60 years, mainly in women, but in men the course is more aggressive. Despite the slow development, there is always a transformation of precancerous pathology into an invasive malignant tumor. Treatment consists of radical resection of the mammary gland or complete mastectomy in combination with hormonal therapy, chemotherapy and radiotherapy. The extent of treatment depends on the extent of the lesion and is carried out after histological examination.
Optional precancerous skin diseases
Diseases in this group are united by a relatively low probability of degeneration into cancer. These mainly include:
- actinic, or solar, senile (senile) keratosis;
- cutaneous horn;
- keratoacanthoma;
Actinic keratosis
It develops, as a rule, in adulthood and old age in people with fair skin in open areas that are exposed to long-term (at least 10-20 years) sun exposure. The basis of the disease is dysplastic processes in the epithelium, as a result of which it can degenerate into squamous cell carcinoma.
Typically, senile keratosis is localized on sun-damaged skin (with uneven pigmentation, thinning) in the area of the back of the nose, cheeks, ears, scalp, lower lip and hands. Depending on the severity of clinical symptoms, stages or types of lesions are distinguished:
- Erythematous, which is the beginning of the disease and is characterized by the appearance of reddish-pink plaques and spots with sharply defined boundaries. The diameter of the elements initially does not exceed a few millimeters, and then gradually increases to 1-2 cm. Spots and plaques may have an irregular, oval or round shape and a lumpy, rough surface, against which telangiectasia occurs and bleeding occurs after slight scraping.
- The keratotypic stage of the precancerous condition represents the further development of lesions. They acquire a yellowish-brown or grayish-black color due to dense, easily detachable fatty layers of horny epithelium in the form of crusts. The lesions are surrounded by a narrow inflammatory border.
- Severe hyperkeratosis - elements protrude significantly above the surrounding skin surface and can transform into a cutaneous horn.
The development of senile keratosis is slow (over several years), after which malignancy in the form of squamous cell carcinoma is possible (20-25%). With malignant degeneration, itching, increased inflammatory symptoms, compaction of the base and increase in the thickness of the lesion, and the formation of an erosive, easily bleeding surface occur.
Single large lesions are removed surgically, by electroexcision, cryodestruction or laser therapy. Treatment of multiple lesions is carried out through applications of fluorouracil ointment, tretinoin, and imiquimod cream.
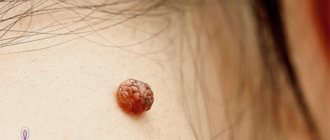
Cutaneous horn
It is an epithelial tumor with pronounced hyperkeratosis and is currently considered as a variant of senile keratosis. The formation can develop both against the background of scars, lupus erythematosus, lichen planus and other keratoses, and on externally unchanged skin.
The cutaneous horn is localized mainly on the head, face, and also on areas of the body that are subject to constant or frequent friction or pressure. In rare cases, it can occur in the red border of the lips.
Clinically, the cutaneous horn is a cylindrical, cone-shaped or branched formation, consisting of a dense accumulation of masses of horny epithelium of a whitish, dirty-grayish, brownish-gray or yellowish-brown color. It is firmly fused to its base, grows quite slowly, reaching sizes generally 0.5-1 cm, but often 4-5 cm.
Malignancy does not depend on the duration of the disease and is possible in 12-15% of cases. Its onset is accompanied by the appearance of pain, hardening of the base, inflammation around the tumor and sometimes a sharp acceleration of keratinization.
Treatment is only surgical. The formation is removed along with nearby healthy tissue.
Keratoacanthoma
It is, as a rule, a single, less often multiple, epidermal tumor, occurring in older people (usually 60–65 years of age). It is characterized by rapid growth, cyclical course and spontaneous regression. Malignancy occurs quite rarely (in 7%).
The development of keratoacanthoma is provoked by prolonged and intense solar radiation, inflammatory forms of dermatoses (seborrheic dermatitis, eczema), exposure to chemicals, and chronic trauma to the skin. The disease begins with the appearance of a small papule, which increases in diameter to 1.5-2 cm within 3-4 weeks.
The morphological basis of a precancerous tumor is the so-called “horny cup”. The formed formation has a grayish-pink color, dense consistency and hemispherical shape. It rises above the surrounding surface and is not fused to the underlying tissue (it is movable when attempting to move). In the “sinking” central part of the formation there are grayish dense horny masses, surrounded by a zone that rises in the form of a roller. Around the “horny cup” the skin texture is smoothed.
In the absence of independent reverse development of a solitary keratoacanthoma, treatment with cryodestruction, laser destruction or surgical excision is necessary, and in rare cases, with the use of radiation therapy. In case of multiple formations, oral methotrexate is prescribed.
Although the primary diagnosis of precancerous skin diseases is based on the clinical picture described above, histological examination plays the main role. In practical terms, the meaning of the concept of “cutaneous precancerous pathology” is that it makes it possible to identify groups with an increased risk of developing cancer from a significant number of people with dermatological pathology and carry out systematic monitoring of these patients with more in-depth studies. In medicine, the current strategy for combating malignant pathology is based on early detection and treatment of various forms of precancerous pathology.
Varieties
What are the types of horny keratomas? In modern medicine, these tumors are divided into two types: primary and secondary. The primary form of the disease begins to develop on healthy skin without obvious prerequisites. Usually it is not preceded by any damage to the skin or inflammatory processes. As a rule, this type of cutaneous horn is benign. Despite this, one should not neglect this disease, since its origin and course are still not well understood.
A secondary (false) cutaneous horn is formed as a result of skin damage, an inflammatory process, or as a result of the degeneration of other formations (warts, papillomas, etc.). This form of the disease is considered more dangerous, since in this case there is a risk of transition to a malignant disease. Treatment of such a neoplasm must begin at the earliest stages of development.
The primary form of the cutaneous horn can turn into a secondary one. Therefore, if such a formation is detected, it is necessary to urgently contact a dermatovenerological clinic for consultation with a dermatologist.
Types of pathology
There are 2 types of horny keratoma:
| View | Description |
| Primary | Horny formation appears on healthy skin for no apparent reason and goes through 3 stages: formation, color change, increase in density. The development of the disease is not accompanied by inflammation or other concomitant pathologies. This type of tumor rarely becomes malignant. |
| Secondary | This type of pathology is characterized by inflammation that develops as a result of injury, growth, malignancy of a wart or papilloma. Secondary cutaneous horn is recognized as the most dangerous for humans and requires special treatment. |
As it grows, the skin horn changes from a small beige lump to the stage of a rod-like growth of brown color.
Symptoms
Most often, the cutaneous horn has obvious external signs.
In the early stages, the disease manifests itself as a yellow growth on the skin. As it develops, the tumor usually takes the shape of a cone or horn, tapering to a point. In some cases, it can have a variety of shapes: straight, curved or spirally twisted. The cutaneous horn is characterized by very slow growth. The formation has clearly defined boundaries and a focus of inflammation at the thickened base. A small red rim is visible at the base, which begins to swell and grow over time. Patients often experience itching at the base of the horn.
During the growth process, grooves begin to form from the base, encircling the formation. At the foot of the cutaneous horn, metabolic processes are accelerated, and blood flows through the vessels to the base. But blood does not penetrate into the tumor, since blood flow and lymph flow in the tumor are stopped.
The tissues of the horny keratoma are similar in composition and density to a derivative of the epidermis - the nail plate. The color of the formation ranges from light yellow to dark brown, almost black. In most cases, the cutaneous horn is single; multiple formations are extremely rare. Most often, the patient does not experience any pain.
The surface layer of the horny keratoma can be smooth or rough, mottled with irregularities and grooves. The height of the tumor is considered a prognostic manifestation of malignancy: a small skin horn has a tendency to degenerate into cancer. If keratoma corneum is a manifestation of another disease, its development and prognosis will depend on the primary pathology.
Horny keratoma has two features that are life-threatening for the patient:
- spontaneous malignancy.
- deterioration in the patient’s quality of life due to discomfort in places where the pathology is localized: in the chest area, under the nail, on the face, in the intimate area (penis), on the buttocks, and so on.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of horny keratoma begins with a visual examination. During the examination, the doctor evaluates the external signs of the tumor. It should be cone-shaped and formed from dead skin (not have sensitivity at the end). An area of inflammation should be observed at the base of the cone. After the examination, a histological examination is prescribed.
Histology analysis allows you to accurately make a diagnosis and not confuse this neoplasm with other diseases. This method identifies all current processes: inflammatory, infectious, etc. If there are signs of a tumor degenerating into a malignant one, phenomena such as excessive development of abnormal epidermal cells and accelerated cell division (pathological mitosis) are noted. Then a biopsy is prescribed.
This method uses tissue samples taken from around the tumor and from its internal contents. Horny keratoma has a vulnerable spot at the base. It is in this place that pathological cells actively grow. For this reason, material for analysis is usually taken from the base of the tumor. A biopsy determines whether the growth is malignant or benign.
Other laboratory and instrumental examinations are prescribed as needed in each specific case.
When diagnosing a cutaneous horn, it is necessary to clearly differentiate this neoplasm from some diseases with similar symptoms or other types of keratosis:
- warts and calluses;
- verrucous nevus;
- atheroma (cyst or wen);
- basal cell carcinoma;
- verrucous psoriasis;
- dermatofibroma;
- lichen planus;
- keratoderma;
- angiokeratoma;
- lupus.
Need to know! To differentiate a cutaneous horn from a plantar wart or callus, it is necessary to cut off part of the thickened skin. If you damage a wart, then it bleeds, but the skin horn does not.
Treatment
The traditional method of treating such a formation is surgical removal of the cutaneous horn. Surgery is used in difficult cases when the tumor has reached a fairly large size. The horny keratoma is removed with a scalpel and the tissue around the lesion is excised, then sutures are applied. As a rule, scars remain on the skin after surgery. The rehabilitation period lasts up to 15 days.
You can also remove the skin horn using cryodestruction - destroying the neoplasm with cold. During this procedure, liquid nitrogen is applied to the affected cells, causing the tumor to die. After exposure to nitrogen, a small scar remains on the skin.
The most modern and safe method of treating keratoma corneum is laser removal. The laser beam completely destroys the tumor, and the operation takes about ten minutes. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and is completely painless. No rehabilitation is required after laser tumor removal.
In addition, methods for removing horny keratoma such as electrocoagulation and the radio wave method are used. These methods are contraindicated in patients with concomitant cancer diseases.
You cannot cut out a horny keratoma yourself at home. Despite its painlessness, this neoplasm can be the focus of a malignant process. Therefore, the tumor must be removed by a doctor in a medical facility.
Often patients with cutaneous horns resort to treatment with folk remedies. Traditional healers recommend applying products such as compresses made from onion peels, plantain, celandine, aloe and propolis tincture to the affected area of the skin. In addition, use an ointment that contains acids or is plant-based (for example, bay leaf).
Therapy methods
Based on the form and type of pathological neoplasm, the method of its treatment depends. Cutaneous horn removal is carried out in a beauty salon when the growth is benign and appears on the face or in oncology and dermatology centers.
Attempts at self-removal are prohibited due to the serious consequences this leads to.
Removal
To eliminate this skin defect, the following methods are used:
- Electrocoagulation;
- Laser method;
- Radio wave;
- Surgical;
- Cryodestruction using liquid nitrogen.
Using these methods you can quickly eliminate formations. However, electrocoagulation, laser or radio wave options cannot be used in people when there are concomitant oncological formations.
The surgical method is considered traditional, but its use requires the use of a local anesthetic and also leaves scars at the site of the operation.
The recommended method, which has no contraindications, is cryodestruction, which is a targeted effect of liquid nitrogen on a pathological formation.
Radiosurgery is a modern treatment method
In many clinics and modern cosmetic clinics, the procedure for removing skin horns on the face is carried out using the Surgitron device.
They evaporate the cells of the affected tissues through repeated point effects of the electrode on them. In the process of processing pathology using this method, layer-by-layer evaporation of the formation is carried out.
A distinctive feature of the device is the ability to use different modes when required:
- Electrocruretage;
- Electrocoagulation.
The peculiarity of this method is to remove the skin horn on the patient’s face and provide:
- Low probability of recurrence of formation;
- Good cosmetic result;
- Surgical healing of the skin surface.
Curettage and electrocoagulation
This method of removing keratin growths up to 2 cm in diameter is used under local anesthesia. Sharp dermal curettes are used to scrape the area, and then electrocoagulation is used to treat the entire surface after removing the growth. 2-3 cycles of such manipulations are repeated, the wound is treated with antibacterial ointment and a bandage is applied to it. The method cannot be used for patients with pacemakers, and also cannot be used to remove large tumors.
Cold treatment
A modern method for eliminating skin defects is cryosurgery, due to the effect of a cooling substance on pathologies. The simple method of applying liquid nitrogen to a cotton swab and treating the formation directly with it is not suitable. This is due to the fact that to eliminate collagen growths a temperature of less than –50 °C is required. The cryogens that create the necessary temperature conditions are:
- Liquid nitrogen applied using a probe has an effect of –196 °C;
- Liquid nitrogen in the form of a spray, creating a temperature of –180 ° C;
- Dry ice –79 °C;
- Nitric oxide –75 °C.
This method is relatively safe for humans
Side effects of cryodestruction
This method of treating cutaneous horns has its negative consequences. So, after freezing and subsequent thawing, pain is felt. The removal procedure consists of 2-3 sessions. When the size of the defect is small, the resulting pain is tolerable, and to eliminate large formations, local anesthesia is used.
When a skin growth is removed, swelling appears in an area with thin and sensitive skin. This is observed when eliminating formations near the eyes or lips. Side effects can be treated with hormonal ointments or other medications containing steroids. After freezing the skin, blisters sometimes appear on it, containing blood inside. This is treated by opening the blisters and then covering the affected area with a dry bandage.
Another side method of cryodestruction is hypo or hyperpigmentation, when whitening or darkening of the upper layer of the epithelium occurs. To prevent this, use sunscreen and clothing to protect from exposure to ultraviolet radiation. It is recommended to protect the affected area from exposure to chemicals.
The method is undesirable for removing cutaneous horn in the scalp due to the death of hair follicles in the treated area.
Prognosis and prevention
After removal of a horny keratoma, it is recommended to undergo an annual examination and monitor all formations on the body. This allows you to do RTM diagnostics. In more than 90% of cases, removal of the skin horn goes well and without relapses. If there is a suspicion of malignancy of the neoplasm, the patient is taken to the dispensary for further observation and treatment.
Several preventative measures for patients who have undergone keratoma keratoma removal:
- protect the operated area of skin from injury and damage;
- avoid prolonged exposure to direct sunlight;
- Strengthen your immune system by adding more vitamins and nutrients to your diet.
Reviews
Alexander. My father developed a cutaneous horn on his temple and grew quite large. They removed it with a laser at the clinic, very carefully and painlessly. 2 years have passed and so far everything is fine.
Natalia. An incomprehensible growth formed on my mother’s eyebrow. It turned out to be a cutaneous horn. At the medical center it was removed using liquid nitrogen. Mom has already fully recovered.
Tatiana. A lump grew near my ear. I thought it was a wart. When I went to the doctor, they said it was keratoma keratoma. When asked how to treat, they suggested removing it with a laser. I'm happy with the result, I recommend it to everyone.