For the first time, it is impossible to take your eyes off your newborn baby. After counting all the fingers and toes several times, the mother notices that the baby has spots on his face, head and body. Immediately after birth, babies often have many spots on their skin. They pass quickly, and those that remain are called moles, or birthmarks.
Not all moles last a lifetime. Some fade over time, but there are also some that remain forever, and sometimes even require medical intervention. After reading this article, you will learn about which birthmarks appear on a child’s body from birth, and which ones appear in later life.
Diagnostics
For differential diagnosis, the following types of studies are used:
- Examination with a dermatoscope, which allows you to see any pathology on the skin with multiple magnification.
- Study of pigment formations with a Wood's lamp, which uses weak ultraviolet radiation. Melanin absorbs ultraviolet light well, so areas with a high pigment content appear darker, while areas with less pigment appear lighter.
- In doubtful cases, computer diagnostics of moles is carried out using a videodermoscope.
- Tissue biopsy with histological examination. Finding cells with signs of proliferative growth is an indication for consultation with an oncologist.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Antifungal agents for toenails and fingernails. Effective and inexpensive, prices, reviews
Hypomelanosis
Hypomelanosis is one of the variants of leukoderma, in which, for various reasons, the formation of melanin or melanocytes in certain areas of the skin is disrupted. There are many forms of this condition, and the genetic characteristics of the body play a large role in its development. Also, in the development of some types of hypomelanosis, the provoking role of ultraviolet radiation, local hypothermia, and the use of certain medications has been proven. In most cases, skin manifestations are the only symptom of this disease, but sometimes they can be accompanied by signs of dysembryogenesis - damage to the central nervous system, malformations of bones, heart, and genital organs. The incidence of hypomelanosis is quite difficult to assess, since patients often do not consult a dermatologist due to the mild severity of symptoms.
Non-infectious causes of white spots
Spots in a child can be either congenital or appear over time. Not all of them require treatment, some remain for life, some disappear on their own.
Hypomelanosis and pityriasis rosea
With this disease, white spots on the body appear in newborns during the first month of life. In this case, a birth defect caused by a lack of melanin is diagnosed. Dyschromia provokes serious problems in the functioning of the nervous system, possibly retarded growth and development.
Frequent viral diseases are also considered a possible cause of hypomelnosis. The baby has general weakness and decreased immunity.
In this case, serious specialized treatment is necessary to avoid harmful consequences for the entire body as a whole. Such a diagnosis can only be made by a specialist and self-medication is dangerous.
There is no need to be scared by the name; this is not the kind of lichen that is contagious and transmitted by contact. The mechanism of its occurrence has not been sufficiently studied, but doctors know one thing for sure - it occurs in children who often suffer from viral and colds against the background of reduced immunity.
Characteristics of formations:
- spots are clearly visible on the skin;
- do not have a specific location;
- the patient does not experience discomfort or pain when pressed;
- The surface of the skin is flaky and may itch slightly.
The disease goes away spontaneously. But pediatricians recommend wiping the affected areas of the skin with salicylic acid to speed up healing.
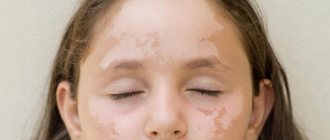
Vitiligo
A white spot on the skin of a child of this nature is caused by discoloration of a certain area. Melanin is completely absent in the epidermis, which causes the presence of white or milky spots on the body.
The “favorite” place for localization in children is the face, hands and knees. These spots do not cause discomfort, only in fairly rare cases there is slight itching a couple of days before they appear.
Modern medicine has not invented an effective cure for vitiligo, nor has it fully established the mechanism of development of the disease.
Possible and proven reasons include the following:
- genetic predisposition;
- autoimmune diseases;
- decreased immunity due to severe viral pathologies;
- constant or prolonged contact with pesticides. Children may be intolerant to washing powders or personal hygiene products;
- hormonal disorders;
- infection with parasites (protozoa and worms);
- stress, psychological discomfort.
Traditional methods of treating white spots are offered (a decoction of St. John's wort for wiping areas of the skin). But they can only have some cosmetic effect, and not affect the very cause or mechanism of development of the disease.
In this case, specific drug treatment is not prescribed. The patient is advised to spend less time in the sun, wear closed clothes, strengthen the immune system and not be nervous.
If the cause is an autoimmune disease, then the underlying pathology is treated.
Pityriasis alba and tumorous sclerosis
A distinctive feature of this disease is oval plaques on the face (this is where they appear first), then they can appear on the arms and neck. The disease affects children from 3 to 16 years old, but does not pose a threat to the life and health of the child.
It is rather a cosmetic defect that spoils the aesthetic appearance, especially of teenage girls. To speed up the disappearance process, you need to moisturize the discolored area as often as possible, do not sunbathe or visit a solarium.
The pathology is quite serious, characterized by the initial appearance of white spots on the face, and then on the neck, arms and torso.
Along with this it is also noted:
- underdevelopment of the nervous system;
- damage to internal organs;
- mental retardation.
Specific treatment is prescribed only after a thorough examination and confirmation of the diagnosis.
Diagnosis of age spots: what examinations are necessary in this case?
If signs of illness are detected, you should immediately consult a doctor. The pediatrician can refer the child to a consultation with a dermatologist, as well as other specialized specialists - this is necessary in order to exclude all possible concomitant pathologies of internal organs.
At the initial appointment, the dermatologist conducts a questioning and collects an anamnesis - during these procedures, he finds out how long ago the pigment spot appeared, how it developed, and whether there are any other disorders in the general condition of the child. The dermatologist also collects allergy and family history (this is necessary to exclude possible genetic diseases, as well as other skin diseases). After this, the doctor conducts an examination: assesses the size, location, shape, color, symmetry of the formation, and the nature of its edges. If necessary, dermatoscopy is performed.
Types of hypopigmentation in newborns
The cause of the development of hypomelanosis is a disorder of melanin synthesis due to the absence of melanocytes in the skin. May manifest as the following pathologies:
Albinism is the disappearance of color pigment in the skin. Disturbances in pigmentation also occur in the hair and irises of the eyes. The disease is considered genetic, but has not yet been studied. Interestingly, the largest percentage of the disease is in the Negroid race.
Albinism is a congenital pathology (lack of pigment on the skin, hair, eyes)
Vitiligo is white spots that appear at birth or appear in the further development of the baby. Discolored areas are no different from the surrounding skin - they do not stand out, do not peel, and cannot be felt. At first the spots are small, but with age they merge into a larger area. In the sun they do not darken or tan. Vitiligo is classified as a cosmetic defect; it does not affect the child’s health in any way.
Vitiligo - white patches on the skin without pigment
Hypomelanosis Ito. The disease begins in utero and is most often influenced by a hereditary factor. White stripes or waves can be seen already in the first days of the newborn. During adolescence, they become more noticeable or, on the contrary, disappear completely.
Age spots in children: main complaints and symptoms
The main complaint that parents make when contacting a pediatrician is pigmentation disorders (excessive pigmentation or depigmentation - white spots on the skin). In most cases, this condition does not bother the child or disturb his condition, however, this does not mean that it is not necessary to monitor the development and progression of the pigment spot.
Nevi, moles and other conditions with symptoms of pathological pigmentation are localized, usually on the face, neck or torso - these are the areas of the body that are most susceptible to adverse environmental factors (including insolation with UV rays). Pigment spots often appear on the arm or leg. The color of these areas of the skin may vary: pink, bright red, brown, and black pigment spots are observed. Often, the color and size of the area with impaired pigmentation is one of the main diagnostic signs.
Some types of pigmentation disorders (such as freckles or medial newborn spots) appear in clusters. In most cases, age spots are round or oval in shape with smooth edges. With some types of hyperpigmentation, dryness and flaking of the skin near the pigment spot may occur.
When moles are dangerous
When moles appear in a newborn, it is necessary to pay attention and regularly visit a dermatologist. The doctor will use a dermatoscope to examine the formation, determine its nature and the presence of cancer cells.
When bathing or changing your baby, you should carefully examine new spots or changes in existing ones. Birthmarks in a baby are not dangerous if there are no alarming symptoms. These signs include: intense increase in size and change in color, localized on the face, clear boundaries have disappeared, blood or clear liquid is released. It is necessary to visit the office of a pediatric dermatologist if the nevus in the area that is swollen and irritated is covered with hair. A cause for concern is the appearance of a bumpy surface or compaction that begins to peel off.
After the examination, the dermatologist will determine the period during which parents need to monitor the spot. If the situation worsens, the doctor will prescribe surgery to remove the nevus to avoid degeneration into a malignant formation. It is allowed to remove the growth after two years if there is no need to get rid of the stain.
What does Dr. Komarovsky say: are age spots dangerous?
The famous pediatrician, Dr. Komarovsky, has repeatedly touched upon the topic of moles, vitiligo and other pigmentation disorders in childhood in his speeches. The doctor says that areas of hyperpigmentation need to be treated with special caution - because cancer cells can develop in them. But this is not a reason to immediately remove moles if they appear. Komarovsky says that the best way to prevent skin cancer (melanoma) is to constantly monitor the condition of nevi. A well-known doctor insists on a monthly examination of the skin, and moles in hard-to-reach places (in the groin folds, armpits, on the scalp) should not be ignored. In order to remember the main signs that it is time to see a doctor, the doctor suggests examining each mole according to the algorithm. This is an abbreviation that stands for:
- asymmetry (should not be observed);
- the edges of the mole (should be clear and even);
- color (the mole should be uniform);
- size (“safe” nevi in diameter do not exceed 6-7 mm);
- dynamics (rapid progression and growth should not be observed).
If a child has a tendency to develop age spots, you need to keep a notebook in which you write down all the data about each mole every month. If you do this regularly and carry out proper examination, you can detect skin cancer in the early stages.
Pigment spots in children are a cosmetic defect, but, in most cases, it does not cause any inconvenience. Often, in order to avoid the progression of tumors and the appearance of complications, it is enough to monitor their condition, undergo timely examinations by a pediatrician, and also protect the skin from the sun and other irritating environmental factors.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Sw0g5JDVlLE
Helpful 1
« Previous entry
Causes of rebirth
Scientists have found that birthmarks are an accumulation of special cells called melanocytes on an area of the skin. They may have excessive pigment or not contain it at all.
In the first case, the mark will be dark in color, in the second it will have a shade lighter than the color of the surrounding tissue. There are also varieties of deep burgundy, wine-colored spots formed by a concentration of blood vessels - hemangiomas.
Scientists call all such formations on the body nevi.
A birthmark is a general name for many neoplasms that affect the human body. They can be different in shape and size. Some rise above the skin, while some, on the contrary, are hidden under its layer.
Above in the photo is an acquired dysplastic nevus. It can be caused by skin diseases, taking hormonal medications, ultraviolet radiation, or skin trauma.
The main causes of malignancy of moles:
- Hereditary factor.
- Excessive solar exposure. In this case, sunburn received in childhood plays an important role. The greater the dose of solar radiation received in childhood, the more likely the appearance of dysplastic nevi in an adult. Such formations have a very high risk of degeneration.
- Tanning obtained in solariums has been a leading factor in the increase in the incidence of melanoma in recent years.
- Decreased immunity (chronic diseases, stress, pregnancy).
- Aging.
When the tumor size is less than 1 mm in diameter, about 90% of patients live more than 5 years. When the melanoma diameter is more than 1 mm, there are already metastases. In the presence of such malignant nevi, the survival prognosis is extremely low.
A mole sometimes undergoes a number of malignant changes.
But what are the causes that a person can prevent?
How you can cause transformation:
- trauma to the nevus - squeezing, tearing, scratching or rubbing - both with violation of integrity and with its preservation;
- excess sunlight or artificial ultraviolet radiation. This can be either careless neglect of protection against UV radiation while relaxing on the beach, or abuse of a solarium.
The reasons for the transformation of a mole into melanoma are as follows:
- mechanical damage - friction with clothing, straps, skin trauma;
- hormonal changes in the body - most often occur during adolescence and pregnancy. Another cause may be thyroid disease.
- damage by ultraviolet rays - sunlight activates the division of melanin cells and causes pathological changes in skin cells.
Light-skinned, fair-haired people with light eye colors, those with red hair and freckles are most susceptible to the effects of ultraviolet radiation.
At risk are pregnant women and those who have a family history of melanoma.
Risk factors include:
- large congenital nevi;
- the appearance of new moles, the growth of old ones;
- nevi that cover the entirety of a specific part of the body.
It is difficult to reliably find out why the tumor became malignant, since any impact on it is undesirable.
- This could be a biopsy, traumatic cosmetic treatment, any damage, as well as an excess of ultraviolet radiation.
- An important factor is a genetic deviation, as well as a feature of the skin - light skin prone to burns from ultraviolet radiation is much more common in patients with melanoma.
Features of the disease
Many doctors are of the opinion that several factors are important in the manifestation of hypomelanosis.
Under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, the destruction of melanin occurs very quickly. Similar changes can occur even in a child. Hypomelanosis Ito (photo)
Phakomatoses of any form are a very rare disease and, due to their hereditary nature, are often foreseen. Some types of the disease are accompanied by congenital immunodeficiency, a high likelihood of premature aging syndrome and the risk of cancer.
Already in the first months of life, the disease manifests itself in the form of skin defects, varying in color and size. Such lesions often progress and are accompanied by the rapid development of eye diseases.
The most common forms of phakomatoses:
- Recklinghausen's disease - characterized by severe damage to peripheral nerves, sometimes the brain. In this case, there are frequent small tumors of the skin and compactions under it;
- Cerebroretinal angiomatosis is a combination of retinal angiomatosis and brain diseases. Often, along with this, tumors of the digestive tract occur;
- tuberous sclerosis - characterized by a multiplicity of tumors, always accompanied by dementia.
- Sturge-Weber disease - characterized by angiomatosamilofrontal region, seizures, and developmental delay. The prognosis may be favorable if the cause of the seizure syndrome is eliminated.
Every person should understand that this is a rather serious disease that requires serious treatment. If treatment procedures are not started in time, the consequences can be dire. There is no need to waste time, it is important to contact specialists.
Changes in the body that lead to phakomatosis begin with human DNA. It is believed that mutations of two genes are to blame - TSC1 and TSC2. This is a group of pathologies with a purely hereditary genesis.
Mutations lead to disruption of the production of two proteins responsible for counteracting tumor processes - hamartin and tuberin. As a result, numerous neoplasms appear in the tissues of various organs and parts of the body. As a rule, the disease develops “out of the blue”, without any preliminary, “warning” symptoms.
Any adverse effects on the fetus can cause disturbances in the development of the central nervous system, and even more so if they affect genetics. Inheritance occurs in an autosomal dominant manner with a probability of 0 to 50 percent. This means that up to half of the representatives of each next generation can receive the mutated gene from their father or mother.
Diagnosis and treatment
For differential diagnosis, the following types of studies are used:
- Examination with a dermatoscope, which allows you to see any pathology on the skin with multiple magnification.
- Study of pigment formations with a Wood's lamp, which uses weak ultraviolet radiation. Melanin absorbs ultraviolet light well, so areas with a high pigment content appear darker, while areas with less pigment appear lighter.
- In doubtful cases, computer diagnostics of moles is carried out using a videodermoscope.
- Tissue biopsy with histological examination. Finding cells with signs of proliferative growth is a good time to consult an oncologist.
- The treatment tactics for pigmented formations, if they do not cause any physical or aesthetic discomfort, consist of dynamic observation. Lightening and whitening external agents for removing areas of pigmentation in children are practically not used.
- Most medications contain hormones or chemicals that are harmful to the baby. After the doctor's permission, spots on a child over 6-7 years old can be treated with parsley, cucumber or lemon juice.
- If a decision is made to eliminate the pathological formation, the method of destruction is selected individually.
- Surgical removal involves excision of the affected area with a scalpel. The tissues are sent for histological examination. After the operation, scars and cicatrices remain. If malignant degeneration of a pigmented formation is suspected, it can only be removed surgically
- Cryotherapy, when destruction is carried out by ultra-low temperatures. Liquid nitrogen causes instant freezing and necrosis of pathological tissues. Used to remove small vascular tumors in children - hemangiomas. After cryodestruction, an inconspicuous spot remains. Damaged tissues are completely regenerated after six months.
- Electrocoagulation is a method of eliminating a skin defect using high-frequency currents. The manipulation is painful and requires the use of anesthesia. Rarely used in children.
- Laser therapy. Small moles and spots are removed instantly using a laser beam. This method allows you to accurately calculate the depth of action and the diameter of the beam, so as not to injure healthy skin. Use only for benign neoplasms.
- Radio wave method. The device is equipped with a tungsten filament that produces high-frequency waves. Pathologically altered tissues are cut away to healthy skin. Epithelization occurs quickly, sometimes leaving a cosmetic scar.
Traditional methods of treatment
Let us briefly consider diagnostic methods to determine the cause of the appearance of spots on the skin.
To determine lichen the following is carried out:
- microscopy of skin scales on affected areas;
- scraping for fungal infections.
To determine psoriasis you need:
- consult a doctor for a visual examination;
- undergo laboratory tests to rule out dermatitis or eczema (blood test and skin biopsy).
If vitiligo or hypomelanosis is suspected, a number of studies are prescribed:
- analysis for worms;
- Ultrasound of the biliary tract;
- Ultrasound of internal organs;
- comprehensive studies of the gastrointestinal tract.
Pale nevus and white pityriasis are diagnosed through a visual examination by a doctor.
Leucoderma can be detected by conducting an in-depth study, including:
- examination of the skin;
- studying the patient's medical history;
- studying information about hereditary diseases;
- laboratory and instrumental studies.
If necessary, the patient is prescribed consultations with highly specialized specialists: an immunologist, ophthalmologist, urologist, cardiologist, allergist.
If tuberous sclerosis is suspected, immediately prescribe:
- diagnostics of the central nervous system;
- CT or MRI of the brain;
- examination by a neurologist and ophthalmologist;
- Echocardiography of the heart;
- Ultrasound of internal organs and genitourinary tract.
If only medications are needed to treat such a complex disease as tuberous sclerosis.
To get rid of harmless stains, there are a number of folk remedies:
- For vitiligo, it is recommended to apply extracts of dill, parsley, duckweed or St. John's wort to pigmented areas of the skin. These herbs increase the skin's sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation, as a result of which the production of melanin increases, which evens out the skin color.
- You can alleviate the condition of psoriasis with the help of a decoction of the string. Tar shampoo is good for treating plaques on the scalp.
- Many folk recipes exist for the treatment of lichen. The most popular method is sulfur treatment. In combination with birch tar and goose fat, sulfur ointment promotes healing of skin tissue. Other folk remedies for treating lichen include: a mixture of propolis and olive oil;
- a mixture of jojoba oil and lavender (good for children);
- essential oils (eliminate itching);
- decoction of warty birch buds;
- white mustard seed paste;
- apple cider vinegar (relieves itching);
- wormwood solution.
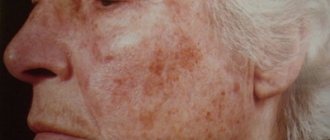
Age pigmentation
The manifestation of age-related pigmentation on the face is characterized by brown spots of various shapes and diameters that appear under excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun, the location of which is determined by the places of melanin accumulation, regardless of skin type. They do not change their shade regardless of any factors, including at certain times of the year, like freckles.
Age-related pigmentation on the face (after 45 years) is caused by changes in hormonal levels due to the onset of menopause and has the appearance of benign neoplasms. Baking malfunctions are also a common cause of blemishes on the face.
There are several varieties of such pigmentation:
- lentigo;
- keratoma (senile wart) is a round plaque with scales, yellow-gray in color, which can degenerate into a malignant neoplasm, so doctors recommend removing it;
- age-related spotty pigmentation (senile hyperpigmentation, senile freckles) is observed on the forearms, the backs of the hands;
- flat xanthoma of the eyelids (xanthelasma) - orange (yellow-orange) oval, ribbon-shaped plaques; These pigment spots are located under the eyes, on their inner corners.
Causes of occurrence in infants
The reason for the appearance of age spots on a child’s face can be internal or external factors. To exclude complications, it is important to know their features:
- Genetic continuity. When mom or dad are susceptible to pigmentary manifestations, there is a risk of passing this feature on by inheritance. Often children and parents have moles located in the same place.
- They pose no physical danger to health.
- Disturbance of the child's gastrointestinal tract.
- Vitamin deficiency and lack of nutrients.
- Decreased immunity.
- In premature babies, the anomaly occurs more often.
- Hemangioma in infancy. This is a congenital defect of the circulatory system. Has a red or brown color.
- Freckles. Congenital rashes appear during periods of active sun.
- "Coffee" blots on the skin. They form at birth and often disappear after a few months. They have a shade from light to dark brown.
- Pink spot. The cause of pigmentation may be the pressure of the mother’s pelvic bones on the fetus during pregnancy.
- "Mongolian" ones occur in dark-skinned babies. In appearance it looks like a hematoma - it disappears by two years.
Types of birthmarks
Many babies are born with skin without defects. But this does not mean that there are no spots on the body. It happens that they are faintly colored and difficult to detect when examining the skin.
Moles in newborns are clearly visible in only one baby out of a hundred. In the rest, the formations are not detected; only by the age of 2–5 years do they acquire their color and become noticeable. There are two types of nevi in newborns:
- pigmented moles of brown or black with blue color;
- red spots (angiomas, hemangiomas) of bright pink, red color.
The color of spots is influenced by the cells that form them. If the mark is formed from actively producing melanocytes, the color of the moles is brown or black. And the nevus from the vascular cells will have a red color.
Most often, pigmented formations occur in infants. A factor influencing the formation of such marks is a large amount of melanin in a small area of skin. Melanin is a pigment produced by pigment cells - melanocytes. It is what affects the color of a person’s eyes, hair and skin tone. The degree of melanin production in the body directly depends on the functioning of the endocrine system. There are several types of formations, the structure of which contains pigment cells:
- Mongolian spot. Occurs in babies with Mongoloid genes. A formation appears in the sacrum area. Outwardly it looks like a large bruise, which then spontaneously disappears by the age of five. It does not have a negative effect on the baby's health.
- Dysplastic marks. They have irregular outlines, different sizes and degrees of color. It happens that formations look like single elements.
- Moles. The formations look like dots of different colors and appear on all parts of the body: stomach, back, limbs, head.
- There is another type of birthmark - this is a congenital nevus, formed from pigment cells. In this case, the lesions are characterized by their extensive size.
The main types of age spots
There are several types of pigment spots in a child, each of them looks different and has its own characteristics of course and therapy. The main types of pathological pigmentation are:
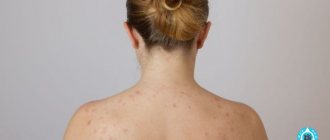
- nevi (moles). These are small round formations with smooth edges, which can be either dark or light. Nevi appear either during fetal development or in the first few years of life. It often happens that such formations are not observed in infants, but by the age of 3 several small moles appear in 95% of children.
- ephelides (freckles). These are small areas of hyperpigmentation that appear in the spring (when the skin is exposed to UV radiation). Most often they are localized on the face, neck, shoulders and back. They may decrease on their own during the cold season and go away with age.
- hemangiomas. This is a red spot that can be localized on any part of the body. Its appearance is due to the fact that in a certain place the vessels grow too much.
- Mongolian spots. Observed in children of the Mongoloid race, they look like small hemorrhages and disappear on their own after a few years.
- medial spots of newborns. These are small spots that are located on the back of the head or neck. They are pale pink in color, but may turn red during physical or mental stress (for example, during physical activity or while crying, breastfeeding). They disappear without a trace after 6-24 months.
- telangiectasia. This is a persistent and constant expansion of subcutaneous vessels (capillaries, arterioles, venules). It occurs as a result of difficult labor and is often observed in premature babies.
- warty neoplasms. They are usually gray or light brown in color, are very rare and, if the skin is extensively affected, require surgical intervention.
- Setton's nevus. This is a large nevus, around which hypopigmentation is observed (like vitiligo).
All age spots should be constantly under the close attention of parents and doctors. If a mole or nevus quickly enlarges, the edges become uneven and asymmetrical - this is a reason for an urgent visit to a medical institution. Consulting a doctor will help determine the type of pigment spot, carry out a differential diagnosis with other skin lesions (for example, infectious or allergic origin), and also take the necessary treatment measures, if necessary.
What's happened
A nevus is a benign neoplasm that is formed from pigment cells. The localization site is any area of the skin or mucous membrane. In most cases, such formations are not dangerous to the child’s health and do not cause him any inconvenience.
The formation of nevus cells begins in the womb. When exposed to a number of factors, cells begin to actively produce pigment, which subsequently appears on the surface of the skin in the form of a mole or birthmark.
Depending on their origin, all moles are divided into two large groups:
- congenital nevus in children - a child is born with a certain number of pigment spots;
- acquired – moles appear during life.
In addition, moles are divided into the following types.
Simple
The spots are orange-pinkish in color. The most common location is the thighs and buttocks of the baby.
Until a child reaches two years of age, simple neoplasms are practically invisible to the human eye. They can only appear when the newborn is crying or tense.
Intraepidermal
Refers to the most common type. The neoplasm has a round shape and a flat surface, with clear boundaries. Color can vary from light to dark brown.
Such nevi form during the first 20 years of life.
Strawberry
Can be presented in various sizes. They have a reddish color and a soft structure.
They are located in different parts of the body immediately after the baby is born. They can also form in the first month of a child’s life. Up to 12 months, such a neoplasm can increase in diameter, but by the age of 10 it goes away on its own.
Cavernous
It is a rarer type that occurs in newborns. It differs from the previous type in its structure. The neoplasm has large elements, and its base is formed deep in the layers of the skin.
In the first 6 months, rapid growth of the spot is observed, then the rate decreases slightly. This formation may finally disappear before the child reaches 5 years of age. As a rule, a scar may appear at the site of such a growth.
Dark spots
In most cases they are presented in small sizes. Can be painted brown. In rare cases they are black. In case of large volumes of tumors, they must be removed.
Brown birthmark
Such neoplasms have a flat surface, which can be brown in varying degrees of intensity. Localized anywhere in the body.
They can appear immediately after birth or after a certain period of time. If there are more than five birthmarks, the baby should be shown to a specialist.
Hanging
This is a benign neoplasm, the formation of which occurs from epithelial cells. May be dark in color or skin tone. The location in most cases is the groin area, armpits, external genitalia or neck.
According to doctors, such moles should be regularly monitored as they may pose a threat to the child's health.
Blue flat
This is one of the types of pigmented nevus. Such formations are most often large in size, difficult to remove and can be dangerous for the baby’s body.
Mongolian spots
They are detected in most cases on the buttocks, thigh or sacral region. In 90 percent of cases, infants with Asian roots are diagnosed with this type of neoplasm.
Fiery
Such spots have a bright red color because their structure consists of dilated capillaries. Most often presented in convex shapes.
If a child has such a formation on his body, this may indicate abnormalities in the growth and development of soft and bone tissue. If the fiery nevus is localized on the face, the child should be shown to a specialist. This condition may indicate problems in the brain.
The danger and causes of café-au-lait spots in a child
Hyperpigmentation affects everyone. For some, these are moles or nevi, for others, pigment spots located on various parts of the body.
Such “marks” appear in children at birth or in the first year of life, have varying degrees of intensity, and require at least a consultation with a dermatologist.
Any coffee stains on the baby’s skin are a signal to the mother about the need to observe them, monitor deformation and changes in color. How dangerous is excess pigmentation?
Causes of appearance on the skin of a child
Coffee pigmentation occurs in 20% of the world's inhabitants.
The formation is benign, has a pronounced uniform color and structure, a smooth surface, the boundaries are not blurred, increases in size in accordance with the growth of the child, and occurs with equal frequency in children of both sexes. In the dark-skinned population, pigment metabolism disorders are diagnosed more often than in people with fair skin.
Spots can be visualized on all parts of the body, but are absent on the mucous membranes. The formation does not pose any danger even if the skin is damaged, has a low risk of malignancy, and is purely a cosmetic defect. The tendency to form age spots is transmitted genetically.
Is it dangerous to appear
Cafe au lait stains on a child do not cause discomfort to a newborn baby. Pigmentation sizes range from a few millimeters to 20 centimeters. Single cases do not require a biopsy; laboratory diagnosis is recommended when there is a possibility of a systemic hereditary disease.
Treatment of coffee stains in a child is carried out if it is necessary to eliminate pigment in the baby on visible areas of the body. Several round-shaped neoplasms up to 4 cm in diameter are not a pathology and are factors that require the attention of a doctor. When visiting a medical facility for the first time, the doctor collects an anamnesis:
- age of appearance of pigmentation in a child;
- whether there is a delay in physical and intellectual development;
- whether the child has photosensitivity, whether he has taken medications that promote photosensitivity;
- whether the patient has had multiple fractures or tumors;
- presence of disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system;
- curvature of the spine, lower leg bones;
- eye pathologies.
The main method of treating coffee stain birthmarks is laser therapy; laser treatment of infants is not advisable unless there are complaints from the patient. In some cases, cryodestruction (liquid nitrogen) or surgical intervention is allowed; such methods are traumatic and can leave scars.
Before laser exposure, the patient is tested on a limited area of the body to check the effectiveness of the effect and prevent hyperpigmentation. Despite the achievements of modern medicine, coffee stains after laser removal can recur; defects in half of the patients respond to treatment.
Relapses are observed 6-12 months after laser therapy; in certain cases, slight lightening of the spot is the maximum achievable therapeutic result. Local treatment with lightening creams does not give the desired effect, despite the fact that the phenomenon is superficial. The laser is contraindicated for dark-skinned and tanned patients.
What diseases may this indicate?
Cafe-au-lait spots on a child’s body, if there are more than 6 of them, require consultation with a dermatologist and geneticist.
The presence of coffee stain birthmarks may be a sign of neurofibromatosis - a genetic disease characterized by the appearance on the body of multiple spherical flesh-colored tumors - neurofibromas, protruding above the skin level, having a diameter of up to 1 cm. The disease occurs in one case in 3300, the type of inheritance is autosomal dominant.
There are several types of the disease, united under the general name - neurofibramatosis, which give a reaction from the nervous system and skin. A common type in children is neurofibramatosis type I, another name for which is Recklinghausen's disease, described in 1882.
If neurofibromatosis is suspected, a child is prescribed a genetic test to detect mutations in the NF1 gene on 17q, the chromosome responsible for the development of the disease. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the patient requires constant monitoring.
The appearance of the first nodules occurs before the age of 10 years; if the disease has not manifested itself before this age, then there is no need to worry about neurofibromas in the future.
The course of the disease is individual for everyone and may be accompanied by:
- Stunted growth.
- Macrocephaly, seizures.
- Difficulty in mastering new information, delayed speech development.
- Problems in neurology: behavioral deviations, hyperactivity.
- Freckles in the armpits and genitals.
- Lisch nodules on the iris.
- Tumors of the optic nerve, spinal cord, and brain.
To make a diagnosis, the presence of several signs is required, since each of them separately does not signal the disease. The presence of coffee stains on a child’s body does not mean neurofibramatosis, just as their absence does not indicate the impossibility of this diagnosis.
Treatment is symptomatic, aimed at relieving pain in the late stages of the disease when multiple tumor nodules form before removing the tumors using hardware techniques or surgery.
Early diagnosis and prescribed therapy guarantee that the disease will not reach the stage of formation of skin tumors - neurofibromas. The risk of tumors degenerating into a malignant formation is low, amounting to no more than 5% of precedents.
There is no connection between the number, size of spots and the severity of the disease. The disease worsens during pregnancy and increases the risk of developing arterial hypertension and spontaneous abortion.
Multiple coffee spots on the skin may be manifestations of other systemic genetic abnormalities:
- tuberous (lumpy) sclerosis;
- Bloom's syndrome;
- McCune-Albright syndrome;
- Russell-Silver syndrome;
- Watson's syndrome;
- Westerhof syndrome.
The disease is differentiated visually by the type of neoplasm and accompanying symptoms.
Komarovsky’s opinion on removing coffee stains from a child’s skin
The World Health Organization does not consider coffee pigmentation on the skin to be a basis for making any diagnosis. The International Classification of Diseases ICD-10 assigned code L81 to this type of spot.
3 The presence of moles, warts or coffee stains on a child’s skin, according to Dr. Komarovsky and other pediatricians, does not require removal if the defects do not cause discomfort to the little patient.
If they are located on the face, hands and other open areas of the body, cause complexes, and are constantly exposed to sunlight, they should be removed.
From childhood, the child should be observed by a dermatologist, ophthalmologist, and neurologist in order to notice the development of pathology in time and prescribe the necessary examination. Consultation with a geneticist is required if there are more than 6 spots on the body with a diameter of 1.5 cm or more. Doctors' recommendation if there is pigmentation on the body is to protect the skin from ultraviolet radiation.
Types of nevi
The moles in the photo are just a few examples of the manifestations of nevi. There are five groups of pigment spots alone, and in each of them there are also varieties of nevi.
Melanocytic nevi of epidermal and dermal origin, respectively, dermal melanosis, Clark's nevus, congenital melanocytic nevi - these groups of nevi are the main ones. The photo above shows a papillomatous nevus belonging to the first group.
According to the nature of their manifestations, birthmarks in the photo may look small (1-2 mm), large (up to 10 cm), red, black, brown, may protrude above the surface of the skin or be flat. Some nevi resemble warts.
The types of moles are many and varied. Moles can be located on absolutely any part of the body and even on the mucous membranes. Depending on the morphological characteristics (color, size, shape, surface), the following types are distinguished:
- By color:
- Red (vascular tumors - hemangiomas).
- Brown and black (birthmarks, common moles and dysplastic nevi).
- Purple (warty, raised moles).
- Blue and blue nevi.
- White (fibro-epithelial growths).
- To size:
- Small (no more than 5 mm).
- Medium (up to 15 mm).
- Large (up to 10 cm).
- Giant (over 10 cm).
- Form:
- Flat (smooth surface).
- Convex (rough surface).
- Warty growths (can grow on a stalk).
There are:
- Melanoma-dangerous nevi are formations that are highly likely to degenerate into a malignant tumor. Such nevi are also called dysplastic, they include:
- Giant birthmarks, colored brown and any shades of this color.
- Elements of blue and cyan color – such formations have the highest risk of degeneration into skin cancer.
- Intermediate - nevus cells are located at the border of the epidermis and dermis. The rate of transformation into skin cancer is very high. The localization of such nevi is the palms and soles.
- Precancerous Dubreuil melanosis is a nevus on the face, the appearance of which resembles a pigment spot. This formation is irregular in shape, like a geographical map. Its size is more than 2 cm, the degree of coloring is different and heterogeneous.
- A melanoma-dangerous nevus, the cells of which are localized in the upper part of the epidermis, found in the vast majority of people:
- Fibrous-epithelial moles (convex, white).
- Verrucous (warty growths of various colors).
- Papillomatous.
- Lentigo - most often, these multiple spots appear on the face and are red or light brown in color, sometimes they are dark. The shape is wrong. Their sizes are small.
- Coffee stains - in some cases, these nevi are related to neurofibromatosis. If several coffee stains appear on the body, you should contact a neurologist.
- Mongolian spots are grey-blue in color, irregular in shape, vary in size and are found in children. They do not pose any danger and go away on their own by puberty.
Moles come in different sizes: from a barely noticeable dot to a large spot located on the skin and in its inner layers.
Nevi are classified into vascular (hemangiomas) and pigmented.
- The first type develops due to the enlargement and fusion of capillaries.
- Pigmented - formed by groups of pathological melanin cells.
By size, moles are divided into:
- small (up to 2 mm);
- medium (up to 6-10 mm);
- large (from 10 mm).
Based on the type of localization, nevi are:
- epidermal (located on the top layer of skin);
- borderline (occupying both the surface and deep layers of the skin);
- intradermal (located in the thickness of the middle skin layer);
Let's consider the types of moles and their meaning in order to understand the possible risks of formations on your body or their significance in your own destiny.
The main difference between nevi is the nature of their formation.
What types of moles are there on the body?
This could be a vascular cluster or a pigmented area of skin with excess melanin.
The form of neoplasms can be different:
- convex;
- flat;
- smooth;
- warty;
- hanging;
- hair.
Vascular moles are divided into capillary (flat) and cavernous (lumpy, in the form of nodules).
- In color, depending on the blood vessels, they can range from bright crimson to purple or blue.
- They occur both on the skin and on mucous membranes, or on the lip.
Premium Aesthetics – Coffee Stains
Premium Aesthetics Library
Coffee spots (café au lait spots, café au lait macules, CALMs) are hyperpigmented areas on the skin with uneven or smoothed edges, the color of which varies from light to dark brown. In foreign literature they are often called “café au lait spots”, which is a combination of the French “café au lait” (coffee with milk) and the English “spots” (spots).
In our company you can purchase the following equipment for removing coffee stains:
In newborns, coffee spots occur with varying probability, depending on the skin phototype:
- 0.3% of children - phototypes I–III;
- 3% of children - IV phototype;
- 18% of children have V–VI phototypes.
Before puberty, such spots can appear with a probability of 13% in light-skinned people and 27% in dark-skinned people.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Coffee stains usually indicate that a patient has neurofibromatosis type I , a multisystem disease characterized by spots on the back, neck, and axillary areas, as well as skeletal dysplasia, benign or malignant tumors of the nerve sheaths (neurofibromas).
The average incidence of neurofibromatosis type I is 1:3000. Its main causes are considered to be mutations or deletions (loss of a section) of the NF1 gene. This gene is responsible for the production of neurofibromin 1, a protein that suppresses the occurrence of tumors of the nervous system.
A decrease in its synthesis leads to the appearance of neurofibromas and other clinical signs of the disease.
Coffee stains on the skin can also occur for the following reasons:
- Albright-McCune-Sternberg syndrome - premature puberty, multiple fibrous osteodysplasia, skin hyperpigmentation.
- Bourneville-Pringle disease - tuberculous sclerosis; a rare genetic disease in which multiple benign tumors form in organs and tissues.
- Fanconi anemia is manifested by a complex of symptoms, the most serious of which are hematological disorders and tumors.
- Coffin-Siris syndrome is characterized by aplasia or hypoplasia of the distal phalanx or nail on the fifth toe, developmental delay, mental retardation, coarse facial features, etc.
Cafe-au-lait skin spots may be the result of RAS mutations —changes in the RAS family of genes and proteins.
These are small GTPases (enzymes that bind and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate, an energy substrate for RNA), which are involved in signal transmission from outside the cell and regulate cell division.
Some RAS mutations promote the emergence and metastasis of tumors.
In 50% of patients, the genetic mutations responsible for the appearance of coffee spots on the skin occur spontaneously. That is, the hereditary mechanism of transmission of the disease in this case is of indirect significance.
As for pathogenesis , coffee spots appear against the background of an increase in melanin production and the presence of giant melanosomes in the skin. In patients with neurofibromatosis type I, the number of melanocytes in age spots increases more significantly compared to other diseases.
Clinical manifestations
Diagnosis of neurofibromatosis type I is based on the search for key criteria - we can talk about the disease if at least 2 of 7 signs are present:
- Six or more coffee spots or macules on the skin with a diameter of more than 5 mm in children (before puberty) and more than 15 mm in adolescents and adults (after puberty) ( Fig. 1 ).
- More than two spots in the groin or armpit areas.
- Two or more typical neurofibromas or one plexiform neurofibroma.
- Optic nerve glioma.
- Two or more hamartomas of the iris are usually detected by an ophthalmologist using a slit lamp.
- Dysplasia of the sphenoid bone of the skull or pathologies of the long bones of the skeleton (for example, pseudarthrosis).
- Family history - the presence of neurofibromatosis in close relatives (father or mother, brothers or sisters).
Many of these signs are not present until puberty, making diagnosis difficult in children. Moreover, if a patient at risk reaches 10 years of age without the appearance of at least one symptom (for example, coffee stains), in the future he will almost certainly not have neurofibromatosis type I.
Neurofibromatosis type I should be distinguished from type II, in which the skin manifestations are relatively poor, but patients have a tendency to develop meningiomas and bilateral acoustic neuromas.
Other syndromes in which coffee stains may appear on the skin (some of them were listed above):
- Silver-Russell syndrome - growth retardation and psychomotor development, triangular face, shortened fingers, syndactyly, characteristic light brown spots on the skin, etc.
- Bloom's syndrome - dwarfism, reduced immunity, increased photosensitivity of the skin, coffee stains, etc.
- Gorlin-Goltz syndrome is a hereditary basal cell carcinoma of the skin with erythematous lesions and skeletal abnormalities.
- Maffucci syndrome is a benign overgrowth of cartilage tissue with bone deformation and dark vascular formations on the skin.
These are not all syndromes in which characteristic café-au-lait hyperpigmentation may occur on the skin. However, they are united by two important factors - relative rarity and overall severity, i.e. the presence of other signs (except coffee stains) that have a much more significant effect on the body.
In general, the following patterns are noted:
- Multiple small coffee stains indicate the presence of one of the above diseases (usually neurofibromatosis type I).
- Single large light brown spots, as a rule, are not associated with other pathologies and exist on their own.
Rice. 1. Coffee stains in the armpits and back (www.medscape.com)
Principles of treatment
Before starting treatment for coffee stains, more serious pathologies should be excluded. For this patient, it is necessary to carefully interview, carefully examine, and prescribe laboratory and instrumental studies. It is impossible to do this in a cosmetology office, so it is important to maintain continuity and maintain contact with doctors of other specialties.
If coffee stains are associated with any diseases, maximum efforts should be directed toward treating the underlying pathology. If coffee stains exist on their own, or the underlying disease has already been treated, but areas of hyperpigmentation remain, you can use hardware methods.
One such technique is the Q-switched alexandrite laser . In a study of 48 people, it showed good to excellent effectiveness in more than half of the patients (51.4%) after an average of 3.2 sessions.
Moreover, relapse was recorded in 10.4% of cases. Laser treatment for coffee spots carries a high risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation - about 50%.
If this occurs, therapy should be discontinued until hyperpigmentation resolves.
IPL therapy has also been successfully used to treat coffee stains . Intense pulsed light (IPL) selectively destroys melanin in areas of excess accumulation, resulting in lighter skin.
Modern IPL devices, such as M22 (Lumenis), are equipped with light filters that allow the skin to be exposed to the required range of the radiation spectrum.
Thanks to this, IPL can be safely used to treat coffee stains on dark skin - up to Fitzpatrick phototype V.
It has been noticed that if the coffee stain is completely removed, then the risk of its reappearance is minimal. If the stain is partially removed, the probability of recurrence is 50%.
Other Indications
- Deep-lying vessels
- Eyebrow tattoo
- Loose skin
Source: //www.premium-a.ru/disease/pigmentnye-dishromii/kofejnye-pyatna/
Ways to get rid of moles and birthmarks
If you decide to get rid of a birthmark or mole, you should listen to the doctor’s recommendations. There are several safe and quite simple ways to remove such tumors:
- Injections of medications directly into the spot, which stimulate the death of overgrown vessels or other tissues.
- Cryotherapy is the freezing of warts or moles using nitrogen. After a few days, the area where liquid nitrogen was applied heals and becomes covered with a crust, after which the crust disappears along with the new growth. With the help of cryotherapy, you can only get rid of small warts or moles (see also: warts on a child’s hands).
- Laser. Using a powerful beam of light, you can remove unwanted formations on the body painlessly and quickly. After the procedure, the healing process takes very little time, especially when compared with cryotherapy.
- Radio waves. Sometimes the doctor recommends getting rid of the tumor using a device that affects the mole with radio waves. First, the doctor will give an anesthetic injection, then remove the nevus. Healing after the procedure is quick and there are usually no scars left.
- Removal with a scalpel. This method is quite traumatic; it is used in cases where the birthmark is large. Despite the fact that today there are more advanced treatment methods, surgical excision remains a fairly popular procedure.
Finally, I would like to advise parents not to panic if their child has spots or moles on his body. You should definitely consult a doctor, or better yet, see another specialist. In this case, it will be easier for parents to make the right decision and protect the child from possible problems in the future.
Forecast
A patient with hypomelanosis is always given a favorable prognosis. The only exception is the form of Ito disease, when congenital disorders play a significant role in determining the prognosis of life.
If you try to avoid constant sun exposure, you will be able to avoid the spread of the disease to healthy tissue.
Hypomelanosis in a child
Guttate hypomelanosis is a type of leukoderma, a skin disease associated with the loss of pigment in the body. With this pathology, dysfunction or absence of melanocytes, cells responsible for the production of melanin, a natural brown pigment that determines the shade of the skin, eyes, and hair, is observed in the epidermis.
Classification
Currently, the classification includes about thirty different forms of phakomatosis.
The most common and well-studied forms are the following:
- tuberous sclerosis;
- neurofibromatosis;
- phakomatosis fifth;
- encephalotrigeminal phakomatosis;
- Ito hypomelanosis;
- Louis-Bar syndrome;
- Klippel syndrome;
- Bourneville disease;
- Sturge-Weber syndrome;
- albinism;
- neurofibromatosis type 2.
In tuberous sclerosis, unexpected gene mutations in chromosomes can be observed.
This form has three obvious signs:
- epilepsy attacks from birth, convulsions;
- abnormalities of mental and mental development;
- the appearance of colorless spots on the skin from birth.
Changes are recorded in the brain from birth, since some convolutions can be distinguished from healthy ones.
Defects in the internal organs of a sick child are also observed: a benign neoplasm in the heart muscle, which leads to death, as well as tumors of other organs.
Neurofibromatosis is characterized by the appearance of neurofibromas under or on the skin - tumors that can reach a meter in diameter.
The formations affect nerve tissue and cause dangerous consequences, such as:
- breathing problems;
- swallowing disorder;
- blurred vision;
- disruption of the functioning of vital organs.
Mental disabilities are also present.
Symptoms of fifth phakomatosis are most often observed in children aged about ten years. Small tumors appear, which over time develop into malignant neoplasms accompanied by ulcers.
Encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis is characterized by the presence of vascular tumors on the back of the head and face of a person. On the face, tumors appear as burgundy-colored spots located on one side of the face. From birth, convulsions on the opposite side of the face, as well as epileptic seizures, are noted.
Ito's hypomelanosis is often accompanied by dementia, baldness, and light spots on the skin that resemble marble stains.
Severe immune disorders, vasodilation and cerebellar pathology are characteristic of Louis-Bar syndrome. About 15% of people who have a history of such phakomatoses often suffer from various forms of cancer.
Klippel syndrome can be diagnosed by the following signs:
- the presence of flat tumors on the leg;
- the presence of a flaming nevus on the lower limb;
- aneurysms and vascular dilations appear at the site of the lesion;
- the limb becomes enlarged and lengthened.
Bourneville disease can also be called tuberous sclerosis. Characterized by pronounced signs of dementia, it is the most severe form of phacomatous disease. The presence of adenoma of the sebaceous glands is noted.
Sturge-Weber syndrome is manifested by a delay in human intellectual development and the appearance of characteristic pigment spots in the face.
Albinism as a form of phakomatosis is caused by a defective gene, due to which melanin is not observed in the body. It is characterized by the presence of pale white skin, white eyelashes, hair and eyebrows.
Neurofibromatosis type 2 is an extremely rare type of phakomatosis. It is characterized by an asymptomatic course, accompanied by the appearance of slowly growing tumors.
There are several categories of hypomelanosis, and each type of disease has its own differences regarding symptoms of manifestation, time of occurrence, causes, etc. In total, the following types of disease can be distinguished:
- Hypomelanosis Ito. It is a genetic feature, rarely transmitted hereditarily, and more often has a sporadic path of origin. On the skin, the pathology appears in a wavy or zigzag pattern. Almost always, this category of disease is accompanied by problems in the neurological sphere, which is caused by disturbances in embryogenesis that occurs during pregnancy. Because of this, other defects in the child’s development are often present.
- Teardrop-shaped. This type of disease affects women who have a reduced amount of melanin in the blood. As a rule, these are representatives with light skin type. Changes develop when the cover is exposed to the sun or ultraviolet radiation for a long time. Due to the fact that the production of melanin occurs much more slowly than its restoration, hypomelanosis develops.
- Idiopathic. This category usually includes all those forms of the disease, the origin of which cannot be reliably identified.
- Progressive macular hypomelanosis. This type of pathology differs in that it is provoked by the activity of bacteria on the skin of the body, during which chemical components are produced that interfere with the normal production of melanin.
The skin of the legs and forearms is most often affected, but otherwise hypomelanosis can spread throughout the body. Rarely, light marks appear on the face.