A rash on the genitals is definitely an unpleasant phenomenon. But the reasons for its appearance are very different - from completely harmless to quite serious diseases. It is important to understand in time what is happening and what needs to be done. This can be harmless enough, but more often than not it is much more serious.
The appearance of a rash on the external genitalia is possible in both men and women, and even children.
The skin here is somewhat different from other parts of the body. It is very sensitive to mechanical irritations and various infections. Diseases that occur elsewhere are observed here, as well as a number of conditions unique to this area. And the reaction to influences and diseases is most often a different type of rash.
Discomfort and irritation in the genital area are often signs of various infectious diseases, including genital herpes, candidiasis and other lesions.
You can use the arrows to view photographs of the most common genital rash conditions, as well as brief descriptions of them.
Psoriasis Caused by increased growth of skin cells. The spots appear anywhere on the body, including the genitals. Crack and bleed
Chestoka
Molluscum contagiosum is a skin infection caused by a virus. The virus causes benign changes on the skin in the form of blisters.
Scabies (scabies mite) Scabies is a skin infection caused by a mite known as Sarcoptes scabiei. These microscopic mites live on you for months. They breed on the surface of your skin and then dive into it and lay eggs. This causes an itchy, red rash.
Genital warts caused by human papillomavirus All genital warts should be treated by a doctor, and in particular, care should be taken to determine whether the warts are caused by strains of the human papillomavirus that can cause cancer.
Anal warts When infected with the human papillomavirus, people may have many warts in the genital and anal areas
Epididymitis is a chronic or acute inflammation of the epididymis. Manifested by constant or intermittent pain in the scrotum, especially when walking.
Genital warts Genital warts are a sexually transmitted infection caused by certain strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV). These growths cause pain, discomfort and itching. They are especially dangerous for women because some types of HPV can also cause cervical and vulvar cancer.
Vaginal Yeast Infection Vaginal yeast infections have a common set of symptoms, such as: • vaginal itching • swelling around the vagina • burning during urination or sex • pain during sex • soreness • redness • rash • whitish-gray vaginal discharge
Granuloma on the penis and groin Granuloma usually begins as a small nodule that develops into an ulcer.
Genital Herpes Herpes blisters are painful, and people complain of pain when urinating if the herpes sores are located close to the urethra in men or women. It is important to remember that herpes spreads from one person to another, even if there are no visible signs of the disease.
Contact dermatitis Most often it is a reaction to active chemicals. There may also be an allergic reaction
Secondary Syphilis During the secondary stage of syphilis, people develop red or reddish-brown sores or spots and are now highly contagious.
Genital herpes It affects about 16% of people aged 19 to 46 years. Transmitted sexually. The symptom is painful blisters filled with fluid.
Balanitis is an inflammation of the foreskin of the penis, usually caused by infections or chronic skin conditions. Poor hygiene can contribute to irritation. Read the material on our website.
Lice feed on human blood and cause severe itching. Pubic lice usually live on pubic hair and are spread through sexual contact. In rare cases, they can be found in eyelashes, armpits and hair. Pubic lice are usually smaller than body lice and head lice.
A latex allergy occurs when your immune system reacts to a normally harmless substance as if it were an invader such as a virus or bacteria. In this case, a reaction to using a condom may occur.
Syphilis The first sign of syphilis is a small, painless chancre. It may appear on the genitals, rectum, or inside the mouth.
Granuloma. A small pimple begins to enlarge, the tissue wears off and becomes velvety, then ulcers and scars appear
Diaper Rash Diaper rash occurs when a baby is left in a dirty diaper for too long. Having diarrhea can make the problem worse.
Vaginal discharge due to chlamydia Some sexually transmitted diseases cause vaginal discharge, and the color, texture, and amount of discharge may vary depending on the disease.
Genital warts caused by human papillomavirus All genital warts should be treated by a doctor, and in particular care should be taken to determine whether they are caused by strains of the virus
Discharge from the penis Some sexually transmitted diseases can cause (or even bleed) from the penis.
Now we will talk in more detail about these unpleasant phenomena.
Types of rashes on the genitals
There are different types of rash.
Primary rashes may be as follows:
- Spot.
It is a local change in skin color, usually with clear boundaries. But it has no relief.
There are spots:
- vascular
- hemorrhagic
- pigment
The first ones are:
- inflammatory – dilated vessels are visualized
- non-inflammatory – these are telangiectasia, vascular moles
Most often, inflammatory spots appear on the skin of the genital organs.
If they are small, they are called roseola. If large, it is erythema. Such spots are distinguished by the fact that they disappear when pressed with a glass slide. As soon as the skin pressure goes away, they appear again.
Hemorrhagic spots are the result of blood leaking from the vascular bed into the tissue. They can have different sizes, which is why they are called differently. Among the people, any such spot is a bruise. In the forensic examination, this is a bruise.
But dermatology uses other terms:
- pinpoint hemorrhages - petechiae
- a little more - purple
- large, irregularly shaped spots – ecchymoses
- large foci of hemorrhage - hematomas
Their color changes over time.
When pressed with glass, hemorrhages do not disappear and do not change color. Pigment spots are freckles, moles, vitiligo, etc.
Their appearance is due to the accumulation of pigment in the skin or a decrease in its amount. There are times when both hyper- and hypopigmented areas appear on one area of the skin. This rash is called leukoderma.
- Papule.
This is the same as a knot. The result of infiltration of the skin of the genital organs. Such elements disappear without scarring.
- Blister.
This is swelling of the papillary dermis. Disappears without a trace. To imagine a blister, think of what your skin looks like after being stung by a nettle or bitten by a mosquito. On the genitals, such elements often appear as a result of allergies.
- Vesicle.
Another name is bubble. It is filled with liquid.
It can be serous, purulent, bloody. The bubbles lift the skin and shine through it. The most common cause of this type of genital rash is genital herpes. Vesicles may appear on a hyperemic base. As a rule, they disappear without a trace.
- Bubble.
Same as a vesicle, only larger in size. They are multi-chambered. Formed in skin diseases. May leave scars behind.
- Pustule.
This is the name for purulent rashes on the genitals. This is a cavity element. There is pus inside.
Can be located:
- superficial – impetigo
- deep
Types of deep pustules:
- folliculitis – with damage to the hair follicle
- acne – with damage to the sebaceous gland
- ecthyma – if the skin without hair and glands is inflamed
Superficial pustules heal without scars. They can form during a deep inflammatory process.
- Tubercle.
Cavityless element of the rash. Same as a papule, only deeper and larger in size. May turn into an ulcer. Heals with the formation of a scar. On the genitals, tubercles can form due to syphilis.
Sometimes they merge, forming an infiltrate.
- Knot.
Same as a tubercle, only larger. It goes beyond the dermis and reaches the subcutaneous fat.
Examples of nodes:
- syphilitic gumma
- furuncle
There are also non-inflammatory nodes: fibroma, lipoma. Rashes can also be secondary.
These elements include:
- Flake.
These are torn layers of skin. They arise as a result of peeling. Characteristic of many skin diseases. Appears with psoriasis. Then the scales have a silvery-white color. With ichthyosis they may be black. On the genitals it can occur due to fungal diseases or erythrasma.
Sometimes the scales come off easily, in other cases it is difficult and painful (lupus erythematosus). Peeling is observed with seborrheic dermatitis.
- Crust.
Forms in place of vesicles or pustules. May contain pus, blood, serous exudate. Often observed during the healing of herpetic eruptions or skin pustules.
- Erosion.
Superficial skin defect. Appears on the genitals with syphilis. Other possible causes on the genitals: eczema, fungal skin infections. Heals without scarring.
- Ulcer.
Same as erosion, only deeper. Usually formed from a tubercle, node, deep pustule. Ulcers appear on the genitals due to syphilis, severe fungal or bacterial infections. Less commonly, the cause is tuberculosis or cancer.
- Scar.
Overgrowth of connective tissue. Formed at the site of the ulcer.
- Lichenification.
Areas of thickened skin. They usually appear against the background of a long-term skin disease, such as eczema.
- Vegetation.
Read also: The smell of discharge after sex.
Overgrowth of the papillary dermis. Observed during human papillomavirus infection.
Balanoposthitis
Balanitis is a manifestation of a disease of the head of the penis, which is characterized by inflammatory processes in it.
Posthitis is the name given to inflammation of the foreskin. Separately, these pathologies are rare, so they are combined under a single name - balanoposthitis.
These diseases of the penis occur due to infection of the smegma that accumulates under the foreskin.
Symptoms of pathology:
- subjective sensations (itching and burning, pain);
- discomfort when opening the foreskin;
- inflammation;
- discharge of pus.
In mild cases, the disease is treated by strict adherence to intimate hygiene and local use of antiseptics. For severe forms, antibiotics are used.
Rash on the genitals due to STDs
Some sexually transmitted infections can cause rashes on the skin of the genitals.
These include infections:
- syphilitic
- herpetic
- candidiasis
- molluscum contagiosum
- papillomavirus infection
- scabies
- phthiriasis
Rarely the rash is caused by:
- trichomoniasis
- gonorrhea
- chlamydia
With these pathologies, red inflammatory spots may appear on the skin of the genital area.
Rashes on the genitals due to syphilis
Initially, erosion appears on the skin. Sometimes there can be 2 or more. This is primary syphiloma.
The formation of erosion is one of the first symptoms of the disease. It is painless and has the color of raw meat. May be covered with a gray or yellow coating.
Occasionally, instead of erosion, an ulcer may form. In this case, after it heals, a scar will remain. Rashes can also appear in the secondary period of syphilis. Papules, spots, erosions and other morphological elements form on the skin. But they appear not only on the genitals. They can also form on other parts of the body.
Treatment of the labia
Inflammation of the labia, their itching and irritation sooner or later lead the girl to a gynecologist. Treatment is not required in cases where itching and swelling are a response, for example, after epilation of a deep bikini, when wearing pads and tampons for a long time, in the absence of proper hygiene of the intimate area, when using certain cosmetics. In such cases, as a rule, if itching occurs, it goes away on its own.
If the symptoms do not go away, then the swelling and itching of the labia minora is inflammation, rather a symptom of some disease, which can be either sexually transmitted or gynecological. In both cases, you need to be examined by a doctor and undergo tests. Self-medication in such cases is strictly not recommended. Possible treatment consists of identifying the causes that caused it and, based on this, prescribing various remedies. Fortunately, modern gynecology can offer a wide range of possible approaches, both medicinal and surgical, or a combination of both.
DRUGS FOR TREATING INFLAMMED LABIA
- Antibacterial agents;
- Antihistamines;
- Antifungals (antimycotics);
- Hormonal;
- Douching;
- Vaginal antiseptics (suppositories);
- Baths and rinses.
By the way, one of the good ways to relieve inflammation of the external genitalia, to perform sponge cleansing of the complex relief of the labia minora and all folds of the vaginal mucosa, is the vaginal cleaning procedure, which you can learn more about by clicking on the picture link below.
- INTIMATE SURGERY
- Plastic intimate surgery
- Labiaplasty
- Virginity restoration
- Surgical defloration
- Vagina reduction
- Levatoroplasty
- Clitoral plastic surgery
- CONTOUR PLASTY
- Intimate contouring
- Narrowing of the vagina
- Labia enlargement
- G-spot enlargement
- Clitoris enlargement
- Urinary incontinence
- Prices for procedures
- INTIMATE COSMETOLOGY
- Intimate cosmetology
- Rejuvenation of intimate areas
- Plasmolifting
- Fractional lifting
- Epilation deep bikini
- Intimate whitening
- Mesotherapy
- Mesoline line
- Laennec therapy
- Removal of condylomas
- Prices for procedures
- GADGETS AND COSMETICS
- Cream Amelan
- Amelania cream
- Whitening cream
- Whitening mask
- Serum Repair
- Collagen mask Tete
- Silk masks
- Cream with snail
- Mesoline Shine
- Mesoline Acne
- Vaginal cones
- Kegel exerciser
- Drug Laennec
- HEALTH AND BEAUTY
- Lymphatic drainage of the body
- Buttocks massage
- Breast correction
- Leeches vaginally
- Vaginal cleanliness and health
- SERVICES AND PRICES
- All services and prices
- Intimate surgery
- Contour plastic
- Intimate cosmetology
- Cosmetics and gadgets
- ARTICLES
- Inflammation of the labia
- Intimate pimples
- Lump on the labia
- Bartholinitis
- G-spot history
- Female circumcision
- Labia
- How to regain innocence
- Laser labiaplasty
- How to widen your vagina
- Boil of private parts
- How to lose your virginity correctly
Promotion! Only on June 30 and July 1, consultation on intimate plastic surgeries is free! Sign up online!
from 05.12.17 until December 30, 2017 NEW YEAR'S SPECIAL OFFER:
from 12/06/17 to 12/29/2017:
from 12/25/17 until January 13, 2018:
THE MOST UNUSUAL GIFT FOR YOUR LOVEDONE FOR THE NEW YEAR!
THIS WEEK'S SUPER OFFER! Give yourself new sensations instead of 32,000 rubles. for only 22,000 rubles! Doctor's work as a gift!
G-spot enlargement 22,000 – all included!
An intimate gift for a man for the New Year:
Copying or reproducing materials from this site is prohibited. Information on the website of the intimate plastic surgery clinic was updated on 10/18/2019
Rashes on the genitals due to fungi
Candidiasis is one of the likely causes of the formation of rash elements. Red spots and papules appear on the skin. In severe cases, pustules may form. A rash on the male genitals is called candidiasis balanoposthitis. The head of the penis is affected.
The skin in the genital area may also become inflamed. Most often, fungal inflammation progresses in the folds.
Rashes on the genitals of women appear in the vulva area. Candida is transmitted sexually. But inflammatory processes are usually caused by decreased immunity.
Another possible cause of the rash is athlete's foot. The fungus is usually brought into the groin from the feet. Men suffer more often. Fungi settle in skin folds.
Risk factors:
- obesity
- sweating
- hot climate
- diabetes
Athlete's foot progresses quickly if there is sufficient moisture. Large red spots of irregular shape appear.
Peeling is possible. Without treatment, the disease can last for a long time, sometimes for years.
Ulcers on the penis with chancriform pyoderma
Chancriform pyoderma is very rare.
This is a severe chronic disease with pronounced inflammatory and purulent manifestations.
External resemblance to hard and soft chancre can make diagnosis difficult.
The exact causes of the disease are not fully known.
Infectious agents are pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic microorganisms.
Most often these are streptococci.
Pathogens enter the body through microtraumas.
Infection with blood flow from other inflammatory foci is less common.
Diabetes mellitus and decreased immunity are considered risk factors.
They predispose to the development of chancriform pyoderma.
Why the infection occurs in this particular form is unknown to modern science.
The localization of the inflammatory and ulcerative process mainly occurs on the head of the penis.
The first sign of the disease is a bubble up to 2 centimeters in size.
It quickly breaks through and an ulcer forms in its place.
The difficulty of differentiating it from chancre is the absence of pain and itching.
But with chancriform pyoderma, regional lymphadenitis occurs with severe pain.
With syphilis, the lymph nodes are only enlarged, and upon palpation they do not cause discomfort to the patient.
An increase in body temperature with chancriform pyoderma is rare.
This is a dangerous symptom.
It may indicate generalization of infection, even sepsis.
When making an accurate diagnosis, doctors first of all rule out infection of the patient with syphilis.
For this purpose, both serological tests and treponemal tests are used.
Microbiological examination reveals a large number of staphylococci and streptococci.
Treatment is carried out using antibacterial drugs.
It is recommended to first test the sensitivity of pathogens to various antibiotics.
This is necessary to ensure the success of the therapy.
In addition to antibacterial therapy, treatment is carried out to increase immunity.
An additional way to speed up the healing of ulcers is local physiotherapy.
Molluscum contagiosum on the genitals
Rashes on the skin of the genital organs appear mainly on the pubis. Papules and nodes up to 1 cm in diameter are formed.
There are depressions in the center of large elements of the rash. A mushy mass is released from them. This is a viral disease.
It is transmitted through sexual contact. Existing inflammatory elements do not disappear for a long time. They can be present on the skin for months.
HIV does not go away at all, even with treatment. If a person wants to get rid of the rash earlier, it can be removed.
The skin heals on its own without scarring. Resolving papules are usually surrounded by a rim of red skin.
Rash on the genitals due to scabies
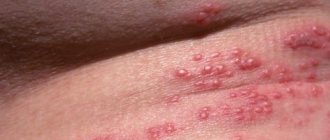
This disease is caused by a tick. It digs passages in the human epidermis and causes severe allergies. Often not only rashes appear in the genital area, but throughout the body.
There are almost no symptoms for several weeks after infection. Then, as a result of an allergic reaction, generalized itching appears.
With repeated infection, it occurs within 24 hours after the scabies mite enters the skin. Some patients do not have a rash. Others develop a large number of red spots, papules and blisters.
The elements of the rash are usually not painful. But they become like this if bacterial complications occur. When examining the skin, the doctor may detect scabies. They are noticeable on the surface of itchy papules.
What is the reason?
All kinds of pathological growths on the penis and labia also appear as a result of a viral infection or parasitic infestation.
In most cases, the characteristic appearance of the rash allows one to determine the cause of the disease, and treatment usually does not cause difficulties. But in any case, this must be taken very seriously.
A genital rash is a symptom that can be caused by a number of health problems and can occur on any part of a man's or woman's genital area. It is usually reddish in color, may be painful or itchy, and may have sores. If you have a rash on your body that you can't explain, you should see your doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
There are many possible causes of acne, ulcers and other unpleasant symptoms in both men and women. These are infections, sexually transmitted diseases, allergies and autoimmune disorders.
Common causes of genital rash.
The most common causes of strange manifestations in the intimate area are various infections:
Ringworm is a fungal infection or ringworm of the groin area. The skin is red, itchy and scaly, and may even become inflamed.
Diaper rash is an infection that affects babies due to the warm, moist environment of diapers. The body turns red, slightly peels, and blisters appear.
A vaginal yeast infection is an infection that affects women and is often caused by taking antibiotics.
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral infection that appears as hard, isolated, round blisters. They are itchy and inflamed.
Balanitis is an inflammation of the foreskin or glans penis, usually caused by poor hygiene. Balanitis causes itching and redness.
Balanitis and balanoposthitis: causes, symptoms, treatment.
Parasite infestation is another possible cause of genital rash:
Pubic lice are tiny insects. They lay eggs in the genital area and spread from person to person through sexual contact. They most often occur in teenagers. An infestation of pubic lice causes itching and sometimes sores.
Body lice differ from pubic lice in their larger size. They live in clothing and on skin, and feed on blood. They also cause itching and irritation.
Scabies is an itchy rash caused by very small mites. They penetrate the skin and cause severe itching, especially at night.
Allergies and autoimmune disorders are the third group of causes:
Contact dermatitis is a common type of rash caused by body contact with an allergen or irritant (most often an active chemical). Latex can also be an allergen that can cause genital rashes as it is commonly used in condoms.
Psoriasis is a general skin disease. The cause of psoriasis is unknown, but doctors suspect it is an autoimmune disorder. It can be accompanied by the appearance of a pinkish, scaly, itchy rash anywhere on the body. In men, psoriasis can also cause sores in the genital area.
Ringworm - less common, but also causes itching. Doctors are not sure of the specific cause, but it is thought to be related to an allergen or an autoimmune disorder. In the genital area, lichen can cause ulcers.
Reactive arthritis, or Reiter's syndrome, is arthritis that occurs in response to infection by certain bacteria, such as chlamydia, salmonella, or shigella. Chlamydia can cause discharge.
Sexually transmitted infections are a likely cause of rashes in those who do not practice safe sex:
Genital herpes is a virus that can cause painful sores in the genital area.
Genital warts are caused by the human papillomavirus. They are small, closely spaced, and cause itching.
Syphilis is a bacterial infection that is spread through sexual contact. It is accompanied by a rash that can appear anywhere on the body. And this place doesn't necessarily itch.
What happens in the initial stages of syphilis?
Granuloma inguinale is a sexually transmitted infection. Causes lesions in the anus, penis and labia.
During the first stage of granuloma development, a small pimple will begin to grow and consume surrounding tissue. When the fabric begins to wear out, it turns pink or faint red. Then the pimples turn into red nodules with a velvety texture that rise above a flat surface. It all happens around the anus and genitals. Although these formations are still painless, they sometimes even bleed if they are damaged by underwear or rubbed.
At the second stage of the disease, bacteria begin to destroy the skin. Once this happens, small ulcers will appear that will spread from the anus to the thighs and lower abdomen or groin area. You will notice that the perimeters of the ulcers are formed by granular tissue. Granuloma may be accompanied by an unpleasant odor.
When the granuloma reaches the third stage, the ulcers become deep and turn into scar tissue.
You can read about genital herpes, warts, molluscum contagiosum and groin scabies in our special materials by following these links.
Molluscum contagiosum in children and adults - what to do?
Here we will talk in more detail about other causes of rashes on the genitals.
Rashes on the genitals due to pediculosis
Phthiriasis or lice pubis causes the appearance of bluish spots. They occur in the hair growth area. Because lice live only on hair.
The disease is transmitted sexually. Less often - within the family through bedding. Papules and scratches appear on the skin.
The disease is accompanied by moderate itching. Upon examination, the lice themselves and their nits are discovered. They measure 1-2 mm. Usually there are not many pubic lice on the skin.
In addition to blue spots, there are allergic rashes at the location of lice. Basically it's hives. A bacterial infection may occur. Then there is an increase in lymph nodes.
Vaginal yeast infections - Genital candidiasis (thrush)
Pain and irritation in the genital area are not always associated with sexually transmitted infections. Inflammation can develop due to an imbalance of microorganisms in the normal microflora, an allergic reaction or eczema.
Vaginal yeast infections, also known as candidiasis, are a common women's condition. A healthy vagina has bacteria and some yeast cells. But when the balance of bacteria and yeast changes, the yeast cells begin to multiply rapidly. This causes intense itching, swelling and irritation.
Vaginal yeast infections have a common set of symptoms, such as:
- vaginal itching
- swelling around the vagina
- burning during urination or sex
- pain during sex
- soreness
- redness
- acne and ulcers
- whitish-gray vaginal discharge
Many people go to the doctor, fearing that they have become infected with genital herpes, although in fact, damage to the skin in the area of the external genitalia can be explained by completely different reasons. These include, in particular, genital candidiasis (thrush). Since it spreads through intimate contact, it occurs in both women and men.
This fungal infection causes irritation, redness and itching in the vulva, foreskin and head of the penis, as well as in the perianal area (around the anus).
Women often experience vaginal discharge and the formation of small cracks, especially when rubbed or scratched.
Candida infection in women often causes inflammation in the vulva and vagina. Often, a whitish, cheesy discharge from the vagina is observed.
In men, redness and soreness are observed in the foreskin and glans penis, and the formation of ulcers is uncharacteristic.
The causative agent of candidal infection is the fungus Candida albicans. The microorganism can live in moist conditions of the groin area and in healthy people.
Unlike genital herpes, with thrush the inflammation covers larger areas; There is no fever or swollen lymph nodes.
To confirm the diagnosis, smears are taken for laboratory testing, although visible manifestations are usually quite typical for identifying candidiasis and prescribing antifungal agents. Using scented soaps or bubble baths often worsens symptoms.
Sensitivity to external influences is a characteristic sign of genital candidiasis.
Irritation of the groin area due to candidiasis can be caused by soap, shower gel or bubble bath, as well as various creams and lotions. In such cases, in order to cope with the problem, it may be enough to abandon these products and rinse the affected area with clean water, followed by applying a water-based emollient cream.
Flavored perfumes and cosmetics also sometimes cause damage to the surface of the genitals, as they contribute to drying, irritation, allergization and exacerbation of candidiasis.
Rashes on the genitals due to HPV
Papillomavirus causes proliferation of the papillary dermis. Papules and vegetations appear in the genital area. They usually do not appear until several months after infection.
Sometimes they are small, almost invisible. In other cases they grow to large sizes.
Symptoms depend on what type of HPV caused the pathology, how many viruses of different types affected the skin, as well as on the state of the person’s immunity.
Diagnostics
Before treating inflammation of the labia, the gynecologist must identify the causes of its occurrence. To do this, he will conduct a standard gynecological examination in the mirrors and examine the patient’s external genitalia. After this, the specialist will conduct a survey. During it, the gynecologist will find out what symptoms are bothering the patient, when they arose and what preceded it. If a woman tried to self-medicate, she should definitely tell a specialist about it.
Further, based on the information received, the doctor may prescribe the following procedures:
As for vaginoscopy, it is usually recommended for young patients. This will help identify pathological changes on the surface layer of the vagina. The hymen will not be damaged.
If the pathology occurs in a girl, she needs to visit a pediatric gynecologist.
Streptoderma on the genitals
Red rashes on the genitals appear due to bacterial skin infections. These can be different pathologies caused by different microorganisms.
Read also: What does yellow, odorless discharge mean in women?
Inflammatory processes are caused by streptococci, staphylococci, and anaerobic flora. Elements of the rash can be superficial or deep.
Appears:
- pustules on the skin
- folliculitis
- inflammation of the sebaceous glands
- erythrasma (red spots caused by corynebacteria)
If lymphatic vessels are involved in the pathological process, lymphangitis develops. Superficial inflammatory processes usually occur without complications. Deep ones can cause the development of abscesses. These are severe inflammatory processes, after which large scars can form.
The abscesses themselves can break into the internal organs (bladder, rectum, etc.) with the formation of fistulas.
Why does pathology develop?
When it comes to 1-stage vulvitis, the labia can become inflamed due to neglect of the rules of intimate hygiene. If a woman does not wash herself every day and rarely changes menstrual pads and underwear, her labia will begin to become inflamed. Another provocateur is wearing synthetic and too tight panties.
Other causes of damage to the inner labia include:
- overheating of the body;
- hypothermia of the body;
- mechanical damage to the mucous membrane;
- use of certain medications;
- hormonal imbalance;
- allergies.
Medicine knows of many cases where inflammation of the labia was diagnosed in girls who had not reached the age of puberty. The immune system is quite imperfect. Alkaline flora cannot suppress the growth of pathogenic flora. Delicate mucous membrane is prone to frequent damage. Masturbation can cause damage to the mucous membrane. Sometimes the cause of the development of vulvitis in girls is insufficient intimate hygiene or the presence of parasites in the body.
Vulvitis is also diagnosed in young girls who have crossed the twenty-year mark. The main reason here is hormonal imbalance. Sometimes this diagnosis is made to women after menopause. The main reason is thinning of the mucous tissues. This contributes to the loss of protective functions. As a result, minor inflammatory processes develop.
Due to infection of the labia majora, 2-stage vulvitis develops. The disease can develop against the background of endometritis, colpitis or candidiasis. Another common cause is a violation of the opportunistic zone.
Rash on the genitals due to HIV
HIV infection itself usually does not cause a rash on the genitals. But in the stage of immunodeficiency, it aggravates the course of other diseases. Candidiasis and herpes develop more often.
In case of infection with HPV or molluscum contagiosum, large rash elements appear. They never disappear on their own. You can get rid of such morphological elements only by removing them.
With HIV, the likelihood of bacterial skin lesions also increases. The ulcers are getting larger. They are often complicated by deep purulent processes.
HIV also aggravates the course of syphilis. All stages of this disease pass faster. Within a year after infection, the infection can affect the brain and other vital internal organs.
What are the consequences of penile disease?
It often happens that various signs of a dermatovenerological disease appear on the skin, glans or inner sheet of the penis. These ailments, unlike many other diseases, are almost always accompanied by rashes, redness and other visual effects. If you ignore these visible manifestations, the disease will not stop on its own, but will only progress. Many people think that with the help of folk remedies, spells or other non-drug methods they can solve their problems with penis disease. But this, as a rule, does not bring tangible results, but only slows down the course of the disease for a short time.
The main feature of herpes viruses is their ability to cause latent infections, characterized by persistent viral vectors and recurrent relapses, which are especially dangerous for immunocompromised patients, both pregnant women and newborns. Human pathogens are 8 herpes viruses, and only two can cause genital infections and cover the skin and mucous membrane of the genital area. Genital herpes viral infections are mainly caused by herpes simplex virus -2 and, less commonly, herpes simplex virus -1, which is the main cause of herpes in the nasolabial region.
Trying to let things take their course can lead to the following consequences:
- complete defeat of the entire member by the disease;
- development of chronic diseases of the internal genital organs;
- loss of erection;
- difficulty urinating;
- swelling or enlargement of the penis due to blisters and blisters;
- loss of sensation of any movements of the penis;
- the stage at which treatment will not help and will only block the disease;
- deterioration of general condition;
- severe pain, fever, etc.
At the first manifestations of the disease, you must urgently go to a specialist for a medical examination.
Genital herpes is a sexually transmitted disease. The frequency of infection is directly related to sexual activity. The most common infection is through sexual or close intimate contact with a partner with an active infection. Infection can also occur through contact with an asymptomatic carrier of the virus. Herpes around the mouth can be transferred to the partner's sexual area and vice versa. Viruses can be found in saliva, hands or vaginal fluids and can be transferred from one part of the body to another by touching or scratching.
What tests to take for rashes
To begin treating rashes on the genitals, you need to know what causes them. This requires laboratory tests.
Most often, an inflammatory rash appears in the genital area. It is usually of infectious origin.
To understand which microorganism provoked this symptom, you need to take a scraping and examine it in various ways:
- microscopy
- sowing
- PCR
Sometimes the diagnosis can be established clinically. For example, with molluscum contagiosum or human papillomavirus infection. But even in this case, it is advisable to confirm the pathological process in the laboratory. The doctor scrapes the skin and examines it under a microscope.
It can detect:
- pseudomycelium of candida fungus, budding cells
- fungal hyphae in dermatophytosis
- a large amount of coccal flora with a nonspecific bacterial infection
In a dark field, pale spirochetes, the causative agents of syphilis, can be identified. The material may be cultured for bacteria or fungi.
PCR is also used. This technique helps identify any viruses, bacteria or other microorganisms. If an allergy is suspected, a blood test is taken for immunoglobulin E. If this indicator increases significantly, skin tests are performed to identify the allergen.
Blood is also donated for infections:
- syphilis
- HIV
- herpes
Parasitic skin diseases are diagnosed clinically or using microscopy.
What to do if there is inflammation of the labia due to injury
If one labia is swollen and itchy, this is most likely caused by trauma to the skin and the spread of infection.
Especially often the condition develops after getting rid of vegetation in the intimate area. In this case, you should not apply alcohol compresses or take hot baths - this contributes to the further spread of the inflammatory process. Irrigations with anti-inflammatory herbs at room temperature can be done.
Orally, in case of severe inflammation, take a broad-spectrum antibiotic, for example, Z-factor
500 mg on the first day, and then 250 mg, course 5 days or
Tsiprolet
500 mg 2 times a day for 5 days.
Baneocin
cream should be applied to the problem area in a thin layer 2 times a day.
If the outcome is a boil, surgical treatment is required.
Treatment of rashes on the genitals
Different schemes are used for various types of pathologies. In the case of fungal diseases, local treatment is often sufficient.
Miconazole, clotrimazole, and nystatin are used locally. These ointments and creams destroy fungi in the skin. Therefore, the rash disappears over time.
Antiseptics and antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections. They are prescribed locally for superficial processes. But in case of deep skin lesions, systemic antibiotic therapy is required. For herpes, acyclovir is prescribed topically.
The same drug or other acyclic nucleosides are used internally. For parasitic diseases, skin treatment with permethrin is required. In the case of human papillomavirus, symptomatic therapy is carried out primarily.
Morphological elements of the skin must be removed. In the future, immunomodulatory therapy can be carried out to prevent relapses.
If molluscum contagiosum is detected, the morphological elements of the skin must be removed. Although you don’t have to touch them if they don’t bother a person. Only the doctor warns him that without treatment, the rash can persist for up to 1 year. If you have an immunodeficiency, it will take even longer.
In cases where the rash is of syphilitic origin, treatment with penicillin is required. The regimen, choice of drugs and dosages depend on the stage of the disease.
Treatment
As practice shows, the greatest success in the treatment of inflammation of the labia can be achieved if systemic and local drugs are used simultaneously. During therapy, it is necessary not only to eliminate the inflammatory process, but also to eliminate the pathological factors that provoked it.
Girls should adhere to the pastel regime for the period of treatment, and adult women should abstain from sexual contact.
Regardless of why the labia are inflamed, women must be prescribed vitamins A, E and C. This will help protect the epithelial layer and speed up the process of its regeneration. Vitamin therapy will also improve the patient’s immunity.
If the causes of the pathology are the presence of an STD, then it is necessary to treat the woman’s sexual partner.
To understand which antibiotics to use for treatment, the gynecologist will prescribe a special test that will show the sensitivity of pathogenic microorganisms to drugs. Antibiotics are used to treat inflammation caused by a bacterial infection.
If the inflammation is caused by trichomoniasis, the patient will be prescribed Trichopolum, gonorrhea - Sumamed, and chlamydia - Erythromycin. Sometimes taking these medications is combined with taking other broad-spectrum antibiotics (for example, Augmentin).
It is worth noting that antibacterial drugs kill not only pathogenic but also beneficial bacteria. That is why, during treatment with antibiotics, as well as for some time after its completion, you need to use medications containing bifidobacteria. This will help restore normal microflora of the intestines and vagina.
Inflammation caused by pathogenic fungi is eliminated with antifungal drugs. Usually this is Flucanazole.
If the inflammation is of an allergic nature, the patient will have to follow a special diet. It means giving up salty, sweet and spicy foods. To achieve the greatest effect, it is also necessary to take antihistamines.
If the labia majora are inflamed as a result of seborrheic dermatitis, it is necessary to use hydrocortisone ointment. In severe cases, systemic hormone therapy may be needed. Steroids and topical antibiotics are used for hidradenitis suppurativa.
If the symptoms of inflammation are severe and do not allow a woman to sleep fully, then doctors can prescribe sedatives, as well as medications with vitamin B and magnesium.
To strengthen the immune system, it may be recommended to take immunostimulants (Immunal, Immunoflazid).
For inflammation, which is combined with atrophy of the mucous membranes (women experience this during menopause), HRT with estrogen will be effective.
If the pathological process is provoked by parasitic infections, treatment will be carried out with anthelmintic drugs.
Local treatment of inflammation involves treating the external genitalia with ointments, using compresses and lotions with eucalyptus infusion or furatsilin solution. To enhance the effect, you can also wash with a weak solution of potassium permanganate or boric acid. Lactagel can give good results in therapy. It helps restore microflora in the vagina.
Triderm will help relieve swelling and other unpleasant symptoms of inflammation. If ulcerations or wounds appear on the surface of the genital organs, then a thin layer of Levomekol should be applied to them. It will speed up the healing process.
For inflammation of the labia minora, the choice of vaginal suppositories will also depend on the causes of the development of the pathology. So, for thrush and trichomoniasis, Neo-Penotran is prescribed, for chlamydia and gonorrhea - Chlorhexidine, and for severe itching and swelling - Terzhinan.
If a woman has any concomitant diseases, their treatment is mandatory.
Folk
To enhance the effect of drug treatment, women can use traditional methods.
If the inflammation is associated with thrush, it can be treated with aloe. To do this, you need to make tampons from the plant. This is very effective if the labia minora are inflamed.
For any form of inflammation, aloe extract will be useful. It is made as follows: peel 100 g of the plant, cut into pieces and mix with 100 ml of water, 150 ml of glycerin and a small amount of lemon juice.
The finished product should be infused in the refrigerator for 24 hours. Then you need to strain it and pour it into a clean bottle. The extract should be stored in the refrigerator. It is used to wash the labia in the morning and evening.