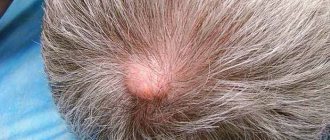
Eczema: variety of forms
Translated from ancient Greek, eczema is a boiling rash on the skin. According to modern concepts, this term refers to acute or chronic inflammation of the human skin with its characteristic symptoms:
- various rashes;
- burning sensation;
- peeling;
- itching;
- tendency to relapse.
The first sign of pathology may be elementary dandruff, which does not go away after using appropriate products.
Eczema under the hair on the head has a rather unsightly, repulsive appearance, but it is not transmitted from person to person, even with very close contact
Various provoking factors contribute to the occurrence of the disease:
- chemical;
- thermal;
- mechanical;
- internal (diseases of various organs and systems, as well as genetic predisposition).
It is believed that eczema is the initial stage of psoriasis development.
This dermatological pathology can manifest itself at any age and in various parts of the body. Depending on the causes and localization of the rash, several forms of eczema are distinguished:
- seborrheic;
- professional;
- true;
- mycotic;
- dyshidrotic;
- callosal;
- nursery;
- microbial, including: varicose veins;
- coin-shaped;
- nipple;
- post-traumatic;
- sycosiform.
Scalp eczema occupies a special place among all types of diseases. Its diagnosis and treatment is initially complicated by the presence of hair.
Diagnostics
When patients complain of symptoms such as itching and rashes, the doctor will have to identify the disease and conduct a differential diagnosis to exclude the possibility that the patient has vulgar psoriasis. The disease can also be confused with cutaneous candidiasis or simple diaper rash (especially in infants), so a thorough diagnosis is extremely important.
For diagnosis, patients are prescribed dermatoscopy - taking a scraping from the affected area and examining the tissue for the presence of pathogenic fungi. If necessary, the attending physician refers the patient for a blood test and allergy tests, and also gives a referral for a gastrointestinal tract examination.
To exclude other diseases, consultation with doctors such as:
- allergist;
- immunologist;
- endocrinologist;
- nutritionist.
Eczema of the scalp
You need to know that eczema does not damage the hair follicles and does not affect hair growth . However, the presence of the disease negatively affects the condition of the skin, disrupting the nutrition and functionality of epidermal cells, which negatively affects the quality and quantity of hair.
When the head is affected, the following forms of eczema are most often diagnosed:
- microbial;
- seborrheic.
Eczema gradually progresses from an acute inflammatory process to a sluggish chronic
Typically, the manifestations of the disease are localized:
- behind and above the ears;
- on the back of the head;
- under the hair on the forehead;
- on the temples.
Scalp eczema often causes complexes associated with imperfections in one’s own appearance.
Reasons for appearance
The following factors are considered common reasons that contribute to the development of pathology:
- profuse, frequent sweating, which provokes the proliferation of all kinds of pathogenic microorganisms;
- diseases of the stomach and other organs of the digestive system;
- genetic predisposition;
- decreased immunity and metabolic disorders due to persistent and systemic diseases;
- hormonal imbalances during pregnancy and adolescence;
- increased activity in the sebaceous glands;
- contact with aggressive environments, poisonous plants and allergens;
- stress and depression;
- mechanical impact resulting in damage to the skin;
- long-term exposure to UV rays;
- insufficient supply of vitamins necessary for the proper functioning of the body.
Previously, there was a misconception that only non-compliance with personal hygiene rules and careless home care were to blame for the occurrence of rashes. Of course, unsanitary conditions can become an additional condition for the development of the disease, but not the main factor.
Eczema of the scalp indicates a deterioration in general health, and disruption of the skin restoration process, caused by various reasons, becomes the basis for the manifestation of symptoms of the pathology. At the same time, fungal infections present in the body of any person are not a provoking factor, but a consequence of dermatitis, that is, a secondary disease.
Stress is a common cause of seborrheic eczema.
Prevention
To prevent the development of this unpleasant disease, it is necessary to take preventive measures:
- fight dandruff and seborrhea of the head in a timely manner, do not let it get worse;
- if you already have seborrhea, be extremely attentive to your condition and at the first signs of eczema (the appearance of a small pink rash) rush to a dermatologist;
- enrich your diet with vitamins and microelements;
- timely treat infectious and endocrine diseases, as well as pathologies of the digestive system;
- do not overuse hairsprays, foams and hair gels;
- by all means to increase the body’s resistance to infection, engage in physical exercise, toughen up, and spend more time in the fresh air;
- protect your psyche from worries and worries.
Video: how to deal with seborrhea
Seborrheic eczema is a long-term condition that requires ongoing attention and treatment. With proper daily scalp care, you can minimize all the unpleasant manifestations of this disease. Eczema on the scalp in the hair can be successfully treated using medications and traditional medicine methods. The main thing is to promptly recognize symptoms, eliminate provoking factors and follow all prescriptions and recommendations of a dermatologist.
source
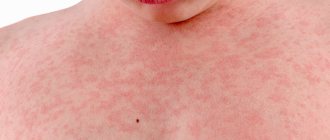
Microbial eczema
Doctors still cannot accurately answer what acts as the true factors in the occurrence of microbial eczema. However, it has been found that weakened immunity allows the infection to spread in the human body, causing various inflammations, including in the skin.
Microbial eczema is a chronic pathology, during which there are periods of exacerbation and remission. In this case, the localization and degree of damage depend on the evolution of the pathological process.
Causes of the disease
Typically, rashes characteristic of microbial eczema appear in places where there are chronic foci of the inflammatory process:
- purulent lesions;
- ulcers;
- infected wounds;
- abrasions;
- fistulas;
- cuts.
The causes of microbial eczema can be chronic and infectious diseases, in particular, pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
Infection in the cell layers of the scalp can cause eczema
Symptoms
The disease manifests itself as follows:
- Initially, unpleasant sensations appear in certain areas of the scalp: itching, burning, pain. Depending on the immune system, eczema lesions may expand their boundaries or remain within the original affected area.
- Since the skin regeneration process is disrupted, characteristic symptoms arise: crusts stuck to the hair. They appear from opened purulent blisters and papules.
- The skin in the affected areas under the hair looks deformed and unhealthy: erythema (redness), swelling, peeling, wetting, roughness.
- If the disease is protracted, then the outcome is known in advance: hair loss in the affected areas. Their complete and irreversible disappearance in certain areas is possible.
Diagnostics
To establish the true cause of the disease, it is necessary to undergo diagnostics and study of skin samples taken from the affected areas. After all, often different forms of pathology have similar clinical pictures, and it is necessary to correctly differentiate them in order to select the appropriate treatment.
To do this, initially carry out a visual examination of the lesions and dermatoscopy. It allows you to distinguish microbial eczema from seborrheic, psoriasis, microsporia, trichophytosis. Then they take tests and scrapings from the damaged areas. Biological material helps to exclude the presence of other skin diseases with symptoms similar to eczema.
At the same time, an examination is carried out for the presence of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. This allows you to identify disorders that affect the condition of the skin. You may need consultations with highly specialized specialists, such as an allergist, neurologist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist.
Dermatoscopy of the head is a simple, painless procedure during which the skin is examined under high magnification.
Treatment of the disease
With microbial eczema, lack of treatment leads to the rapid onset of pronounced symptoms. Its causative agents are often staphylococci or fungi. Accordingly, therapy is prescribed based on what triggered the development of inflammation.
The fight against pathology is always complex and consists in the following:
- A course of treatment with antibacterial/antifungal drugs is administered orally or intramuscularly. The period of use of a particular medication in such cases does not exceed 7 days. If the product does not have the expected effect, it is changed to something else with another active substance. Antibiotics:
- Penicillin;
- Erythromycin;
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Lincomycin.
- Antifungal agents:
- Fluconazole;
- Ketoconazole;
- Intraconazole.
- Furacilin;
- Cynovit shampoo has antiseptic, wound-healing, antimycotic effects;
- Prednisolone;
- B vitamins:
- Milgamma;
- Solcoseryl;
- Radevit;
- Persen;
- Phimethicone;
To treat microbial eczema, not only systemic and local drugs are used, but also physiotherapy, traditional medicine, and dietary nutrition.
Drugs used in the treatment of microbial eczema - photo gallery
Dermovate is a steroid drug used to relieve inflammation, itching and allergic reactions.
Penicillin helps with microbial eczema to cope with infection
Ketoconazole is an excellent antifungal agent
Likanshuang is a Chinese medicine based on natural ingredients.
Milgamma - vitamin B complex, helps in cell regeneration
Persen is a sedative for relieving nervous tension and ensuring restful sleep.
Festal helps in the treatment of eczema associated with digestive disorders
Atoderm protects against the negative effects of external factors
Akrustal is an excellent remedy for treating lesions
Triderm is a complex drug for the treatment of eczema, containing simultaneously several active components with different effects.
Sulfur ointment has a disinfecting effect
Solcoseryl accelerates cell regeneration
Prevention
To prevent exacerbations, it is recommended:
- switch to a healthy lifestyle with a full 8-hour sleep;
- treat chronic diseases that can trigger a relapse of seborrheic eczema;
- to reduce sebum secretion, follow a diet: limit, or better yet, exclude from the diet fatty, fried, spicy, sweet, canned foods, as well as foods that cause allergies;
- avoid regions with hot, humid climates;
- do not visit the bathhouse or sauna;
- avoid stressful situations;
- wear underwear and clothes made from natural fabrics (linen, cotton).
As for skin care itself, it is recommended:
- use shampoos that contain antifungal components and zinc;
- choose skin care products according to its oil content;
- use only natural cosmetics;
- Do not overuse hair coloring.
source
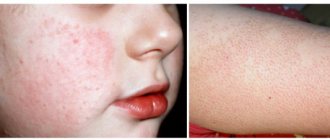
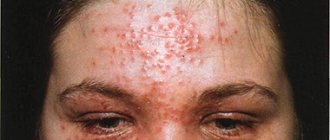
Seborrheic eczema
Seborrheic eczema most often occurs on the scalp. It develops slowly, gradually expanding the affected area. Sometimes the rashes are localized on the eyebrows, parts of the forehead, folds near the nose, but the largest focus is located under the hair.
Causes of the disease
Alas, the pathogenesis and exact causes of the disease are currently poorly understood. An important role in influencing the development of this type of eczema is assigned to dysfunction of the sebaceous glands, which occurs against the background of:
- ingress of pathogenic microorganisms;
- allergies;
- genetic factors;
- stress;
- metabolic disorders.
Seborrheic eczema may appear as patches of thickened, dry skin with a distinct pattern.
Symptoms and development process
The symptoms of the development of seborrheic eczema are partly similar to the manifestations of the microbial form of the disease, but there are still some features:
- Initially, yellow-pink nodules appear at the affected sites. Over time, they turn into crusts and white plaques.
- The spots gradually increase in size, acquiring a variety of irregular shapes.
- At the same time, thickening of the skin layers occurs.
- Fatty plaques begin to itch, grow and, if left untreated, spread to open areas of the body.
- All lesions are covered with scales, when removed, a moist but not weeping red spot appears.
It must be remembered that at the first feeling of tightness of the scalp under the hair, you need to urgently consult a dermatologist. Otherwise, the disease will begin to progress and will be quite difficult to stop. In such cases, the rash can spread to the periocular area, causing purulent conjunctivitis, or the disease spreads to the back of the head and ears, forming an eczematous helmet.
Eczematous helmet - fused plaques covering the entire scalp.
Alas, seborrhea can develop without painful symptoms or discomfort. A person learns about it only when the affected areas begin to be visible through the hair. In the later stages, the rashes turn into dirty yellow greasy spots. And over time, alopecia (baldness) develops due to the complete destruction of hair follicles.
Very often, pathology occurs against the background of ordinary untreated seborrhea. A peculiarity of this form of the disease is its obligatory manifestation in HIV-infected and AIDS patients. Unlike other people, in such patients eczematous manifestations spread throughout the body.
Diagnosis of the disease
Initially, the doctor conducts a visual examination and prescribes a number of laboratory tests and instrumental examinations, which are similar to those required to identify microbial eczema:
- dermatoscopy;
- skin scraping;
- bacterial sowing;
- luminescent diagnostics.
Such measures are necessary to detect fungal spores and/or pathogenic bacteria. After all, seborrheic eczema in almost 50% of cases is accompanied by a secondary infection and/or an allergic reaction.
Luminescent diagnostics is a simple, inexpensive and painless method for identifying fungal diseases and dermatoses
If background pathologies and foci of chronic infections are detected, patients with seborrheic eczema are prescribed examinations by other specialists. In particular, patients need:
- Ultrasound of the peritoneal and pelvic organs;
- gastroscopy;
- hormonal and immunological blood tests;
- pharyngoscopy and other types of diagnostics.
Mandatory differentiation of the disease with true, occupational and microbial eczema, psoriasis, trichophytosis and microsporia is necessary. The location of the lesions on the head and the absence of the negative influence of factors associated with the patient’s work activity makes it possible to exclude the presence of an occupational nature of the disease.
With the seborrheic form of the disease, there are no vesicular rashes and associated weeping. Less dense plaques and less massive scales make it possible to distinguish it from psoriasis. Microsporia and trichophytosis of the scalp are characterized by changes in the structure of the hair, non-greasy peeling and detection of fungal mycelium during examination, which is unusual for seborrheic eczema.
Treatment
Drug therapy does not require hospitalization and is carried out at home. Therapeutic measures for this form of the disease are aimed at eliminating the causative factors and severe symptoms.
The principle of combating eczema of the scalp is similar in both seborrheic and microbial forms. However, all drugs are selected individually in each individual case. And the emphasis in curing the disease is on organizational methods.
For mild damage, it is enough:
- local antimicrobial drugs: Radevit;
- Eplan;
- Kanizon plus;
- Desitin.
- salicylic acid solution;
- clioquinol;
- Apulein;
- Methyluracil;
In case of severe damage, when the lesions have strong layers of scales and there is an active inflammatory process, in addition to the above treatment, the following is used:
- exfoliating local antifungal and steroid-containing drugs: Pimafucort;
- Triderm;
- Triacutan.
- Tetracycline;
If there is low effectiveness of local use of antifungal agents, then (in the absence of contraindications for the patient) the doctor prescribes systemic antifungal drugs:
- Ketoconazole;
- Terbinafine;
- Fluconazole;
- Itraconazole
In advanced cases of the disease, the doctor may recommend sebum-suppressing medications, for example, Isotretinoin, which reduces the activity of the sebaceous glands and reduces their size by almost half. This remedy simultaneously has an anti-inflammatory effect.
In combination with the above drugs, treatment is carried out using:
- vitamin complexes;
- sedatives: Novopassit;
- Sedavit;
- Glitsed;
- Persen.
- Hilak-forte;
It should be noted that treatment of eczema of the scalp is more difficult due to difficult access to the skin. If the lesions are voluminous and the hairline is thick, it is recommended to cut the hair.
The use of special antiseborrheic shampoos, which have an easily penetrating formula and suppress the activity of harmful microorganisms, is mandatory. The most recommended are:
- Nizoral;
- Sulsena;
- Tar shampoo;
- Sebozol;
- Vishy Derkos;
- Keto plus;
- Friderm;
- Dandruffed;
- Dermazol.
The shampoo is selected depending on the patient’s condition and his individual characteristics: hair type, skin, allergies.
Antiseborrheic shampoos - photo gallery
Nizoral stops the formation of phospholipids that promote the growth of fungal cells, reduces fat secretion, soothes the skin, relieves inflammation
Sebozol has antibacterial properties, eliminates itching, relieves inflammation, and resists fungus
Sulsena prevents the proliferation of fungi, quickly exfoliates the dead layer, normalizes the functions of the sebaceous glands
Vichy Dercos has antibacterial properties, eliminates itching, relieves inflammation, and resists fungus
Dermazol - its active ingredient ketonazole inhibits the activity of fungi, exfoliates dandruff, removes excess fat
Tar shampoo inhibits the activity of fungi, relieves itching, exfoliates dead particles, eliminates excess fat
Dandrhotal inhibits the spread of fungus, eliminates flaking and itching
Friederm tar has an antifungal, anti-inflammatory effect, reduces the separation of fat, has astringent properties, eliminates flaking, itching, redness
Keto plus - antiseborrheic shampoo against fungus
Treatment of eczema - video
Causes
Studies have shown that up to 80% of people suffer from seborrhea caused by the fungus Pityrosporum ovale, the remaining 20% from Candid and staphylococcus. There are predisposing factors. Seborrheic eczema may have the following causes:
- congenital nature of eczema;
- genetic predisposition;
- imbalance in fat metabolism;
- dysfunction in the gastrointestinal tract;
- gastritis, stomach ulcer;
- hepatitis, liver cirrhosis;
- hormonal surges;
- stress;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- some chronic diseases;
- constant overwork.
Physiotherapy as a method of treating the disease
In addition to drug treatment, it is possible to use physiotherapy in the fight against any eczema of the scalp, of course, taking into account the absence of contraindications for the patient. The following procedures are usually used:
- electrosleep is a manipulation aimed at reducing the excitability of the nervous system and improving metabolic processes in the tissues of the epidermis;
- magnetotherapy - a procedure involving a magnetic field;
- Ozone therapy is aimed at enriching damaged skin tissue with oxygen;
- thalassotherapy - a range of procedures (masks, compresses, wraps) using seafood: algae, sea salt, plankton extracts, mud;
- balneotherapy - the use of mineral waters for baths and other procedures;
- cryodestruction - exposure to very low temperatures to treat inflamed areas and remove tissue that cannot be restored;
- laser therapy is a procedure that allows using a light beam to restore the functionality of various tissues;
- PUVA therapy is a special manipulation based on the mutual influence of long-wave UV irradiation and photoactive medications;
- darsonvalization - a procedure based on the influence of current using a comb electrode, preventing early baldness;
- microionization is a technique that involves the introduction of active substances under the skin of the scalp in combination with iontophoresis;
- ultrasound therapy - restoration of hair structure and damaged skin using ultrasound;
- UV rays help the body produce the necessary vitamins for the regeneration of epidermal cells.
The use of cryodestruction in the treatment of eczema makes it possible to provoke the replacement of irreparable skin with healthy
Traditional medicine in the fight against eczema
In addition to drug treatment and the use of physiotherapy methods, traditional methods are often used with the permission of a doctor. There are general recipes applicable in the fight against microbial and seborrheic eczema, but there are also a number of recipes for targeted action.
To speed up the healing of lesions, relieve symptoms of inflammation and suppress itching, use the following:
- Herbal infusion. Take 5 grams of calendula flowers, chamomile and string grass. The mixture is poured with a glass of boiling water and left to infuse until it cools completely. Strain. The resulting solution is used for lotions and rinsing.
- New potato juice. Freshly squeezed juice is used to wash lesions so that healing proceeds faster.
- Burdock root tincture. Juice is separated from plant materials using a juicer. Dilute it with vodka in a 1:1 ratio. This product is rubbed into the scalp after washing.
- Natural honey. Applying this product to the affected areas can reduce flaking and itching. Before use, honey is diluted in half with water, and then gently rubbed into the damaged areas for 2-3 minutes. At the end of the procedure, wash your head with regular shampoo.
- Oak decoction. Take 40 grams of crushed oak bark. Pour a glass of boiling water and bring to a boil over low heat. The solution is left to stand for 12 hours, filtered, and 1 tablespoon of natural honey is added. Mix everything thoroughly until completely homogeneous. The finished product is applied to eczematous areas in the form of lotions or applications. After an hour, rinse your head with water.
There are a number of recipes for directly treating microbial eczema:
- Viburnum infusion. Take 4 tablespoons of dried viburnum berries, pour two glasses of boiling water over them, leave for 5 hours in a dark, warm place. Strain. Take 200 ml orally twice a day before meals.
- Black radish gruel. The root vegetable is grated on a fine grater (you can use a blender). The resulting mass is applied to the affected areas until it dries completely. Wash off with water.
- Fresh cucumber compresses. The vegetable is cut into thin circles. They are bandaged to sore spots. Keep the compress on all night.
- Flatbread made from barley flour. Pour a little 9% vinegar into the flour, stirring until the consistency of thick sour cream is obtained. The prepared mixture is applied to areas affected by microbial eczema.
For the treatment of seborrheic eczema, people have other recommendations:
- Strawberry compress (wild or garden). The berries are ground to a uniform mass and applied overnight under a bandage to the affected areas. Wash off with water.
- Sage lotions. Take 1 tablespoon of the herb of this plant, add 300 ml of water and boil over low heat for 5 minutes. Strain, add 1 tablespoon of honey to the solution, stir thoroughly. The product is used as a lotion 2-3 times throughout the day.
- Ointment from young branches of black currant. The raw materials are ground until a homogeneous mass is obtained. Mix with 200 ml of cream. The mixture is simmered in a water bath for 5 minutes. Cool and apply to eczematous areas, gently rubbing.
- Tansy decoction. Take 100 grams of plant flowers, add three liters of water and keep in a water bath for 20 minutes. Infuse the resulting decoction for 12 hours. Strain. You can wash your hair with this product.
- Garlic and onion mask. Take the pureed ingredients in equal quantities, mix thoroughly, apply to the damaged areas and leave for half an hour under a film or swimming cap. After the procedure, the head is washed with antiseborrheic shampoo.
Nutritional Features
For treatment to be effective, you must adhere to some diet. The following food products and dishes must be excluded from the menu:
- seafood;
- citrus;
- chocolate;
- fried, smoked and spicy foods;
- alcohol and strong coffee;
- nuts;
- mayonnaise;
- spices and seasonings.
Fresh vegetables must be present in the patient’s diet
Dietary preferences should be:
- fresh and boiled vegetables;
- hypoallergenic fruits;
- lean varieties of fish and meat;
- cereal porridge;
- dairy products.