What is a pinguecula of the eye?
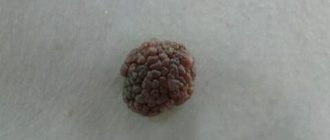
In ophthalmology, a pinguecula is a degenerative benign non-tumor neoplasm, a thickening that occurs on the conjunctiva of the eye.
The conjunctiva of the eye is the mucous membrane that covers the eyeball and the adjacent inner surface of the eyelid.
A thickened area of the mucous membrane is tissue that is pathologically altered as a result of excessive deposition of protein, calcium and cholesterol. This formation is round or triangular in shape, opaque or translucent, almost does not transmit light, has an elastic structure, yellowish or pinkish color, and rises somewhat above the surface of the eye. It very slowly increases in size, gradually covering an increasing area of the eyeball.
A pinguecula is a yellow or white formation that appears on the conjunctiva of the eye.
More often than in the outer corner, the pinguecula appears in the inner corner of the eye (from the side of the nose). This happens probably because this side of the eyeball is more exposed to sunlight. The disease can develop in one eye or both at the same time.
This is interesting! In two eyes at once, this tumor begins to grow in approximately every second case.
Pathology is diagnosed in both men and women. Since this disease is typical for older people, ophthalmologists believe that it is caused by the phenomenon of natural aging of the conjunctiva. However, pinguecula sometimes occurs in 25-45 year old patients. And only in exceptional cases does it develop in front of children who spend a lot of time in the sun.
Pinguecula occurs in the area of contact between the conjunctiva and cornea of the eye.
Pinguecula is a widespread pathology. Since it does not bother the patient in any way, does not impair the visual function of the eye and does not have a tendency to malignant degeneration, people, as a rule, do not seek medical help. However, being a cosmetic defect, pinguecula greatly spoils a person’s appearance. If dust gets into the eye, it can cause irritation, discomfort and inflammation of the conjunctiva (conjunctivitis). In addition, the presence of a growth makes it impossible to wear contact lenses.
Due to the very slow growth of the pinguecula, people, as a rule, go for treatment when its size is quite large.
Structure of the eye - video
Possible reasons
A growth has appeared on the eyelid, a photo of which can be compared with similar formations on the Internet at the initial stage of manifestation, and this should be the first signal to contact a specialist. Any growths can appear on both the upper and lower eyelids. In most cases, the main causes of tumors in the lower and upper eyelids can be:
Chronic infectious diseases
Chronic infectious diseases that provoke inflammatory processes on the skin and glandular formations of the eyes manifest themselves as compacted bumps on the eyelid, red in color.
The inflamed areas often itch and hurt when pressed due to the accumulation of purulent formations inside. These include barley, in which the infection affects the hair follicle in the eyes or the sebaceous glands, and a bacterial infection.
Decreased immunity or dietary changes
A sharp drop in immunity or a violation of the diet, in which any bacteria, infections or metabolic disorders progress sharply and cause a growth on the skin of the eyelids. Most often they manifest themselves as lipomas or benign fatty growths, which gradually grow, thicken and begin to create discomfort in everyday life.
Older people are more likely to experience xanthelasma, or a light yellow fatty plaque on the surface of the eyelid, which is a metabolic disorder and is not dangerous to the body.
papillomavirus
The papilloma virus, which causes tissue growth on the skin, is contained in the patient’s blood. It may not show itself right away. A sharp deterioration in health or hormonal changes can become an impetus for the active growth of brown papillomas on the upper or lower eyelid.
Similar diseases include warts, which begin to actively grow and multiply with a sharp drop in immunity, spread throughout the body by blood. Warts can appear as small bumps, which over time grow and become denser.
Heredity
A growth on the eyelid may appear due to a hereditary predisposition, which is embedded in the human gene and is most often a safe cause of the disease. By inheritance, which can be traced from the photo, moles on the eyelids are passed on, which can be benign and do not create discomfort for a long time.
Damage to moles on the eyelids can cause inflammation or an increase in these growths. If there is any suspicion that the growth is malignant, the mole is removed along with the base.
Growth on the eyelid. Photo
A nevus is also inherited and is a benign black or brown formation that can quickly increase in size. If significant discomfort occurs, the nevus must be removed.
Cancer
Malignant and benign formations are most common in older people. These include cysts (reddish lumps filled with fluid that can suddenly burst), causing pain, itching and discomfort.
Malignant manifestations of cancer appear in the form of a small spot, which gradually thickens and grows, can change color and bleed. Melanoma, sarcoma and adenocarcinoma tend to grow rapidly with the appearance of metastases and ulcers, and therefore require immediate treatment.
Plexiform neuroma is a subtype of benign formation that forms a nodular mass in certain areas of the upper eyelid. The thickening interferes with the eye's ability to function normally and requires surgery.
Burn
Burns to the eyes or eyelids heal slowly and often heal with the growth of scar tissue. Painful red growths on the eyelids can thicken over time and cause discomfort, so they are removed.
Chalazion
Complete blockage of the meibomian gland in one of the eyes is manifested by the formation of a purulent node, which gradually enlarges, turns red and begins to hurt.
The amount of pus is growing every day, and the neoplasm begins to put pressure on neighboring tissues, which requires immediate surgical intervention.
Self-medication and lack of hygiene
Insufficient hygiene and self-treatment of lesions and papillomas often become causes of inflammation on the eyelids, where infection can be spread by hand. In this case, the eyelid may be completely affected, provoking redness and purulent processes in the skin, eyes and tear ducts, so treatment for such diseases begins immediately.
Causes of growths on the eyelid:
| infectious | papilloma |
| barley | |
| wart | |
| related to immunity | lipomas |
| warts | |
| cancer | melanoma |
| sarcoma | |
| adenocarcinoma | |
| hereditary | moles |
| papilloma | |
| nevus | |
| damage | scarring |
| burns | |
| chalazion |
Causes and development factors
The causes of pinguecula are not yet fully understood. However, some features have been noticed in people suffering from this cosmetic defect, for example, these patients, due to their occupation or profession, are forced to stay in the sun for a long time (gardeners, foresters, agricultural workers, welders, geologists, sailors, fishermen, as well as football players, tennis players and etc.) In addition, risk factors include:
- Wearing contact lenses, especially poorly or incorrectly fitted ones.
- Metabolic disorder leading to increased formation of fat and protein in all tissues of the body.
- Chronic irritation of the conjunctiva by dust, wind, smoke, corrosive toxic fumes when working in hazardous industries (in a quarry, mine, woodworking or chemical industry).
- Age over 50 years.
- Prolonged living in unusually dry or hot climates.
Thus, it can be assumed that the aging of the conjunctiva, coupled with the irritating effects of ultraviolet radiation, dust and very dry wind, can easily provoke the appearance of a pinguecula on the eye.
Forms of neoplasms
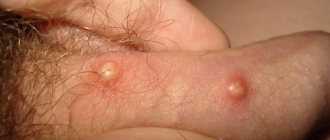
Barley
An eye stye is a common problem that appears as a dense lump on the eye. The disease brings discomfort to a person caused by pain, itching and burning; in addition, it is not recommended to get it wet. The main reason for the formation of stye is a foreign body or infection of the eyeball through dirty hands. Even before the formation of a lump, the pathology manifests itself as severe itching and redness in the lower eyelid of the eyes, because of this the eye is constantly injured and a lump is formed.
Symptoms in children and adults
The onset of the disease is usually asymptomatic. An almost imperceptible whitish-yellowish thickening appears on the conjunctiva. It does not interfere with vision and does not feel painful.
The early stage of the disease does not manifest itself in any way
Gradually, over many years, the neoplasm grows in width and height, and increases in volume. Sooner or later, patients begin to feel the presence of a foreign body, “sand”. A person rubs his eye, tries to wash it out to remove the “speck,” but this only injures the pathological growth, introduces an infection and provokes an inflammatory process.
Local inflammation of the pinguecula is called pingueculitis. It is characterized by the following symptoms:
- severe redness (hyperemia) of the eye;
- swelling of the pinguecula, germination of its vessels;
- swelling of the tumor;
- dry eye;
- burning and itching;
- “sand” in the eye when blinking, as with conjunctivitis.
If pinguecula is complicated by pingueculitis, the patient should immediately consult a doctor to prescribe treatment.
Prevention
General preventive measures to prevent the formation of growths:
- healthy lifestyle (nutrition, sports, recreation);
- maintaining immunity;
- eye hygiene;
- eye protection from adverse factors (glasses, protective mask);
- preventive examination by a doctor.
It is recommended to show all neoplasms in front of the eyes to a specialist. They are dangerous because they can turn out to be cancer and lead to rapid death.
Have you ever had any growths on your eyelids? Tell us about it in the comments. Share the article on social networks. Take care of your health. All the best.
In most cases, growths on the eyelids are benign, the main cause of which is often HPV (human papillomavirus).
But in some cases, neoplasms pose a danger to human life.
Therefore, if you identify a wart or bump, you should immediately seek advice from an ophthalmologist.
Diagnosis and differential diagnosis
An ophthalmologist easily diagnoses this disease by simply examining the conjunctiva at the patient’s first visit. The neoplasm is clearly visible to the naked eye and has a specific location, color and appearance. Additional laboratory tests are not required to make a diagnosis. To obtain the most complete picture of the pathology and a detailed study of the structure of the neoplasm, a specialist can examine the affected eye using a slit lamp.
The pinguecula can sometimes resemble a pterygium in its appearance. These eye diseases have very similar symptoms, but an experienced doctor can easily distinguish one from the other. The pinguecula, like the pterygium, grows towards the pupil, but never even reaches the iris.
Important! Pinguecula, unlike pterygium, does not grow into the cornea and is localized within the subepithelial (inner) layer of the conjunctiva.
Treatment
An uncomplicated pinguecula is completely harmless and harmless to the patient, is not prone to malignancy (malignancy) and does not require treatment. A person is forced to see a doctor only by psychological discomfort caused by a clearly expressed cosmetic defect.
Once formed, a pinguecula will never “resolve” on its own. If it is not removed surgically, it will exist on the patient’s eye for the rest of his life, while steadily increasing in volume.
Conservative treatment is recommended when an inflammatory process occurs - with the help of special eye drops you can relieve inflammation and dryness.
Unfortunately, at the moment there are no conservative methods to reduce or remove the tumor. The only way to completely get rid of pinguecula is through surgery.
Drug therapy
The pain caused by pinguecula can be significantly reduced with the help of medications.
- Drops Artificial tear, Lakrisifi, Hilokomod, Cromohexal or Oksial alleviate dry eye syndrome and can even eliminate the feeling of “sand” in the eye. All these drugs have a softening and moisturizing effect on the conjunctiva, replacing the tear film without causing irritation or allergic reactions.
- If the pinguecula is edematous and swollen, then the doctor usually prescribes Maxitrol or Diclofenac eye drops to relieve inflammatory edema.
- When a bacterial infection occurs, ophthalmic anti-inflammatory drugs are used, such as Dekelios drops, Maxidex, Oftan Dexamethasone, Sofradex, Tobradex or Hydrocortisone-POS ointment. To eliminate the symptoms of pingueculitis, local treatment with glucocorticoid drugs such as Fluorometholone is also carried out.
If wearing contact lenses causes pain and discomfort, then it is better to refuse them so as not to continue to injure and irritate the pinguecula.
Eye drops, ointments and other drugs for the treatment of pinguecula - gallery
Artificial tears are designed to relieve dry eyes
Cromohexal has a moisturizing effect
Lacrisify replaces the tear film
Maxitrol relieves inflammation and swelling
Oxial moisturizes the conjunctiva
Tobradex is an anti-inflammatory drug
Hilokomod has a softening effect
Removal of formation with laser and other surgical methods
Removal of a tumor is most often performed at the insistence of a patient suffering from a cosmetic defect. However, in some cases, the ophthalmologist refers the patient to surgery for medical reasons, such as frequent pingueculitis that is not amenable to drug therapy, or serious discomfort caused by a large growth.
It is possible to get rid of pinguecula only through surgery. Today there are two methods of intervention:
- knife;
- laser.
Currently, the laser method of pinguecula removal has gained wide popularity. For this purpose, an excimer laser technique is used, similar to that used for laser correction of myopia. The operation is performed on an outpatient basis and consists of the following:
- the eye is fixed in an open and motionless state with holders;
- anesthetic drops (for example, Innocaine) are instilled into the eye;
- the outer (epithelial) layer of the conjunctiva is cut off with a special device above the pinguecula;
- A laser beam is directed at the open pinguecula, the formation is evaporated under computer control for several minutes or even seconds (depending on the size of the defect);
- the evaporated area of the eye is treated with a disinfectant gel;
- return the originally cut piece of conjunctiva to its place, fixing it with special eye glue;
- A blindfold is applied to the eyes, and the patient must sit or lie down with his eyes closed for 2 hours, after which he can go home.
Laser surgery is safe, bloodless and almost painless for the patient, lasts 10–15 minutes and leaves no scars or marks on the eye. After the procedure, the patient should come to the ophthalmologist only for routine check-ups and to prevent complications. For several months after the intervention, it is recommended to put moisturizing drops into the eyes, and also to follow a gentle regime for the eyes: if possible, do not use the computer, read less, sleep more, take vitamin complexes.
To avoid infection, it is advisable to avoid getting water in your eyes for a month after the procedure, do not swim in ponds or pools, and do not use decorative cosmetics.
During the recovery period, redness of the eyes and rapid fatigue with visual stress are possible - these phenomena disappear within several months.
Folk remedies
Unfortunately, there are no folk remedies that help get rid of pinguecula or at least relieve the symptoms of pingueculitis. You can often find advice on the Internet to drop aloe, onion or beet juice into the eye. But official medicine has not yet known a single case of “miraculous healing” from pinguecula using such methods, but infection in this way is quite possible.
It is strictly unacceptable to instill any foreign substances not recommended by a doctor into the eye or into the conjunctival sac!
However, to strengthen the blood vessels of the eyes and enrich the body with vitamins, you can try the following folk methods:
- Raw beet juice is actually very beneficial for the eyes if consumed correctly. Drink half a glass of freshly squeezed juice every day or eat half of this root vegetable raw, grated.
- Seaweed. Dry seaweed can be bought at a pharmacy or supermarket. Brew them like tea - 2-3 tbsp. l. pour a glass of boiling water over the seaweed, cover and let it brew until it cools completely. Strain the cooled infusion, then pour it into ice cube trays and freeze in the freezer. Every morning, massage your eyelids and area around your eyes with this ice cube.
- Blueberries are a storehouse of vitamins for the eyes. The benefits of blueberries for the eyes are undeniable and well known, so if possible, eat them fresh as much as possible. Or use a vitamin complex from a pharmacy, known as Blueberry Forte. Compotes and jelly made from fresh or dried blueberries are very beneficial for eye health.
- Raw carrots are a source of vitamin A, which is essential for visual function. It should be noted that vitamin A is absorbed only together with some kind of fat, so eat carrots with sour cream, mayonnaise or cream.
A salad made from grated raw carrots with garlic and sour cream is tasty, healthy and easy to prepare.
Folk remedies for maintaining eye health - gallery
Ice cube massage with seaweed is extremely beneficial for the eyes
Blueberries are the best remedy for good vision
Fresh carrots are a source of vitamin A
Beetroot juice will give elasticity to the blood vessels of the eyes
Methods for eliminating pathology
It is possible to remove a watery formation on the whites of the eye only after a comprehensive diagnosis and clarification of the cause of its formation. In mild cases, it is possible to get rid of the bubble on the eyeball through medications. When the disorder is caused by an allergic reaction, the tumor goes away on its own after taking antihistamines. To eliminate the bubble, the medications listed in the table are often used:
| Drug group | Name |
| Antiviral eye products | "Ophthalmoferon" |
| "Virgan" | |
| "Virolex" | |
| "Zovirax" | |
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | "Indocollier" |
| "Akuvil" | |
| "Medrolgin" | |
| "Oftanal" | |
| Immunomodulators | "Kagocel" |
| "Altabor" | |
| "Amizon" |
In particularly advanced cases, surgical intervention is performed.
In advanced cases, when the bubble has grown to a large size and significantly affects visual function, surgical intervention is performed. The tumor is eliminated radically using a scalpel. This treatment method is often prescribed in case of cyst formation. During manipulation, the wall of the cystic neoplasm is excised so that the bubble does not form again in the future. The patient does not experience discomfort or pain during surgery, since the procedure is performed under local or general anesthesia. The rehabilitation period is short and easy. A few hours after excision of the vesicle in the area of the eyeball, the patient is allowed to go home if there are no complications.
The most effective and less painful way to remove a bubble on the mucous membrane of the eye is cauterization with a laser beam.
Reviews about the treatment
I saw this happen before my eyes. I came to the eye clinic, they carefully cut everything off and sewed it up. They did it with anesthesia, it didn’t hurt at all. 8 years have already passed. The eyes are clear - there is nothing. True, after the operation you should not strain your eyes for a week. And it’s better to wear sunglasses, otherwise your eyes will be red and people will be embarrassed.
Zosia
https://www.woman.ru/beauty/face/thread/3914838/1/#m20022386
I also had surgery, the doctor explained that it was excess cholesterol in the body, maybe from the wind, sun, etc. The procedure with pain relief, everything is OK.
amateur
https://www.woman.ru/beauty/face/thread/3914838/1/#m20023255
3 months after this operation, I went to Helmholtz, and there they told me that these were scars, and they remain in any case during such operations, since the sclera cannot heal smoothly, without consequences. And I went there to find out if something could be done about it, maybe some kind of surgery. So no, because the more operations, the more scars there will be! In addition, I usually always wore lenses, and now when I wear lenses, these places where there were surgical interventions constantly turn red. They blush even without lenses, but now they blush even more. As a result, I also lost the opportunity to wear contact lenses! It would be better to live with these pingueculas! They didn't interfere with anything. But it turns out that it was also undesirable for me to have this operation, because I have keratoconus, and now it can progress. So weigh everything very carefully before doing it. If you don’t have keratoconus, then maybe it’s worth just going to a good specialist who will do it most carefully.
Marina
https://www.woman.ru/beauty/face/thread/3914838/1/#m20023255
I want to unsubscribe after the passage of time... I wrote above that after the operation everything looked terrible for me, but time passed, 4-5 months, and everything returned to normal, the redness went away, almost nothing is noticeable, I can easily wear lenses, so everything is fine, the operation can be done. It just took me too long to recover.
Guest
https://www.woman.ru/beauty/face/thread/3914838/1/#m41522519
Maybe my description of this removal procedure will help someone: there was a pinguecula in both eyes, it was surgically removed at Fedorov’s clinic. Now 10 days have passed. The left eye looks perfect, the right eye is worse, but there was more formation there and the doctor said that it would take longer to heal. Immediately an antibiotic was given, and now they prescribed drops for redness that would resolve the bruise. The operation itself is completely painless, only after 4 days the feeling of a foreign body in the eyes, which has now passed.
Nata
https://www.woman.ru/beauty/face/thread/3914838/2/#m48224790
Hello! I had the pinguecula surgically removed on March 11; at first the eye looked so bad that I regretted doing it! The stitches were removed after two weeks, and now even after two weeks, the eye looks good. Tobradex was dripped for two weeks, and now Oftan Dexamethasone, there is no more redness.
Olga
https://www.woman.ru/beauty/face/thread/3914838/2/#m55893479
Treatment prognosis and possible complications
Pinguecula is a benign formation, so the prognosis of the disease for vital functions and preservation of vision is favorable. Occasionally, a pinguecula can be complicated by a pterygium (pterygoid hymen), which can seriously impair visual function.
Surgical removal of the growth, as a rule, does not cause complications, but the pinguecula has a tendency to recur. Unfortunately, after its removal with a laser, in about 10% of cases the disease may return (relapse), that is, the pinguecula forms again.
In case of relapse, a benign formation grows even more rapidly and quickly acquires large sizes.
To prevent recurrence of the disease, you need to take care of your eyes and follow preventive and precautionary measures.