Our skin is a barrier between the body and the environment, which is why it is often attacked by bacteria and many environmental factors and can suffer from various diseases, the unpleasant symptoms of which can cause discomfort. It is important to notice dermatological diseases of the skin of the hands in time and consult a specialist. The main symptoms of hand diseases include:
- redness, spots on the skin;
- rash, papules, watery pimples;
- skin pigmentation disorders (dark or light spots);
- peeling and itching;
- spots on the nails, absence or growth of the cuticle, change in nail color;
- cracks and sores.
If these symptoms of hand skin diseases appear, you should stop using cosmetics and consult a doctor.
Hand skin disease dermatitis
One of the most common hand skin diseases is allergic dermatitis . All its manifestations are a consequence of the body’s reaction to an allergen affecting the skin (therefore the disease is called contact dermatitis). Upon contact with an allergen, the body begins to secrete antibodies, which lead to the appearance of symptoms of allergic dermatitis: red spots on the skin, papules, rashes in the form of watery blisters, itching, peeling and cracks.
The main allergens that can trigger dermatitis are latex products, cosmetics, house cleaning products, varnishes and paints, jewelry made from various materials, and clothing.
When the first symptoms appear, you should take an antihistamine. It is better not to use cosmetics, soap and other irritating products until all manifestations of dermatitis are completely cured. For prevention, it is necessary to protect the skin of your hands from contact with allergens: use hypoallergenic cosmetics, use gloves when cleaning the house, and periodically take courses of antihistamines.
IMPORTANT: you should not treat allergic dermatitis with folk remedies. You can provoke a stronger reaction, and then it will be more difficult to get rid of the consequences.
Classification of pyoderma
The types of diseases depend on the cause that causes them, therefore they are divided into staphylococcal, streptococcal and mixed pathologies. Each type of disease can be superficial and deep, acute and chronic. In the superficial form, the infection affects the epidermis and dermis, in the deep form – the dermis and hypodermis.
Staphylococcal species
Among pyoderma with an acute course of the disease there are:
- Superficial form: ostiofolliculitis, folliculitis, bullous impetigo (in children), pemphigoid in infants.
- A deep variety, found with boils, folliculitis, carbuncles, hidradenitis.
The chronic stage of staphylococcal skin diseases is:
- Superficial, as in vulgar sycosis.
- Deep – with furunculosis, folliculitis decalvans.
Pyoderma is a fairly common disease.
Streptococcal infections
The acute form is characteristic:
- For superficial types of impetigo and diaper rash.
- For deep erysipelas and ecthyma.
The chronic stage occurs with diffuse streptoderma.
Mixed type
Streptostaphylococcal pyoderma in acute form is:
- Superficial, like impetigo vulgaris.
- Deep – vulgar ecthyma.
Chronic forms of mixed pyoderma are distinguished:
- Ulcerative pustular disease.
- Ulcerative-vegetative pyoderma.
- Abscessing pyoderma.
Pustular skin diseases occur on completely clean skin or on the basis of previous skin problems - scabies, eczema, lice, dermatitis.
Eczema
Hand skin disease eczema is redness on the skin, the appearance of which is accompanied by pain and itching. Often the affected areas peel and crack. The reason for such external manifestations is inflammation of the upper layers of the skin.
There are several types of eczema:
- atopic: the main cause is contact of the body with an allergen;
- professional: develops due to exposure to chemicals on the skin;
- microbial: the skin becomes inflamed due to the activity of bacteria or fungi;
- idiopathic: occurs due to nervous experiences and stress.
The main symptoms of eczema are redness of the skin of the hands, which itch, hurt, crack and peel. Swelling, discharge of ichor and the appearance of a rash may also occur.
To diagnose and treat eczema, it is necessary to undergo scrapings, general tests and consult a dermatologist and neurologist to identify the exact causes and choose the optimal therapy. It is not recommended to use cosmetics and aggressive detergents even after the symptoms of the disease disappear.
Clinical features
The rash with pustular infections is polymorphic. The type of primary rash will depend on the degree of tissue damage.
Staphylococcal pathogens multiply on hair follicles and sweat glands and provoke inflammation.
Rashes with pyoderma polyphora
Different types of skin lesions can look the same, for example, follicular pustules occur with ostiofolliculitis, folliculitis and sycosis, and an inflammatory nodule can be a sign of folliculitis or just a boil. Streptococcal infections prefer smooth skin.
The main external symptom of superficial streptoderma is a bubble. With a thin stratum corneum, it has a flabby appearance (phlytena); with hyperkeratosis (on the palms, soles), the surface blisters are harder, filled with serous fluid.
If the infection is deep, the rash will be in the form of ecthyma - an epidermal pustule with local necrosis, edematous erythema with a growing focus of inflammation (for example, erysipelas).
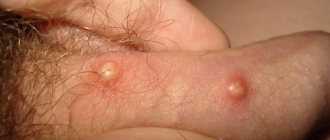
Staphylococcal skin infections
- Ostiofolliculitis is inflammation of the follicle. It looks like a small (2-3 cm) abscess in the shape of a hemisphere or cone with cream-colored pus, surrounded by a halo of hyperemia. An infection develops on an open part of the body (on the face, neck, head, bends of the arms and legs). These areas are often exposed to mechanical and chemical irritants (friction, shaving, household and industrial chemicals). After 2-3 days, the redness disappears, the brown crust dries out. After its rejection, the skin color changes slightly. With friction or maceration, the disease can progress and become more severe.
- Folliculitis is a purulent inflammation that affects the hair follicle. The superficial process begins, like the previous pyoderma, with a small abscess deepening into the mouth. The surrounding skin turns red and thickens, the abscess increases to 5-7 mm in diameter. If the infection is primary, the papule is in the shape of a cone or hemisphere up to 5 mm in diameter. After 2-3 days, a dense pustule appears, disappearing after a week. After peeling off the dried crust, stagnant redness is observed. In the deep form, the entire hair follicle is affected. The painful process is accompanied by redness, swelling, infiltration
- Impetigo develops in a child already in the maternity hospital (if hygienic standards of care are violated). Staphylococci that have penetrated into the dermis produce exfoliatin, which destroys the epidermis. Yellow purulent blisters form. The pathology is called infantile pemphigus. In children, the disease develops in the first week or month of life. Upon examination, you can see blisters the size of a hazelnut with a purulent filler. They appear on clean skin surrounded by an inflamed halo. When the bubble opens, wet erosion remains with the remains of the top layer without a crust. The rash can be seen on the chest, back, and in the folds of the limbs. The malignant form affects the entire body of the child. The illness begins with fever, increased erythema on the navel, around the mouth, in the folds. The skin peels off and hangs like petals on the damaged areas. Without timely treatment, impetigo in children can be fatal.
- Vulgar sycosis is a chronic form of the disease. The main signs: periodically manifested ostiofolliculitis and superficial folliculitis with infiltration of the problem area. Adult men are more often affected; rashes can be observed near the mustache and beard, on the pubic area, under the arms, eyebrows, eyelids and head. Prerequisites for pustular diseases of the scalp can be frequent shaving and chronic infections of the scalp. Inflammation begins with individual pustules that constantly recur in one area. Gradually, new follicles are involved, and the lesion grows. The skin in the problem area turns blue and infiltrates. When pustules are opened, accumulations of crusts are observed; after their peeling, a wet spot remains. The hair is removed painlessly, and in its place you can see a glassy muff. The disease lasts a long time, with periodic relapses. The discomfort is minor: itching and burning. If left untreated, the condition will normalize spontaneously after 2-3 months.
- Lupoid sycosis is a rare type of pathology when the skin atrophies, baldness is observed even without ulcers. The causative agent is Staphylococcus aureus, and other microflora are likely to be present. The prerequisites are a decrease in immunity in diabetics and chronic infections. Affects men over 40 years of age. Colonies populate around the mustache and beard, on the temples and crown of the head. With erythema with easily detachable crusts and gray scales, nodes and pustules develop in groups, forming a dark red plaque Ǿ 2-3 cm. Over time, it turns pale in the center, becomes thin and smooth and seems to be drawn inward. All signs of its atrophy are observed, new follicles no longer appear, individual hairs remain. The radius of the inflammation (up to 1 cm) is filled with follicular papules, its size gradually increases, the spot takes on an asymmetrical shape, apple jelly syndrome is not observed during diascopy. The process takes several years. Discomfort occurs only on the head due to the proximity of the aponeurosis.
- A furuncle is a deep inflammation of the follicle and tissues. The node develops around the affected follicle, where pus accumulates. Gradually, the disease covers the tissues and sebaceous gland, turning into a painful node. Swelling is noticeable on the face. After 3-4 days, a fistula is formed; after its opening, an ulcer with a green necrotic core at the base is obtained. After 2-3 days it is rejected with bloody discharge. Pulsation and pain decrease. At the site of the ulcer there will be a retracted scar. The furuncle settles anywhere with hair follicles. On the face they are most traumatic and, if irritated, can provoke thrombophlebitis of the face with swelling, high fever, and confusion. Injured boils of the extremities are dangerous due to complications in the form of acute glomerulonephritis.
- Furunculosis is boils with periodic repetitions in the acute form and isolated manifestations in the chronic form. It can be local or widespread. The acute form is provoked by exogenous factors, the chronic stage is caused by diabetes mellitus, infections, vitamin deficiency, dietary errors, poisoning, and decreased immunity.
- Carbuncle is a severe pyoderma that involves deep layers of skin and many follicles. Diabetes mellitus and immunosuppressive state are of particular importance in the pathogenesis. Localized on the lower back, neck, arms and legs. The formation of a node is accompanied by headache, fever, and blackening of the inflammatory zone. The carbuncle opens after 5-7 days. The ulcer gradually heals and the condition returns to normal. Without medical assistance, the process drags on for 2-3 weeks. A carbuncle on the face can cause complications in the form of venous thrombophlebitis, embolism, sepsis, and brain thrombosis.
- Hidradenitis is an inflammation of the apocrine glands in adulthood as a result of skin trauma or improper use of deodorants. It is localized under the armpits, but it may affect the area of the nipples, genitals, and navel. At first, the node under the skin can only be determined by touch. Gradually the area turns red and blue, and pain appears. The fistulas are opened and a yellow-green exudate is released. The scar at the site of the fistula is retracted. If treatment is prompt, an abscess can be avoided.
Streptococcal and mixed pyoderma
- Streptococcal impetigo most often affects children and women, especially in the summer. The rashes are localized near the ears, nose, mouth, arms and legs. The infection is transmitted through contact, injury, and maceration. Surrounded by a red border, the yellow-green crusts gradually grow. After opening the phlyctene, the infection progresses quickly. With a positive course, erosion epithelializes without lasting traces. Complications are possible in the form of lymphangitis and imphadenitis, eczematization, and in children – glomerulonephritis. Vulgar impetigo is provoked by pathogenic streptococci, staphylococci gradually join, causing suppuration and drying yellow-green crusts. Most often it affects children, and outbreaks of the epidemic are possible.
- Streptococcal diaper rash is a long-term, often recurring inflammation of contact tissues. With poor hygiene, the contact surface in the folds becomes irritated and sweat secretions decompose. Inflammation is often accompanied by yeast. Type 2 diabetes mellitus, obesity, gout, and seborrheic dermatitis contribute to diaper rash. In the edematous folds the skin becomes wet, erosions and cracks appear. Complaints of pain and itching. With regression, pigmentation remains.
- Streptoderma diffuse is a chronic skin disease of the skin of the legs after hypothermia, maceration, and problems with blood vessels. The lower legs are most often affected, especially in the presence of wounds and fistulas. The ulcers dry out, leaving erosions with serous pus under the crusts. When the lesion grows, complications are possible: lymphagitis and lymphadenitis. Without timely treatment, the disease becomes chronic.
- Ecthyma vulgaris is a deep type of streptoderma that develops against the background of trauma, pollution, impaired blood flow in the legs, and intoxication. In addition to the legs, damage to the thighs, buttocks, and lumbar region is possible. It starts with a large bubble with a cloudy filling and a red border. After necrosis, an ulcer with a brown crust forms. It heals on its own within a month, leaving a hyperpigmented scar. Possible complications in the form of phlebitis, lymphangitis, lymphadenitis.
- Erysipelas is a deep skin lesion, with symptoms of intoxication and fever. Sources of infection are any patients with streptococci (tonsillitis, rhinitis, tonsillitis, streptoderma). Frequent injuries, cracks, and scratching provoke relapses, leading to scarring and the formation of elephantiasis of the legs. The onset of inflammation is acute: swelling occurs with hot skin. Complaints of pain, burning, bloating, fever. There are the usual form (with erythema and edema), bullous-hemorrhagic, phlegmous (with suppuration) and gangrenous (with gangrene). Complications are severe: elephantiasis, phlegmon, abscesses, gangrene. On the face, sepsis and thrombosis of the sinuses of the brain are possible. It is advisable to hospitalize patients with erysipelas.
Toxidermy
- a disease of an allergic nature. As a rule, it manifests itself in the form of damage to the skin and mucous membranes. Often localized on the skin of the hands. This is usually a reaction to drug allergens. Manifestations of the disease occur after the allergen enters the body through injections or the digestive tract, sometimes through inhalation.
There are two forms of toxicoderma: fixed and widespread. The first is characterized by the appearance of red spots on the hands (usually raised above the surface of the skin), which are subsequently covered with a brown crust, or a watery bubble forms in the center, which bursts under mechanical stress. Symptoms disappear after stopping the drug that causes the allergy.
Loading…
Common toxicoderma manifests itself more pronouncedly: not only the skin, but the entire body suffers. There may be an increase in temperature, irritability, nervousness, problems with the digestive and respiratory systems. This is a more severe form of the disease: skin lesions can develop into Lyell's syndrome - the appearance of blisters with serous contents on the skin, which burst and leave behind extensive bright red ulcers. It is important to ensure the sterility of the area of skin lesions and hospitalize the patient, because with this form of dermatitis there is a high probability of blood poisoning.
Please note : if symptoms of this disease appear, you should immediately consult a doctor!
Acne
Acne is a lesion of the skin and its deep layers in the form of large purulent pimples. There are acne of exogenous and endogenous origin. Exogenous types of acne refer to external factors, and endogenous types refer to internal causes of the appearance of the rash.
In addition to origin, different types of acne are determined. They can be medicinal, inverse, piled up, spherical, seborrheic. Acne is more common in adolescents than in adults, and is completely absent in young children. As for gender, acne is one and a half times more common in women than in men.
Signs of the disease
The main symptom of the disease is the appearance of acne. The rash may be small and watery or larger and purulent. It all depends on the stage of the disease. There are three of them: light, medium and heavy. The first ones are easier to deal with because they do not touch the fiber of the epidermis.
Large pimples are not completely visible from above; most of them are located inside the skin, which complicates treatment. “Favorite” acne locations: face, décolleté, chest, upper back. Very rarely in other parts of the body.
Causes of acne
The key factor in the occurrence of the disease is clogged pores. The following factors contribute to this:
- use of hormonal drugs or nutritional supplements that contain certain steroids;
- excessive production of sebum by the body;
- bacterial infection;
- inflammation of the hair follicles;
- hereditary predisposition;
- age-related hormonal changes;
- abuse of cosmetics or use of products that are inappropriate for the structure of the skin;
- unhealthy food predominates in the diet;
- frequent stress or constant nervous tension.
Acne treatment
You need to understand that acne is a disease and needs to be treated. Acne should not be underestimated; in the absence of proper treatment, the consequences can be unpleasant. It is important to know the reason that served as the impetus for the development of the disease. Treatment should begin with its elimination. To get rid of acne, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, in most cases, for external use.
This could be “Synthomycin Liniment”, “Depantol” ointment, “Sledotsid”, tea tree oil. Additionally, use herbal decoctions for daily washing. Suitable chamomile, calendula, string.
In severe stages, medical procedures such as laser or chemical skin peels, as well as antibiotics and steroid medications, are used. In addition, it is important to take vitamin complexes containing vitamins A, C, E, and D.
Acne prevention
Despite the patient’s age, severe acne can be avoided if you follow some recommendations:
- If you are prone to increased production of sebum, you need to follow a diet;
- Choose cosmetics that suit your skin type;
- To wash your face, use herbal decoctions or special products;
- It is recommended to use ice for inflamed areas;
- If you need to stay in the sun for a long time, protect the skin surface with a cream with a high level of ultraviolet radiation.
Fungal diseases of the skin of the hands
Next, we will consider diseases of the skin and nails of the hands. Mycosis of the skin of the hands is caused by dermatophyte fungi. Most often, fungal infections are localized on the hands and nails; the internal organs are not affected. The disease manifests itself in changes in the skin: dark or white spots, peeling, crusts appear, the color of the nails changes, their surface becomes uneven, often the nails can begin to break and peel.
The fungus is present on many things that surround us: on vegetables and fruits, on the skin of other people; You can also become infected through manicure accessories, towels and clothing. Some types of fungus are also present on healthy skin, but do not manifest themselves until conditions become favorable for their reproduction. Fungus on the hands can appear against the background of gastrointestinal diseases, nervousness, during a weakened immune system, or due to excessive consumption of sweets.
To diagnose, a doctor only needs to examine and examine the scraping. Antifungal agents: tablets and ointments help to cope with the disease. During the treatment period, it is recommended to avoid aggressive detergents and cosmetics; it is recommended to apply the ointment at night under cotton gloves, which must be washed and ironed daily
.
Preventive measures
It is possible to prevent ulcers in different areas of the skin by following hygiene rules. It is worth taking a responsible approach to the choice of cosmetic skin care products. An important preventative measure is the correction of lifestyle and nutrition, which includes giving up bad habits and bad food.
Prevention consists of quality care for the newborn. Wash your face only with boiled water at a comfortable temperature and twice a day. Bed linen and baby clothes are washed only with hypoallergenic products intended for children. After washing, iron everything. Children's clothes should only be made of cotton or flannelette fabric.
It is very useful to add decoctions of medicinal herbs to the water when bathing the baby. This perfectly tones the skin and disinfects it. When using disposable diapers, they are changed at least 4-5 times a day. The butt is washed, dried and the skin is allowed to breathe for about half an hour. Pediatricians recommend taking off diapers at home and putting them on only when going for a walk or to visit the doctor.
Candidiasis
Candidiasis of the skin of the hands is also a fungal disease. It is caused by fungi of the genus Candida, which are a conditionally pathogenic flora of our body, but can turn into a pathogenic state and cause candidiasis (can manifest itself in the form of thrush, stomatitis and fungal skin lesions).
The main manifestations: the appearance of red itchy spots on the skin of the hands, swelling of the lesions, the appearance in their place of papules, blisters and various types of rashes. It often begins with a harmless itching that bothers you at night, and then develops on injured skin.
Diagnosed by external signs and scraping analysis results. Treatment is usually local, but in particularly advanced forms it can be general. Standard antifungal drugs are prescribed, and more careful hygiene is recommended.
Types of boils in children
Furunculosis in children has a code according to ICD 10 (International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision) L02.
The following types of boils fall under this code:
- single boils, regardless of their location;
- cystic acne on the face in adolescents, affecting the deeper layers of the dermis;
- pilonidal sinus - boils in the intergluteal fold when wearing tight underwear, sweating and insufficient hygiene after defecation;
- Hidradenitis suppurativa is a purulent inflammation of a large number of sweat glands located in places of increased sweating (groin, armpit), recurrent.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic skin disease that is accompanied by the appearance of pink plaques, spots and peeling. Itching is also a characteristic symptom of psoriasis. The reason for the appearance of scaly plaques is that the cells of the epidermis begin to divide several times faster, which leads to the fact that most of them do not have time to develop and die, subsequently peeling off, which is accompanied by itching. The immune system begins to control the process: it begins to act against its own cells, which leads to the formation of inflammation in the affected area.
There are several types of psoriasis, each of which differs in the nature and intensity of the disease. Plaque, guttate or pustular psoriasis most often develops on the skin of the hands. Sometimes seasonality is observed: the disease worsens in the spring and autumn.
The main causes of psoriasis are not known for certain. There are many assumptions: hereditary factor, stress, genetics, disorders in the endocrine system. However, it is impossible to say exactly what can trigger the disease.
Treatment consists of complex therapy: relief of itching, elimination of external manifestations of the disease in order to alleviate the patient’s condition. Along with treatment with external agents, it is necessary to periodically undergo a course of general therapy.
Contrary to popular belief, psoriasis is not a contagious disease. It is not transmitted through contact with the skin of a patient or through household appliances.
IMPORTANT TO KNOW: even if all plaques disappear and there are no symptoms, preventive therapy and periodic visits to a dermatologist should not be neglected!
Therapeutic measures
For treatment to be effective, it is necessary to find out the causes of the pathological condition and direct efforts to eliminate it. Recommended:
- normalize the functioning of the digestive tract;
- restore hormonal balance;
- maintain personal hygiene;
- avoid stress;
- maintain a balanced diet.
An important step is cleansing the skin; for this you can use scrubs and homemade masks. You also need to contact a cosmetologist who will prescribe a course of procedures that will help dissolve sebaceous plugs, as well as exfoliate dead epidermal cells. The most effective procedures are considered:
- ultrasonic cleaning;
- chemical peeling;
- cryotherapy;
- mesotherapy.
Chemical peeling of the face
Attention! Procedures can be started only after the inflammatory process has been eliminated. Otherwise, there is a risk of spreading the infection.
Drug therapy
In complicated cases, it becomes necessary to prescribe antibacterial drugs. Most often used:
- Unidox Solutab.
- Erythromycin.
- Tetracycline.
- Doxycycline.
The selection of medications, dose, and duration of treatment is carried out by the doctor.
In parallel with this, the following are prescribed:
- Retinoids, which eliminate excess activity of the sebaceous glands and regenerate epithelial tissue. The drugs of choice are Tretinoin, Adapalene, Isotretinoin.
- Sorbents, dietary supplements with lactobacilli. The products help normalize the intestinal microflora, removing toxic substances from the body. This group includes medications: activated carbon, Polysorb, Linex, Lactofiltrum.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes. These include vitamins: E, A, C, as well as zinc.
Topical agents are also used, but only after consultation with a doctor. Effective are:
- Iodine. It is used for spot application to affected areas; it eliminates the inflammatory process and disinfects well.
- Zinc ointment. The drug has a wound-healing effect, prevents tissue necrosis, and protects against the negative effects of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Levomekol. It is recommended to apply the product to the affected areas for 2-3 hours, then rinse with water.
- Salicylic acid. Effectively fights bacteria, eliminates hyperemia and dead cells.
- Alcohol tincture of calendula. Has a wound-healing, anti-inflammatory effect.
Also, the effect is observed from taking baths with sea salt or potassium permanganate; they have a disinfecting and drying effect. Do not use hot water.
The use of folk recipes
Before using folk remedies, it is recommended to consult a doctor. The following is considered effective:
- Aloe juice helps draw out pus. A plant leaf, without the top skin, is applied to the affected area. You need to leave it on all night, so that it does not slide off, it needs to be attached with a band-aid. In severe cases, the procedure is performed several times.
- Calendula infusion. To prepare 1 tbsp. l. raw materials are poured with 500 ml of boiling water and left for 30 minutes. The infusion is used to wipe the skin. If you add honey to it at the rate of 1 tsp. per glass of solution, then it can be used for lotions. To do this, soak a cotton pad in the solution and apply it to the affected area for 20 minutes.
There is a second way to prepare the tincture. To prepare it you need 2 tbsp. l. pour calendula flowers with 50 g of alcohol, 40 g of water, 80 g of cologne. The mixture is left in a warm place, and then 1 tsp is added to it. 5% boric alcohol and ½ tsp. glycerin. Wipe the affected areas with the product twice a day.
- Fresh leaves of birch, nettle, dandelion root and burdock. You need to take 2 tbsp. l. mixture, pour 500 ml of boiling water, boil for 15 minutes, strain and cool. It is recommended to drink 100 ml of the decoction three times a day.
- Onion applique. In order for the pus to come out faster, you need to apply a baked onion to the affected area and secure it with a band-aid. It is better to leave the application overnight.
Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a skin disease, the main symptom of which is a violation of natural pigmentation, which occurs due to the destruction of the melanin pigment. On the skin of the hands, it appears in the form of milky-white spots with clear boundaries. There are no peeling, itching, cracks or other symptoms. Only a cosmetic defect causes inconvenience to patients.
Doctors identify several main reasons for the appearance of vitiligo on the hands: autoimmune disorders in the body (antibodies begin to attack the body’s own tissue components), genetic predisposition, stress, liver disease.
There are several stages of disease development:
- Initial stage. One spot appears on the skin.
- Stationary stage. The spot does not change shape and size, remaining on the patient’s skin for many years.
- The repigmentation stage (not always) is the restoration of the normal shade of the affected skin area.
- Progressive stage. The spots increase in size and invade new areas of the skin.
Treatment is mainly aimed at suppressing further progression of the disease. The main drugs used are glucocorticoids, substances aimed at blocking autoimmune processes in the body.
External means
To act directly on the lesion, doctors prescribe treatment with various ointments. Combination therapy using systemic and external medications helps to quickly cope with the pathology. Ointments are especially necessary for furunculosis, since several abscesses cause severe discomfort.
Levomekol is an antibacterial drug that is highly effective. Has antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory effects. When using the medicine at the initial stage of the pathological process, it is possible to avoid complications. The ointment promotes the outflow of pus and the rapid breaking of the capsule out. After the purulent contents are released, the possibility of infection is eliminated, since the product is used for another 5-7 days.
It is recommended to apply a bandage to the wound formed after a breakthrough. It will enhance the effectiveness of the drug. The regimen of use is determined by the doctor.
Oflokain is an ointment with antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. Helps relieve swelling, pain, redness. After 7 days of regular treatment of the lesion, the symptoms significantly weaken and the patient’s condition improves.
Syntomycin ointment is an antibacterial ointment that is highly effective. Suppresses the development and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms, dries the wound when the capsule breaks through, and prevents bacteria from entering it. Used for 2 weeks.
The ointment should be prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the individual characteristics of each patient’s body, since medications have the ability to provoke allergies, especially if there is a tendency to it.
Scabies
Scabies is a skin disease that is caused by the active activity of the scabies mite. There are several types of scabies: typical, nodular, complicated, and so on. The main symptom is the appearance of a red, often watery rash on the skin (mainly between the fingers and on the sides of the palms). Usually accompanied by severe itching, which intensifies during sleep (the period when the mite is especially active). Scabies can also be distinguished by the nature of the localization of the rash: pimples on the skin are usually located in pairs.
Infection occurs through direct contact with the patient’s skin and personal belongings. The disease often does not manifest itself in the first days after infection, because the incubation period is 7-10 days.
To prevent complications such as a purulent infection (which can develop from scratching the rash), it is necessary to use soothing agents and control the itching.
The disease is diagnosed by visual examination by a dermatologist and examination of the mite and scraping. Scabies is treated externally with special preparations, along with which the doctor can individually prescribe general treatment with immunomodulators and sedatives. It is recommended to thoroughly wash and iron things that the patient comes into contact with.
Diagnostics
Before treating furunculosis, the dermatologist performs the following diagnostic procedures:
- visual inspection of the site of inflammation using a device (dermatoscopy);
- bacteriological culture of a boil fragment;
- carrying out a blood test.
If a patient has a lot of boils on his body, then he needs to donate blood for sugar. It is also necessary to carry out urine culture. An ultrasound of internal organs and x-rays may be required.
Be sure to read:
What ointments can be used to treat boils
The presence of complications implies the need for blood cultures to be tested for sterility. The patient may be referred for a CT scan and MRI.
Palmar pustulosis
Skin diseases on the palms of the hands cause more discomfort. Palmar pustulosis (other name: pustular bacterid) is a skin disease of unknown etiology, characterized by the appearance of small (pinhead-sized) pustules on the palms, which subsequently dry out, forming crusts. External manifestations are periodic; during an exacerbation, the patient may experience pain, itching and increased temperature in the affected area. When nails are damaged, they become deformed and brittle.
It can be treated both externally and internally. Complex therapy is usually prescribed: from emollient ointments to hormonal drugs. The disease often recurs. It is typical for both men and women aged 20 to 50 years.
During the period of remission, preventive treatment with external medications and careful hygiene are recommended.
Treatment of boils in children
Since June 8, 2007, there has been Order No. 408 of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation, which determines the standard of treatment for boils and other purulent skin diseases in children and adults. It concerns the provision of specialized medical care for any location, form and stage of diseases under code L20, regardless of the presence of complications in a hospital setting.
The standard includes diagnostic and therapeutic measures based on a hospital stay of 14 days. Standard examination includes:
- history taking, visual examination, auscultation, palpation and percussion within the general therapeutic framework;
- measurement of blood pressure, respiratory rate, pulse and temperature;
- general blood test with leukocyte count;
- chest x-ray, ECG;
- culture from the source of inflammation, in some cases puncture of the abscess.
Treatment and diagnostic standard measures in the hospital:
- expansion of blood test parameters (counting red blood cells, platelets, determination of hematocrit);
- biochemical blood test (total protein, albumin, creatinine, alanine and aspartame transaminases);
- Analysis of urine;
- examination for syphilis, HIV, carriage of hepatitis B and C viruses;
- determination of blood group and Rh status;
- examination by an anesthesiologist.
Pharmacological groups according to the standard allow their use in 30-100% of cases.
- Analgesics and NSAIDs, narcotic (Trimeperidine, Fentanyl) and non-narcotic (Tramadol, Ketorolac).
- Means for treating and preventing infection are antibiotics and antifungals.
- Antiseptics and disinfectants (Povidone-iodine, Chlorhexidine).
- Solutions for infusion therapy.
- Anesthetics and muscle relaxants for anesthesia and local anesthetics (Lidocaine, Ropivacaine topically).
- Drugs affecting the central nervous system (Diazepam, Droperidol).
Treatment at home is allowed for typical boils in “non-dangerous” localizations in children over 1 year of age.
Carbohydrates should be excluded from the diet of a sick child, including cereals, pasta, potatoes, soda and sweets.
Treatment of boils in children with folk remedies
Treatment of a boil in a child with folk remedies is permissible only with the permission of the surgeon. They recommend oil compresses with fir, camphor and sea buckthorn oils, treatment with herbal decoctions of string, chamomile, eucalyptus. Rabbit cabbage juice and ficus leaf puree are unlikely to fall into the category of treatment methods recommended by a doctor.
Wherever the child’s boil is located, a doctor should treat it. No self-medication, no proven folk methods can be used without permission!
Treatment of furunculosis in children with medications
The advisability of prescribing antibiotics for single boils is determined by the following condition.
For children under one year of age, intramuscular antibiotics are recommended for any location of boils, especially with widespread furunculosis.
Boils in children over 1 year of age are treated with antibiotics only if the ulcers are located on the face and neck, if we are talking about single ulcers. There are no reasons for refusing antibiotics in the treatment of furunculosis in children.
Which ones are preferable?
Amoxiclav, Doxycycline, Clindamycin, Clarithromycin, Cefuroxime, Ciprofloxacin are the drugs of choice.
Local treatment of boils is carried out using solutions of antiseptics and disinfectants and ointments (Ichthyol, Syntomycin, Tetracycline, Zinc). If surgical opening of the abscess and removal of the rod was performed, as well as after its spontaneous removal, dressings are recommended to be done daily until the skin defect is completely healed.
To speed up repair, the doctor may prescribe physiotherapy.
You can get rid of furunculosis only with an integrated approach to the problem:
- sanitation of foci of chronic infection;
- immune system support;
- vitamins, iron supplements;
- vaccine therapy according to indications.
Harmless stains
People who are attentive to their health often notice various changes in the skin, which can be a symptom of serious diseases. However, an itchy spot or pigmented area is not always a sign of disease. Often these can be completely harmless manifestations of the body’s reaction to certain factors.
A red spot or itchy papule may appear on the hands due to contact with an allergenic plant or after an insect bite. Also, the cause of stains on the hands can be too aggressive powders, detergents or soaps.
Sometimes pigmentation on the skin is related to sun activity, and this should not be a cause for concern.
Remember that if the symptoms described above appear, it is recommended to stop taking suspicious medications, cosmetics and detergents. You should also contact a dermatologist and undergo the necessary tests in order to receive treatment recommendations in a timely manner.
Your health is in your hands!