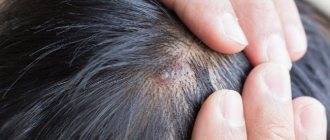
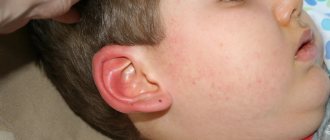
Causes and mechanism of development
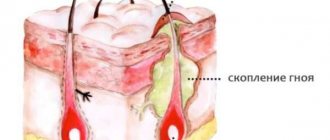
Purulent inflammation caused by infection is called an abscess. The infection process in this case occurs as follows. As a result of the injury, a small wound appears on the body. Then pathogenic bacteria enter it. And if a person does not treat the injured area in a timely manner, then the protective properties of the skin weaken and it cannot build a barrier against penetrating infections. In this case, an abscess appears. An abscess boil has an important feature: the pus from it remains in the subcutaneous fatty tissue, and does not come to the surface, as with a regular boil. Purulent inflammation of the follicle of an asphalt nature can occur for the following reasons:
- weakening of immune defense caused by independent illness or exacerbation of a chronic illness;
- features of professional activity (frequent contact of the skin with harmful substances of any physical state);
- hypovitaminosis;
- hormonal problems resulting from hyperfunction of the adrenal glands, diabetes mellitus; this leads to disruption of the trophism of the outer integument and a decrease in local immunity;
- insufficient personal hygiene of the skin, frequent skin contamination;
- untreated infectious disease;
- regular contact of a body area with rough material, sutures;
- improper treatment of boils;
- the use of thermal procedures to accelerate the exit of the necrotic rod;
- improper treatment of the wound after removal of the boil;
- hyperhidrosis, aggravated by a violation of the protective function of the skin;
- contact of infectious secretions (with rhinitis, sinusitis, frontal sinusitis) with the skin.
Abscess of the maxillary
Description
A paramaxillary abscess is a purulent inflammation with the formation of a limited focus of decay in the tissues of the maxillofacial area. Etiology Mixed flora, mainly streptococci and staphylococci. The source of infection is periapical and pericoronal foci of inflammation and periodontal pockets. Pathogenesis Associated with the spread of infection into adjacent soft tissues through the lymphatic and venous channels or through bone resorption. Symptoms Limited swelling, fluctuation under hyperemic and tense skin or mucous membrane. The severity of general phenomena (headache, chills, leukocytosis) is determined by the size and location of the abscess. Subgingival abscesses may rupture spontaneously. Treatment Abscesses of the tongue, parapharyngeal space, maxillofacial groove and other localizations are subject to opening. The abscess cavity is drained. Antibiotics are prescribed for fever and intoxication. Prognosis Favorable. Short-term disability. Prevention Timely atraumatic endodontic treatment and elimination of periodontal pockets.
Stages of development
The boil develops in several stages:
- Infiltration. At this stage, the boil sometimes resolves on its own with unexpressed suppurative processes - this is the so-called dry boil. Otherwise, the infiltrate moves to the next level of development.
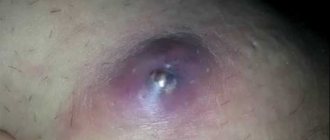
- Formation and rejection of a purulent-necrotic rod. The hair follicle and adjacent sebaceous gland undergo purulent melting. The zone of hyperemia increases. The infiltrate rises even more above the skin level; in the center, under the dermis thinned by inflammation, a gray-green mass begins to be visible - a purulent-necrotic core. The pain gets worse.
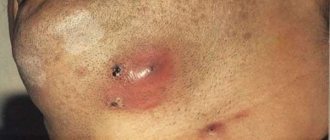
- Scarring. Purulent-necrotic masses are rejected, and a small defect is formed on the skin, which is replaced by connective tissue. A scar is formed. Based on the presence of multiple scars after boils and the activity of the process, a doctor can diagnose furunculosis.
Soft tissue abscess
Description
Etiology Occurs as a result of infection penetration into soft tissues due to skin injuries, including microtraumas. The abscess is usually located superficially. The causative agent is mostly staphylococcus in combination with Escherichia coli (sometimes anaerobes). Symptoms In the initial stage, an infiltrate appears without clear boundaries, subsequently an abscess forms with typical signs: pain, redness, swelling, fluctuation, fever. With superficially located ulcers, fluctuation appears early, with more deeply located ones - late; Diagnosis For diagnosis in such cases, ultrasound or diagnostic puncture of the infiltrate with a thick needle can be used. Treatment Wide opening and drainage of the abscess cavity. For deeply located ulcers, a closed method of treatment can be used - a small incision, curettage of the inner wall with aspiration of the contents, drainage of the cavity with a double-lumen drainage with lavage and active aspiration. This method makes it possible to reduce the treatment time for patients.
Symptoms and diagnosis
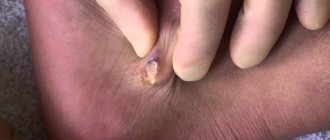
A patient with an abscess boil complains of the following manifestations of pathology:
- Acute pain in the area of the inflammatory process.
- A yellowish core of pus located under the skin at the site of inflammation.
- Increased body temperature.
- Headache.
- General weakness and sweating.
To prescribe a course of therapy, the following diagnostic methods are prescribed:
- collecting anamnesis (obtaining information about the patient’s living conditions, the presence of chronic pathology, previous diseases);
- examination of the affected area (determination of the localization of the phlegmonous process, clinical manifestations, general condition of the patient);
- general blood test (determining the level of leukocytes, erythrocyte sedimentation rate);
- cultural diagnostics (carried out to confirm the staphylococcal nature of the disease, determine the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibacterial drugs).
Diagnostics is an important stage for making a correct diagnosis and prescribing the correct scheme of health-improving measures.
Subhepatic abscess
Description
Etiology, pathogenesis Occurs as a result of delimitation of the inflammatory process in destructive cholecystitis due to the greater omentum, hepatic angle of the colon and its mesentery. The duration of the disease is usually more than 5 days. Symptoms Patients have severe pain in the right half of the abdomen, high temperature, sometimes of a hectic nature. Diagnosis Upon examination, the tongue is coated, the abdomen lags behind during breathing in the right half, sometimes a formation is detected by eye, which moves in a limited way when breathing. On palpation - muscle tension and a painful, immobile infiltrate of varying sizes. A general x-ray examination of the abdominal and thoracic cavity reveals paresis of the colon, limited mobility of the right dome of the diaphragm, and possibly a slight accumulation of fluid in the sinus. Very rarely the fluid level in the abscess cavity is detected. Ultrasound examination of the liver and biliary tract helps in diagnosis.
Treatment methods
Experts say that the most effective and fastest way to treat an abscess boil is surgery. But for some patients, pharmacological and traditional methods of treatment are effective.
Medicines
Drug treatment involves completing a course of local and general therapy. Local treatment involves treating the skin around the inflammation with salicylic or camphor alcohol, as well as applying applications with antiseptic solutions. General therapy is the use of ointments and compresses with medications. To achieve the fastest results, treatment measures must be comprehensive (taking antibiotics, increasing immune defense and using stretching ointments).
Systemic action
Antibacterial agents have a generalized effect on the body and fight infection from the inside. To select an effective drug, you need to take a blood test to determine the causative agent of the infection. Dicloxacillin is considered one of the most effective antibiotics (used to eliminate staphylococcal bacteria). Also in the fight against boils, drugs such as Erythromycin and Tetracycline are used.
Abscess
Description
An abscess is a purulent inflammation of tissue with the formation of a limited focus of decay. Etiology, pathogenesis The causative agents of soft tissue abscess are most often staphylococcus and streptococcus; in abscesses of other localizations, the nature of the flora depends on the cause of its occurrence in combination with non-clostridial anaerobic flora and cocci. With an abscess, there is a clear demarcation of the source of inflammation from the surrounding tissues. In the early stages it is granulation tissue; during subsequent development, a connective tissue membrane is formed around the granulation tissue. The presence of a pyogenic membrane sharply impairs the penetration of antibiotics from the bloodstream into the abscess cavity, however, intoxication of the body due to the absorption of toxic products from the site of decay remains. When the pyogenic membrane is disrupted (a sharp increase in pressure in the abscess cavity) or a decrease in general and local immune mechanisms, the infection spreads from the abscess, accompanied by sepsis and purulent leaks. Treatment Only surgical, the type of intervention depends on the size and location of the abscess.
Possible risks and complications
If a skin abscess is not treated correctly, a person may experience serious complications after its removal.
It is important to promptly recognize emerging tumors and urgently seek help.
In the first stages, it is difficult to identify the origin of the pathology, since its symptoms often resemble the development of an ordinary abscess.
There is a high probability of developing dangerous diseases such as:
- meningitis (in the presence of an inflammatory process on the back of the head, neck and face);
- sepsis (pathogenic microorganisms from the affected area can spread through the blood vessels, causing blood poisoning);
- thrombophlebitis of the facial veins (extreme form - paralysis);
- deformation of the nose (if the boil is localized in this area);
- malignant tumor of the lips (if an abscess has formed on the lip).
Abscess appendicular
Description
Appendiceal abscess is a complication of destructive forms of acute appendicitis (found in approximately 2% of all types of acute appendicitis). Pathogenesis Initially, an appendiceal infiltrate is formed, which then either resolves under the influence of conservative therapy, or, despite appropriate treatment, abscesses. Symptoms At the onset of the disease, the typical pain syndrome of acute appendicitis is noted. As a result of late presentation or incorrect prehospital diagnosis of acute appendicitis, the disease can follow two paths: progression of peritonitis and delimitation of the inflammatory process. In the latter case, after 2–3 days the pain decreases and the temperature drops. Diagnosis Upon palpation in the right iliac region, an infiltrate is determined. From the 5th-7th day the temperature rises again, the pain in the right iliac region and dyspeptic symptoms intensify. The pain increases with coughing, walking, and shaking. On examination, the tongue is moist and coated. The abdomen lags behind during breathing in the right lower quadrant, and bulging can also be detected here. On palpation - some muscle tension, pain in this area (sometimes very pronounced), weakly positive symptoms of peritoneal irritation. With deep palpation, a sharply painful, motionless infiltrate is determined (fluctuations almost never occur). There may be mildly expressed phenomena of paralytic intestinal obstruction - with a survey fluoroscopy of the abdominal organs, fluid levels and intestinal pneumatosis can be detected in the right half of the abdomen. On rectal or vaginal examination there is pain; sometimes the lower pole of the formation can be palpated. In the blood - high leukocytosis with a shift to the left. During dynamic observation, an increase in leukocytosis is noted, the temperature takes on a hectic character. The pain syndrome gradually increases, the infiltration and pain in the right iliac region increase. The size of the abscess and its exact location are determined by ultrasound examination. Treatment: Surgical. Premedication with antibiotics and metronidazole is required before surgery. Under general anesthesia, the abscess is opened; it is better to use extraperitoneal access. The cavity is washed with antiseptics and drained with double-lumen drainages for active aspiration of the contents with rinsing in the postoperative period. It is better to refrain from inserting tampons into the wound. In the postoperative period - detoxification therapy, antibiotics (aminoglycosides) in combination with metronidazole. Complications: Sepsis, pylephlebitis, liver abscesses, breakthrough of an abscess into the free abdominal cavity with the development of diffuse peritonitis. Prognosis Serious, depends on the timeliness and adequacy of surgical intervention.
Prevention
To avoid an abscess boil, you need to take preventive measures. There are several rules to help avoid infection:
- maintaining personal hygiene;
- proper nutrition;
- choosing clothes according to the weather;
- avoiding contact with questionable objects;
- strengthening the immune system.
If the boil does not cause concern or discomfort, and is small in size, you can fight the disease yourself. If the inflammation causes severe pain and home therapy is ineffective, you should urgently consult a doctor, as the consequences can be very serious. It is important to remember: only a specialist can select the appropriate treatment and help avoid complications.
Interintestinal abscess
Description
Etiology, pathogenesis Located between the intestinal loops, mesentery, abdominal wall and omentum. The mesentery of the transverse colon is a barrier to the spread of the abscess to the upper floor of the abdominal cavity. Interintestinal abscesses are often multiple. The exact location and size of the abscess is determined by ultrasound and computed x-ray tomography. Diagnosis Often, an interintestinal abscess is combined with a pelvic abscess. Diagnosis is usually difficult. It is possible to suspect the development of an interintestinal abscess in a patient who has suffered peritonitis with incomplete recovery, with a recurrence of symptoms of purulent intoxication of the body. Upon examination, tension in the abdominal muscles and severe pain in the area of the abscess are determined, in some cases - asymmetry of the abdominal wall (especially with abscesses that have contact with the abdominal wall). On palpation, a pathological formation can be determined, moderately painful and immobile. During a survey fluoroscopy of the abdominal organs, the level of fluid, the phenomenon of intestinal paresis, and the displacement of intestinal loops during a contrast study. Treatment: Opening and draining the abscess. Before surgery, premedication with antibiotics and metronidazole is required. Access depends on the location and number of abscesses. With multiple abscesses, it is necessary to open the abdominal cavity widely. Complications: Sepsis, breakthrough of an abscess into the free abdominal cavity with the development of peritonitis. The prognosis for single ulcers is usually favorable.
What is an abscess boil?
Every person, regardless of gender, race and occupation, has encountered such a problem as a boil. It is also called boil. Abscessing boil is the most painful form of the disease, the development of which is caused by some type of staphylococcus bacteria that penetrate the hair follicle.
Inflammation most often affects the face, neck and back. Also, a purulent formation can appear on the buttocks, groin area, arms, legs.
Furuncles do not form in areas of the body where there is no hair. Thus, the pathology represents inflammation of the sebaceous gland in a specific location. In some cases, the pathological process spreads to adipose tissue. Over time, the boil becomes larger and resembles a ball in appearance.
Post-injection soft tissue abscesses
Description
Etiology, pathogenesis Occurs with the introduction of infected contents or improper introduction into the subcutaneous tissue of drugs intended only for intramuscular administration. In the latter case, aseptic necrosis of the tissue may occur, followed by purulent melting of the tissue, but the pus remains sterile. Symptoms A few days after the injection (usually 3–6), increasing pain in the injection area, an increase in temperature appear, an infiltrate is detected locally, painful on palpation, skin hyperemia, swelling, and after another 2–3 days a fluctuation appears. More often, post-injection abscesses occur in the gluteal areas. Diagnosis Usually made after a diagnostic puncture with a thick needle. Treatment In the initial stage (before the development of purulent melting) conservative treatment: UHF, anti-inflammatory drugs, in some cases antibiotics. If an abscess occurs (early diagnosis using ultrasound or diagnostic puncture of the infiltrate with a thick needle), it is opened. The prognosis is favorable, it depends on the underlying disease for which the injection was performed. A long delay in surgical treatment can lead to sepsis and massive leakage of pus into the cellular spaces. Prevention Use of disposable syringes and needles. For intramuscular injections, you cannot use needles intended for intradermal, subcutaneous and intravenous injections, since the thickness of the subcutaneous tissue in the gluteal region can sometimes reach 8–9 cm. It is necessary to change the side of the injection each time.
Therapy
Surgical treatment of an abscess boil involves treating the skin with 70 percent ethyl alcohol or 2 percent salicylic alcohol at the initial stage. Before surgical opening, the boil is lubricated with antiseptic solutions such as iodine or brilliant green. During the operation, the doctor makes a neat incision from which pus, particles of dead skin and the rod are separated.
Device for UHF therapy
To reduce the time of suppuration and for the sake of an analgesic effect, it is recommended to use dry heat from different sources in parallel (from a Sollux lamp, UHF, heating pads), but warming compresses should be avoided.
If abscess boils are localized on the face or in another place with complications, a course of antibiotics is prescribed. Drug treatment and hospitalization are used for the malignant stage.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Severe itching in an intimate place in women
Throughout the entire period of illness, healthy skin surrounding the affected area should be treated hygienically. To do this, use camphor alcohol or a 2 percent solution of salicylic acid.
If multiple manifestations are not detected, but the boil occurs from time to time in the same place (relapse), specialists perform immunotherapy (for example, staphylococcal vaccination).
Those pathologies that entail furunculosis and its abscess stage can only be detected during a medical examination. The most vulnerable group are people suffering from diabetes and Staphylococcus aureus. In this case, doctors carry out parallel correction of the underlying disease and its symptoms manifested in furunculosis.