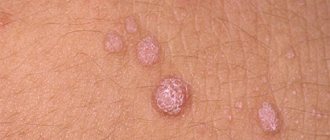
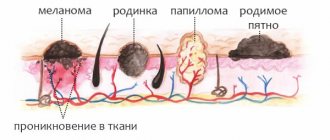
A wart is a benign neoplasm on the skin that looks like a voluminous spot or nodule. The need for its removal is due not only to a cosmetic defect, but also to the likelihood of degeneration into a malignant formation. This is especially true for those warts that are located in places subject to constant mechanical stress (shaving, friction with clothing, etc.).
Electrocoagulation is considered one of the most reliable, effective and affordable methods of getting rid of tumors today. Using electric current, you can remove a wart on any part of the skin, even on the face. However, there is one exception - plantar warts (growths that are found on the soles), as they are denser, rougher and have a deeper root.
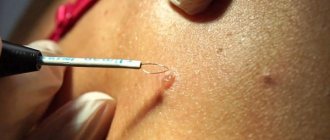
To carry out electrocoagulation, there is a special device - an electrocoagulator. This is a small device that operates on high frequency current. Pathological tissues are heated by electric current, which ultimately leads to the destruction of the wart body. The principle of operation of the electrocoagulator is that a special loop is heated using a high-frequency current - the main part of the device, which simply burns the formation. The coagulation method is most effective for excision of those growths that are located in easily accessible places.
Removal of moles by electrocoagulation in our clinic
Our medical center, along with others, uses this method of treatment, since cauterization of moles with an electric knife is convenient and painless for patients, and also has a number of other advantages:
- minimal percentage of development of undesirable consequences after removal
- no need for hospitalization
- the opportunity to conduct a histological examination of the tumor
- short recovery period
- no need to use general anesthesia
- The procedure takes no more than 20 minutes
- positive aesthetic result
- affordable price of service
Removal of moles using electrocoagulation is indicated for most patients who contact our clinic to solve this problem. However, it is not always possible to use an electric knife for such purposes. You can find other methods and indications for their use here and here. Before performing electrocoagulation, it is necessary to identify the presence of contraindications.
Interesting fact! Moles can appear and disappear without a trace throughout your life. On average, there are from 25 to 100 nevi of various shapes and sizes on the human body.
Features of the method
To remove tumors by electrocoagulation, a special device equipped with electrodes or a metal loop is used. Upon contact with the nozzle, the papilloma is burned out, and in most cases there is no bleeding, due to the sealing of the capillaries penetrating the skin. The specialist treats the wound formed at the site of the growth with an antiseptic.
Electrocoagulation is a painful procedure, so it is performed under local anesthesia. Children are given general anesthesia before tumor removal. Cleansing the skin may take from 1 to 20 minutes. The duration of the session is affected by the size of the growth, its shape and location. It is easiest to remove papillomas on a thin stalk. Flat formations are burned out in layers so as not to damage healthy tissue.
Cauterization of papillomas with current is considered a reliable and proven method. Like any method of cleansing skin from growths, electrocoagulation has its pros and cons. The following advantages of the procedure are highlighted:
- Safety, ability to treat both skin and mucous membranes.
- Suitable for patients of any age.
- Sterility of the instrument is ensured by heating it to high temperatures.
- The ability to adjust the force of impact, depending on the size of the papilloma.
- No blood loss.
- The ability to use the removed growth for histological examination.
- Relatively low cost of the procedure.
There are also negative aspects of diathermocoagulation associated with the peculiarities of the technique. Before deciding to undergo the procedure, you should pay attention to the following points:
- During the session, the patient feels a burning sensation, especially if sensitive areas of the body are treated.
- Healing of the epidermis lasts on average 10-14 days, which exceeds the recovery time of the skin after treatment with a laser or radio wave method.
- Due to the risk of scar formation, the method is not used to get rid of growths that occupy a large area of the epidermis.
Preparing to remove moles with an electric knife
Proper preparation is the key to the successful completion of every medical procedure. Cauterizing a nevus with an electric knife is no exception, but in most cases does not require special preparation. We prescribe tests before the procedure for removing a nevus using electrocoagulation if you have a history of heavy bleeding or there are doubts about the benignity of the mole. In the above situations you will need:
- Clinical blood test.
- Coagulogram (determination of blood clotting indicators).
- Blood test for tumor markers.
Since removal of moles with an electrocoagulator does not require general anesthesia, there is no need for a “fasting” regime on the eve of surgery.
Possible complications
Most of the negative experiences of removing papillomas with an electric knife are associated with a violation of the technology of performing the procedure. The specialist must select the correct nozzle for the electrocoagulator, depending on the size of the growth and location. The strength of the supplied current discharges also matters. If a patient violates the rules of skin care during its recovery period, this can also lead to serious consequences. After electrocoagulation, the following complications may occur:
- excessive bleeding if the patient has impaired blood clotting or a large vessel was damaged during the cauterization of the papilloma;
- allergic reaction;
- if the tumor is not completely removed, several growths may grow from the remaining cells at once;
- infection in the wound, development of the inflammatory process, release of purulent masses;
- scar formation;
- If the wound remaining after surgery is repeatedly damaged, a malignant tumor may appear in its place.
How does mole burning work?
The procedure for removing a nevus with an electric knife includes the following steps:
- Visual inspection of the birthmark.
- Treating the surgical field with a skin antiseptic to prevent infection from entering the wound.
- Local application of a local anesthetic.
- The procedure for removing a nevus using an electric knife.
- Treatment of postoperative wound.
Burning out a nevus with an electric knife takes place in one movement, so you will not feel pain or burning. Some patients experience a slight tingling sensation where the device comes into contact with the skin.
Important! Self-removal of skin tumors is strictly prohibited. This can lead to the development of undesirable consequences such as inflammation, sepsis (blood poisoning), skin cancer. If necessary, you should contact a specialist at a medical clinic.
The essence of the procedure
Electrocoagulation is the effect of electric current on skin defects, maximally heating the tissue and burning them. To carry out the procedure, an electrocoagulator is used - a device that generates high-frequency electricity - about 800 degrees Celsius. The treatment is carried out with a coagulator loop, from which a current is released.
There is no preliminary preparation before the procedure. The main thing is the absence of contraindications and the doctor’s recommendation for the use of this method.
Removal of warts by electrocoagulation occurs according to the following scheme:
- The area of skin on which one or more warts have formed is treated with an antiseptic. Then local anesthesia is administered.
- The loop of the device is applied to the growth. Then current is supplied to it. The discharge has a high thermal effect, causing the wart cells to die within a few seconds. Thanks to anesthesia, cauterization does not cause pain to the patient.
- The high discharge cauterizes the capillaries that ran under the skin near the warty seal. Therefore, there is no bleeding after the procedure.
Electrocoagulation takes place quickly - the session lasts only a few minutes, during which up to several units are burned simultaneously. The duration of removal depends on the number and size of warts. The procedure can be completed immediately after consultation with a specialist, on the day of treatment.
Contraindications to burning moles
New growths on the skin can be benign or malignant. Removing moles with a coagulator is considered safe provided that the nevus does not show signs of developing a cancerous tumor. The doctor determines the primary signs during a visual examination. You cannot remove a nevus using an electric knife if you suspect the formation of a malignant process. Also contraindications include:
- bleeding disorders
- intolerance to electrical procedures
- allergic reactions to local anesthetics
- herpetic infection in the acute phase
- an inflammatory skin disease at the site where a mole was burned out with an electric knife
Any such case must be eliminated before electrocoagulation is performed.
The essence and mechanisms of tissue coagulation
Coagulation, both laser and electrical, is a medical procedure, however, it is often used in cosmetology.
In the process of exposure of a certain nature, the cells of the skin or mucous membranes lose moisture, their internal structures are destroyed, as a result of which they die.
The term “coagulation” itself is borrowed from physics and chemistry, and is of Latin origin. Literally, coagulation is translated as “coagulation” or “thickening”, and refers to the process of particle gluing that occurs during their Brownian or thermal motion. Due to this bonding, the particles are collected into so-called aggregates - secondary particles. Simpler particles interact and are held together by intermolecular forces.
Content:
- The essence and mechanisms of tissue coagulation
- Differences between laser and electrocoagulation methods
- Condylomas: concept and types
- Indications and contraindications for the procedure: when is electrocoagulation prescribed?
- Features of the procedure
- Wounds after the procedure: how to treat
- Rehabilitation period after electrocoagulation
In order to catalyze the coagulation process in a certain system, it is necessary to increase its temperature - this leads to a violation of aggregate stability.
Coagulation of condylomas provokes cell death, after which these skin formations undergo necrosis. Most often, electric current or laser treatment is used to get rid of condylomas.
Refusal to cauterize a mole
Refusal to remove the tumor in some cases leads to undesirable consequences. This is especially true for protruding birthmarks located in those parts of the body that can be easily injured. This, in turn, leads to heavy bleeding or degeneration of the nevus into a cancerous tumor. If the mole is located on an open area of the body, constant exposure to ultraviolet rays may also contribute to this. These complications pose a serious threat to human health. Therefore, it is better to seek medical help from a specialist in time and undergo, if not removal, then at least a visual examination and obtain a conclusion that the mole is not a malignant formation. But remember that you can 100% declare this only after histological analysis.
Interesting fact! There is a belief that a birthmark is located above a diseased organ and warns a person about a possible disease. Official medicine does not find confirmation of this. Most likely, this belief came to us from Eastern practices.
Benefits of removing warts with electric current
Despite the fact that electrocoagulation is considered a relatively old method, even today it is quite popular and in demand. Compared to other methods of removing tumors, electric current has the following advantages:
- Painless;
- No relapses;
- Efficiency of the procedure;
- Short rehabilitation period;
- Low price;
- Safety;
- No bleeding.
As a rule, after electrocoagulation, formations do not reappear. This is due to the fact that cauterization of the wart prevents the spread of viruses that cause this type of growth.
Is a relapse possible after removing a mole with an electric knife?
After surgery using the coagulation method, in most cases there is no relapse. The occurrence of complications is possible only if the technique of performing the manipulation is violated. This happens, for example, when there is insufficient tissue capture. As a result, pigmented cells remain in the deep layers of the skin and a new mole appears at the site of removal. This point usually depends on the skill of the doctor. We also employ a certified doctor, whose experience you can find here.
In our clinic you will receive professional medical services. A specialist doctor will examine the tumor and give recommendations for treatment. Together with the doctor, you can determine the tactics of further actions and sign up for the necessary medical procedure, or do it right away.
If you still have questions, you can ask them to the administrator by phone listed on the website or request a call back. We warn you that administrators have general medical education and cannot always help with the details and subtleties of certain procedures. For a detailed consultation, make an appointment with your doctor.
Primary source honey / September 2018
What determines the speed of wound healing?
Wound healing occurs in several stages. Initially, crusts appear at the sites of removed tumors. They then fall off, leaving a pink or whitish patch on the skin. Finally, the skin color is evened out, and the location of the wart becomes indistinguishable from healthy tissue. In order to speed up this process, the doctor recommends wound care products.
Hygiene procedures after removal
To prevent suppuration of the wound, the crust should be protected from moisture, exposure to heat and sunlight. Do not apply cosmetics to avoid causing irritation. Do not cover the wound with a plaster, as favorable conditions are created under it for the crust to soften and the wound to become infected.
The doctor who performs electrocoagulation explains in detail how to treat the wound after removing the wart. He may recommend a weak solution of potassium permanganate, 5% iodine, brilliant green or other remedies. The preparations are applied daily until the crust falls off. Then the young epidermis can be treated with Hydrocortisone ointment, Solcoseryl and other agents that accelerate the regeneration process. If there are signs of inflammation, you should consult a doctor.
How long will it take to recover?
Recovery times may vary and depend on health, bad habits, and the state of the immune system. As a rule, the crust disappears 8-10 days after electrocoagulation. After 1-2 months, an inconspicuous pigmented spot remains. After 3-5 months, the skin color evens out.
Removal of papillomas with celandine: pros and cons
Celandine got its name due to the fact that it has properties to treat skin diseases. Its orange juice is healthy, but poisonous, as it contains chelidonine and alkaloids.
Therefore, it should not be overdosed; it must be used according to prescriptions, and sometimes under the supervision of a doctor.
If you break the stem of the plant, bright orange juice will appear. To treat papillomas and warts, you need to lubricate the affected areas with the juice of a medicinal herb. Essentially, it burns the tumor, similar to chemical cauterization. The juice of the plant is used externally, and tinctures and decoctions are used internally.
Is it possible to cauterize papillomas with celandine?
It is possible to remove papilloma with celandine, but only after prior consultation with a doctor. And that's why:
- Skin cancer is sometimes mistaken for papilloma and time is missed for adequate treatment. Do you need it?
- After treatment at home, the papilloma may grow abnormally. This occurs due to incomplete removal of the growth, which, under the influence of an aggressive environment, is activated and begins to grow with renewed vigor.
- The possibility of malignant degeneration of the growth: after cauterizing it with celandine, the transformation of benign cells into cancerous ones will proceed faster.
- Celandine is a poisonous plant, its juice has a scalding effect. This, in essence, is treatment. However, using the herb incorrectly can result in unsightly scars and burns.
Condylomas: concept and types
Medicine knows many types of skin tumors, among which are condylomas.
Cutaneous condyloma acuminata is a warty formation, the appearance of which is caused by the human papillomavirus. Most often, condylomas are located in the genital area and anus, on the skin and mucous membranes around the mouth.
The disease is chronic and manifests itself with relapses from time to time. The disease affects both men and women.
There are no symptoms of the initial stage of HPV infection. In an inactive (latent) form, which can last from several months to several years, a person’s skin remains clean, no discomfort is felt, and the virus in the body awaits favorable conditions in the form of a decrease in the immunity and defenses of the human body - that’s when its activation occurs. As the disease enters the open stage, subcutaneous deformations of the stratum spinosum are formed. The deep skin layer grows, due to the keratinizing layer, a subcutaneous compaction is formed. The growth process is uneven, so the seals under the skin take on the appearance of balls.
Among the varieties of condylomas there are:
- exophytic;
- endophytic;
- giant or Buschke-Loewenstein tumor.
Genital condylomas are fibroepithelial formations that look like small cones and cylinders of flesh-colored or pink color, rising above the surface of the skin or mucous membrane. Structurally, condyloma is represented by a stalk and a base.
Endophytic condylomas grow inside the epithelium and are not always noticeable on the surface of the mucosa, where they form. They can be:
- flat;
- atypical;
- inverted.
Giant condyloma, or Buschke-Loewenstein tumor, is quite rare and is localized mainly in the anogenital area. Initially, the disease begins with the appearance of many closely spaced genital warts or papillomas, which then merge with each other, turning into a single exophytic formation.
Intervention process
Surgical cutting algorithm:
- The doctor administers local or general anesthesia.
- The papillomas are cut along the border, slightly capturing part of the healthy skin.
- A suture is placed at the excision site.
- The wound heals with the subsequent formation of a scar.
If a transition to a malignant course is suspected, the material is sent for histological examination. The result is known after 7 days.
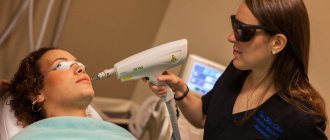
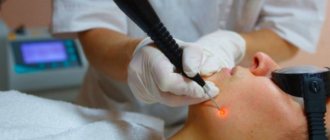
Laser removal algorithm:
- An anesthetic injection is used.
- The field for laser exposure is treated with an antiseptic.
- Set the laser installation - duration and power in accordance with the type of skin.
- The tip of the equipment is directed to the papilloma, and evaporation begins.
- Each growth is evaporated layer by layer.
- After removing the papilloma, the wound is treated with a solution of potassium permanganate, and a patch is applied on top.
Papilloma is a benign growth that requires surgical intervention. Otherwise, there is a risk of developing serious complications for the body. Prices for the procedure in different Moscow clinics are based on the qualifications of doctors, the rating of the medical institution and the method of removal.
Indications for electrical excision of papillomas
Electrocoagulation is carried out according to certain indications:
- A person wants to get rid of a cosmetic problem on his body. The manipulation is carried out in hard-to-reach and sensitive areas (on the face, eyelids, under the arms).
- The papilloma increased in size to 10 mm in a short period of time. This phenomenon first requires consultation with a dermatologist-oncologist. The doctor determines further treatment tactics.
- The wart has changed in color and shape. It became darker, with fuzzy, blurred boundaries.
- The surface of the formation is rough and elevated.
- Flat, smooth papilloma.
- Numerous growths throughout the body are a direct indication for removal with a coagulator.
- The method is used in gynecology for the treatment of erosion and stage 0-1 cervical cancer.
- Moles, pigmented spots, keratomas.