Human papillomavirus is a large group of related viruses, each of which is assigned a personal digital code. Each species has a unique DNA set, and this characteristic distinguishes it from others and determines its properties.
The disease is transmitted with equal frequency to both men and women, but according to statistics, every third case of the disease in women occurs without the manifestation of acute clinical signs, while in men the symptoms are almost always pronounced.
HPV types:
- HPV, which manifests itself as warts (HPV 1-5): warts (calluses) located on the soles of the feet - HPV types 1-4;
- flat warts - HPV types 3, 10, 28, 49;
- common warts - HPV type 27.
1
Diagnosis of papillomavirus infection
2 Diagnosis of human papillomavirus infection
3 Diagnosis of human papillomavirus infection
Prevention of papillomas
Preventive measures for the papilloma virus are possible without special knowledge and skills. Conditions for a healthy lifestyle, monogamous relationships, and personal hygiene are available to every person. Modern scientists have developed several vaccines, vaccination with which significantly reduces the risk of developing HPV with a high oncogenic potential (6, 11, 16 and 18). "Gordazil" is a drug manufactured in the USA, containing four active components that protect the body from papillomavirus. His “partner” from Belgium is “Cervarix”. The vaccine, consisting of two elements, is designed to prevent the most dangerous strains. The most suitable age for vaccination is considered to be between 10 and 25 years. The effective period of the vaccine is approximately 6.5 years. Vaccinations are suitable for both girls and boys.
HPV. Symptoms
The papilloma virus is constantly present in a person’s blood, but is activated only when immunity decreases. With weakened immunity, HPV begins to accumulate on the skin or mucous membrane and leads to the appearance of tumors.
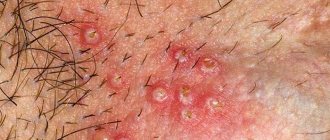
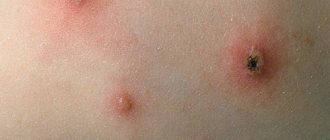
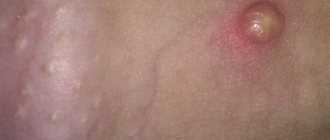
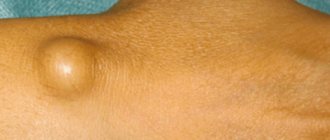
At a young age, HPV manifests itself as warts that are located on the fingers, elbows, and knees. Then a papilloma grows on a person’s skin (a soft-to-the-touch round formation on a stalk, with the help of which the papilloma is attached to the skin). Most often, papillomas are located on the skin of the face, neck, armpits, and papillomas are also found on the labia.
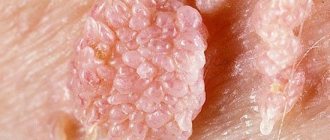
One of the most common manifestations of HPV is condyloma (uneven to the touch, soft, attached to the body with a stalk or a wide base, grows quite quickly, sometimes in a few hours).
Thus, warts, papillomas and condylomas are different signs of the same papillomavirus infection. Papilloma is a benign formation that can “show off” on a person’s face and body, not too pleasing to him aesthetically, but without causing much harm. Unlike papilloma formations, human condyloma tends to inflame and damage the skin and mucous membranes.
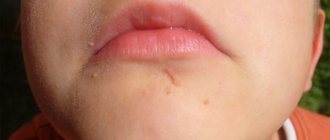
Condylomas
Condylomas are formations on the skin of the genitals, on the pubis, inner thighs, in the urethra, around the anus (anal condylomas) and inside the anus, having a lobed structure, flesh-pink in color, pedunculated or with a wide base, from a few millimeters to ten centimeters (eg, giant Buschke-Levenshtein condylomas).
Condylomas usually come in 2 types:
- condyloma lata, wide neoplasms with a wide base with which they attach to the skin, these neoplasms are considered a sign of secondary syphilis;
- genital warts, similar to soft pinkish bubbles with a thin stalk.
Condylomas acuminata
Genital warts are small flesh-colored formations that choose the genitals and anus as their location. In appearance, condylomas are sometimes confused with pearlescent papules, which are not a disease. Unlike pearlescent papules, genital warts are soft to the touch, attached to a thin stalk, and can be of different sizes.
Pointed papillomas are transmitted only sexually (through all types of sexual contact), therefore they belong to the group of sexually transmitted infections.
Causes of condyloma
There are various reasons for the appearance of condyloma, among which there are several main ones:
- having multiple sexual partners;
- long incubation period (time from infection to clinical manifestations);
- complex diagnostics;
- the presence of many types of PVI viruses;
- combination with other sexually transmitted infections;
- lack of protection effect using condoms from infection, etc.
1 Urethroscopy for diagnosing HPV
2 Urethroscopy for diagnosing HPV
3 Urethroscopy for diagnosing HPV
Treatment for men
It is impossible to completely get rid of HPV, like the herpes virus. Treatment of papillomas in men is as follows: all therapeutic and surgical measures are aimed at leveling the manifestations of the pathology and increasing the period of remission.
Specialist who will help
To develop optimal tactics to combat papillomavirus, it is necessary to undergo examination by a number of specialists. (Venereologist, proctologist, urologist and, if necessary, oncologist). At first, you can contact your local therapist, who will coordinate your further actions.
Removal of papillomas
When identifying viruses of types 16 and 18, removal of all kinds of growths is a must. After which a course of drug therapy is prescribed, which is able to suppress the causative agent of the disease and at the same time maximize the body’s natural defenses. A radical method of getting rid of papillomas is used if conservative treatment does not lead to the desired result.
The procedure is carried out in different ways:
| Type of intervention | Method of implementation | Purpose and features of the procedure |
| Surgery | The tool is an ordinary scalpel. The choice of anesthesia depends on the affected area, medical prescription and the wishes of the patient. | Used mainly for oncological papillomas. |
| Laser | With the help of infrared rays, pathological growths are “burned out”. | It is characterized by minimal complications and the possibility of complete removal of damaged tissue. |
| Excision using a radio knife | Impact on education with high-frequency waves. | An effective, fast and painless way. Often used to remove papillomas under the head of the penis. |
| Electrocoagulation | Impact of electric current on papilloma. | It is distinguished by a protracted healing process (up to two weeks). A painful method, according to customer reviews. Subsequently, a scar remains. |
| Cryodestruction | Liquid nitrogen is used. | Based on patient comments, this is a rather inconvenient method. |
| Chemical methods | Local use of various synthetic agents. | Do not use on overly sensitive areas of the body, such as the head of the penis. Damage to healthy tissues is also possible. |
Attention! It is strictly forbidden to get rid of papilloma yourself at home or to smear it with iodine. Such damage can lead to a transition from a benign tumor to a cancerous tumor.
Other therapeutic methods
Conservative treatment of papillomavirus in representatives of the stronger sex consists of taking medications.
Typically, specialists prescribe the following drugs:
- Stopping increased cell division: creams, ointments.
- Local agents on a natural basis (celandine) are sold in pharmacies at an affordable price.
- Promoting the activation of independent synthesis of interferons in the patient’s body.
- Immunomodulatory tablets.
- Antiviral drugs.
The dosage, regimen, and duration of the course are determined only by the attending doctor. During therapy, qualified monitoring of the effectiveness of the chosen tactics and timely detection of possible allergic reactions is necessary. Any virus cannot be treated with antibiotics. The need for their use is taken into account by the doctor, depending on the course of the disease. The use of folk recipes for HPV in no case can replace medical prescriptions. The use of various herbal decoctions is possible subject to prior consultation with a specialist. This fact should not be ignored if there are chronic intestinal pathologies.
HPV in women
HPV in women manifests itself not only as papillomas on the body, but also causes the development of cervical erosion , precancerous conditions, and cervical cancer . Condyloma in women is quite difficult to detect; it can exist in a woman’s body for a long time without any symptoms, and is discovered purely by chance at an appointment with a gynecologist. That’s why it’s so important to visit a specialist regularly, once every six months!
Symptoms of condyloma include:
- genital warts, which can appear on the genitals (condyloma on the labia, vaginal condyloma, cervical condyloma), in the oral cavity, on the skin of the anus (anal condyloma);
- disturbance in the maturation of epithelial cells (there are 3 stages of the process, the third stage is precancer);
- the development of a malignant formation from the epithelium lining the cervix.
Preventive actions
Prevention of the appearance of papillomas in men and genital warts helps prevent the active reproduction of papillomavirus and the growth of tumors. It is recommended to avoid casual sex and, if possible, use barrier contraception. They will protect not only from genital warts, but also from sexually transmitted infections. It is also recommended to pay attention to strengthening the immune system, since human papillomavirus tumors appear mainly when the body’s natural defenses are reduced.
Development of the disease
HPV infection can occur through all types of sexual contact (vaginal, oral, rectal), while condoms are not a guarantee of protection, since condylomas can be localized on unprotected areas of the skin and the size of the virus is smaller than the pore size of condoms. In addition, the virus can also be transmitted to the baby during childbirth if the woman is a carrier of the virus.
The human papillomavirus (HPV) has a tropism for the skin and mucous membranes of the genitals, oral cavity, and anus. The amount of virus depends on the state of both the immune system as a whole and local immunity. The more productive the individual factors of the immune system are, the more actively the division of the virus is blocked, and the less of it is contained. That is, a person can be infected with HPV without having any external clinical symptoms.
Risk factors
These are conditions that increase the likelihood of contracting human papillomavirus. The following risk factors can be identified:
- 1Early onset of sexual activity, a large number of partners and their frequent change.
- 2 Neglect of barrier contraception (condoms).
- 3 Associated sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia, gonorrhea, genital herpes, syphilis, trichomoniasis).
Vitamin deficiencies, other somatic diseases and factors leading to immunodeficiency increase the likelihood of clinical manifestations.
Clinical picture
Condylomata acuminata are formations of flesh-pink color, lobulated, ranging in size from 2 millimeters to ten centimeters, with exophytic growth, in which the apex of the genital condyloma is often wider than the base. Externally, the growths may resemble cauliflower or cockscomb.
The incubation period can range from 2-3 months to 2-3 years or more. The growth rate of formations varies, which is often associated with the state of local immunity, the presence of concomitant STIs, and sexual activity.
Complication after condylomas
Human condyloma is not just a harmless lobular growth on the genitals, it is a reservoir for the human papillomavirus. In recent years, cases with localization of genital warts in the oral cavity and throat have become more frequent, and there are condylomas on the lips.
The virus, accumulating in tissues, causes a change in the genome of epithelial cells of the skin or mucous membranes, which can lead to the development of severe complications. In men, HPV can lead to penile cancer . HPV in women threatens the development of cervical cancer . With these diseases, HPV is found in almost all patients.
Establishing diagnosis
How to treat papillomas on the head of the penis? Visiting a dermatologist is the first step towards healing. The initial appointment with a specialist includes a thorough visual examination of the mucous membranes and skin. A detailed survey of the patient is also conducted, and individual complaints are listened to.
If the presence of a virus is suspected, the patient is sent for additional examination:
- Blood and discharge from the bladder are donated for analysis. Based on the obtained indicators, the causative agent of the virus is isolated from the general DNA material.
- A biopsy of condylomas is performed. The result determines the presence or absence of cancer cells.
- A cytological examination of the mucous membranes is performed.
- Sometimes ureteroscopy is required.
After the final history, the doctor makes a conclusion and determines the treatment complex.
Asymptomatic carriage of human papillomavirus (HPV)
In reality, many more people are infected with HPV than statistics show. Most of them simply do not know about it, since there are no symptoms of condyloma.
The virus may not manifest itself in any way for a long time, since the human immune system does not allow it to develop to the required extent. However, at any time, with a decrease in both general and local immunity, this can happen, and then papillomas and/or condylomas appear.
1 Laboratory diagnostics
2 Dermatoscopy
3 Extended colposcopy
Papilloma virus. Diagnostics:
- Consultation with a dermatovenerologist . Only a dermatovenerologist can make a diagnosis during an initial examination, assessing the clinical picture, conducting a test with acetic acid, and, if necessary, using the dermatoscopy method.
- Laboratory diagnostics. It is necessary to conduct a HPV test using the PCR method, which will allow you to estimate the amount of the virus, as well as determine which type of HPV is present in this case (they are divided into types with high and low risk of oncogenicity). A PCR test must also be performed on all sexual partners of a patient with genital warts. A positive test result in the absence of clinical manifestations of the disease means that treatment is necessary to suppress the development of the virus in the body.
- Urethroscopy is a study of the condition of the urethral mucosa using special endourethral endoscopes. Considering the increase in recent years in the number of patients with endourethral condylomas, this study is necessary for all patients, both men and women.
- Extended colposcopy - examination of the cervix using a colposcope and performing a test with acetic acid and the Schiller test. It is necessary for all women to undergo laboratory confirmation of papillomavirus infection, since the presence of flat condylomas on the cervix is possible.
- Immunogram is a study of the state of the immune system. This will allow for the most effective HPV therapy.
Let's sum it up
If a gentleman is as attentive to his health as possible, he will be able to prevent the insidious papillomavirus from developing into an oncological disease.
It is necessary to seek help from oncologists, dermatologists and surgeons, and then carefully follow all their treatment instructions. It is strongly recommended to engage in HPV prevention, since with a high level of resistance to stress and excellent immunity, you can live with carrier status for many years without problems.
Carriers of papilloma have a chance to live a full life, since a vaccine against it has been developed.