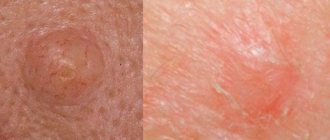
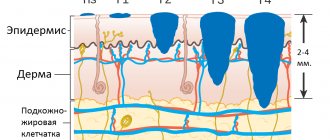
Melanoma is a tumor, a malignant cancer that develops from colored (pigment) cells and produces a mass of melanin.
Factors for the appearance of a tumor are divided into components:
- Frequent spending time in the sun and the use of artificial ultraviolet light (solarium).
- Damage to moles.
- Injuries that damage age spots or birthmarks.
- Let's consider treatment when formations are detected. Surgical removal of the tumor:
- Removal under local anesthesia, the cut is sutured with an intradermal suture, the result is sent for histology.
- In skin melanoma, relapses occur and wide excision is used.
- Micrographic removal is used when localized on the face.
- Amputation is used when limbs are damaged in the deep-lying elements of muscles, skin and bones.
- Dissection of lymph nodes.
Radiation exposure to modified cells (radiotherapy). Radiation therapy involves the destruction of cancerous tumors with rays. Used in the initial stage and after surgery, especially during relapses. Brachytherapy is used for ophthalmological diseases, in particular choroidal melanoma. The disease is characterized by the formation of malignant cancer on the choroid of the eye.
Melanoma of the eye
Targeted therapy. It is performed after surgery to remove cancer cells. It consists of destroying paraneoplastic syndrome and does not affect healthy cells.
Chemotherapy. Introduction of drugs into the body to completely destroy the tumor. Can be used intravenously and orally. The disadvantage of treatment is that the chemistry in the drugs affects the entire human system, destroying healthy cells. It is considered an effective method of removing cancer, but there are many side effects.
Checkpoint inhibitors
This is the most modern group of immunotherapy drugs. Scientists and doctors have high hopes for it. Checkpoint inhibitors can slow disease progression and prolong the life of patients with incurable melanoma when other treatments are ineffective.
How do checkpoint inhibitor drugs work? The immune system protects the human body not only from pathogenic microbes, but also from its own cells that have gotten out of control. To prevent a person from developing severe autoimmune conditions, it is very important for the immune system to distinguish between “us” and “strangers” and stop its aggression in time. For this purpose, special signaling molecules are used - checkpoints.
When a particular receptor protein on the surface of an immune cell interacts with another protein found on, for example, an antigen-presenting macrophage, the immune cell becomes inactive. The body seems to be telling her: “everything is fine, everyone here is friendly, there is no need to attack anyone.”
In malignant tumors, control points interfere. Because of them, immune cells do not understand that an enemy has settled in the body and needs to be fought.
Checkpoint inhibitors help activate the immune system and direct its efforts to fight cancer.
PD-1 inhibitors
PD-1 is a signaling molecule that is found on the surface of T lymphocytes. It can be blocked with the immunotherapy drugs Nivolumab (Opdivo) and Pembrolizumab (Keytruda). During clinical studies, it was proven that such treatment for melanoma in late stages helps to reduce the size of the tumor and prolong the life of the patient. It is unknown whether remission can be achieved with immunotherapy. Not a single case has been described.
Keytruda and Nivolumab are administered intravenously once every 2–3 weeks.
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
CTLA-4 inhibitors
From this group of drugs, one drug is used for immunotherapy of melanoma - Ipilimumab (Yervoy). The CTLA-4 protein is also located on the surface of T-lymphocytes and, when activated, suppresses their activity.
Yervoy is prescribed for advanced melanoma with metastases, when surgical treatment is impossible. It helps to increase the patient's life expectancy. The drug is administered intravenously once every 3–4 weeks.
Experts' opinions on immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is a relatively new practice in the treatment of cancer, and some oncologists are wary of prescribing immune-boosting drugs. The therapy is especially not widespread in the outbacks of Russia, since doctors in the field of oncology have insufficient education.
Experienced doctors in the field of cancer in oncology consider this type of immune therapy to be more effective and with less damage to the body compared to chemotherapy.
Drug components and artificial immune clone cells increase the survival rate of patients who are prohibited from surgery, reduce the risk of metastases and stop the growth of tumors.
The use of immunotherapy is applied to different stages of cancer individually. Immunity therapy sometimes allows melanoma to be completely cured.
Cytokines
Cytokines are proteins in the body that stimulate the immune system. For melanoma, two substances from this group are used: interferon-alpha and interleukin-2 (IL-2). They are prescribed at different stages of the disease.
Immunotherapy with interferon and IL-2 can be used for advanced melanoma in advanced stages. In combination, these drugs help shrink tumor lesions in 10–20% of patients. At the beginning of treatment, interferon and interleukin are always administered intravenously. In the future, subcutaneous injections are possible; patients and their relatives can give injections themselves at home. But if IL-2 is included in the treatment regimen, serious side effects are possible, in particular, fluid retention in the body and deterioration of the patient’s condition. Therefore, this drug is administered only in specialized clinics.
In addition, interferon immunotherapy for melanoma is used as an adjuvant treatment after surgery. This is true if the tumor is thick, which means there is a high risk that it has managed to spread in the body. Activation of antitumor immunity helps reduce the risk of relapse.
In order for interferon to have a pronounced effect, high doses are needed, and they are fraught with serious side effects. Therefore, when prescribing this drug for adjuvant therapy, the physician must evaluate the potential benefits and possible risks.
Prescription of immunotherapy
After collecting an anamnesis, the patient undergoes a full examination of the body or, after surgery to remove the tumor, immunotherapy is prescribed. Based on contraindications, the optimal medications are selected.
Indications for therapy
Therapy is needed during the recovery period after surgery to remove malignant tumors. The size of the formations reaches 1 millimeter, relapses and rapidly developing cancer cells equally become an indication for immunotherapy.
The immunotherapy system is prescribed for almost any stage of the tumor on the recommendation of an oncologist and is an addition to the main treatment against melanoma.
Contraindications to immunotherapy
The main contraindication is personal intolerance to the composition of the drugs. Before prescribing the drug, the body is examined for allergens included in the structure of the immunomodulating agent.
There are general contraindications associated with diseases of the heart and vascular system, these include ischemia, heart attack and angina. Pregnancy and breastfeeding are complete contraindications for use.
Autoimmune diseases, lupus, Lyme disease and others will not allow immunostimulants to do their job, since the immune system itself provokes diseases.
Oncolytic viruses
Viruses are not always enemies to humans; sometimes they are useful. For example, they can be modified in the laboratory so that they help destroy a malignant tumor. Such viruses are called oncolytic, and they have a therapeutic effect in two ways:
- They directly infect tumor cells and destroy them.
- They stimulate the immune system and force it to fight malignant tumors.
For melanoma, a modified herpes simplex virus is sometimes used. The drug is called T-VEC. It is injected directly into the melanoma or affected lymph nodes every two weeks. This helps shrink the tumor, but has no systemic effect—it does not help fight metastases in other parts of the body.
In what cases is it prescribed
Treatment of melanoma with immunomodulatory drugs is indicated if:
- There are many moles and age spots on the patient’s body, and some of them are gradually increasing. This condition is a symptom of the body’s predisposition to new malignant tumors.
- The patient underwent radiation therapy or underwent surgery for metastases that had penetrated the lymph nodes. Immunotherapy reduces the risk of complications, promotes normalization of immunological parameters and good health.
- A patient with melanoma is an elderly person. Treatment with immunomodulatory drugs helps improve the patient's general health and prolong his life.
- The stage of metastasis develops—a difficult-to-treat stage of the disease. Since the body’s defenses are depleted, it simply needs support in the form of immunotherapy.
- The oncological process is accompanied by a genetic defect or other disease. First, treatment is prescribed with drugs that affect the secondary pathology, after which all the body’s defenses are directed to fight the tumor.
Reviews from our patients
- Feedback on lung cancer treatment
Review of lung cancer treatment June 15, 2020Sergei Nikolaevich contacted us for treatment of lung cancer. Before that, he went to other medical institutions, but they could not help. In a matter of days, our doctors examined the patient. Based on the results of the interdisciplinary consultation, treatment tactics were prescribed. It consists of combined courses of chemotherapy, targeted and immunotherapy. The first stage of treatment has already been completed. There are no side effects. “My impressions are positive. The situation itself...
read more
- “Medicine 24/7” is the only place where we could help
“Medicine 24/7” is the only place where they could help on April 9, 2020.
Our clinic became the only place where they could help the patient. All the others refused it due to age and concomitant diseases. The reason for hospitalization was the threat of a fracture of the first lumbar vertebra due to a secondary lesion. The patient underwent CT-guided vertebroplasty and the first course of immunotherapy. Further treatment is ahead. “The only clinic where we found help and very good specialists. I express my gratitude to doctors...
read more
- Treatment lasts a year. Patient's review
Treatment lasts a year. Review from a patient November 11, 2019
Before us is a case of a medical error, a struggle for life and its successful outcome. Natalya was admitted to us in critical condition caused by a brain tumor. Thanks to the patient’s persistence, the treatment gave good results. She was not going to despair and give up, and we only gave her the opportunity to return to a full life. Natalya has been in another hospital for three years...
read more
Possible side effects
Immunotherapy helps fight cancer cells, but long-term use of immunomodulatory drugs can cause side effects. On the one hand, special treatment improves the quality of life of a cancer patient, on the other hand, it is dangerous, causing disruption to work:
- gastrointestinal tract;
- nervous system;
- liver and kidneys;
- endocrine organs.
Side effects from immune therapy can appear both during the treatment period and several months after the course. Therefore, immunomodulatory medications may be discontinued early. The most common side effects of immunotherapy are skin rash, fever, nausea and vomiting. Subsequently, the improper functioning of the immune system is corrected through hormonal therapy.
The fight against melanoma continues
Scientists continue to search for new effective drugs against melanoma. There is a large list of molecules that could become targets for checkpoint inhibitors in the future. Among them are proteins CD40, CD47, CD73, CD137, etc. They control various processes in the immune system.
Adaptive T-cell therapy involves using the patient’s own immune cells: they are isolated from the blood, “trained” to attack tumor cells, and then returned to the body. This is a very complex and expensive treatment method, it has not yet been fully studied. Perhaps one day such procedures will become available in cancer clinics around the world.
Research into antitumor vaccines is underway. There is hope that it will be possible to use measles, coxsackie, and vaccinia viruses as oncolytic viruses.
Progress does not stand still. As soon as new drugs against melanoma and other malignant tumors are registered in Russia, we immediately begin to use them. Patients at the Medicine 24/7 clinic receive the most modern, effective types of treatment. Contact us to learn about immunotherapy options for melanoma at our clinic.
The material was prepared by the deputy chief physician for medical work of the Medicine 24/7 clinic, candidate of medical sciences Sergeev Petr Sergeevich.
Percutaneous methods
Proposed alternatives to surgical treatment of RCC include percutaneous, minimally invasive, image-guided procedures such as percutaneous radiofrequency ablation, cryoablation, microwave ablation, laser ablation, and high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation.
• small incidentally discovered neoplasms in the renal cortex in elderly patients; • genetic predisposition of patients to the development of multiple tumors; • detection of bilateral tumors in a patient; • the presence of a single kidney in a patient and a high risk of complete loss of kidney function due to surgical removal of the tumor.
• life expectancy