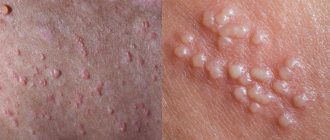
Atopic dermatitis is allergic dermatitis in a chronic form. This disease will be characteristic of those people who have a predisposition to atopy at the genetic level. The disease is characterized by a relapsing course. Symptoms include exudative or lichenoid rash, hypersensitivity to allergens and nonspecific irritants. It is distinguished by a clear seasonal dependence of relapses and periods of remission.
Heparin ointment, one of the remedies for atopic dermatitis
Drug therapy for atopic dermatitis
Drug treatment of atopic dermatitis is considered basic and involves the prescription of a wide range of drugs. Traditionally, the treatment regimen for the disease includes drugs from the group of corticosteroids, which can be administered orally or externally. Medicines from this group have different strengths of action: weak - hydrocortisone, medium - Elokom, strong - Dermovate. However, when prescribing such drugs, the doctor must take into account that recently their effectiveness has been questioned by many specialists, since often after taking them the patient develops a complication of a secondary infection.
Names of tablets for dermatitis
The most effective and popular drugs to help cope with dermatitis are still antihistamine tablets, which cope well with the external signs of skin diseases, remove irritation and itching, as well as swelling. Such drugs have only one side effect - they cause severe drowsiness.
The new generation of antihistamine tablets for dermatitis no longer have this drawback, and they are also non-addictive, so they can be taken for a long time. Among modern medications, the most effective are Zyrtec, Claritin, Loratadine, and Cetirizine.
For dermatitis, you can also take corticosteroids - these drugs contain hormonal substances, and in addition they provide a high-quality anti-inflammatory effect.
But this medicine should not be taken for a long time, as it can cause skin atrophy. Names of tablets for dermatitis (corticosteroids): Dexamethasone, Prednisolone, Flumethasone, and Fluticasone.
Also, when treating dermatitis, it is impossible to do without immunosuppressants. The substances included in these medications completely suppress the immune system, thereby helping the body reduce the skin reaction to a minimum. Among this group of drugs, Myelosan, Chlorbutin, and Cyclophosphamide are considered the most effective.
Glucocorticosteroids
The most commonly used drugs from the group of glucocorticosteroids include the following:
- afloderm - can have an antipruritic and anti-inflammatory effect, reduce swelling caused by inflammation, and constrict blood vessels;
- hydrocortisone - reduces pronounced redness of the skin, and also inhibits the development of edema at the site of inflammation and the manifestation of an allergic reaction;
- elocom - has a strong antipruritic effect and eliminates swelling;
- dermovate - immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory effects.
What pharmacological actions does Zyrtec have?
The drug belongs to the therapeutic group of antihistamines. They are used for treatment that is aimed at eliminating the source of the pathological process in allergic reactions. Tablets are widely used for atopic dermatitis.
The active microelement of Zyrtec, cetirizine, belongs to the group of antihistamines. It stops specific cell receptors that respond to the action of allergy neutral mediator compounds, in particular histamine. Therefore, when the level of histamine in the human body increases as a result of allergic phenomena, the active substance has an antihistamine effect.
The influence of the drug consists of the following pharmacological effects:
- Reducing the severity of irritation on the skin, which is caused by the stimulation of histamine sensitive endings.
- Eliminating swelling of soft tissues - blocking nerve endings to histamine.
- Reduced convulsions of the smooth muscles of the hollow organs - a pronounced increase in muscle tone, provoked by histamine.
- Elimination of rashes on the skin, which is considered the result of an inflammatory process.
Zyrtec also stabilizes tissue immune cells, which, when an allergic reaction develops, synthesize histamine, thereby reducing its level and other inflammatory mediators. The active component of Zyrtec does not provoke a sedative or hypnotic effect.
After taking the drug orally, the active component is instantly and completely absorbed from the upper digestive organs into the blood. It distributes evenly throughout all tissues of the body, followed by metabolism in cells to inactive metabolic products. They are usually excreted from the body in urine. The half-life is approximately ten hours.
Antihistamines
For atopic dermatitis, antihistamines are also indicated, which have an antiallergic effect on the body. These drugs effectively block the release of histamine, thereby eliminating swelling, redness and reducing severe itching. Drugs are prescribed in the form of tablets, less often - in the form of injections. Antihistamines include drugs such as loratadine, clemastine, suprastin and others. Fenistil gel has also proven its effectiveness, which successfully blocks P1 receptors, which prevents the release of histamine:
- clemastine - eliminates swelling and itching;
- suprastin - taking this drug blocks histamine receptors and prevents its release;
- loratadine - eases the allergic process and eliminates redness;
- ketotifen - blocks the release of mediators, thereby eliminating their effects.
Injections
The most severe is atopic dermatitis, characterized by a persistent chronic course with alternating periods of exacerbation and remission. If therapy with tablets and local agents does not have a therapeutic effect, hormonal drugs are administered by injection (subcutaneously or intramuscularly).
The most commonly used means are:
- Prednisolone;
- Dexamethasone;
- Hydrocortisone;
- Kenalog;
- Metipred.
For severe allergic dermatitis, antihistamines can also be prescribed in injection form. Clemastine, Suprastin, Tavegil, Promethazine are administered intramuscularly or intravenously.
Sedatives
Many patients diagnosed with atopic dermatitis complain of severe and even painful itching. This condition sooner or later leads to emotional and mental disorders. Therefore, for successful treatment it is extremely important to normalize the patient’s emotional background in order to prevent exacerbation of the disease. To eliminate tension and stress, the patient is prescribed sedatives - herbal remedies (tincture of passionflower or motherwort) and tranquilizers (tofisopam, alprazolam):
- tofisopam - taking 3-6 tablets of this drug helps relieve tension and has a stress-protective effect;
- bellataminal - has a calming effect on the body and relieves excitability;
- persen - has a hypnotic effect;
- atarax - taking 2 tablets of the drug per day promotes a mild hypnotic and sedative effect;
- amitriptyline - normalizes the emotional background and eliminates severe overstrain;
- diazepam - relieves anxiety and nervous tension.
Tablets for seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis occurs on the scalp and face if there is excessive colonization of the fungus malassezia furfur.
Antihistamines help with seborrheic dermatitis.
These drugs effectively relieve redness, itching and swelling. They should be taken for no more than a week (maximum 10 days). Antihistamines are chloropyramine, clemastine, loratadine, which relieve inflammation and relieve itching.
Seborrheic dermatitis can be treated with a variety of pharmacological agents. There are tablets for seborrheic dermatitis of various types and medicinal groups:
- Antihistamines - Citrine, Telfast, Loratadine;
- Complexes of minerals and multivitamins, including Merz dragees, nicotinic acid, Multitabs, Alphabet, vitamins B2 and A, as well as Perfectil.
If you start treatment in a timely manner, take pills for dermatitis and follow the doctor’s recommendations, the disease will go away quickly enough.
It should be noted that dermatitis on the torso and face is cured faster than seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp - its scalp. Longer therapy is needed here.
Antifungal tablets for seborrheic dermatitis
In some cases, antifungal tablets are used to treat seborrheic dermatitis.
They contain nizoral, lamifene, orungal.
Antifungal tablets for seborrheic dermatitis Orungal are an antimycotic used to destroy infections resulting from the appearance of pathogenic fungi. These can be yeast-like, yeast, mold forms. The drug has a fairly wide spectrum of action.
Terbinafine is an allylamine that works well against fungal parasites that affect hair, skin, and nails. It effectively destroys dermatophytes.
Exifin dermatitis tablets include terbinafine hydrochloride (a synthetic substance belonging to the allylamine group), and have a wide range of antifungal activity.
Small concentrations of terbinafine can have a fungicidal effect on dermatophytes, as well as molds and...
Sorbents and preparations for normalizing flora
An integral element of the treatment of atopic dermatitis is the normalization of intestinal functions. Often it is gastrointestinal pathologies that cause atopic dermatitis. Such drugs are prescribed in the acute period of the disease for one week. At the end of the course of treatment of dermatitis with sorbents, drugs are recommended that normalize the flora and restore the protective properties of the intestines:
- smectin - protects the intestinal mucosa and absorbs toxic substances;
- lignin - removes harmful microorganisms and toxins from the intestines, has a detoxification effect and increases local immunity;
- bifidumbacterin - increases nonspecific immunity and normalizes intestinal microflora;
- hilak forte - restores the intestinal mucosa, increases its protective properties and regulates the balance of intestinal flora.
Introduction
As is known, AD is an allergic skin disease that usually occurs in early childhood in individuals with a hereditary predisposition to atopic diseases, has a chronic relapsing course, age-related features of the localization and morphology of inflammation, characterized by skin itching and caused by hypersensitivity to both allergens, as well as to nonspecific stimuli. AD is also accompanied by sleep disturbances to varying degrees, disturbances in general condition, the development of neurotic symptoms, decreased or lost ability to work, and social maladjustment, which significantly affects the quality of life [1]. The main symptom of AD is itchy skin. Currently, the mechanism of the occurrence of itchy skin remains poorly understood. It is important that the nerve endings that perceive itching contain receptors that are sensitive to agents that cause itching, for example, histamine, which is the most important mediator of the allergic process, including in AD [2]. During allergic inflammation, histamine is released from mast cells and reaches high tissue concentrations. In the skin of patients with AD, the histamine content is increased, but at the same time, skin sensitivity in response to the application or intradermal administration of histamine is reduced. It is possible that in AD, the density and affinity of H1 receptors is reduced or there is an increased breakdown of histamine in the skin [3]. Some authors attribute to these features the low effectiveness of some H1-antihistamines in patients with AD. In practice, the use of antihistamines for AD is clinically justified, firstly, by many years of experience in their successful use and, secondly, by the lack of alternative antipruritic drugs [3, 4]. Their effect in AD is to competitively inhibit H1 receptors and normalize vascular tone in the skin. A decrease in peripheral vascular resistance and an increase in perfusion through affected tissues contribute to the normalization of metabolic processes. Thus, antihistamines modify the clinical effect observed in the early phase of allergic inflammation [5].
The rationale for the use of antihistamines in AD are the following:
- participation of histamine in the itching mechanism along with other mediators;
- the presence of concomitant respiratory manifestations of allergies, as well as prevention of their development;
- sleep disturbance and need for sedation (H1 antihistamines with sedative effect);
Cetirizine is a carboxylated metabolite of hydroxyzine. This drug has the following properties:
- high affinity for H1 receptors;
- low metabolic rate;
- the presence of an additional, possibly independent of the effect on H1 receptors, antiallergic effect;
This substance binds to a small extent with serotonin, dopamine and adrenergic receptors. Cetirizine almost does not penetrate the blood-brain barrier. These properties of the drug make it possible to prescribe it to patients for whom even a slight inhibition of central nervous system activity is undesirable. 70% of cetirizine is eliminated unchanged by the kidneys within 72 hours. The half-life of the drug is 10 hours in adults and 7 hours in children; in chronic renal failure, it can increase to 17 hours. The long elimination period allows the drug to be administered once a day, which allows to achieve patient compliance. Cetirizine does not inhibit the cytochrome P450 system. Cetirizine blocks the skin response to platelet-activating factor, an important mediator of chemotaxis in the late phase of the immune response, and reduces the histochemical formation of the morphological element [6].
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of the drug cetirizine dihydrochloride using the example of Cetrin® (Dr. Reddys Laboratories Ltd.) in patients with AD.
This study was conducted at the Department of Allergy and Skin Immunopathology of the State Scientific Center “Institute of Immunology of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia”.
Skin moisturizers
Since atopic dermatitis manifests itself as serious lesions of the skin, its treatment must necessarily include healing and moisturizing drugs. Moisturizers include preparations based on lanolin and thermal water. They are usually prescribed during the period of remission of the disease - during the chronic period of its course:
- ichthyol ointment - has a strong antiseptic effect, prevents infection of wounds and excessive keratinization of the skin;
- Isisa cream - activates metabolic processes in the skin, moisturizes the skin and restores its lipid layer;
- silver sulfathiazole - promotes faster healing of wounds and also prevents the spread of infection;
- Topicrem - eliminates the feeling of skin tightness, relieves itching and promotes wound healing;
- atoderm eliminates hypersensitivity of the skin, moisturizes it and restores the normal lipid layer;
- xemosis - has a calming effect on the skin and relieves irritation;
- solcoseryl - heals damaged tissues and activates restoration processes in the area of inflammation;
- actovegin - accelerates metabolic processes, thereby promoting faster wound healing;
- methyluracil ointment - has an anti-inflammatory effect and accelerates wound healing.
In the treatment of dermatitis, drugs of both local and systemic action are simultaneously used. The choice of one medication or another depends on the severity of the disease and its stage. If dermatitis occurs in the acute stage, it is characterized by the appearance of crusts and other lesions on the skin, so patients are usually prescribed the use of emulsions, aerosols and tinctures. If in the acute stage of the pathology the process of maceration (softening of the skin) is not observed, pastes and creams can also be used. Ointments are indicated for the treatment of chronic atopic dermatitis. Sedative and antihistamine medications are mainly prescribed in tablet form.
Reviews about the drug
I have always treated my allergies only with Loratadine or its analogue Claritin. This is the only medicine that really helps in the fight against allergy symptoms, stabilizing the condition and improving well-being. I never had any side effects during the entire period of taking it.
I try to start taking the drug on the eve of the flowering of plants, I take it when the poplars shed fluff and I try to always take it with me on business trips - an allergy can strike at any time. There is no addiction when taking it, which is very pleasing. Drowsiness and lethargy are also not about this drug.
I have suffered from allergies throughout my life. I tried a lot of drugs that belong to the antiallergic category. After Quincke's edema, I had to completely trust my doctor, who prescribed me Loratadine (or its analog Claritin) - this is the only medicine that really helped me cope with my condition and stabilize it. The drug has no side effects, which is especially important for me, a person who constantly drives.
Two types of medications are prescribed for the treatment of skin diseases:
- systemic action - injections, tablets, capsules, suspensions;
- local action - sprays, liniments, gels, creams, ointments, solutions.
In most cases, to eliminate signs of the disease and restore damaged skin, tablets for dermatitis on the face are used, which can have a systemic effect on the entire body.
Treatment also comes down to the use of hormonal ointments and creams with anti-inflammatory and anti-exudative effects. They must be applied strictly in short courses, since corticosteroids provoke side effects and also reduce the body's protective functions.
General principles for eliminating allergic dermatitis with tablets:
- Enterosorbents cleanse the body of allergens and irritating microelements.
- Antiviral, as well as antifungal, antimicrobial medications eliminate the cause of allergies.
- Corticosteroids neutralize the inflammatory process and also help restore the affected areas of soft tissue.
- Antihistamines eliminate itching, flaking, swelling and redness on the skin.
For dermatoses of autoimmune origin, drugs in tablet form are recommended that suppress the body's protective functions - immunosuppressants. With prolonged use, they reduce the severity of inflammatory processes in the skin. Due to this, the general condition of the patient improves and tissue restoration is accelerated.
When the rash spreads sharply, hormonal therapy is used. Corticosteroid drugs are used in short courses of three to five days, which is associated with the likelihood of adverse reactions. Nettle rash and other types of allergic diseases are eliminated with the following medications:
- "Triamcinolone".
- “Prednisolone.”
- “Dexazon.”
- “Fortecortin.”
- "Megadexan".
They have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect, so they instantly eliminate swelling and redness on the skin.
Non-drug treatment of atopic dermatitis
Physiotherapeutic procedures occupy an important place in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. However, they are prescribed exclusively during the period of remission. Also, the patient should not have any complications of the underlying disease. Physiotherapeutic procedures are always selected individually, depending on the severity of the disease. The main procedures include electrosleep, ultraviolet irradiation, electrophoresis, dynamic currents, and paraffin therapy.
During the period of remission, the patient is also indicated for spa treatment, which helps prevent possible relapses of atopic dermatitis. The maritime climate is considered the most optimal. Patients who have suffered from dermatitis for a long time confirm that in the summer atopic dermatitis is much easier or completely recedes. This is due to increased air humidity and exposure to sunlight on the skin. It has been proven that ultraviolet rays in moderate quantities have antipruritic, antiallergic and immunomodulatory effects on the skin. Also at resorts, in addition to sunbathing, radon and hydrogen sulfide are recommended for patients.
During the acute period of the disease, hospitalization of the patient may be required. Typically, inpatient treatment is resorted to in cases where outpatient treatment at home has not produced a positive effect. Hospitalization will also be required if the patient’s well-being rapidly deteriorates, caused by damage to most of his skin (for example, erythroderma may appear, which is characterized by severe peeling of 90% of the skin). The main goal of hospitalization is to isolate the patient as much as possible from the factors that provoked atopic dermatitis. These factors include stress, temperature changes and physical activity.
Atopic dermatitis: diet therapy
Drug and physiotherapeutic treatment are considered the basis of treatment for a disease such as atopic dermatitis. However, without correcting the patient’s diet, it will not be possible to get rid of the disease. Diet therapy is based on the following principles:
- exclusion from the diet of allergenic foods and histamine liberators (they contain elements that extract histamine from cells - the main factor in allergic reactions);
- eliminating the load on the liver, ensuring cleansing of the body from complications and consequences of allergies;
- providing the patient’s body with vitamins and elements that promote rapid skin regeneration;
- ensuring normal bowel function;
- keeping a food diary;
- decreased gluten intake as gluten tolerance decreases during allergies.
Each patient with atopic dermatitis is individually prepared with a special diet, taking into account the characteristics of the course of the disease, external provoking factors and area of activity. First of all, the patient must undergo several tests for allergenic foods, which are then excluded from the diet. If these tests have not been carried out, then all traditional allergens are excluded from the food.
- Meat and meat products: fatty pork, lamb, duck, goose and chicken (patients can eat rabbit, turkey and beef, preferring to stew or steam them).
- Fatty fish (trout, salmon, chum salmon, mackerel), mussels, crayfish, oysters, lobsters, crabs, caviar (you can replace them in the diet with pike perch, hake, cod).
- Fruits and vegetables: Replace orange and red varieties with white and green varieties. Melon, peaches, tangerines, oranges, persimmons, pomegranates, mangoes, strawberries, raspberries, wild strawberries, cherries, peppers, eggplants, beets, tomatoes, pumpkin are considered allergens. It is allowed to eat green pears, gooseberries, white cherries, plums and currants, cabbage, zucchini, potatoes, spinach, green peas, turnips.
- Cereals: white bread, semolina, pasta, and confectionery should be excluded from the diet. It is allowed to eat oatmeal and pearl barley. Buckwheat, bran bread, crackers, crackers.
- Dairy products are considered classic allergens that must be removed from the daily diet of a patient suffering from atopic dermatitis. You should not consume whole milk, cream, fermented baked milk, or cheese.
- Products that provoke the release of histamine: pineapples, strawberries, pork liver, chicken eggs, honey, coffee, chocolate, cocoa, alcohol, food additives (dyes, preservatives, flavor enhancers, flavorings) included in many semi-finished products.
- Products that put stress on the liver: margarine, confectionery fat, lard, strong tea or coffee, carbonated drinks, seasonings and sauces.
Correcting the patient’s diet involves not only excluding certain allergenic foods from it, but also introducing healthy foods into it. First of all, you need to add foods to your diet that will promote faster restoration of damaged skin. Omega-3 and omega-6 acids contained in vegetable oils cope most effectively with this task. For atopic dermatitis, it is useful to eat flaxseed, corn, sunflower, cedar and rapeseed oil as salad dressings.
With atopic dermatitis, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract is often observed, which is why the body's reaction to allergens becomes more pronounced and acute. Therefore, it is useful to introduce into the diet foods that ensure normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract: stewed zucchini or cabbage, baked apples, yogurt, barley, oatmeal, pearl barley and buckwheat porridge. It is also worth considering that the body of a patient with dermatitis very poorly absorbs gluten, which is found in large quantities in wheat. That is why it is advisable to replace products made from wheat flour with those made from buckwheat, corn or oatmeal.
Nutritionists advise that if an allergy to a certain product is detected, not simply exclude it from the diet, but replace it with a similar, but more healthy one. For example, cow's milk can be replaced with goat's, sheep's or even vegetable (soy) milk, and chicken eggs with quail's. Doctors also put forward a number of requirements for the food preparation process:
- To cook potatoes, you must first soak them in cold water for a couple of hours so that all the excess starch comes out of the vegetable;
- since heat treatment of foods significantly reduces the likelihood of an allergic reaction to them, it is better not to eat raw vegetables and fruits;
- Cook porridge using the third broth - the first two need to be drained after the water boils;
- When cooking meat, you should also drain the first broth.
What is an allergy? How does it arise?
An allergy is a condition in which the immune system begins to react to completely harmless substances (allergens) as if they were dangerous viruses and bacteria. Therefore, antibodies to them are formed and active substances (mediators) are released, which cause various manifestations of allergies.
At the same time, the formation of mediators aimed at combating real bacteria and viruses is suppressed. This explains why children with allergies often suffer from ARVI, and proves, first of all, the need for proper treatment of an allergic disease, and not the prescription of immunostimulating drugs.
Why do some people have allergies and others not?
Allergies are genetically determined diseases, i.e. The predisposition to developing allergies is inherited. So, if one of the parents suffers from allergies, the probability of an allergic disease in the child is 25-40%. If both parents suffer from allergies, the probability increases to 50-75%. It also depends on a number of other factors that contribute to the development of allergies in children, which include: the level of antigenic load (living conditions, unhealthy diet), ecology, etc.
Unfortunately, today every fifth person suffers from allergies, and according to some data, every third person. At the same time, in recent decades there has been a steady increase in the prevalence of allergic diseases.
Most often, allergic diseases begin in children with atopic dermatitis!
What is atopic dermatitis?
The first manifestations of this disease in everyday life are most often called diathesis and, accordingly, they do not take it very seriously. If your baby develops small rashes on his elbows or his cheeks turn red, it’s okay, it will pass. In this approach lies one of the biggest mistakes of parents - when children with minor skin lesions (exudative diathesis) are either not treated at all, or are treated incorrectly. Today it is reliably known that atopic dermatitis, which mothers, pediatricians, dermatologists and allergists begin to fight at the earliest stages, goes away in 92% of cases. This allows us to conclude that with proper treatment and care by adolescence, your child and you together have a chance to forget about this problem.
What are the first manifestations of atopic dermatitis?
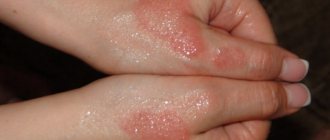
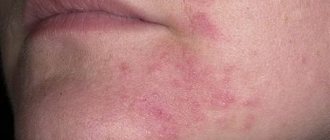
Atopic dermatitis, as a rule, occurs in a baby in the third month of life and can manifest itself as slight redness of the cheeks, rashes in the form of peeling, and dry skin. If treatment is not started in time, skin lesions can spread throughout the body and intensify; lesions with severe redness, weeping, cracks, and induration may appear. The disease is almost always accompanied by painful itching. Atopic dermatitis occurs in waves: a period of exacerbation is followed by remission. Problems may also arise from the gastrointestinal tract: bloating, regurgitation, unstable stool with mucus.
How dangerous is atopic dermatitis? What is the “atopic march”?
The “atopic march” is a consistent expansion of the range of allergic diseases in a child with age. That is, atopic dermatitis can serve as the initial step for the development of a systemic allergic disease: first - the upper respiratory tract (allergic rhinitis, laryngitis, adenoiditis), and then the lower respiratory tract (allergic bronchitis, bronchial asthma). Thus, 50% of children with atopic dermatitis subsequently develop bronchial asthma. By controlling the course of atopic dermatitis, doctors try to prevent the “atopic march” and the development of bronchial asthma.
The task of parents is not to miss the moment and to “capture” the disease at the very beginning of its appearance.
What to do and how to help the child?
Treatment of a child with atopic dermatitis should be comprehensive - the prescription of medications is selected individually, depending on the severity and severity of the disease, as well as associated complications.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis includes several items:
What are the causes of atopic dermatitis?
The most important thing in the treatment of any allergic disease is to identify and remove the allergens that are its cause.
In young children, food allergens (cow's milk, eggs, citrus fruits, chocolate, fish, poultry) are decisive in the development of atopic dermatitis. Sometimes skin reactions are caused by foods that are harmless in the generally accepted sense, for example, some cereals, potatoes, apples. This can be either one product or a whole group.
After 3 years of age, the importance of food allergies decreases, but the role of inhalation allergens (dust, pet hair, aquarium fish food, bird feathers, detergents, house dust mites, mold spores, etc.) increases. Therefore, in addition to diet, it is necessary to take measures aimed at reducing the concentration of allergens in the apartment where a child with atopic dermatitis lives. To do this, it is recommended: replace woolen, down blankets and pillows with synthetic, flannelette, and cotton ones; remove carpets from the premises, do not have animals, glaze bookshelves in cabinets, reduce their number, and also use modern vacuum cleaners to clean the premises (in the absence of a child), purchase an air purifier. In addition, daily wet cleaning of the apartment is mandatory. These measures help reduce the allergenic load on the child’s fragile immune system.
How to determine the significance of a product in the development of a disease?
At the first stage, you need to describe in detail to the doctor the connection between the occurrence of the child’s symptoms and the consumption of the products; the appearance of symptoms without eating foods; sequence of symptoms and their duration.
If necessary, the doctor may recommend an allergy examination: skin prick tests and/or determination of the level of specific immunoglobulins E (IgE) in the blood serum.
What is an allergy screening?
Allergy testing reveals only increased sensitivity to allergens contained in various products, and does not confirm the presence of an allergic reaction to them at the moment.
How to choose a diet?
The doctor concludes that it is necessary to exclude a certain product from the child’s diet. The exclusion of the allergen should be as strict as possible, while taking into account the possibility of its hidden presence as a component in other foods and the presence of cross-hypersensitivity. Thus, some foods have similar allergens to others, and cross-allergies can occur between them. For example, with an allergy to cow's milk, in 90% of cases there is an allergy to goat's milk and in 10% of cases to beef meat.
| Allergenic food product | Foods and non-food antigens that cause cross-allergic reactions |
| Cow's milk | Goat's milk, products containing cow's milk proteins; beef, veal and meat products from them, cow wool, enzyme preparations based on the pancreas of cattle |
| Kefir (kefir yeast) | Molds, mold cheeses (Roquefort, Brie, Dor-Blue, etc.), yeast dough, kvass, penicillin antibiotics, mushrooms |
| Fish | Sea fish, river fish, seafood (crabs, shrimp, caviar, lobsters, lobsters, mussels, etc.); fish food (daphnia) |
| Egg | Chicken meat and broth; quail eggs and meat; duck meat; sauces, creams, mayonnaise, including chicken egg components; feather pillows; medications (interferon, lysozyme, bifiliz, some vaccines) |
| Pork | cat fur |
| Carrot | Parsley, celery, L-carotene, vitamin A |
| Strawberry | Raspberries, blackberries, currants, lingonberries |
| Apples | Pear, quince, peaches, plums; birch, alder, wormwood pollen |
| Potato | Eggplants, tomatoes, green and red peppers, paprika, tobacco |
| Nuts (hazelnuts, etc.) | Other types of nuts, kiwi, mango, flour (rice, buckwheat, oatmeal), sesame, poppy, birch and hazel pollen |
| Peanut | Soybeans, bananas, stone fruits (plums, peaches, etc.), green peas, tomatoes, latex |
| Bananas | Wheat gluten, kiwi, melon, avocado, latex, plantain pollen |
| Citrus | Grapefruit, lemon, orange, tangerine |
| Beet | Spinach, sugar beet |
| Legumes | Peanuts, soybeans, peas, beans, lentils, mango, alfalfa |
| Plum | Almonds, apricots, cherries, nectarines, peaches, wild cherries, cherries, prunes, apples |
| Kiwi | Banana, avocado, nuts, flour (rice, buckwheat, oatmeal), sesame, latex, birch pollen, cereal grasses |
The most acute issue of diet therapy is in young children who have hypersensitivity to cow's milk proteins. If the child is breastfed, then foods containing allergens are excluded from the mother's diet. If breastfeeding is not possible, it is necessary to use special formulas for children with allergies to cow's milk proteins.
How long to stick to the diet?
The duration of exclusion of a significant product from the diet of children with food allergies depends on the allergen and is at least 1-2 years. Since the immaturity of the immune system and gastrointestinal tract plays a significant role in the occurrence of food allergies, most children, subject to all doctor’s recommendations, “outgrow” food allergies over time. In particular, by the age of 3, food allergies disappear in 70-90% of children. However, in relation to the most “evil” allergens, the reaction persists into older age. Thus, by the age of 5, hypersensitivity to cow's milk remains in 10% of patients, to eggs - in 20%, to peanuts - in 60% of patients.
What is a hypoallergenic diet?
Hypoallergenic (without specifying a specific allergen) is a diet that excludes from the child’s diet, first of all, the so-called triggers or provocateurs, which may cause an exacerbation of allergies. These include: non-perishable products containing dyes, spices, preservatives, stabilizers, food additives marked on the packaging with the letter “E”, canned foods, meat broths, chocolate, cocoa, red and orange vegetables and fruits, fish, seafood, tomatoes , mushrooms, honey, nuts, sauerkraut, sausages, pork liver, spinach. Triggers are also foods high in tyramine: cheeses (Roquefort, Camembert, Brie, Grillard, Cheddar, processed), brewer's yeast, pickled herring, avocado. However, as a rule, it is impossible to confirm an allergic reaction to them with examinations. This can only be done by observing the child.
This diet is recommended for all children with allergic pathologies, especially children under 3 years of age.
How are medications prescribed for atopic dermatitis?
Only a doctor should prescribe medications to a patient with atopic dermatitis, since the prescription of certain external therapy agents for each specific patient must be strictly individual. In addition, constant monitoring of the dynamics of the disease is necessary in order to timely replace the medication.
To exclude hypersensitivity to a topical drug, a pharmacological test should be carried out before its application to patients with hypertension. To do this, the product is applied to a limited area of healthy skin in the forearm for 15-20 minutes. In the absence of a local reaction, the drug can be used for treatment.
What drugs are used for exacerbation of atopic dermatitis?
According to the mechanism of action, external agents for relieving exacerbations can be divided into several groups:
External (topical) corticosteroid drugs that have a pronounced anti-inflammatory and antipruritic effect. Drugs in this group are divided, depending on activity, into classes: strong, medium and weak.
Calcineurin inhibitors, which have a local immunosuppressive effect, have anti-inflammatory and antipruritic effects.
When a secondary infection occurs, it is necessary to use antibacterial and antiseptic agents.
Most of these drugs are prescription drugs and are used only on the recommendation of a doctor.
An alternative to hormonal drugs can be a group of drugs based on activated zinc pyrithione (Skin-cap), which can be bought at a pharmacy without a prescription. The skin cap does not contain hormones, but at the same time has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect, antibacterial and antifungal effect.
The drug is selected depending on the severity and severity of clinical manifestations, using a stepwise approach.
In case of an acute inflammatory process, medications are prescribed in the form of lotions and wet-drying dressings (for weeping), emulsions, pastes, creams, mash and aerosols (the use of ointments that can contribute to weeping is contraindicated).
In case of severe exacerbations (severe redness, weeping, infiltration, swelling of the skin, cracks, etc.), it is necessary to prescribe strong topical corticosteroid drugs, as they have a pronounced anti-inflammatory, antiallergic and antipruritic effect. This leads to rapid relief of the pathological skin process and the disappearance of itching (for weeping - in the form of aerosols, emulsions; for acute inflammation without weeping - ointments, creams).
To reduce the burden of hormonal drugs, it is advisable to combine them with the non-hormonal drug Skin-cap, which has a complex effect (anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antifungal).
As a rule, for widespread manifestations, the use of antihistamines is recommended.
In some cases, with very severe exacerbations , it is necessary to use systemic (by injection or orally) corticosteroid and/or antibacterial drugs.
For mild and moderate exacerbation, it is advisable to use non-hormonal drugs based on activated zinc pyrithione (aerosol and Skin-cap cream), and topical calcineurin inhibitors.
As a rule, during an exacerbation, a secondary infection develops on damaged skin, which is most often of a mixed nature (microbes and fungi). Therefore, in local therapy, preference is given to drugs that have a complex effect (anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antifungal (Skin-cap)).
If necessary, antihistamines can be used.
Is it harmful to use corticosteroid drugs?
Drugs in this group should be prescribed only by a doctor for severe exacerbation of atopic dermatitis, when the severity of the disease outweighs the risk of side effects.
To prevent the development of side effects, you should not use these drugs uncontrollably, without a doctor’s prescription. It is important to follow the basic rules for prescribing topical glucocorticoids in children:
- Use only for the treatment and not for the prevention of atopic dermatitis.
- Do not apply simultaneously to more than 20% of the body surface.
- Use in short courses (no more than 14 days) (at the discretion of the doctor, in some cases the duration of their use can be extended to 3-4 weeks).
- If the skin inflammatory reaction decreases, switch to therapy with modern non-hormonal drugs (Skin-cap).
In what cases is it possible to use topical calcineurin inhibitors?
Local immunosuppressive drugs can only be prescribed by doctors for mild to moderate exacerbation of atopic dermatitis without weeping, not complicated by a secondary infection. It is not recommended to apply the drugs to skin affected by an acute viral infection. Their use is contraindicated for herpes virus infection. In the case of bacterial or fungal skin lesions, the use of calcineurin inhibitors is recommended after the infection is cured. Excessive sun exposure and UV therapy are not recommended during the period of drug use.
When to use Skin-cap?
The drug Skin-cap is used for moderate and mild exacerbation of atopic dermatitis. For severe exacerbations of atopic dermatitis, the drug can be used in combination with topical corticosteroid drugs. For rashes with pronounced swelling of the skin and weeping, Skin-cap aerosol is prescribed, after the weeping disappears, Skin-cap cream is prescribed.
The drug is recommended for rashes complicated by secondary infection, as it has a complex effect: anti-inflammatory, antifungal, antimicrobial (including against Staphylococcus aureus).
Timely use of the drug with minimal manifestations of atopic dermatitis allows you to stop and stop the development of inflammation, prevent the development of severe exacerbations, and reduce the frequency and duration of use of topical corticosteroids.
Is therapy necessary during remission of the disease?
It is necessary, since this therapy in most cases makes it possible to prevent the development of exacerbations and progression of the disease, and to stop the “atopic march”.
During the period of remission of the disease, basic therapy is selected for the patient, which consists of eliminating the allergen, proper skin care, and, if necessary, prescribing membrane-stabilizing drugs, antihistamines, products containing polyunsaturated fatty acids, vitamins and various physiotherapeutic procedures.
Taking care of your baby's skin - is it really that important?
In the skin of children suffering from atopic dermatitis, disturbances occur in the structure of the epidermis (upper layer of skin), which leads to disruption of its protective (barrier) function, loss of moisture, development of dryness and, as a result, itching, formation of microcracks, which further promotes penetration allergens and microorganisms and the development of inflammation.
Sometimes only proper care for atopic skin can prevent or sharply reduce the number of exacerbations of blood pressure, as it allows you to protect it from harmful external factors, retain moisture, and prevent infection. These measures can significantly increase the duration of remission.
Is it possible to bathe a child with atopic dermatitis? What cleaning products should I use?
A common mistake is to prohibit children with atopic dermatitis from bathing, especially when it worsens. It is necessary to bathe the child daily, which cleanses and moisturizes the skin, enhances the penetration of external medications, creates a feeling of comfort, and gives him pleasure. A 20-minute bath in the bath is optimal for saturating the stratum corneum with water. When swimming, you must follow the following rules:
- It's better to take a bath than a shower.
- Bathing water should not be hot (35-36? C) and, preferably, dechlorinated (water should settle for 1-2 hours).
- When bathing, you should not use washcloths.
- After bathing, you only need to pat your skin dry with a towel without wiping it dry. After swimming in a pond, dry it more thoroughly.
- For washing, use high-quality detergents (special soaps, gels, mousses) with a neutral pH of 5.5.
- In case of exacerbation of atopic dermatitis, it is necessary to use detergents with anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial effects (gel, Skin-cap shampoo).
How to properly moisturize your skin?
In patients with atopic dermatitis, the skin becomes depleted of lipids (ceramides, cholesterol, etc.) and other essential substances, which leads to loss of moisture and dryness, and disruption of the protective layer. Therefore, modern products for the care of atopic skin not only moisturize it well, but also partially replenish the defective structure of the epidermis, which helps restore the barrier function.
It is necessary to moisturize the skin daily with special creams recommended for atopic skin, at least 2 times a day, or rather, as much as the skin of a particular patient “requires”. At the beginning of therapy, with severe dryness, it is sometimes necessary to moisturize 4-5 times a day, then, as the skin recovers, you can switch to moisturizing 1-2 times a day (depending on the dryness). But every day!!!
Today there are a large number of different creams and emulsions for the care of atopic and dry skin - it is better to choose them at the pharmacy.
Nonspecific factors that provoke exacerbation of blood pressure are irritants (clothing made of wool and synthetic fabrics, tobacco smoke), excessive dryness and temperature (more than 22°C) in the apartment, emotions, stress, climatic factors (cold season, sudden climate change).
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic disease that requires long-term treatment, the success of which largely depends on active cooperation with the doctor, great attention and patience on the part of parents.
Doctors' efforts are aimed at suppressing allergic skin inflammation and reducing the effect of allergens. A properly selected diet, excluding food allergens from the diet, can significantly improve the condition and outcome of the disease. It is very important, under the supervision of a doctor, to choose effective and most importantly safe products for caring for your child’s skin.
Parents should try to properly organize the environment of an atopic child: eliminate contact with dust, mold, pollen, etc., establish a child’s daily routine, and create a favorable climate in the family.
Atopic dermatitis: treatment for children
Drug therapy for children with atopic dermatitis includes almost the same drugs as therapy for adults. Since atopic dermatitis is manifested by damage to the skin, itching and redness, local treatment is of great importance in its elimination. To eliminate skin damage, the child is prescribed moisturizing creams, antifungal ointments, local antifungal agents that destroy bacteria on the surface of the skin, and wet compresses with anti-inflammatory or antibacterial drugs. For systemic treatment, antibiotics, sedatives, glucocorticoids and antihistamines are prescribed.
It is extremely important to eliminate the allergen that triggered the development of the disease in the child at the very beginning of therapy. If this allergen is a food allergen, then it must be removed from the diet of the mother and child. In case of exposure to a household allergen, daily wet cleaning, regular change of bedding and good ventilation of the room are recommended. It is necessary to carefully adhere to the rules of child hygiene, and the baby should be bathed more often. using hypoallergenic products. All baby’s toys should always be clean, or even better, disinfected.
Particular attention is paid to a woman’s diet during breastfeeding. The mother needs to avoid eating any foods that may cause an allergic reaction in the baby. It is advisable to completely exclude nuts, chocolate, strawberries, canned food, coffee, citrus fruits, spices, smoked foods, honey, bananas, raspberries and foods with preservatives and dyes from the diet. As for the child’s diet, it needs to be expanded gradually - one new product should be introduced every two weeks. At the same time, the mother should observe the baby’s reaction. If a child shows the first signs of an allergy, the new product should be disposed of. If the baby is bottle-fed, then you need to buy him hypoallergenic formulas based on amino acids or goat's milk.
It is quite possible to prevent atopic dermatitis in a child. To do this, it is advisable for a woman who plans to become pregnant to undergo medical consultations and laboratory tests in advance. In particular, before pregnancy you need to quit smoking, give up coffee, start watching your diet and leading a healthy lifestyle. During pregnancy, it is recommended to avoid taking certain medications (if possible), as well as avoid products that contain preservatives and other unnatural food additives. After the birth of the baby, the woman will need to strictly follow a hypoallergenic diet.
Instructions for use
The non-hormonal allergy medicine Loratadine should always be taken before a meal (preferably 20-30 minutes before) regardless of the time of day.
The drug is indicated for the treatment of children (upon reaching the age of twelve) and adults. The recommended dosage is one tablet of the drug per day or 2 tsp. syrup (10 ml in a beaker with a scale).
The maximum course of treatment usually does not exceed two weeks. When prescribed individually, course therapy can last up to a month.
note
Loratadine is not prescribed to children under one year of age. Its safety for babies has not been proven, and no research has been conducted in this area.
Children should be prescribed Loratadine treatment by a pediatrician. The recommended daily dosage for young patients from three to twelve years of age is ½ tablet. If syrup is taken, the dose is one teaspoon.
Interesting to know
If the child’s weight exceeds 30 kilograms, regardless of his age, then the daily dose is equal to one tablet or two teaspoons of the drug.
Side effects
Following the instructions for use when treating a disease with Loratadine tablets, side effects virtually never occur. Treatment is almost always well tolerated. In rare cases, undesirable symptomatic phenomena may appear in the form of:
- aching pain in the back of the head and temples;
- dry mouth;
- drowsiness;
- unpleasant pulling sensations in the stomach;
- malfunctions of the liver and kidneys.
Anaphylactic shock and confusion are almost 100% excluded. When treating children, side effects are usually expressed in the form of anxiety, a constant desire to sleep, and slight lethargy.
Interesting to know
The occurrence of side effects from the use of Loratadine was detected in the same number of patients as in the case of placebo.
Providing a hypoallergenic environment
It must be remembered that exacerbation of atopic dermatitis can be triggered by inhaling dust containing mites. In the house, sources of dust include mattresses, blankets, pillows, carpets, carpets, upholstered furniture and curtains. Patients with atopic dermatitis are recommended to sleep on pillows and mattresses with synthetic filling, since fluff and wool are considered a favorable breeding ground for mites. They also belong to epidermal allergens. Bed linen must be changed at least twice a week (in this case, it must be boiled once a week). All sleep accessories that cannot be washed must be treated with special preparations.
It is advisable that the house have a minimum number of carpets, which must be treated with special agents that destroy ticks. It is recommended to replace all curtains and curtains with blinds made of polymer materials. During the flowering period, windows can be sealed, since plant pollen can aggravate the course of dermatitis. Areas of increased dust accumulation also include figurines, books, and souvenirs, which are best removed from the room or placed in cabinets.
Sanitary standards
Particular attention is paid to observing the rules for putting things in order in the room in which a person prone to dermatitis lives. Prevention of the disease involves systematic cleaning of the house: wet cleaning should be done every day, and general cleaning should be done once a week. In this case, it is advisable not to use conventional vacuum cleaners, since mites can penetrate through the filters and then spread throughout the apartment.
It is best to clean with special vacuum cleaners with air filters. When cleaning, it is advisable not to use products containing a lot of chlorine or strong fragrances. Since mold is considered one of the most common allergens, surfaces in the bathroom and kitchen should be wiped dry and treated with special products once a month.
Personal hygiene
A person prone to atopic dermatitis must comply with a list of personal hygiene requirements that will help him prevent exacerbation of the disease. First of all, you need to give up all cosmetics that contain alcohol. Particular attention should be paid to bathing: give preference to the shower, swim for no more than 20 minutes in warm water with a temperature no higher than 36 degrees, do not visit public bathing places (especially swimming pools). People prone to dermatitis are advised to wear underwear made from natural materials and loose clothing that does not fit tightly to the body.
Effective folk remedies
To alleviate the patient's condition, to alleviate the symptoms of itching, prepare an infusion: combine in a bowl an equal amount of dried nettle leaves, tricolor violet flowers, crushed burdock root, and yarrow flowers. Mix everything thoroughly.
Pour 1 cup of the mixture into a large saucepan and add 3 liters of boiling water. Close the lid and insulate the pan. After 2-3 hours, strain the prepared infusion and pour it into a prepared bath of water. Take 20-30 minutes. Then dry the skin with a towel, lubricate with anti-allergenic or regular baby cream.
Apply freshly squeezed apple or cucumber juice to the affected skin as often as possible. This remedy will effectively relieve burning and itching.
Mix equal amounts of glycerin, fresh whole milk, rice flour (starch). Mix everything thoroughly. Apply the resulting paste in a thin layer to damaged skin and leave overnight. In the morning, rinse with warm water.
When taking medications for treatment using folk remedies, it is necessary to follow a special diet with the complete exclusion of foods that cause allergies and aggravate the disease. Be healthy!
Proper skin care
Since the skin of a person prone to dermatitis is usually very dry, this provokes damage to the skin, which allows viruses, bacteria and fungi to penetrate into it. This problem can be eliminated if you choose the right cosmetics for cleansing, moisturizing, nourishing and regenerating the skin. To cleanse the skin, it is not recommended to use cosmetics that contain alcohol, preservatives and fragrances, as they aggravate dryness. The best option would be products with a neutral acid-base balance and a hypoallergenic composition.
To maintain an optimal balance of skin moisture, it is advisable for the patient to use products containing thermal water, which, in addition to moisturizing, also helps eliminate itching. Moisturizing compresses are indicated to prevent itching. Daily skin care must include nourishing creams containing almond, coconut or olive oil. If the patient has been sick before, his skin usually recovers from damage over a long period of time. Therefore, it is advisable to eat foods that are rich in vitamins A, C, B, E, PP, as they activate the regeneration processes of the epidermis.
Exclusion of nonspecific factors
Prevention of the disease also involves the exclusion of all nonspecific factors that are not allergens, but can aggravate the course of the disease. Triggers that need to be addressed to prevent the disease include:
- Stress aggravates the course of the disease. It has been proven that during times of strong experiences and emotional discomfort, itching and rashes on the skin become more intense. This is why a quarter of atopics begin to develop psychological disorders over time. To combat stress, doctors recommend playing sports, getting proper rest, engaging in various hobbies, and using techniques that help relax muscles.
- Excessive exercise - sweating increases during intense exercise. In combination with tight clothing, this process increases the itching of the skin. Atopics should not give up sports altogether, but it is still advisable to reduce physical activity.
- Climatic influences - temperature changes have a negative impact on the course of the disease, as they can aggravate it. It has been proven that exacerbation occurs during the cold season, so it is advisable to use protective creams in autumn and winter. In the warm season, atopics need to protect their skin from exposure to direct ultraviolet rays. In the room where an atopic person lives, a comfortable microclimate must always be maintained: the air temperature should not exceed 23 degrees, and the humidity should not exceed 60%.
- Diseases of other body systems aggravate the course of the pathology, so it is extremely important to detect and treat them in a timely manner. Diseases that can provoke or aggravate the course of atopic dermatitis include weak immunity, dysfunction of the endocrine and nervous systems, gastrointestinal diseases (hepatitis, cholecystitis, gastritis), ENT diseases.
Attention!
This article is posted for informational purposes only and under no circumstances constitutes scientific material or medical advice and should not serve as a substitute for an in-person consultation with a professional physician.
For diagnostics, diagnosis and treatment, contact qualified doctors! Number of reads: 1776 Date of publication: 08/01/2018
Dermatologists - search service and appointment with dermatologists in Moscow
List of antihistamines for skin allergies
If you have a skin reaction to an allergen, then you cannot independently compile a list and prices of medications in alphabetical order that help with allergic rashes and which you should try on yourself. You should contact specialists.
At an appointment with an allergist or dermatologist, patients ask: “Please advise which antiallergic medications to take? Tell me the names of effective antiallergic drugs for itchy skin?”
List of medications for skin allergies
The doctor will not recommend the first thing he comes across; he can help an allergy sufferer when he conducts a comprehensive examination.
The doctor is obliged to talk with the allergy sufferer, find out about other diseases, drug intolerances, and be sure to conduct an examination to determine the cause of the disease.
Only after this can the doctor tell you the name of the antihistamine that can help in the treatment of skin allergies, the most powerful in a particular case.
Despite the fact that allergic dermatosis manifests itself externally, it is necessary to treat it from the inside.
Why is this important to know? Because you need to choose the right dosage form of the drug, that is, use primarily not external medications (cream, ointment), but drugs in the form of tablets, drops and solutions.
Itching due to skin allergies
The choice of medications for skin allergies today is huge: there are good Russian medications known since Soviet times, as well as modern anti-allergy drugs that do not cause drowsiness.
Further in the article we will analyze the most famous allergy pills and make a small rating of the best for adults and children.
All antihistamines prevent the production of histamine and block the development of the following symptoms: redness, itching, swelling of the skin, and also normalize the patient’s blood pressure and breathing: they block spasms in the bronchi and laryngeal swelling. A sign of a strong remedy is also a decrease in lacrimation and redness of the whites of the eyes and eyelids, the disappearance of allergic cough and runny nose.
1st generation antihistamines
The first generation of antihistamines are very rarely prescribed nowadays. They have a number of common features: the drugs are inexpensive, but cause side effects that seriously affect the allergy sufferer’s body and his lifestyle.
Common features of this group of antihistamines:
- Low cost (the main price tag most often does not exceed 300 rubles);
- A short-term effect (you need to drink them several times in one day) and quick addiction (they need to be alternated with other medications from this group every couple of weeks).
Symptoms of using first generation antihistamines:
- increased heart rate (tachycardia).
- constipation.
- blurred vision.
- depressed state of the nervous system (the appearance of drowsiness and a decrease in the speed of reaction to environmental factors (decreased concentration of attention)).
1st generation antihistamines
All these side effects complicate the patient’s existing lifestyle and daily routine. These antihistamines can make a person less mobile.
Antihistamine drugs from this group are not popular, except for Suprastin, a cheap drug from the list of essential drugs, established by law as vital. It is better to take these drugs for adults, as they have less side effects. Let's look at them in a table that shows their differences.