Risk factors for melanoma
The main cause of tumor development is considered to be excess ultraviolet radiation. Ultraviolet light, whether natural or artificial, damages the DNA of cells.
The body has a powerful gene restoration system, but it is not omnipotent. Over time, changes accumulate. Cells cease to obey body signals that regulate their division and growth. They lose the ability to die naturally and begin to multiply uncontrollably - becoming malignant. In addition, excess sun impairs the immune system, reducing the activity of natural killer cells. It is these cells that are responsible for identifying and destroying malignant tumors at an early stage. Mutations that provoke the development of malignancy often occur in the body, but usually the immune system manages to detect and destroy them at the stage of a single altered cell.
Sunburns received in infancy and childhood are especially dangerous. But in approximately 10% of cases, melanoma in a child is hereditary and is caused by a congenital mutation of genes that normally suppress tumor growth.
The main predisposing factors that increase the likelihood of developing a neoplasm:
- Appearance features: pale skin, blond or red hair, blue or gray eyes, freckles. Such babies belong to the so-called phototype 1–2, which is especially sensitive to the sun.
- Previous sunburns, the duration of which does not matter.
- Frequent sun exposure.
- A large number of moles (more than 50).
- Pigmented formations with an atypical structure are dysplastic nevi. These are moles with uneven contours and mixed colors.
- Heredity: cases of melanoma in blood family members.
- Xeroderma pigmentosum is a hereditary disease in which the activity of the enzyme that restores DNA damaged by ultraviolet radiation is disrupted. It manifests itself as increased sensitivity of the skin to the sun and active uneven pigmentation even after a short stay in the sun, with the further development of dermatitis and skin atrophy.
- Existing congenital giant nevi.
Is it possible for melanoma to appear in children and how dangerous is it?
Melanoma is a malignant neoplasm of the skin. An aggressive tumor characterized by rapid metastasis. Melanoma in children is a rare pathology, but its diagnosis and treatment at this age is extremely difficult.
Causes and features of melanoma
Among childhood oncopathologies, skin cancer accounts for 1% of all cases of disease. Melanoma is more common in adolescent patients than in infants or kindergarteners.
Under normal conditions, skin pigment cells do not change or grow chaotically. The reasons that cause uncontrolled division of melanocytes have not been determined at the current stage of medical development.
Features of the disease:
- the probability of rebirth does not depend on gender or race;
- the tumor may be dark and unpigmented;
- localization - dermal layer, mucous membrane of the eyes, mouth, vagina, rectum. In rare cases, subungual melanoma is diagnosed;
- quickly metastasizes to regional lymph nodes. Even if they are not affected, they are removed;
- pathways of metastasis – lymphogenous and hematogenous;
- There is no reaction of the body to the appearance of a tumor. This explains the rapid spread of malignant cells.
Does it happen in children?
Melanoblastoma manifests itself in 2 age periods. These are 4–6 years old and 11–15 years old. The favorite localization of the tumor is the neck, head, legs, and places under the nail. According to medical statistics, in 50% of cases, carcinoma develops from a congenital pigment spot of a benign nature.
Types of skin cancer in children:
- Congenital form - develops during the pregnancy stage.
- Infantile melanoma - appears during the first year of a baby's life. Formed from complex nevi.
- Classic - symptoms, causes, course of the disease are similar to the manifestations of pathology in adult patients.
This formation is distinguished from nevi by the following characteristics:
- size;
- rises above the skin;
- there is no hair on the neoplasm.
Risk factors in infants and young men
The reasons for the degeneration of nevi into a malignant formation at the current stage of development of medicine are not known. But there are a number of factors that contribute to the development of skin carcinoma:
- The presence of a congenital large birthmark in a child.
- Northern phenotype - blondes with light skin, blue or gray eyes.
- Albinism.
- Toxic effects on the fetus during gestation, severe intrauterine viral diseases.
- Exposure to ultraviolet radiation - excessive sun exposure, extensive sunburn, love of tanning beds.
- A large number of moles on the skin.
- A strong family history – cases of skin cancer with a fatal outcome in close relatives.
Features of treatment for children
At an early stage, the disease is curable. Parents should contact a medical facility if there are any changes in the appearance and size of the birthmark, the appearance of ulcers, or bleeding.
The disease is treated by a pediatric dermatologist and oncologist. For diagnosis, the following measures are indicated:
- inspection and analysis of complaints;
- excisional biopsy - a smear impression of the skin. It is examined under a microscope. Traditional tissue sampling is prohibited - melanoma can grow rapidly;
- dermatoscopy – examination of the skin using a microscope;
- CT scan – to determine the presence of secondary tumors in the lymphatic system, liver and lungs.
Treatment of malignant skin tumors is difficult. They respond poorly to chemotherapy drugs and radiation.
At the initial and second stages, surgical removal of tumors is indicated. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia. The volume of intervention depends on the size of the tumor and the degree of damage to the lymphatic collectors. If lymph nodes are involved, they must be resected.
In later stages, complex therapy with aggressive drugs is used.
Important! The doctor must prescribe at least 4 different antitumor drugs. These are dangerous drugs. They reduce the child's immunity. Additionally, the use of antibiotics, antimycotics, and vitamin complexes is indicated.
The main chemotherapy drugs for malignant changes in the dermis:
- Doxorubicin - dosage is determined individually for each episode of treatment. It is administered intravenously. The installation of an infusion pump is shown. This allows you to clearly dose the administration of the drug strictly on time.
- Vincristine - administered intravenously. Contact with the skin or muscle layer should be avoided. Destroys the protein component of cancer cells.
- L-asparaginase – the drug reduces the production of asparagine. This protein is necessary for the proliferation of tumor cells. It is administered intravenously, dosages are selected strictly individually.
- Dacarbazine - used in pediatric practice to reduce the rate of cell growth.
The treatment is long-term. It is carried out on the basis of a medical institution. Vitamin complexes for melanoma are indicated to be administered through infusions.
At stages 3 and 4, radio irradiation is used locally or with nearby lymphatic collectors. Physiotherapy is not used as a means of active therapy. It is prescribed during the recovery period.
There are no traditional methods for treating melanoma, including juvenile melanoma. Delay will lead to dire consequences.
Forecast and prevention of occurrence
The prognosis is unfavorable. Currently, the five-year survival rate is about 50%. Parents should pay attention to small changes in nevi on the body of a newborn baby, older toddlers and teenagers.
Prevention of malignant neoplasms – protecting the child’s delicate skin from exposure to ultraviolet radiation. It is better to start tanning and the sea at the age of three. If you decide to introduce your child to the sea, then sunbathe at the recommended time and under an awning.
Melanoma in infants is a rare disease. But, according to doctors and parents, she is extremely aggressive. Monitor the condition of the child's skin. Especially if the family history is burdened with malignant pathology of any organ. This is the case when it is better to examine the mole - its size, color and symmetry - than to then fight the disease and remove it during surgery.
Link to main publication
articles:
Loading…
Didn't find suitable advice?
or see all questions...
Source: https://ProMelanin.ru/bolezni/melanomy/u-detej.html
Types of melanoma
By type of growth
- superficial spreading (70% of cases): grows mainly horizontally and relatively slowly;
- nodular or nodular (15%) – grows mainly in the thickness of the skin, relatively quickly penetrates into the deep layers, which is why it has an unfavorable prognosis;
- acrolentigionous or subungual (10% of cases) - located on the tips of the finger and, as the name suggests, under the nail plate;
- lentiginous, also known as Dubreuil's melanosis, also known as Hutchinson's malignant freckle (5%) - usually develops on the face at the site of a large pigment spot with uneven edges, such pigment spots are often described as “ugly”, “ugly”;
- achromatic or non-pigmented melanoma - white, pink or flesh-colored.
According to cellular (histological) structure
- epithelial;
- spindle cell;
- mixed;
- small cell.
According to clinical manifestations
- local – limited to one neoplasm;
- locally advanced;
- disseminated - many foci, including metastases.
By depth of distribution (level of invasion according to Clark)
- I - within the epithelium, without reaching the basement membrane - the boundary between epithelial cells and deeper skin structures;
- II – penetrates the basement membrane, spreading to the germinal layer of the dermis;
- III – penetrates the reticular layer of the skin, but does not yet grow beyond its limits;
- IV – to the level of the sweat glands, that is, it goes beyond the skin itself (dermis);
- V – penetrates into the subcutaneous fat layer.
Stages of melanoma growth according to Breslau
- thin melanoma: up to 0.75 mm;
- intermediate: 0.76 – 3.99;
- thick: more than 4 mm.
Skin melanoma in a newborn
Melanoma is a malignant tumor that occurs in people of all ages, including newborns and adolescents.
Melanoma in children is a rare disease, but due to late diagnosis, it progresses to the next stage of development, which requires a full examination and a long course of treatment.
If melanoma is detected, it is necessary to seek qualified help as soon as possible, as there is a risk of developing serious complications.
Causes of melanoma in childhood
All the reasons that can affect the appearance of melanoma are still not known for certain. One of the main reasons is considered to be changes in the structure of the skin, which influenced the transition of melanocyte cells into malignant neoplasms.
Does melanoma occur in children as a consequence of various injuries - yes. Melanoma in children can develop for various reasons, including mechanical damage.
You can see what melanoma looks like in children in photos on the Internet. Symptoms and symptoms of melanoblastoma exist in children in various manifestations. The child's symptoms will vary from person to person.
The development of the disease can be influenced by many factors, including the individual characteristics of the body. The most common causes of melanoma in children include:
- predisposition at the genetic level. The risk of developing the disease increases if one of your relatives has or has once been diagnosed with skin cancer;
- negative impact on the body of a pregnant woman of chemicals, including paints or paint products;
- the presence of severe diseases in a woman during pregnancy caused by infections that lead to mutational changes in the fetus;
- viral diseases suffered during pregnancy, especially those leading to complications;
- a specific reaction of the child’s skin to sunlight, prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation or sunburn;
- mechanical damage to areas of skin covered with moles or age spots;
- hormonal disruption in the body, both of the mother during intrauterine development and of the child;
- the presence of atypical moles or negative phenomena that appeared after dysplastic nevus syndrome;
- an excessive number of moles on the skin that are benign in nature.
It is worth noting that children who suffer from albinism or have too light skin color are most susceptible to melanoma.
Forms of melanoma in children
There are several forms of melanoma in children. Each of them differs in the form of manifestation and further development. Types of melanoma:
- intrauterine. This type of disease occurs in the child while still in the womb. A common reason for its appearance is the negative impact of environmental factors on the body of a pregnant woman. Intrauterine melanoma can be detected both during diagnostic studies of the fetus and immediately after birth. Most often it manifests itself in the form of changes in areas of skin on the baby’s face or head;
- infantile. Typical for children under one year of age. Initially, such formations are benign in nature, but over time and under the influence of various factors they turn into malignant. The most common cause of transition is excessive sun exposure;
- youthful. Appears in children under the age of fifteen. This type of disease is most often diagnosed only in the later stages. This is due to the fact that initially the neoplasms are benign in nature and look like moles or warts. It has the properties of rapid change towards a malignant tumor. The main difference from other species is the presence of a standard color for moles, containing a variety of shades of brown. Most often it forms on the neck, head or limbs;
- teenage It affects teenagers aged 15 to 19 years. The cause of occurrence is a sharp change in hormonal levels due to puberty. Most often diagnosed on the extremities;
- amelanotic. It is always malignant and capable of rapid development. Promotes the development of metastases. It can be treated only in the early stages of development. The main distinguishing feature is the presence of gray color. Most often diagnosed on the feet, fingers or back.
Melanoma is also divided into 5 stages of development. Each of them differs from each other in the area affected and the depth of penetration into the skin. The last stage is characterized by the appearance of metastases and spread to other areas.
Melanoma is a malignant growth of the skin
TNM stages
This classification is used by all oncologists in the world, determining treatment tactics and prognosis.
- T1: thickness up to 1 mm;
- T2: 1 to 2 mm;
- T3: 2 to 4 mm;
- T4 – thicker than 4 mm.
When determining the stage of a tumor, its diameter does not matter, only the depth of penetration of malignant cells is important.
- N1: damage to 1 regional lymph node;
- N2 – metastases to 2–3 nearby lymph nodes or satellite metastases (screenings of tumor cells at a distance of up to 2 cm from the primary formation);
- N3 - more than 3 regional lymph nodes are affected or they form conglomerates, or lesions in the lymph nodes are combined with satellite metastases.
Regional lymph nodes are considered to be the ones into which lymph drains from the tumor-affected area.
- head, neck – parotid, submandibular, cervical, supraclavicular;
- chest - axillary;
- arm - in the area of the ulnar fossa and axillary;
- lower back, buttocks, abdominal wall, anus and genital area - inguinal;
- leg – popliteal, inguinal.
- M0 – no distant dropouts.
- M1 – there are distant metastases.
Characteristics of stages
- Growth depth is up to 2 mm, lymph nodes are not affected, there are no metastases;
- Up to 4 mm in skin thickness, lymph nodes are not affected, there is no metastasis;
- Thickness more than 4 mm, or any depth of tumor growth with existing damage to regional lymph nodes;
- Any condition of the tumor and lymph nodes with the appearance of distant metastases.
Indications and types of surgical intervention
Surgery is the main and most effective treatment for melanoma. With early diagnosis of the pathological process, the procedure can be prescribed after special preparation of the child’s body (taking drugs to strengthen the immune system, therapeutic methods).
If melanoma is detected in an advanced form, then surgery is prescribed as an emergency. Surgery can completely eliminate the disease, but only if it is carried out in a timely manner.
The following types of surgical procedures are used to eliminate melanoma:
- cryosurgery (the effect on skin formation is carried out using low temperatures);
- radiation therapy (surgery is prescribed if the disease has reached the third or fourth stage of development);
- electrosurgical excision of the tumor (the affected area of skin is removed, and the edges of the epidermis are brought as close as possible, but not completely sutured).
Clinical manifestations
In the early stages of growth, skin melanoma in children is completely curable. Therefore, you need to pay attention to early symptoms indicating possible malignancy of the mole:
- begins to grow rapidly;
- it becomes asymmetrical, compacted areas appear;
- the mole begins to be “felt” - itching, tingling, burning, a feeling of skin tension and other unpleasant sensations appear in this area; it darkens or, conversely, becomes discolored;
- there is redness around;
- hair falls out from the surface of the nevus, if it was there before;
- cracks, wart-like growths, and areas of bleeding appear.
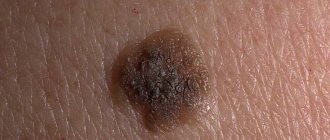
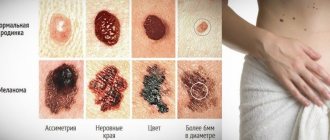
ABCDE criteria
Used to determine the danger of a nevus:
- A – Asymmetry. Asymmetry of the spot.
- B - Border irregularity. Fuzzy boundaries
- C - Color irregularity. Uneven coloring.
- D – Diameter. More than 6 mm (diameter of the eraser at the end of the pencil).
- E – Elevation. Raised surface (option: variability).
As the tumor grows, its surface becomes ulcerated. Satellites may appear around the primary lesion - small neoplasms, local metastases. In rare cases, the primary lesion can spontaneously regress and disappear, leaving skin and distant metastases.
The lymph nodes involved in the process increase in size and become painful.
How to detect?
Many types of formations can appear on the skin, which may visually resemble melanoma. The disease can be suspected by the presence of several signs.
If they appear, it is necessary to contact a medical institution as soon as possible
The most alarming sign of melanoma is bleeding of the skin lesion. This symptom most often accompanies the complication stage of the pathological process.
immediately consult a doctor if your child has the following signs:
- the child’s moles and age spots begin to cause discomfort or are accompanied by itching;
- nevi have changed their color and structure;
- pathological inclusions appeared in nevi;
- The edges of the mole have become uneven.
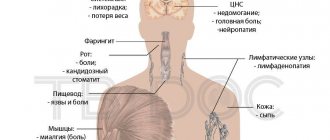
Distant metastases
They show signs of damage to those organs in which dissemination occurred.
- lungs - cough, first dry, then with purulent discharge and hemoptysis;
- liver – increase in size, jaundice, ascites (fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity);
- bones – areas of osteoporosis, pathological fractures;
- brain - headaches, dizziness, vomiting, loss of sensitivity in various parts of the body, seizures.
In addition to the skin, melanoma can also occur in other organs - on the mucous membrane of the mouth and gastrointestinal tract, and genitals. In such a situation, the disease goes undetected for a long time and is often discovered only after metastases appear in vital systems.
Melanoblastoma can also develop in the choroid of the eye - the so-called uveal melanoma. It is manifested by decreased vision and the appearance of dark spots before the eyes. As the tumor grows, the color of the iris changes, dark spots appear on it, and the vessels of the sclera dilate. Hemorrhages appear in the retina, which further impairs vision. After the malignant neoplasm extends beyond the eyeball, exophthalmos (bulging eyes) becomes noticeable. Distant metastases then occur, as with other types of melanoblastoma. Uveal melanoma is usually identified by an ophthalmologist during a fundus examination.
Features of the disease
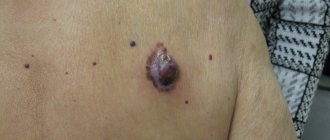
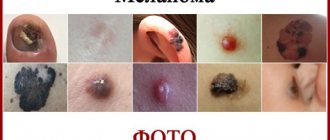
Nail melanoma is a type of cancer. Characterized by rapid development and reproduction. The prevalence of this oncology is 4% of known cancers. Experts say that the most dangerous place is at the nail on the thumb of the right hand.
The initial stage goes unnoticed. It is difficult to detect a malignant tumor externally. The nail is painted in dark brown, dark blue colors. The tumor can also be colorless. This happens due to the small amount of melanin inside.
Slowly the structure of the nail is destroyed. Melanoma leaves no time to recover. Timely detection facilitates a quick response and the doctor prescribes treatment. It will be easier for the doctor to establish the correct diagnosis.
Neither hands nor feet are protected from damage. There is a weak point under the big toe nail. He suffers from a high risk of injury. Even if the formation does not have any shade, you will notice a change in the appearance of the finger on your hand immediately. Try to look closely at every suspicious detail.
Diagnostics
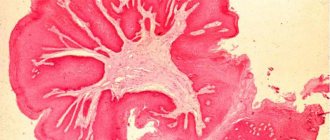
- For early diagnosis of skin melanoma, it is examined using a dermatoscope - a special device that allows you to examine a suspicious mole under high magnification. If the doctor detects signs of malignancy (changes in blood vessels, the nature of pigmentation, the appearance of a blue-white veil), the suspicious mole must be removed and subjected to histological examination and examination under a microscope. Under no circumstances should moles be removed using a laser, cryodestruction or other methods, after which there is no material left for research.
- In order to detect metastases in the lymph nodes in a timely manner, the lymph nodes that are located first along the lymph flow from the affected area are examined. This method is called sentinel lymph node biopsy.
- To identify distant metastases, radiography, ultrasound, computed tomography and MRI are used.
- The main criterion for diagnosis is histological confirmation. Without it, it is impossible to talk about the malignancy of the tumor.
- Juvenile melanoma, also known as nevus Spitz (Spitz), requires special attention in terms of differential diagnosis. This tumor is formed by melanocytes, but does not contain melanin and is benign, despite its name.
What does skin melanoma look like in children: photos and symptoms of the initial stage
Melanoma in children, as well as in adults, most often develops from moles (nevi).
What is the trigger for the degeneration of a pigment spot into a malignant tumor has not yet been fully elucidated. There is a strong opinion that an overdose of ultraviolet radiation can greatly harm children with congenital age spots. From early childhood, it is necessary to monitor the number and size of age spots. Their growth is an alarming sign.
At the first “bells” that may be harbingers of degeneration, you need to sound the alarm and consult a doctor.
Description and characteristics
What does the pathology look like? Skin melanoma - photo:
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer and is one of the malignant tumors of the skin. In most cases, the pathological process progresses in the area of existing pigmented areas of the epidermis.
The risk of developing the disease increases with skin injuries that a child may receive at birth or in subsequent years of life. Melanoma is characterized by a rapid transition from mild to severe form.
Melanoma can occur in the following areas of the skin:
- head;
- neck;
- limbs;
- soles of feet;
- back area.
Melanoma has a neuroectodermal etiology . The disease can recur in almost all organs of the body through hematogenous and lymphogenous routes.
First, metastasis occurs in the lymph nodes, then the pathological process spreads to the liver, lungs, brain and bone tissue.
Melanoma is considered one of the most malignant tumors , difficult to treat. The prognosis for this disease is in most cases unfavorable.
Read about the indications for the removal of hemangiomas in children here.
What triggers the occurrence?
The reasons for the development of melanoma in children by modern medicine remain incompletely studied.
The main factor that provokes the disease is considered to be a violation of the structure of the skin, as a result of which melanocytes become malignant.
certain prerequisites are always necessary , which may relate to the individual characteristics of the child’s body, heredity or negative factors that arise during the stage of intrauterine formation of the fetus.
The following factors can cause the development of melanoma in children :
- Genetic predisposition (having relatives diagnosed with skin cancer increases the risk of the disease).
- Exposure of a woman’s body to harmful substances, which include paint, chemical compounds or paint products (especially during pregnancy).
- Development of mutation in the fetus under the influence of severe infectious diseases during pregnancy.
- Consequences of viral infections in the body of a pregnant woman.
- The specific reaction of a child’s skin to exposure to sunlight.
- Injury to moles and pigmented areas of the skin.
- Atypical moles and consequences of dysplastic nevus syndrome.
- Consequences of insolation (excessive ultraviolet radiation of the child and frequent sunburn).
- The presence of an excessive number of moles on the skin (benign in nature).
- The child’s skin tone is too light (such children are called “albinos”).
How to get rid of atheroma on a child’s head? Find out the answer right now.
How to detect?
Many types of formations can appear on the skin, which may visually resemble melanoma. The disease can be suspected by the presence of several signs.
If they appear, it is necessary to contact a medical institution as soon as possible
The most alarming sign of melanoma is bleeding of the skin lesion. This symptom most often accompanies the complication stage of the pathological process.
immediately consult a doctor if your child has the following signs:
- the child’s moles and age spots begin to cause discomfort or are accompanied by itching;
- nevi have changed their color and structure;
- pathological inclusions appeared in nevi;
- The edges of the mole have become uneven.
Prognosis for subungual melanoma
The prognosis for subungual melanoma depends on many factors, the key ones being the Breslow tumor thickness, the level of invasion and the presence of distant metastases.
The 5-year life expectancy in the absence of metastases is about 60%, the average median survival is 50-55 months. In the presence of metastases, median survival ranges from 7-8 months.
However, radical surgery does not affect life expectancy.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7
Types, forms and stages
Pediatric melanoma is divided into three main categories—melanoma, infantile melanoma, and congenital melanoma. If a child is born with this disease, then the onset of the pathological process occurred at the stage of its intrauterine development .
The infantile form in most cases appears during the first year of the baby’s life.
Initially, this type of melanoma is benign, but the risk of becoming malignant reaches its maximum.
Types of melanoma occurring in childhood and adolescence:
- Amelanotic type (the color of such a formation is most often gray, compactions can appear in the back, on the fingers or soles of the feet, the degree of localization depends on the stage of development of the pathological process).
- Adolescent or juvenile type (in most cases, the disease occurs in adolescence and is a formation on the skin of the face that resembles a mole, but is much larger in diameter, its color can range from pink to black).
In medical practice, melanoma is divided into five stages of development.
At the first stage, malignant cells are concentrated in the epidermis. At the second stage, the pathological process spreads to the basal type membrane.
The third stage is characterized by damage to the papillary dermis. The fourth stage of the disease is accompanied by complete damage to the dermis. metastasis occurs .
Reasons for appearance
Subungual melanoma has previously been observed in older people. Today, the younger generation is also susceptible to the disease. Among people with cancer, nail cancer occurs in 3% of women and 4% of men. Scientists have not identified the exact causes of the tumor. There are a lot of assumptions about the circumstances influencing the formation of a malignant tumor:
- Moles and warts are susceptible to developing into a tumor state.
- The presence of defects on the skin of a person’s fingers from birth.
- The process of tumor development in organs and parts of the body that can affect the structure of the nail.
- Past fungus or viral infection of the nail plate.
- Permanent injury to the tumor site due to severe physical conditions.
- Untimely treatment of the injured part with antiseptics.
- Burns from ultraviolet irradiation are an ideal place for malignant formations. Constant sunbathing and solariums provoke the development of oncology.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Lack of melanin.
Additional circumstances include poor diet, lack of sleep, and low physical activity. The body does not receive the necessary vitamins, is not charged with energy and ultimately weakens. In this state, the body is unable to fight disease. Weakened immunity allows the formation of nail melanoma.
These factors become the root cause of cancer. As a result, subungual melanoma is formed. Its signs finally appear in the later stages of development. Scientists do not have exact information, but they are sure that the tumor is a consequence of the injury.
Types of nail melanoma
Symptoms and signs
Symptoms of melanoma in children may be associated with skin formations, but in some cases the pathological process can develop on clean skin . In this case, the disease can be detected by palpation of the epidermis.
A characteristic compaction with a certain localization will be felt on the child’s skin.
Skin formations may not cause discomfort for a long time, so timely diagnosis of melanoma largely depends on the attentiveness of parents .
The development of melanoma in children is accompanied by the following symptoms :
- skin itching of varying intensity;
- formation of asymmetric nevi;
- change in the area and appearance of pigmentation on the skin;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes;
- the formation of seals in certain areas of the skin.
Recommendations for the treatment of plantar warts in children can be found on our website.
Which doctor should I contact?
Many patients are interested in the question of which doctor prescribes treatment if nail melanoma has developed. Before starting medical measures, you should visit a dermatologist. This doctor specializes in skin diseases of various origins.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D-sEj9ZiH28
If the tumor nature of the disease is confirmed, the patient will be referred for consultation to an oncologist. It is the oncologist who will deal with further treatment. If necessary, surgeons, therapists, infectious disease specialists, and immunologists may be involved in therapy.
Diagnostics and research
At the initial stage of the examination, the doctor collects an anamnesis of the disease.
The specialist needs to find out how the structure and appearance of nevi or age spots in the child have changed, what provoked the existing diseases and draw up a general clinical picture of the child’s health.
Particular attention is paid to the fact of hereditary predisposition to melanoma. After collecting general information, the child is prescribed special examination procedures that are necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
When diagnosing melanoma in children, the following procedures :
- thermography (comparing skin temperature);
- radiophosphorus test (the procedure allows you to determine the degree of development of the pathological process);
- skin biopsy (mandatory);
- cytological studies (the procedure is necessary to confirm the diagnosis);
- CT scan of internal organs (the procedure is performed after confirmation of the diagnosis of melanoma);
- histological studies (the method is a mandatory stage in diagnosing the disease).
Why are they dangerous?
Melanoma is characterized by a tendency to progressive metastasis. This feature of the disease is one of the main reasons for its ability to provoke the death of a child.
The disease affects not only the internal organs and skin of the child, but also disrupts the natural processes of growth and formation of his body. The most common consequence of the pathological process is growth retardation in the baby.
Melanoma in a child can cause the following complications :
Source: https://gidroz.ru/onkologiya/melanoma-u-detej.html
Treatment
The surgical method, that is, removal of the tumor, is the main method of treatment. The operation is not performed only in a situation where the tumor has grown so much that it is impossible to remove it at once. The removed material is examined under a microscope to clarify the diagnosis. The depth of excision is to the sheath of the underlying muscles.
If melanoma cells are found during a sentinel node biopsy, the entire group of lymph nodes is removed.
Immunotherapy is used according to indications. Malignant cells are able to “hide” from the body’s defense systems. Immunotherapy makes them “visible”, after which the body begins to fight the tumor. Traditionally, interleukin-2 and alpha-interferon drugs were used for this type of treatment, but the effectiveness of such treatment remained low - 10–15% of cases.
Since 2020, a fundamentally new drug for immunotherapy of melanoblastoma, ipilimumbab, has been registered in Russia. Unfortunately, in our country it is not approved for use in children under 18 years of age, although in the USA the FDA commission has approved the use of this drug in children over 12 years of age.
Melanoma is poorly sensitive to radiation and chemotherapy, so they are used only in situations where other treatment methods have failed or for palliative purposes - to improve the patient’s quality of life, for example, to reduce pain from bone metastases.
Forecast
The prognosis depends on the degree of development of the disease and the treatment used. It is favorable in cases where contacting a medical institution and starting full treatment was still in the initial stages of development. In advanced cases, even after completing the full course of treatment, the child’s life expectancy is no more than five years. Depending on the body’s resistance to the disease, general physical condition and other factors, the period may be significantly reduced or increased.
Any disease requires early diagnosis and timely treatment. This is especially true for melanoma, which is one of a number of diseases that can lead to death. A timely visit to a specialist can not only prolong, but also save the child’s life. To prevent the onset of the disease, women are advised to carefully monitor their health during pregnancy, and after childbirth undergo regular examinations by pediatricians.
Prevention
The main prevention of melanoma is to avoid sun exposure if possible. This is especially important for the population of the middle zone, who prefer to spend their holidays in hot countries. At this time, you need to wear loose clothing that covers as much of the body as possible, wide-brimmed hats, and be sure to use sunscreen and special umbrellas on the beach. It is strictly not recommended for children under 5 years of age to be in the sun while on the beach - they need awnings or special beach umbrellas. Solariums are extremely unhealthy - if you visit them more than once a month, the risk of melanoma increases by 2.37 times.
Large and giant pigmented nevi are recommended to be removed simultaneously, involving at least 1 cm of healthy tissue, followed by plastic surgery of the excised area.
It is not recommended to remove dysplastic nevi prophylactically, but their carriers need to consult a dermato-oncologist at least once a year, always undergoing dermatoscopy.
Causes
To date, the main factors provoking the development of melanoma have not been fully studied. It is believed that the main reason for the appearance of the pathological process is a violation of the integrity of the skin, as a result of which the cellular structures degenerate into a malignant form.
The disease never appears just like that. This state must be preceded by certain prerequisites.
Based on this, we can identify the main reasons under the influence of which a child may begin to develop melanoma.
On this topic
- Oncodermatology
Skin spots due to cancer
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 5, 2020
First of all, experts highlight genetic predisposition. If your immediate family has a history of skin cancer, the likelihood of it occurring in the child increases several times.
When a woman's body is exposed to any harmful substances during pregnancy, abnormal degeneration of cellular structures cannot be ruled out.
If a woman suffered from some kind of infectious pathology during pregnancy, cell mutations in the fetus are also possible.
In addition, experts highlight factors such as:
- viral infections
- frequent injury to moles;
- prolonged exposure of the child’s skin to direct sunlight ;
- dysplastic syndrome ;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- a large number of moles on the body.
Children with fairly light skin tones are also at increased risk.
Classification
There are three main categories of childhood melanoma, including:
- Congenital melanocytic nevus. Approximately 5-10% of nevi develop into melanoma with age. This type of growth appears as a large, pigmented mole or birthmark. A nevus is formed in utero and is discovered only at the birth of a child.
- Common melanomas. Rarely diagnosed before puberty. Clinical features of this pediatric melanoma have some similarities with adult melanoma,
- Epithelioid nevus (Spitz nevus). Melanomas of this type are round in shape, uniform in color and nodular in nature. They often do not share the genetic mutations seen in adult melanoma. Currently, the reason for the appearance of these formations is not known.
Research has shown that the location of the primary tumor is an important prognostic factor, with melanomas of the scalp and neck having a worse prognosis than those that arise elsewhere. Melanomas of the eyes or mucous membranes are rare forms of the disease but can also occur in children.
Symptoms
Timely detection of potential melanoma involves monitoring the size, shape and color of moles. Often mistaken for warts or mosquito bites, melanoma in children may look very different than in adults. Therefore, parents should pay attention to the features of formations on the child’s skin, for example:
- asymmetrical edges of the mole;
- uneven edges of the mole (torn, blurred);
- nevus of irregular shape;
- large diameter (more than 6 mm);
- uneven color of the formation with shades of black, blue-brown or red;
- nevus growth;
- itching and bleeding.
Parents should also be aware that their child may not have signs of melanoma. A significant number of pediatric melanomas have well-defined edges and are light in color. This discrepancy in the symptoms of melanoma in a child can lead to a serious delay in diagnosis. That is why it is so important that parents promptly contact a specialist if suspicious formations appear. At the initial stage, the formation affects only the upper layers of the skin. Hence, if detected early, melanoma is 100% curable. It is worth remembering that swelling can appear not only on skin that is exposed to the sun. Therefore, it is necessary to examine the skin of the child’s head, arms, torso and legs.
Children who have been diagnosed with melanoma will need to undergo periodic skin examinations by a dermatologist. Observation by an oncologist is necessary. It is also recommended to use methods to prevent skin damage. In addition, protection from harmful solar radiation is mandatory.