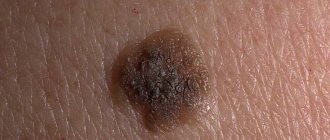
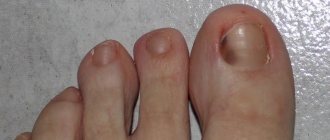
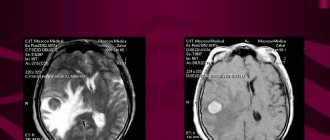
Here I will post photos of melanoma sent by blog readers. In principle, of course, you can just “pick up” a photo from the Internet, but I think that it will be much more useful and informative to tie the photo to a specific case - that’s what we found and that’s how it all ended. There are photos in the corresponding posts, but this format, it seems to me, is more convenient for perception.
The point is this: if you find something similar on your beloved body, you should urgently move this same body to an oncologist’s office (at least to a clinic) or a dermatologist. Please remember that the main component of the success of melanoma treatment
is early detection of sores!
If you have already visited this page, press Control+F5 to refresh. Otherwise, you may not see new photos.
How melanomas form
Every person has cells in their body that produce melanin. Melanin is a pigment that contains:
- in the skin
- in the hair,
- in the iris of the eyes,
- on mucous membranes,
- in human internal organs.
The presence of pigment determines the color of skin, eyes and hair. When the cells become overfilled with pigment, nevi appear in these places, which in common parlance are called “moles.”
Moles are benign skin formations, but some of them are oncogenic, and this suggests that under the influence of certain factors from the benign form, nevi can degenerate into melanoma.
This suggests that preventing the disease is easier than treating it. And in order to prevent a dangerous disease, oncogenic moles must be identified at the initial stage.
Moles, mostly benign formations
Prognosis of survival and subsequent life
The favorable prognosis is determined by the level of malignancy of the process, the duration of the course and the presence of metastases. In the case of a stage 1 tumor, the prognosis is relatively favorable: the five-year survival rate is 85%. In the presence of metastases and a more malignant course, the prognosis decreases to 50–30%. In isolated cases, in the presence of distant metastases, the survival prognosis drops to 15%. According to some data, survival and prognosis for subungual melanoma are more favorable than for palmoplantar melanoma. Such disappointing outcomes are often due to late diagnosis of the disease. Therefore, in case of any changes in the skin, you should immediately contact a dermatologist.
How to spot potential signs of melanoma
Moles do not pose a threat if their surface is smooth, the color is uniform, and the shape of the nevus is round. It is also a good sign if the mole is not convex and is no larger than 6 millimeters in diameter. But if there are moles on the body that fall under the description below, then it is necessary to visit an oncologist in order to examine the nevi and, if necessary, remove them surgically. You should only contact highly qualified specialists.
You need to visit an oncologist and dermatologist if:
- The pigmentation of the mole is uneven: one part of the nevus is lighter and the other is darker.
- The skin around the mole begins to peel and become inflamed.
- The contours of the neoplasm are blurred, there are no clear edges.
- The mole is compacted and has begun to increase in size.
- Cracks appeared on the surface of the nevus.
- There is no hair on or around the mole.
- One mole split into several new ones.
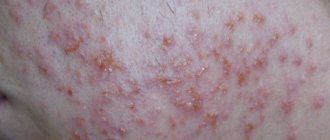
Using the listed criteria, you will not be able to determine 100% whether a nevus is degenerating into melanoma or not, for the reason that with the help of a visual examination, the accuracy is only 50-75%. For this reason, the oncologist prescribes reliable and accurate diagnostic methods, such as skiascopy and dermatoscopy. After this, a histological examination of the tissue is carried out, which will give an accurate answer whether the mole is prone to degeneration or not.
Cracks and peeling of moles, signs of melanoma
Diagnostic stages
The first is self-assessment of the skin of the legs, including the feet and nails. If changes in birthmarks are noticed, you should consult a doctor.
The second is an examination by a specialist to identify a malignant tumor.
The third is the dermatoscopy method. Using optics, the affected area is enlarged several times, which makes it possible to identify the disease at an early stage.
The fourth is the biopsy method. Excision of the tumor is performed under general anesthesia. The tissue is sent for analysis.
Fifth – diagnosis using ultrasound.
Causes of degeneration of moles
There are a number of reasons that “help” nevi degenerate into malignant neoplasms over time. These include:
- prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays (tanning under the rays of the sun and solarium),
- hormonal changes in the body - during pregnancy and puberty,
- thyroid disease,
- mechanical impact - friction with a washcloth, clothing, damage from a razor, burns and other types of mechanical injuries.
Classification of nevi
The sizes of moles can vary: from a small, barely noticeable speck to a large spot, which is located not only on the surface of the skin, but also inside the dermal layer.
Moles are divided into:
- Pigmented, formed by the connection of pigment cells.
- Vascular (angiomas) - formed by enlargement and fusion of lymphatic or blood vessels.
Based on size, nevi are divided into:
- small size (from 1 to 2 mm),
- medium size (from 3 to 10 mm),
- large size (from 10 mm and more).
Nevi can be localized:
- in the epidermis (upper) layer of skin,
- in the dermis (middle) layer of the skin.
A mole located in the upper layer of the skin
How long does it take for melanoma to develop?
How quickly melanoma grows directly depends on the stage and type of tumor. The stage of melanoma determines how long the treatment will take and how effective it will be. For example, if melanoma is detected at an early stage, when the thickness of the tumor is no more than 0.75 mm, then in 98% of cases after treatment there is a favorable outcome, or rather, recovery.
Stage one
In the first stage, the tumor is located in the primary focus. The development process of the first stage of melanoma lasts from 1 to 5 years. The thickness of the tumor is up to 2 millimeters. The skin around the tumor is not inflamed, there is no metastasis.
Stage two
In the second stage, the thickness of the tumor is 2–4 millimeters.
The second stage is characterized by a risk to human health. After all, tumor cells can develop intensively within two or three months.
Stage three
The third stage of skin tumor development differs from the second in that metastasis begins in the lymph nodes. Survival prognosis is 59% (5–6 years) and 43% (10–12 years).
Stage four
The fourth stage of melanoma is the most severe and most advanced stage. Since melanoma develops over several weeks. The process of metastasis occurs in the internal organs. Patients with stage 4 skin cancer survive up to 5 years in only 15–20% of cases. And in 10–15% up to 10 years.
Stage 4 melanoma metastasizes to internal organs
Treatment methods
Melanoma develops rapidly and forms metastases in just a few months. It is difficult to cure the pathology; several stages are required, let’s consider the main ones.
| Stage | Basic treatment |
| 1 | Removal of the tumor through surgery. Healthy tissues are affected. |
| 2 | A biopsy is performed. Removal of lymph nodes if they are damaged. Taking alpha-interferon drugs to reduce relapse. |
| 3 | Removal of formations and lymph nodes located nearby. This stage does not require effective treatment. Immunotherapy, radiation, and chemotherapy are used. Let's take interferon and similar pharmaceutical drugs. |
| 4 | Difficult to treat. The tumors are cut out, the fingers are amputated, and the pain is relieved with the help of medications. Chemotherapy, drugs dacarbazine, temozolomide are used. To reduce the tumor and improve well-being, immuno- and chemotherapy drugs are taken together. The fourth stage has been little studied and involves participation in clinical trials to identify new treatments. |
Forms of skin melanoma
What forms of skin melanoma are there, and how they differ from each other, every person needs to know. The thing is that this disease is especially dangerous and, moreover, it qualifies as a latent form of the development of dermatological cancer. This means that signs of the development and degeneration of a birthmark or mole into a dangerous melanoma can pass almost asymptomatically.
The most common forms of neoplasm:
- nodal,
- lentigo maligna - melanoma,
- superficial – spreading (39-70%).
Nodular melanoma
Nodular melanoma is a malignant neoplasm of the skin. Tumor development occurs due to the degeneration of melanocyte pigment cells. The main factor by which the degeneration of melanocytes into cancer cells occurs has not been fully established.
A secondary reason is the effect of ultraviolet rays on nevi. Nodular melanoma is one of the most devastating forms of cancer.
External signs of nodular melanoma
A nodular tumor is a type of cancer that in a short period of time penetrates into the dermis of the skin and spreads metastases to internal organs. A distinctive feature of this tumor is the vertical growth of malignant cells.
In the first stage of nodular melanoma, the tumor looks like a node that quickly increases in size. After a few months, melanoma penetrates into the deeper layers of the skin and affects the lymphatic system and internal organs.
Nodular melanomas vary in color: brown, black, dark blue and pigmentless
Distinctive features of a nodular tumor:
- the color is uniform,
- the surface is covered with a crust,
- inflammation around the nevus, itching,
- dome shape,
- tumor size from six to seven millimeters,
- localization in the head and neck area.
Nodular melanoma has a dome appearance
Diagnostic methods
In order to identify malignant melanoma, it is necessary to carry out several types of diagnostics.
These include:
Scanning confocal laser microscopy
Using this equipment, it is possible to obtain images from damaged areas of the skin without violating the integrity of the melanoma, that is, without damaging the tumor as when taking a biopsy. If you conduct a CLSM study at an early stage, then in 95% of cases an accurate diagnosis is determined.
The study is carried out using a device that takes pictures in horizontal and vertical planes. After this, the images are viewed on a monitor in a three-dimensional image, making it possible to evaluate the skin, cells and blood vessels.
Biopsy
A small part of the mole is taken for further examination. In order to “pinch off” part of the tumor, local or general anesthesia is performed. The resulting cells are examined under a microscope. The disadvantage of a biopsy is that there is a risk of damaging the tumor and increasing its growth.
Treatment of melanoma
Treatment for this type of tumor is surgical excision. During the operation, tissues close to the tumor are removed, covering from 4 to 8 centimeters from the tumor. And if the tumor is enlarged by 1 millimeter, then you need to remove tissue by 1 centimeter. In most cases, melanoma is completely curable, provided that the growth of tumor cells is horizontal.
If the tumor grows vertically, then treatment methods such as chemotherapy and immunotherapy are prescribed. But in this case, the prognosis is less favorable.
After completing the course of treatment, you need to be observed by an oncologist. During the first year after surgery, you must visit the doctor once a month, and in subsequent years once every 6 months.
Surgical removal is the only way to get rid of the tumor
Malignant lentigo melanoma
Lentigo, melanoma is a malignant neoplasm of the skin. Of all melanomas, lentigo occurs in 5-15%. External signs of the tumor: melanoma looks like a yellow or dark brown spot. The size of the tumor is approximately one to two centimeters.
Causes
Dehydration of the skin and exposure to ultraviolet rays can provoke degeneration and growth of the tumor.
This tumor can begin to develop in any organism, but most often it affects a contingent of the population that falls into the risk zone due to certain characteristics. These include:
- light skinned people,
- due to prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays,
- women 55 years of age and older.
Precursors of lentigo melanoma include age spots and other skin pathologies.
Light-skinned people are at risk of developing malignancy
Symptoms of the development of lentigo melanoma
If a tumor is detected at the initial stages of development, then there is a possibility of curing this tumor.
In the primary stages, signs appear:
- the size of the affected areas is from 6 millimeters or more,
- itching,
- inflammation around the birthmark,
- uneven pigmentation of the birthmark,
- raised areas on age spots,
- uneven edges of skin growths.
Diagnostic methods
Blood analysis
To check the level of an enzyme that is characteristic of the tumor.
Dermatoscopy
To study the structure and boundaries of the tumor.
Biopsy
Since this type of melanoma is most often localized in the area of the nose and cheeks, when taking material, it is necessary to exercise maximum caution and also use ultra-thin and high-quality instruments.
Morphological blood test
A blood test involves determining the presence of a disease through chemical changes in the blood.
A blood test will show the presence of malignant cells
Treatment of lentigo melanoma
Tumor treatment: surgical excision. The melanoma is excised along with an area of healthy skin around the tumor. This is done to prevent malignant cells from starting to develop again.
Superficial spreading melanoma
This type of tumor is quite common. Of all types of melanoma, according to statistics, 70% are superficial spreading melanoma. Most often, older people are susceptible to the disease.
Signs of a tumor
Reasons why you need to see an oncologist:
- the size and color of the spot changes,
- a dark brown bulge appears with specks of pink, black or gray,
- the surface of melanoma looks like a glossy plaque,
- changes in the structure of the tumor occur over several years.
After this, the tumor grows vertically, oncogenic cells enter the skin, and a malignant tumor develops. According to forecasts, melanoma is not dangerous until it begins to grow deeper into the skin.
If the tumor begins to grow vertically, the following symptoms will be present:
- itching and burning,
- thickened area of affected skin,
- bleeding of the tumor surface.
- change in melanoma color.
The formation can change shape and bleed
Diagnostics
If superficial spreading melanoma is detected at the initial stage, then in 100% of cases after treatment there is a favorable outcome.
Diagnosis is carried out visually in specialized oncological institutions.
A smear of the tumor is also used for further examination.
Danger and possible risks
The danger with acral-lentiginous melanoma is the same as with other malignant neoplasms. This concept includes metastases, tumor growth deep into nearby tissues, its disintegration and ulceration. Often, the risk of complications is due to late diagnosis of the tumor. In the subungual form of the disease, the tumor destroys the nail plate, as a result of which the nail begins to peel off. With a long course, nodes begin to appear in the pathological focus, which indicates a complication of the process.
Acral-lentiginous melanoma is studied based on blood tests, histology and hardware examination.