Subungual melanoma is a malignant neoplasm, which is formed on the basis of degenerated epidermal cells located directly under the nail plate of the finger. The altered cellular structure begins to actively produce the substance melanin, which changes the color of the skin. Degenerated cells are not controlled by the body and begin to divide independently. In this regard, melanoma develops very quickly with the spread of metastases to the bone, lymphatic channels and surrounding tissues of the epidermis. Subungual melanoma is a formation that can form from a previously benign epithelial growth in the form of a papilloma wart or mole, or arise from its own dermal cells. The main factor that provokes the appearance of melanoma under the nail is excess ultraviolet radiation from the sun.
Causes of nail melanoma
The direct factors that cause the degeneration of healthy cells into cancer cells have not yet been identified by medicine. Most often this occurs due to a nail injury or mole. But there are a number of other reasons why people may develop melanoma of the nail plate, they are listed below:
- fair skin, blond hair, blue eyes and freckles;
- presence of blood relatives with melanoma;
- age over 50 years;
- frequent exposure to UV rays - in the sun, in a solarium, under a bactericidal lamp.
What is melanoma
Melanoblastoma is an outdated name for a malignant tumor. The tumor is a type of skin cancer and appears as a dark brown spot. The process begins with damage to melanocytes, the skin particles responsible for pigmentation. The source of the disease can be just one cell. The tumor changes from a benign state to a malignant one. If the pathology is not stopped in time, there is a high probability of the disease spreading to other parts of the body.
Statistics point to skin cancer leading the way. The peculiarity is the rapid growth of metastases and the occurrence of complications leading to increased mortality.
The disease appears for the following reasons:
- Under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, when a person is exposed to direct rays of the sun for a long time, melanin production occurs at this moment.
- Various injuries, burns, and poor environmental conditions provoke the appearance of the disease.
- No less important is the genetic factor due to the presence of similar diseases in the family. The risk of disease increases by 50%.
- The period of menopause and pregnancy can be dangerous, as it triggers the degeneration of moles into melanoma.
- When depilating legs and cleaning feet, pay attention to new growths so as not to damage the skin.
- Weak immunity provokes the formation of melanomas on the legs. Surgical interventions, transplantations, chemotherapy lead to a decrease in immunity and the development of pathology.
Symptoms of melanoma of the nail plate
In the first stages, it is very difficult to notice the tumor. Signs of the disease may change during development. The main symptoms of nail melanoma include:
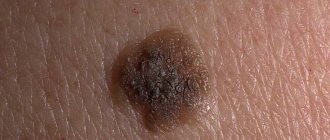
- the appearance of a small dark pigmented formation under the nail plate;
- sometimes instead of a spot, a thin vertical stripe of dark brown color is formed;
- the defect does not disappear after 10 days, as with a regular hematoma;
- the size of the spot begins to grow rapidly;
- the neoplasm has unclear boundaries;
- Over time, the tumor moves to the lateral edges of the nail plate;
- peeling and cracks appear, from which blood and ichor are released;
- the surface of the nail becomes deformed and becomes bumpy.
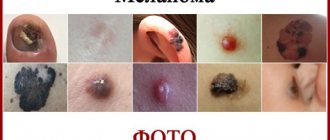
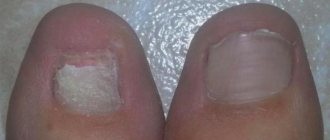
About 20% of cases of this disease have no pigment. Because of this, it is not possible to recognize melanoma in the initial stages. The first symptoms in such cases appear only at the third stage, when metastases begin to spread throughout the internal organs and bones of the skeleton. The speed of development of this disease is very fast, sometimes the transition from the first to the third stage takes only a few months. Pay attention to the photo of melanoma under the nail provided below to know exactly what the symptoms look like and be able to recognize the disease as soon as possible.
Melanoma most often forms on the big fingers and toes.
Reasons for development
The presence of one or a complex of negative factors can cause the degeneration of epidermal cells by the subungual plate of a finger. The following reasons for the development of the oncological process in this part of the human body are identified, namely:
- the presence of benign growths on the skin in the form of nevi, hemangiomas, moles, papillomas, warts, the epithelial cells of which began to degenerate into malignant ones and form a tumor body in the form of melanoma of the subungual layer;
- congenital skin defects that look like atypical growths present on the surface of the patient’s finger from the first days of his life;
- seborrheic keratoma, which is a precancerous formation that can at any time provoke uncontrolled division of epidermal cells;
- initially cancerous formations, which include basilioma, sarcoma, skin lymphoma, squamous cell carcinoma, fibroscarcoma;
- the presence of an oncological process in other organs and parts of the body, the metastases of which have affected the nail fold;
- the formation under the surface of the nail plate of an extragenital chancre of infectious or fungal origin;
- frequent mechanical injury to the nail caused by difficult working conditions;
- daily exposure of the skin surface of the fingers to direct sunlight with a high concentration of ultraviolet radiation.
These are the main risk factors that can start the oncological process in the skin, which is located under the nail plate of the finger of the upper or lower limb and lead to a diagnosis such as melanoma.
Stages of the disease
- First stage. At this stage, the disease is very similar to a hematoma from a bruise; no pain is observed. The thickness of the tumor is about 1 millimeter, the surface of the nail is not changed, there are no wounds or ulcers. Look below at what the initial stage of subungual melanoma looks like in the photo.
- Second stage. The thickness of the tumor has already reached 2 millimeters; by the end of this stage, bleeding and ulceration may appear, the formation takes the form of a mushroom.
- Third stage. As a rule, patients are admitted to an oncology clinic at this stage of development. Cancer cells have already spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- Fourth stage. The rapid spread of metastases continues. At the fourth stage, they affect internal organs: lungs, liver, kidneys, brain and skeletal system.
Successful treatment of nail melanoma is possible only in the first two stages. If the tumor has spread metastases, in most cases this leads to death.
Symptoms
External symptoms of subungual melanoma include:
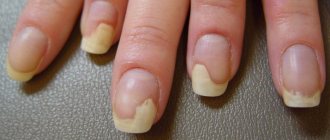
- the appearance of a vertical pigment (brown or black) strip under the nail, reaching its edge;
- an increase in pigmentation and its transition to the nail fold and fingertip;
- change in the shade of the nail surface (becomes dark or purple), later it may be completely covered with a new growth;
- deformation, thinning and delamination of the nail plate (characteristic of the phase of invasive growth of the tumor). As a result of this, complete detachment of the nail from the bed occurs: a lumpy brown or black ridge with ulcerations that bleed on mechanical contact becomes visible;
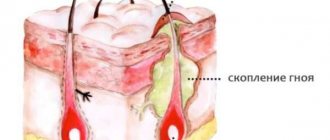
- discharge of pus from under the affected nail.
Other signs of pathology include:
- pain in the affected area (pain intensifies when pressing on the finger);
- pulsation in the lesion;
- feeling of fullness, burning and itching;
- weakness;
- weight loss;
- temperature increase.
Diagnosis of subungual melanoma
The presence of a cancerous tumor can be determined using the following tests:
- taking a blood test for tumor markers;
- examination of the formation through a dermatoscope;
- performing a biopsy of the affected area;
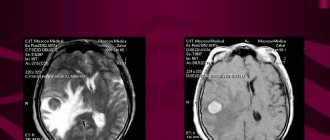
- the use of ultrasound diagnostics and magnetic resonance imaging to identify metastases in internal organs.
Based on the results of the tests, the doctor will be able to establish an accurate diagnosis and stage of tumor development.
In the first stages, nail melanoma looks like a regular bruise
Diagnostics
Not every dark spot under the nail is melanoma. It can easily be mistaken for a hematoma, nevus, or hemangioma. You can understand the nature of the tumor using dermatoscopy - a visual examination with high magnification.
Often this is not enough. If additional information is needed, a cytological examination of the smear and a biopsy with histological examination of the tissue are performed.
Studying tissue cells under a microscope provides the basis for a confident diagnosis. In this case, additional studies are prescribed - blood tests, urine tests, MRI, ultrasound, CT to study the condition of internal organs and lymph nodes.
Treatment for melanoma under the nail
Treatment consists of excision of the tumor, along with the nail plate and adjacent part of the dermis. The size of the tissue to be removed is determined by the area occupied by the formation. In some cases, it is necessary to completely amputate the phalanx of the finger. Upon completion of the operation, the affected tissues are sent for histological analysis. If cancer cells spread to the lymph nodes, they are also removed.
In the later stages after surgery, the following is also prescribed:
- chemotherapy;
- radiation therapy;
- immunotherapy.
With successful treatment of melanoma, it is extremely important to constantly undergo examination by a doctor so as not to miss the possible occurrence of a relapse. If dark pigment spots or pain appear, you should immediately inform your oncologist.
Removing melanoma on the nail
Oncology clinic in Moscow
Oncology clinic in Moscow ¦ TREATMENT OF MELANOMA IN THE EUROPEAN CLINIC ¦ Subungual melanoma
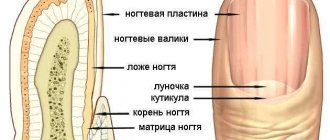
Previously, subungual melanomas were found in the elderly in the vast majority of cases, but now they are increasingly being diagnosed in younger people. They can occur on both the hands and feet, and mostly, as practice shows, it is the thumbs that are affected. Today, scientists identify several varieties of this form of melanoma:
- melanoma tumors arising from the nail matrix;
- melanoma tumors arising from under the nail plate;
- melanoma tumors arising from the skin adjacent to the nail.
The reasons for the development of subungual melanomas are still not precisely established. Often the diagnosis is verified at a late stage, since in almost every second patient these tumors are not hyperpigmented and are practically invisible during visual examination.
It is possible to suspect their presence already when the melanoma increases in volume and lifts the nail upward. In the second half of patients, at first the neoplasm resembles a spot localized under the nail plate, which usually has a black color or a bluish-red tint, sometimes dark inclusions can also be noticeable pigment.
As the malignant oncological process progresses, after several weeks or even months, this spot increases in size and becomes wider (especially in the cuticle area). Subsequently, the nail fold is involved, and after some period of time a nodule is formed, bleeding erosions and ulcers appear, which ultimately leads to thinning, cracking and deformation of the nail plate, i.e. to the so-called nail dystrophy.
Advanced subungual melanoma is characterized by the appearance of a tumor of a very unusual mushroom-shaped form. Sometimes a tumor may not bother a person in any way and cause absolutely no discomfort or pain until an extremely advanced tumor deeply infiltrates the underlying tissue and reaches the bone, which causes very severe pain.
Melanoma can metastasize both lympho- and hematogenously, and the rate of its dissemination throughout the body can be completely different, even lightning fast. A signal for immediate contact with a doctor for qualified help and, above all, for a thorough examination, should be a change in the usual pigment group (color) of the nail plate, as well as an increase in its thickness to three or more millimeters. During diagnosis, doctors always use a dermatoscope - a special microscope, with the help of which the stratum corneum of the nail and skin is illuminated in a special way.
Histological examination is carried out on samples of tumors removed together with an area of healthy skin or nail matrix. It is necessary to clearly understand that, be that as it may, it is easier to exclude the diagnosis of subungual melanoma than to then try to get rid of it in the final, advanced stages. It may well turn out that changes in the nail are caused by a subungual hematoma, taking certain medications, fungal infection, psoriasis, paronychia, purulent granuloma, etc. Treatment of subungual melanoma today involves surgical excision of the tumor focus along with subcutaneous fat and muscle way.
Depending on the extent of the malignant oncological process, only the nail can be removed, or the distal phalanx of the finger and even the entire finger can be amputated. According to indications, regional lymphadenectomy (lymphodissection) is performed and palliative therapy is prescribed.
| European Oncology Clinic Request for consultation and treatment +7(925)191-50-55 Moscow, Dukhovskoy lane, 22b |
| Melanoma - classification |
| Melanoma - causes and predisposing factors |
| Skin melanoma symptoms |
| Melanoma screening program |
| Early diagnosis of melanoma: digital dermatoscopy and whole body mapping |
| Diagnosis of melanoma - analysis of BRAF gene mutation |
| Sentinel lymph node biopsy (Sentinel procedure) |
| Diagnosis of metastatic melanoma: CT, MRI, PET/CT |
| TIL melanoma treatment program |
| Targeted therapy for melanoma |
| Imatinib in the treatment of melanoma |
| Dabrafenib in the treatment of melanoma |
| Ipilimumab in the treatment of melanoma |
| Keytruda in the treatment of melanoma |
| Methods for surgical removal of melanoma |
| Micrographic Surgery Mohs |
| Lymph dissection for melanoma |
| Radiotherapy and proton therapy in the treatment of melanoma |
| Photodynamic therapy |
| Chemotherapy in the treatment of melanoma |
| Recommendations after treatment of melanoma |
| Prevention of melanoma and malignancy of nevi |
| Preventive removal of suspicious nevi |
| Extracutaneous forms of melanoma |
| Subungual melanoma |
| Melanoma Center in Moscow |
+7(925)191-50-55 — European treatment protocols in Moscow
REQUEST TO THE CLINIC
Life forecast
Contacting the clinic at an early stage of melanoma often helps the patient to be completely cured. A tumor that has spread metastases to the lymph nodes and internal organs leads to death within a year after the onset of metastasis.
Treatment carried out at the first stage of the disease gives the patient an 80% chance of five-year survival. In the second stage, within five years, three out of four patients survive. At the third stage, when the disease has affected the lymph nodes, the chances of recovery are reduced to 40%. Metastases in the bones, liver, kidneys, brain, lungs or other internal organs at the last stage give hope to only 20% of patients and only with constant treatment.
Timely treatment gives a chance to cure a disease such as nail melanoma. The photos provided in the article will help you identify the disease at an early stage, prevent the development of the disease and the occurrence of irreversible consequences.
Treatment
Before you begin restoring a damaged manicure or pedicure, you should go to the hospital for medical advice. For diagnosis, they usually contact one of three specialists:
- Surgeon.
- Pathologist.
- Dermatologist.
If pronounced pigmentation is associated with a fungal infection, the patient is referred to a mycologist.
The girl undergoes an examination at the doctor's office and takes tests prescribed by the doctor; based on their results, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes a full-fledged treatment regimen.
Melanoma cannot usually be cured if one-sided, incomplete treatment is used, since pathogenic bacteria quickly spread throughout healthy epithelial cells, increasing inflammatory processes.
There are several ways to neutralize melanoma:
- Surgical intervention. The surgeon performs a minor operation that involves removing infected areas of skin. If melanoma has progressed throughout the finger, the doctor may prescribe amputation of any area. If the tumor has penetrated deep into the bone tissue, it may be necessary to remove the nerve ending that was affected by the disease.
- Chemotherapy. Therapy is carried out in any type of oncological diseases, as it helps to stop the proliferation of pathogenic microflora and extinguish inflammatory processes. Chemotherapy should be carried out before surgery, as well as after it - to completely eliminate the defect and prevent relapse.
- Cryotherapy. In the early stages of the disease, the doctor may prescribe the use of liquid nitrogen, which envelops the girl’s limb and gradually normalizes her condition. The equipment acts locally on epithelial cells affected by a malignant tumor.
- Laser removal. The use of a laser is allowed only at the initial stage of the formation of the disease, when it fills only part of the nail plate or one nail. The device also locally affects infected cells, gradually removing the neoplasm from them.
Specific treatment is always prescribed by a specialist, since it depends on the complexity of the lesion and the form of its development. The sooner the girl went to the hospital, the less likely it was that she would have to resort to amputation of the phalanx or finger.
Sometimes, to eliminate the tumor, the doctor may prescribe surgical removal of the nail. Surgery is also usually performed at the initial stages of the problem’s progression, because the tumor quickly spreads to the epidermis and other nails.
After completing the treatment prescribed by the doctor, the girl needs to undergo a period of rehabilitation, which will help prevent relapse.
Recovery consists of eliminating the symptoms that arose after the operation; for this purpose, medications are prescribed that eliminate pain, boost immunity, and strengthen nails. If a girl has undergone surgery to amputate or remove a nail, she will have to visit the hospital daily to change the sterile dressing, which helps the manicure gradually heal. A healthy nail grows normally in 5-6 months.
In any case, after completing treatment measures, the woman needs to periodically visit the oncologist so that he can examine the work area and promptly notice the occurrence of a relapse.
Disease prevention
Preventive measures to prevent the risk of subungual melanoma formation are as follows:
- In case of nail injuries and signs of damage persisting for a long time, you should definitely consult a doctor;
- choose shoes that are loose and do not squeeze your toes;
- visit a dermatologist twice a year if you have a predisposition to cancer;
- strengthen the immune system with vitamin complexes, and also reduce the frequency of visits to public places where humidity is high in order to avoid infection with fungus, HPV and other diseases that predispose to the development of melanoma;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- lead an active lifestyle that strengthens the entire body, get rid of bad habits;
- exclude or minimize exposure to the open sun in the summer from 10 to 16 hours, if there is an urgent need to wear closed clothes, refuse solarium sessions;
- Do not use another person’s shoes, as well as various cosmetic accessories such as scissors or tongs.
pT2a Nx Mx acral lentiginous melanoma, vertical growth phase, degree of invasion according to Clark - IV, according to Breslow - 1.25 mm pT2a Nx Mx
The situation would look quite standard if there were not one “BUT”, this is a description of melanoma called:
Therapy
The main goal of treatment is to remove the nail melanoma, which is considered the primary lesion. Next comes the fight against metastases. All procedures are aimed at increasing the patient’s life expectancy.
Treatment methods:
- Removal of the tumor while preserving the nail - this method is used if melanoma develops near the plate and has not yet affected it.
- Nail Removal – Most surgical procedures require plate removal. Oncological particles can be destroyed by ultra-low temperature and cut out with nearby healthy tissue.
- Amputation of a finger - with an increased risk of relapse, a decision is made to remove the phalanx. The method is used if the oncological process has spread far to neighboring tissues.
- Chemotherapy – the patient is given cytostatic drugs. A course of therapy is carried out before surgery to stabilize the oncological process and after surgery.
- Radiation therapy is a method used as the final stage of treatment. Highly active X-rays destroy not only particles of the primary tumor, but also possible metastases in the lymph nodes.
For many patients, removing a nail raises the question of whether it will grow back. If only one plate is removed, then after a while it will grow back. The patient will have to be patient.
The exact method of therapy is determined only by a specialist after a full examination. You should not select medications yourself, so as not to harm the body.
About the disease
The medical name of the pathology is acral-lentiginous melanoma. It is a rare disease and is diagnosed in 4% of all cancer pathologies.
The fingernails and toenails are equally susceptible to the tumor process. Most often the disease affects the thumb . This is due to the fact that the nails of the thumbs are more susceptible to injury.
Typically, melanoma manifests itself as darkening of the nail, which is destroyed over time by the tumor. But in 20% of cases, a malignant neoplasm may be colorless. This is due to the absence or insignificant amount of melanin in the tumor.
The color of the formation on the skin of the finger is black-brown or reddish-brown. The neoplasm under the nail is blue-red, black-blue, and purple in color.
The disease develops quickly, spreading metastases. It is important to diagnose it in a timely manner and begin to treat it.
Video selection of photographs of the neoplasm:
Signs of the disease
There are two most common signs of subungual melanoma, which at the same time can be signs of not only this terrible disease, but also completely harmless ones:
- The first sign of this type of melanoma is the appearance of a strip starting from the nail fold and ending at the edge of the nail, which can be brown or black. This condition is called longitudinal melanonychia. But retinoids and Docetaxel used for treatment can lead to the appearance of such stripes; This symptom also occurs when the nail is infected with a fungus, pigmented nevus of the nail bed;
- The second common sign of the disease can be considered Hutchinson's symptom - the process of pigmentation transferring to the tip of the finger or nail fold, but this symptom can also be present with a transparent cuticle.
In most cases, symptoms are not observed in the early stages. And at later stages the following picture of the disease is formed.
The emerging spot or stripe of dark color begins to increase over several months or even weeks. This new growth changes color to light (dark) brown and expands wider in the cuticle growth area, and later can completely cover the entire surface of the nail.
The neoplasm spreads to the nail fold surrounding the nail plate. Nodules may occur that lead to deformation, cracks and thinning of the nail plate, and there is also a risk of bleeding ulcers. Pus may ooze from under the damaged nail.