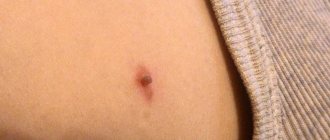
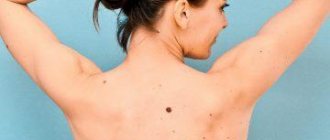
Moles are benign formations caused by the accumulation of melanocytes. They appear on the body from six months of age and increase in size and number over the years. Most are benign. Caution should be exercised when the mole has become convex. It is necessary to establish the reasons for the changes and undergo an examination.
Causes of moles
If you are not the owner of one, then you must have seen convex moles from friends or just photos, and therefore you should understand what they are. They are not rare, but they can be quite different visually.
There are different reasons for the appearance of raised moles, and we will look at the main ones. Most often this is due to pathological changes in the skin - a certain level of deformation. We are talking about the proliferation of skin cells, as a result of which seals appear on the surface of the body, which may increase slightly in size over time.
In some situations, melanin can come into play, especially if we are talking about an open area of skin. The fact is that direct sunlight promotes the production of melanin, a pigment that changes the color of the skin of the body. In this case, the mole may darken a little.
In addition, ultraviolet radiation can contribute to the appearance of new birthmarks on the body, and most often they will not be convex.
I would also like to include genetic inheritance here. Often, the predisposition to the appearance of moles is determined by the genes of the parents, which is why they are often located in the same places as the mother or father.
The development of the body also plays an important role, which increases the likelihood of a raised mole appearing on the body during adolescence. At this time, the child’s hormonal levels are disrupted, which can cause formations on the skin, including convex ones.
Injuries and damage to the skin can also cause the appearance of such moles. We are talking about both serious injuries and banal friction, for example, from a backpack strap on an open area of skin.
Criteria for identifying moles that are hazardous to health
There are a number of criteria by which you can determine how dangerous a nevus is:
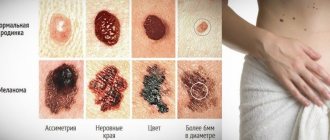
- It has an asymmetrical shape - this is abnormal; safe nevi are characterized by a rounded symmetrical shape.
- The boundaries of the formation are unclear - a mole that is safe for health has clear outlines on the skin.
- A raised mole should have a diameter of no more than 6 mm; if the mole is larger, it requires more careful observation.
- The color of a benign nevus should be uniform. You should immediately consult a doctor when the color changes from one shade to another or there are dark spots on the convex nevus. But this sign alone does not mean that the mole becomes melanoma-dangerous.
- Unusual sensations in the area of nevi, that is, burning, itching, tingling, pain.
If a flat mole has become convex, changed its color or shape, then this may be the process of degeneration into a malignant neoplasm.
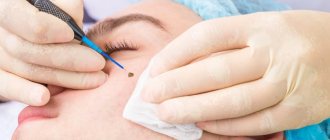
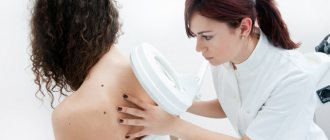
You can only diagnose by eye whether a mole poses a threat to health, but a more in-depth and accurate diagnosis can be carried out by a dermatologist using a special microscope that has 10x magnification.
A dermatological microscope allows a doctor to diagnose a mole
Causes of defects
Many people often do not understand why moles can become raised and what is the reason for this. As we said earlier, in more than half of the cases, such moles appear on the sites of spots of melanin pigment.
Further, the usual cell division, characteristic of the human body, can proceed, in the process of disruption of which convex moles are formed.
Pregnant women have their own reasons for the appearance of hanging moles, which are primarily associated with an interesting position. It's no secret that pregnancy greatly affects the female body, primarily on hormonal levels.
If we talk about children, then moles start before birth, after which it takes several more years for them to begin to appear on the baby’s body.
Types of convex nevi
According to the method of formation, all convex moles can be divided into melanocytic, or pigmented and vascular.
Pigmented neoplasms
Formed by a cluster of melanocytes. Their color depends on the depth of occurrence and the predominant type of melanin. If melanocytes are saturated with eumelanin, the color will be more likely black. If there is more pheomelanin, then a brown nevus is formed.
Types of convex pigmented nevi:
- Fibroepithelial nevus. This is a flesh-colored neoplasm. Slowly increases in size. Often covered with hairs. Melanoma-dangerous formation. Most often found on the back, chest and limbs.
- Intradermal nevus. A round formation, without hair, the color is brown and all its shades. Can be localized on the mucous membranes of the body.
- Papillomatous nevus. Located on the scalp, covered with hair. The surface is uneven, rough, nodular.
If the nevus is red, then in this case it is no longer a pigmented, but a vascular formation.
Vascular neoplasms
Vascular nevi are called agiomas. These are small nodules of a benign tumor, consisting of overgrown blood vessels. The color of angioma ranges from pale pink to dark red.
Convex angiomas do not pose a health risk. However, they can be a serious cosmetic defect when localized on the face. Angiomas on closed surfaces - the back and chest, if they are small in size, are not recommended to be removed.
Angiomas are small in size and have a characteristic color. It is important not to confuse an angioma with an injured pigmented mole. If a brown, raised mole turns red and looks like a red nodule, go to the dermatologist immediately!
Hormones
Where would we be without them? We have already discussed several types of hormonal instability. But there may also be more unusual factors, such as illness. Problems with certain internal organs often cause hormonal imbalances in a person.
At the same time, in other cases, corticosteroids are used as treatment, which also leave their strong imprint on the internal state of a person.
Cause for concern
The very fact of your concern is already a reason to contact an oncologist. In this case, even a subjective feeling that “something is wrong” with the nevus will be grounds for consultation with a professional. Let us clarify which moles are considered dangerous and which are safe.
A raised mole can be of any color and located on the back, arms or other parts of the body. Significant signs of its good quality:
- Size up to 6 mm.
- Symmetrical shape.
- Smooth edges.
- Uniform color.
A melanoma-dangerous nevus can form on the basis of an ordinary convex mole and has the following characteristic features:
- asymmetrical shape;
- uneven, “torn” edges;
- the color is heterogeneous, interspersed with black and red pigment;
- peeling;
- bleeding;
- size greater than 5 mm;
- glossy surface;
Any change in the condition of the nevus - size, shape, sudden appearance or change in color - is a good reason to visit an oncodermatologist.
Experts tend to consider convex moles as favorable objects for manipulation due to the fact that their protruding surface often attracts the patient’s attention. Any changes quickly become obvious, and a person can seek help early.
Birthmark on a child
Parents often overreact to everything that concerns their precious child. This is understandable, especially if this is the first baby in the family. We often overprotect our firstborn and worry about the simplest issues. Moles are coming here more confidently than ever.
Even if it is convex, you shouldn’t start worrying right away. If the mole is small, neatly shaped and uniform, or maybe even completely colored, then most likely everything is fine with it. You should worry if it starts to grow very quickly or bothers the child.
Is it possible to remove raised moles?
Convex nevi form on different parts of the body: face (nose, forehead, cheeks), body (groin, neck, back, stomach, legs, arms). The danger is minor injury. Do not be alarmed if, after an examination, the doctor suggests removal. This is a preventive measure against dangerous consequences. It is important not to delay the decision, to get rid of the problem faster.
Medicine offers several safe methods:
- electrocoagulation. Eliminates birthmarks using high frequency electric current. Reduces the risk of relapse, leaves thermal burns;
- laser. The treatment is carried out with a laser beam, which vaporizes the mole. The technique is widespread, despite the presence of contraindications. After the procedure, there is no material left for histology; previously studied benign formations can be removed. Advantage: no bleeding, no pain;
- radiosurgery. The body of the nevus is cut off from the surface of the skin by high-frequency radio waves. Used for small elements;
- surgery. Rarely used for large and dangerous growths. The doctor works with a scalpel, cutting off the problem area and the skin around it to prevent metastasis. After the operation, stitches are placed on the wound.
When selecting a technique, the doctor takes into account many factors. For all options, except laser surgery, contraindications are childhood, pregnancy, and the presence of diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Getting rid of convex nevi at home increases the risk of consequences. The folk recipe is selected by the treating dermatologist and carried out with his help. Before a course of procedures, it is imperative to examine the rough, dark, convex element for good quality, so as not to provoke degeneration.
Celandine or its pharmacy equivalent, Supercelandine, will help you quickly remove pubic or body growths. Verucacid and Ferezol received recommendations.
The home method is dangerous due to secondary infection and inflammation. An important condition for a safe procedure is maintaining sterility, protection from dust and dirt.
Diagnostics
To ensure that a raised mole does not become the cause of the development of a cancerous tumor, it is important to consult a specialist in a timely manner. At the initial stage of diagnosis, exclusively conservative examination methods are used, including physical examination, medical history, ultrasound, and radiography.
Tissue collection for histological examination is practiced only when removing a convex mole. Thus, an indication for the removal of a neoplasm may be suspicions regarding the risks of degeneration of a birthmark.
Signs of melanoma
You can suspect the formation of a cancerous tumor based on the following symptoms:
- rapid increase in the size of a mole more than 6 mm in diameter;
- pain on palpation;
- itching;
- secretion of ichor;
- ulceration, formation of a crust on top of the growth;
- the appearance of a black dot on a mole;
- irregular shape, unclear edges.
The first sign of melanoma is the growth of a mole, change in color and shape.
Removal methods
Methods for removing birthmarks can vary significantly depending on the size, shape, specificity, and location of the formation. For example, if there is a suspicion of a malignant nature of the neoplasm, it is permissible to use only surgical removal, which will allow the collection of tissue from the birthmark for histological examination.
If there is no such need, other, more gentle methods are used:
- Radio wave excision. Several years ago, this method was the most gentle and also in demand. Today it has somewhat lost popularity, which is due to its fairly high level of trauma. The use of radio wave surgery allows you to remove a raised mole in one procedure. In this case, healthy tissues are also affected, but this particular feature makes it possible to exclude the development of bleeding. After removing the birthmark, a slight scar remains on the skin, which subsequently completely disappears.
- Laser therapy. This innovative method is not only extremely effective, but also gentle. Laser therapy can be used to remove raised moles of any size; after the procedure, the risk of bleeding and the appearance of scar tissue is eliminated. However, the use of this method is excluded if there is a suspicion of malignant degeneration of the mole. This is due to the fact that the laser completely burns out the tissue of the spot, which excludes the possibility of conducting a histological examination.
- Cryodestruction or cauterization with liquid nitrogen. To obtain the desired effect, that is, complete removal of the tumor, several procedures may be required. The method of destruction of raised moles is quite painful, which necessitates the use of anesthetics.
- Surgical excision. If there is suspicion of the development of a malignant tumor, surgical excision is required, which allows tissue sampling for histology. This method is especially painful and involves leaving scars. Surgical excision is carried out using local anesthesia followed by suturing.
It should be noted that, regardless of the specifics of the procedure performed, after removal of a convex mole, the patient is recommended to undergo regular preventive examinations by a specialist, which will help identify signs of the development of malignant diseases if there was a risk of degeneration of the convex mole.
Until what age is the growth of moles normal?
The appearance of moles on the skin is a natural process.
The pigment reduces the negative effects of ultraviolet rays.
Nevi appear as a result of hormonal changes. The growth of dark marks as a person grows older does not affect health. Each person’s body is unique - there is no exact age at which formations appear.
Approximate intervals for a child to grow up with the formation of a favorable nevus:
- early infancy - from 6 months to 2 years, nevi do not grow until six months of age;
- eve of adolescence - 6-7 years;
- Beginning of puberty is 12-14 years.
During these periods, the skin structure increases melanocytes - cells that produce dark pigment.
Growth and increase in bulge without changes in hormonal levels is a deviation from the norm and a reason to visit a doctor.