Normal healing process
It is considered normal for the mole removal site to hurt for several weeks. If the nevus is large, it will likely take longer to heal. Everything will depend on the specifics of each human body.
Signs of healing
- Minor pain;
- Slight redness of the skin;
- Crust formation.
© shutterstock
If after surgery a person is bothered by any extraneous signs, it is better to go to the hospital in a timely manner to avoid serious complications.
Treatment options
After a few days, a crust appears on the wound, which cannot be wetted or torn off independently in order to avoid infections.
Conservative methods of treating pain after mole removal include:
- Potassium permanganate;
- Healing ointments;
- Sunscreens.
Should you see a doctor with these symptoms?
If deviations appear after removing a mole, atypical symptoms, pain, even if the symptoms stop spontaneously, it is recommended to consult a doctor to avoid complications.
There is no need to self-medicate or use traditional medicine methods. You can aggravate the pathological condition and provoke complications after removal. It is forbidden to scratch the postoperative wound.
It is necessary to pay attention to acute symptoms. If certain signs appear, you should immediately contact the dermatology department:
- atypical discharge from the wound - blood, pus, serous clear liquid - one-time or constant;
- raising body temperature to 39-40 degrees. Prolonged hyperemia, which is poorly treated with antipyretics and NSAIDs;
- acute and throbbing pain, difficult to relieve with medications. Taking ibuprofen or aspirin should be avoided: they increase the risk of bleeding from a postoperative wound.
The doctor will determine the nature of the changes, conduct diagnostics, and help differentiate pathological symptoms from normal processes of epithelization of the postoperative wound. If necessary, he will prescribe additional biochemical tests or histological examination of tissue from the surgical area.
Infiltrate
Removing a mole is a common manipulation in medical practice, which takes place without complicated consequences. But sometimes a red bump appears at the site of mole removal - an infiltrate that can cause pain.
© shutterstock
This phenomenon is explained by the fact that cellular elements with blood and lymph have accumulated in the tissues. The cause of the disease is:
- Damage to soft tissues;
- Poor blood clotting;
- Improper postoperative care;
- Penetration of infection.
Signs of infiltration
The disease does not manifest itself with many symptoms, but among them are:
- Pain from touching the place where the mole was removed;
- Local redness of the skin.
If the disease does not provoke inflammatory processes, signs may be completely absent.
Under any circumstances, it is worth visiting your doctor again in order to avoid unpleasant outcomes.
Treatment options
To eliminate infiltration, doctors use:
- Regeneration therapy;
- Antibacterial drugs;
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
All medications must be strictly prescribed by a doctor.
Complications
In rare cases, the restoration of the integumentary tissue does not go so smoothly.
Cosmetic defect
If for some reason the wound does not heal by primary intention (multiple removal of the crust, repeated trauma to the surgical site), then the scar is not so flawless. The connective tissue spreads over a larger area, and there is a strong decrease in elasticity, which means limited mobility. But, sooner or later, in this case too, the functions will be restored, and healing will occur fully.
Keloid scar
An even rarer complication after mole removal is a keloid scar. This is a very unpleasant consequence that occurs for unknown reasons. It is believed that the following factors can provoke the appearance of excessive skin growths instead of the formation of a neat scar:
- deep damage to the epithelium;
- decrease in the body's immune forces;
- tendency to allergies;
- special conditions, for example, pregnancy, puberty.
But the most significant reason for the occurrence of a keloid scar is considered to be a genetic predisposition. In this case, a hypertrophied growth can occur even without visible tissue damage (in this case we are talking about a tumor of keloid origin) or at the site of the smallest scratch.
Thermal burn
When a person decides to remove a mole, he should carefully study each technique and make the right decision. For example, if, after removing a mole, the place where burning with liquid nitrogen was carried out hurts, then this is a thermal burn. It is formed due to the substance entering healthy tissue.
© shutterstock
This method has some caveats and is contraindicated for people who:
- Infectious diseases;
- Herpes;
- Arterial pressure;
- Mental disorders;
- Lactation;
- Pregnancy.
Signs of a burn
- Burning;
- Local redness;
- Edema.
Treatment options
You can get rid of a burn with the help of wound-healing ointments, which should be prescribed by your doctor.
Hypertrophic scar
As a rule, after professional removal of a mole, a barely noticeable scar or no trace remains on the body. Of course, it all depends on the chosen method, including :
- Laser;
- Radio waves;
- Electrocoagulation;
- Cryodestruction;
- Surgery.
© shutterstock
But, if healing is accompanied by some disturbances, then a hypertrophic scar appears at the site of the removed mole - stretched skin, causing pain and discomfort.
This disease occurs due to excess collagen produced by multiplied cells. Fibroblasts are cells that are supposed to eliminate excess collagen formation. As a result of these disorders, a hypertrophic scar is generated.
Signs of illness
Signs of the disease include:
- Pain in the affected area;
- Discomfort of movements;
- Visible skin changes.
Treatment options
When a scar from a mole hurts, doctors prescribe:
- Drug therapy;
- Physiotherapy;
- Radiation therapy;
- Laser grinding.
Summarizing
There is no need to engage in self-treatment, as this leads to unforeseen consequences. If the scar hurts after removal, you should visit a clinic where they can determine the true cause of the pain and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Found an error? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter.
Mole removal is a surgical procedure that involves excision of a spot. It can be carried out with a scalpel or minimally invasive methods: laser coagulation, diathermoelectrocoagulation, cryodestruction, radio wave method. It is necessary to follow the rules of preparation and postoperative care, otherwise keloid scars appear, the mole itches after removal, the state of health is disturbed, pain occurs, recurrence of the nevus, and suppuration of the wound area.
Suppuration
After removal of the nevus, pain is caused by suppuration, which can be seen by everyone. In case of such manifestations, it is recommended to immediately visit a doctor.
© shutterstock
The consequence of suppuration is:
- Negligent attitude to the doctor’s rehabilitation instructions;
- Staphylococcus;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- Various microbes;
- Chronic inflammatory process;
- Lack of personal hygiene;
- Dirty water.
Signs of illness
Signs of suppuration include:
- Poor wound healing;
- Local redness;
- Paroxysmal pain;
- Heat;
- Purulent discharge;
- Swelling.
These signs are evidence of a serious complication that requires urgent and appropriate treatment.
Treatment options
To treat suppuration that has formed at the site of a removed mole, antibacterial therapy is used, including:
- Antimicrobial ointments and powders;
- Zelenka;
- Potassium permanganate;
- Sometimes, antibiotics.
Treatment of postoperative scars
Uncomplicated healing processes after mole removal do not require special therapy. In some cases, a dermatologist may recommend emollient ointments and creams; in case of a large healing area, a course of physiotherapy is prescribed.
Keloid scar is a complex case. On the one hand, any physical impact can provoke rapid growth of connective tissue. On the other hand, in the absence of treatment, a significant cosmetic, physical and functional skin defect develops. Therefore, in each specific case, dermatologists resort to individual schemes for restoring skin smoothness. Doctors have the following tools in their arsenal:
- absorbable ointments (“Karipain”, “Kotnraktubex”, etc.) - daily rubbing, applying bandages;
- corticosteroids (“Triamcinolone acetonide”, etc.) – injection of a suspension of the drug into the growth approximately once a month;
- physiotherapy (electrical and phonophoresis with the flow of ions of absorbable agents into the tumor area);
- constant grinding of the skin surface - effective at the first signs of a keloid or after its surgical removal;
- excision of scar tissue with subsequent prevention of an increase in the amount of scar connective tissue;
- tight bandaging (bandage) with absorbable agents at the first signs of overgrowth.
Important! Keloid scar is a chronic phenomenon that requires periodic courses of treatment. But with age, aggressive tissue proliferation gradually decreases, and after 40 years it is much less common than in childhood and youth.
The positive point in this situation is that keloids are not prone to degeneration into a malignant tumor.
Thus, the scar after mole removal in the vast majority of cases is neat and does not cause trouble to the person who underwent the operation. In rare cases of excessive scar growth, the dermatologist will select a treatment that is recommended to be strictly followed.
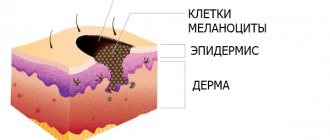
Melanoma
Many people are interested in whether it hurts to remove a mole, but few are interested in the consequences, because beauty and comfort always come first. Sometimes, the mole itself becomes the cause of illnesses. But, before you go for an operation to remove it, you should find out the nature of its occurrence and possible consequences.
© shutterstock
Pain after mole removal is caused by melanoma, an oncological disease that is a type of skin cancer. According to statistics, 200 thousand people in the world die from melanoma every year.
Scientists to this day have not been able to find out the exact causes of the disease, but they have been able to identify some factors that contribute to the development of melanoma, which causes pain after mole removal:
- Genetic predisposition;
- Ultraviolet irradiation;
- Hormonal imbalances;
- Sunburn;
- Age category over 50 years.
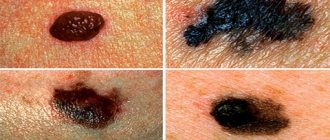
Signs of illness
Signs of melanoma formation include:
- Pain at the site of the removed mole;
- Itching;
- Burning;
- Redness of the skin;
- Edema.
Proper removal of a mole is a reliable measure for preventing the disease. Pain and tumor formation can provoke the following cases:
- Traumatic removal methods;
- Incomplete removal of a mole;
- The presence of cancer cells in the body.
Therefore, if after removal of a mole pain appears or the area begins to itch, you should immediately seek advice from specialists.
Treatment options
To get rid of melanoma that causes pain after removing a mole, doctors do a repeat procedure, including:
- Surgical intervention;
- Chemotherapy;
- Immunotherapy;
- Radiation therapy.
© shutterstock
Causes and dangerous consequences of mole removal
The consequences of mole removal are the result of individual characteristics of skin regeneration, the immune system, the method of exposure - freezing of the deep layers of the skin, burns in the absence of adjustment of the laser temperature - non-compliance with recommendations for preparation for the procedure, care of the suture, wound surface after surgery.
Symptoms that may bother the patient are a reason to consult a dermatologist for advice. If the site of the formation hurts, itching, peeling of the epidermis appears, the addition of secondary microflora is observed with the release of pus or blood from the wound, rapid fatigue - such a clinical picture should alert a person. Relapse is possible. Incomplete removal of a birthmark can provoke malignant cell growth.
Pain at the surgical site
If the site of mole removal hurts, you should pay attention to the time interval from the moment of excision of the nevus. It is important whether the postoperative scar aches several weeks or months after the intervention, or whether the open wound causes discomfort.
If the scar begins to hurt after removing a mole 14-18 days later, this is a reason to consult a doctor who performed surgery to eliminate the pigment formation.
In case of discomfort when pressing and redness of the surrounding tissues, concomitant pathology may occur.
Very itchy
Removing a mole is often accompanied by itching and swelling. Wounds on the hands and feet may itch due to frequent washing, treatment with disinfectants, and soap. On the back - due to increased sweating - hyperhidrosis - friction of the postoperative wound on clothing.
Scars itch after mole removal for various reasons:
- Normally, itching occurs as a result of healing and scar formation. There is no inflammation or pain;
- the addition of pathogenic microflora with the development of bacterial inflammation. An infectious agent can penetrate the wound surface if the rules of asepsis and antisepsis are not followed;
- Complications after a laser burn may occur due to swelling, edema and itching;
- disruption of the healing process, suppuration of the wound can provoke itching.
Burning
Burning and pain occur with superficial and deep burns of the skin. Normally, when the postoperative area heals, the feeling that the skin begins to “burn” does not appear. It can be observed due to insolation and lack of protection with sunscreens with a high level of SPFSFA.