2824
0
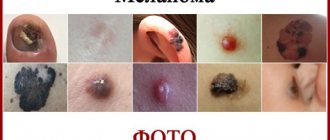
One of the most aggressive types of skin cancer is called melanoma. It is largely dangerous not so much in itself as in its ability to rapidly spread infected cells to other systems and parts of the human body. Therefore, melanoma can cause metastases in the lungs, liver, lymph nodes and other organs.
Causes of metastatic melanoma
Melanoma begins its development with a mutation of skin pigment cells. This process proceeds aggressively, so over time a cancerous tumor forms. Its cells break away from the tumor and, with the help of the lymphatic flow or bloodstream, begin to migrate throughout the body. Where they settle, a secondary cancer focus forms.
The primary tumor is constantly growing and producing new numbers of atypical cells, so vital organs are quickly affected. Oncologists point out that melanoma up to one millimeter thick is still unable to metastasize. A tumor with a size of 4 millimeters has an average ability to progress. Formation larger than 4 mm has a high degree of aggressiveness.
The lymph nodes closest to the tumor are affected first. Often, when fatal cells migrate, metastases settle in the skin (in 60% of cases) or affect the lungs and liver (in 35% of cases), the brain (in 20% of cases), bones and organs of the gastrointestinal tract (in 17% of cases) ).
There are many reasons for the formation of melanomas. One of them is a hereditary factor. In 70% of patients, transformation of ordinary moles and warts occurs: malignancy begins due to constant trauma, excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation, and hormonal imbalances.
How liver metastasis manifests itself: main symptoms
Melanoma with metastases is a dangerous disease that is difficult to diagnose at the initial stage of development. The penetration of cancer cells into the liver indicates the progression of the disease. Metastasis occurs by hematogenous route. When blood is filtered by the liver, metastases are retained in the organ. At the same time, a macropreparation is detected in the tissue - areas of accumulation of melanin. Liver damage leads to dysfunction of the organ, which negatively affects the condition of the whole organism, and has the following symptoms:
- presence of seals;
- increase in organ size, tissue tuberosity;
- pain syndrome;
- yellowness of the skin;
- enlarged spleen;
- weight loss;
- loss of appetite;
- frequent nosebleeds;
- violation of the biochemical composition of the blood.
Against the background of intoxication, the patient rapidly loses weight, experiences constant weakness, and possibly an increase in temperature.
There are disturbances in liver function and bile outflow.
The liver damaged by metastases cannot cope with its functions. The bile duct is compressed until it is completely blocked. Impaired bile flow leads to jaundice. Metastases provoke the establishment of collateral circulation - blood circulation through the lateral vessels. This contributes to the development of palmar erythema, in which the patient's palms turn pink. Bruises appear on the skin due to burst capillaries.
Forms of pathology
Dermatology systematizes this disease according to clinical types, degrees of development and color.
There are two forms of pathology:
- horizontal,
- vertical.
In the first stages, melanoma only grows in width, the affected area does not extend beyond the boundaries of the epithelial layer of the skin. In this phase, cancer cells are not yet migrating.
When the tumor begins to grow vertically, the process spreads to the dermis and subcutaneous fat. The vessels located here act as distributors.
The forms of melanoma and their symptoms are presented in the table:
| Name | Damage area | Morphological characteristics | Features of formation |
| Superficial | Skin of the head, neck, torso, lower leg and thigh | It has a flat shape and forms next to a mole or papilloma. Outwardly it looks like a sliding stain. When the tumor grows into the deep layers of the skin, an ulcer appears on the surface, which itches very much | It takes a long time to develop and gradually goes into the deeper layers of the skin, so the disease is highly treatable |
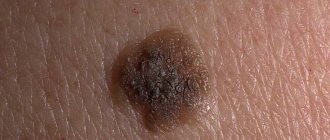
| Nodular (nodular) | Scalp, face, back | The tumor is dome-shaped and brown or black in color. There are sometimes inclusions on the surface. The upper part, which rises above the epidermis, is dense to the touch | It grows quickly both in breadth and depth, so it metastasizes almost immediately |
| Tumor at the site of lentigo maligna | Open areas of the face and body | This type of melanoma does not have clear shapes or boundaries. The tumor looks like a blurry spot of brown or gray color. This type can be confused with freckles | Grows over ten to fifteen years, always appears in older people |
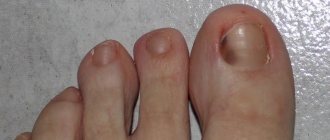
| Acral lentiginous | Palms, fingers and toes | The formation looks like a large spot or a dark brown ribbon | It develops from lentigo and may not transform into a malignant tumor for a long time. It progresses quickly in older people |
| Spindle cell | Skin of the head, neck, arms and legs | Melanoma is dome-shaped, pink or brown in color, and has a smooth or warty surface. | Found in children and adolescents |
According to the degree of coloration, melanoma can be:
- pigmented (have a pronounced color: red, brown, black),
- non-pigmented (white or flesh-colored).
The first are formed from chromatophore cells. The latter have the appearance of a bump that is rough to the touch, around which swelling, redness and itching develop. In later stages, such melanoma ulcerates and bleeds. The main feature of a pigmentless tumor is the ability to metastasize in the early stages. It can appear on the skin of the body and mucous membranes, and on the eye.
What's the forecast?
If melanoma grows on the surface of the skin, and not deep into the tissues, the probability of complete elimination of the pathology is 97-100%.
When the liver is damaged by metastases, the patient is prescribed treatment methods that improve the quality of life and eliminate symptoms. It is difficult to influence the course of development of the pathology, so the prognosis is unfavorable. According to statistics, most patients die within 12 months after detection of liver tissue disease. Organ transplantation prolongs life by several years. In 6% of cases, survival is 2 years.
Melanoma with metastases: who is at risk
Within a few months or weeks, melanoma metastases can affect vital organs.
Factors influencing its aggressiveness:
- hereditary predisposition,
- age over 50 years,
- exposure to ultraviolet radiation,
- skin characteristics (people with phototypes I and II are at risk).
Metastasis will occur more quickly if the patient has a history of concomitant chronic disease or decreased immunity.
What is the reason for the high mortality rate?
Many doctors consider melanoma to be the most aggressive tumor. And mortality statistics from such a disease often confirm this opinion. The high mortality rate in melanoma is explained by:
- The high growth rate of this tumor.
- The ability to metastasize early and sometimes even rapidly.
- The ability to metastasize through the blood (hematogenous route) and lymph (lymphogenous route) to almost all organs.
- A considerable number of risk factors for development.
But at the same time, melanoma, due to its localization, can be diagnosed earlier than other cancers. It is timely seeking medical help for any warning signs that helps avoid death from such a disease.
Clinical picture
The development of the clinical picture of metastatic melanoma depends on where the cancer cells accumulate and which internal organ they affect. Possible manifestations are clearly demonstrated in the table.
| Localization of metastases | Symptoms of the lesion | Diagnostics | Treatment |
| Liver | The skin and whites of the eyes turn yellow, the patient constantly feels bouts of nausea, and pain appears in the area of the right hypochondrium. The organ gradually increases in size, fatigue appears, weight loss | Blood test, liver ultrasound, CT scan | First, surgical removal of metastases is performed, then chemotherapy, radiotherapy, immunotherapy and symptomatic treatment |
| Abdominal organs | If metastases have affected the stomach or intestines, constant pain appears in the abdominal area, the patient may complain of constipation or diarrhea, nausea and vomiting. While maintaining appetite, weight rapidly decreases. Fluid gradually accumulates in the peritoneum, and dropsy develops | CT, MRI | Surgery to remove metastases, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, treatment of symptoms |
| Joints and bones | Frequent, spontaneous dislocations and fractures, accompanied by severe pain. High levels of calcium are found in the blood. This phenomenon causes signs of dehydration and confusion. | CT. MRI, PET, radiography | Surgery to remove metastases, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, strengthening the immune system, radiofrequency ablation, elimination of symptoms |
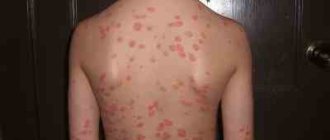
| Leather | Multiple formations appear on the surface of the skin, looking like dark spots. They have an asymmetrical shape, paneled edges, and uneven coloring. The formations are constantly increasing in size. They may ulcerate and bleed | Dermatoscopy is performed, a biopsy of the affected areas is performed, followed by histological examination | Surgical excision of the affected areas (in case of multiple lesions, cryodestruction is used - destruction of malignant cells with liquid nitrogen). Then laser therapy and chemistry are added |
| Lungs | The patient complains of difficulty breathing, persistent cough, and the presence of symptoms of a secondary infection. Fluid accumulates in the chest | CT, fluorography of the chest wall | A surgical operation during which metastases are removed, followed by radiotherapy and chemotherapy. At the same time, measures are taken to strengthen the immune system |
| Brain | Severe headaches, seizures, epilepsy attacks | CT, MRI, neurological studies | Surgical removal of metastases, chemotherapy, immune boosting, steroid treatment |
Where does it metastasize?
The list of organs and systems where melanoma metastasizes is quite extensive. Many experts suggest that with this type of cancer, distant secondary lesions can be found in any part of the body. In general, doctors identify three main ways of spreading cancer cells with this disease:
- Contact. With this spread, melanoma grows into nearby organs and tissues.
- Lymphogenic. If metastases are spread along with lymph, they can settle in nearby or distant lymph nodes, as well as in some organs.
- Hematogenous. With this method of spread, cancer cells affect various internal organs, most often their target is the liver, lungs, bones, and brain. It is with blood that metastases can reach the spine.
Surprisingly, melanoma itself can also be essentially a metastasis - caused by another cancerous tumor. In this case, doctors talk about the secondary nature of such cancer.
Tumor in the lymph nodes
Damage to the lymph nodes occurs at the third stage of melanoma development: it noticeably increases in size, grows deep into the dermis and skin-fatty tissue. The surface of the tumor bulges, and the patient’s general health deteriorates. He appears:
- symptoms of anemia,
- weakness,
- migraine.
There is a sharp weight loss, body temperature rises, and the liver increases in size. Some patients experience neuroses. Lymph nodes increase in size and become painful.
Metastases are similar in their histological structure to the primary tumor, but their degree of differentiation is lower. Therefore, they develop rapidly and are less treatable. At this stage of the disease, signs of intoxication and pain appear.
Methods for identifying the disease
The following methods help to detect the presence of melanoma metastases in the lymph nodes and the extent of their prevalence:
- Staining of pathological cells. Dyes are injected subcutaneously or intravenously, then a puncture is made using a syringe. The presence of colored pathological cells in its contents provides an accurate diagnosis.
- Application of radioisotopes. A drug containing a radioisotope is injected into the lymph node, then the extent of the damage is determined by scanning.
- Removal of a lymph node. The operation is performed under general anesthesia, and the excised tissue is sent for histological examination.
- Biopsy (fine needle aspiration). Under ultrasound control, a puncture is made, fluid is taken from the lymph node, which is then sent for histology.
Treatment of melanoma with metastases in the lymph nodes
If damage to regional nodes is observed, then surgical excision of the primary lesion and removal of the lymph nodes closest to it are performed.
To prevent relapse, therapy with interferon and drugs (Cisplatin, Dacarbazine) is carried out. Their chemical formula kills cancer cells. The combination of chemotherapy and immunotherapy gives a good effect, but this treatment option also has side effects.
In case of multiple lesions of the lymph nodes, radiation therapy is used. If the disease is advanced, the patient is prescribed the drug Ipilimumab.
What treatment is used?
Surgery is performed in 5-10% of cases, since melanoma is characterized by multiple, hard-to-reach metastases. Surgery is performed if cancer cells have accumulated in a relatively safe area. If surgical intervention is not possible, the following treatment methods are used:
- Treatment is ineffective and is aimed at alleviating the condition.
Chemotherapy. Slows down the growth and development of secondary tumors, reduces existing lesions. - Intra-arterial chemotherapy. Involves the administration of a drug into the renal artery.
- Irradiation. Reduces the intensity of pain.
None of the existing methods can completely eliminate cancer. The prognosis is unfavorable in any case. The goal of therapy is to eliminate symptoms and prolong the patient’s life. Immunotherapy strengthens the body's protective functions and improves the general condition of a person. The use of non-traditional methods of treatment is allowed, for example, the use of the drug ASD-2, which has proven itself in the fight against cancer, and herbal medicine.
Traditional medicine
Many patients are looking for alternative ways to treat skin cancer and use traditional medicine. But such therapy cannot be carried out for metastases. Some prescriptions can only be used as an additional measure to enhance the effect, but they must be confirmed by the attending physician. Those that strengthen the immune system show good results. Best suited for these purposes:
- green tea with honey and lemon,
- a healing decoction of berries and herbs (mint, fireweed, lemon balm, chestnut flowers, cherries, strawberries, currants and viburnum),
- a drink made from cranberries, walnuts and green apples (pass everything through a meat grinder, add a glass of water and sugar, boil, drink cooled),
- paste of dried apricots, raisins, walnuts and prunes (all ingredients are ground and mixed with honey).
The following have an excellent biostimulating effect: pollen, tinctures of echinacea, ginseng, and yarrow. However, if abused or incorrectly dosed, the body may become depleted (this is caused by excessive consumption of enzymes).
Attention! It is allowed to develop a regimen for taking traditional medicine only under the guidance of the attending physician.
Forecast
On average, in the presence of regional metastasis after lymph node dissection, the five-year survival rate is about 43%. Moreover, the survival rate for patients under 50 years of age is much higher.
About 40% survive more than 5 years after surgical removal of metastatic lesions.
On average, with a single metastasis, survival rate is 53%, while with multiple metastases (more than 4 metastases) it barely reaches 25%. On average, survival for skin cancer with metastases in stage 4 is about 7-10 months.
Therefore, an important factor in survival is an adequate assessment of the state of the oncological process and the correct approach to the selection of treatment methods. It has been proven many times that effective treatment can greatly increase the chances of long-term survival and significantly prolong the life of a cancer patient.
Prevention
After removal of melanoma, the consequences are not always predictable. Therefore, it is necessary to visit an oncologist once a month for a year and undergo an examination to detect a relapse. This measure allows for timely detection of metastases.
To prevent the development of metastatic melanoma, experts recommend that everyone who has large and small moles on their body constantly examine the body and monitor the formation of any skin formations. If signs of malignancy of the spots are detected, immediately contact the oncology hospital.
To prevent melanoma, it is important to protect moles from the rays of the active sun, avoid visiting a solarium, and prevent injury to benign tumors.
Diagnostics
When making a diagnosis, doctors conduct a thorough examination, which includes:
- x-ray of the affected area;
- biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes for histology;
- fine needle aspiration biopsy;
- PET (positron emission tomography);
- CT (computed tomography);
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging);
- Ultrasound (ultrasound examination);
- lymphoscintigraphy;
- blood test for tumor markers.
We recommend reading Breast adenoma - treatment, causes, types
After diagnostic measures, the patient is sent for treatment to the oncology department.
What are the forecasts?
The prognosis is influenced not only by the damage to the lymph nodes, but also, first of all, by the type of tumor and its stage. Different types of cancer have different five-year survival rates—the proportion of patients who remain alive five years after they are diagnosed. Talk about this with your doctor, ask what your prospects are, what types of treatment you plan to use, and what results the doctor expects.
In cases where it is impossible to achieve remission, the patient can still be helped: to slow down the progression of cancer, relieve symptoms, and prolong life. At the Medicine 24/7 clinic, we use the most modern methods for this; our oncologists prescribe treatment for cancer metastases in the lymph nodes according to the latest versions of international protocols. Contact us to learn more about our capabilities and get advice from our specialist doctor.
The material was prepared by the deputy chief physician for medical work of the Medicine 24/7 clinic, candidate of medical sciences Sergeev Petr Sergeevich.