Scabies
is a common parasitic skin disease caused by the microscopic mite Sarcoptes scabiei and is highly contagious. The incidence of scabies is quite high, and, despite the fact that scabies is considered a disease of asocial individuals, it affects people of all social classes. Typically, scabies causes severe itching, which intensifies towards the end of the day.
Scabies, like many skin diseases, can serve as a kind of sign indicating the presence of other sexually transmitted infections. There is an explanation for this - the body affected by one infection cannot cope with other diseases. Skin affected by mites is an open “entry gate” for STDs (sexually transmitted infections).
Scabies
Scabies is a skin disease caused by the scabies mite. One of the ways the disease spreads is through sexual contact, so many experts classify this infection as an STD.
In the countries of the Ancient East, about 4 thousand years ago, this disease was already known, which was caused by one of the types of skin parasites - the scabies mite, or, as it is also called, scabies itch (Sarcoptes scabiei).
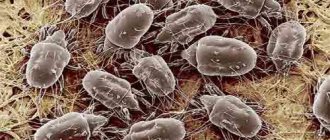
Scabies is a microscopic mite (of the arachnid family) that is capable of penetrating under human skin, creating colonies there, and feeding on skin tissue. The scabies mite penetrates into the thinnest and most delicate areas of the skin, which are easily injured.
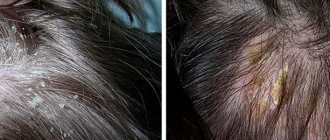
The entry points for infection are most often the spaces between the fingers, in children - the elbows, face, armpits, in women - the mammary glands.
The Russian version of the name of the disease, “scabies,” is clear: the main symptom of scabies is itchy skin.
The severe itching that occurs with scabies is a type of allergic reaction to the presence of a mite in the body. Itching may intensify and subside depending on the activity of the mite under the skin.
Focal and extrafocal forms of scabies spread
The scabies mite that causes the disease can be transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person through various types of contact: through direct (family or sexual) contact or indirectly through shared objects (clothing, bedding, shower accessories).
Doctors warn that scabies is an extremely contagious (contagious) disease and is more common than other parasitic skin diseases.
About 300 million cases of scabies are registered annually; the density of the disease is especially high in countries with a low level of hygienic culture of the population. An increase in diseases is recorded during wars, social and natural shocks, and economic downturns. At the same time, outbreaks of scabies are observed in relatively prosperous countries when the living conditions of certain social groups deteriorate.
Today, scabies is such a common disease in Russia that we can talk about an epidemic. This is facilitated by hotbeds of military action in various regions of the country and neighboring states, an increase in the number of migrants from Central Asian countries, including illegal ones, an increase in the number of people without a fixed place of residence, street children, and socially vulnerable citizens.
It should be noted that the spread of scabies is also facilitated by the development of crime, an increase in the number of people who drink alcohol and drugs, and practice promiscuous sexual relations.
In modern Russia, there is a weakening of immunity in the vast majority of residents, which also affects the progressive spread of scabies
In modern Russia, there is a weakening of the immune system in the vast majority of residents, which also affects the progressive spread of scabies. There are experts who believe that there is a connection between periods of increased solar activity and an increase in the number of cases of scabies.
These factors contribute to the creation of spontaneous foci of the disease. The focus of scabies can be considered a group of people in which there is a patient who can infect others. A focus in which there is only one infected person is considered potential, and if there are two or more patients in the group, then such a focus is classified as a radiating or active focus of scabies.
Infection with scabies mites most often occurs within a family, where the mite was brought by one of the family members - this is the most common route of transmission of scabies and is recorded in 90% of registered cases. In such cases, medical workers identify a family outbreak of scabies infection.
Somewhat less common are cases of infection of relatives or acquaintances who are not constantly in the family, which is a hotbed of scabies.
Half of the people who are the primary sources of family scabies infection are in the age group of 17–35 years. In a family, most often these are children of different ages, husbands. Infection occurs both sexually and through common objects. Within a family, one spouse infects the other, children can become infected through household means (the indirect route of infection is no more than 13%).
Prevention measures
To protect yourself and your loved ones from scabies infection, you should follow simple preventive measures.
- Wash your hands after visiting public places, shops, or any contact with domestic or street animals.
- Periodic examination of children, especially those who cannot yet explain and talk about their feelings on their own, will also help to detect signs of scabies in time. After playing in the sandbox or contacting animals, they must be checked for bite sites. Children should wash their hands very often, as this will protect not only from scabies mites, but also other harmful microbes.
- If there is a sick family member in the house, you should start treating him as soon as possible and limit contact with him for a while.
- After the treatment is completed, all clothes, bedding and other household items that the sick person came into contact with should be boiled. In very hot water, ticks die immediately; after 5 hours they die in the cold. At normal temperatures, the lifespan of a tick is about 5 days. This period increases if the environment for the insect is favorable, that is, humid. In such conditions they can live for about two weeks.
- Any toys that cannot be cleaned of parasites in another way: washing or disinfection should also be frozen.
- Carrying out wet cleaning with the use of disinfectants will significantly reduce the number of ticks, and after final recovery it will destroy the remaining ones.
If you have had contact with a sick person, you should immediately consult a doctor who will conduct an examination and, if necessary, prescribe treatment.
To reduce the risk of contracting scabies, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system, since people whose bodies are sufficiently hardened are less likely to become infected with scabies. And if a person does get sick with this disease, there is no need to worry. After all, curing scabies is now very simple.
Causes of Scabies
The scabies mite (Sarcoptes scabiei) is not an insect, but a representative of an arachnid. The length of the female scabies mite is about 0.5 mm. She lives for about a month. Females make passages under the stratum corneum of the skin, laying there 2-3 eggs daily, from which larvae hatch.
The larvae go through several stages of development and become adults.
All this happens in the patient's skin. There they leave the products of their vital activity. They then rise to the surface of the skin and mate. The males, having fertilized the female, soon die. The fertilized female implants itself into the skin of the previous or new host. After leaving the host, the scabies mite can live for 2–3 days at room temperature. When boiled or exposed to frost, they die almost immediately.
A fertilized female forms an itch tract in the stratum corneum of the skin, in which she lays 2-4 eggs per night. Ticks dissolve skin keratin using special proteolytic enzymes contained in their saliva (they feed on the resulting lysate). Males form short lateral branches in the female's scabies passage. The lifespan of a female does not exceed 4-6 weeks. The larvae hatch after 2-4 days and immediately begin to form burrows in the very top layer of the skin. After another 3-4 days, the larvae molt and turn into protonymphs, which in turn molt after 2-5 days into teleonymphs. Teleonympha develops into an adult male or female in 5-6 days. In total, the formation of an adult tick occurs in 10-14 days.
The mite can be infectious at any stage of development, but more often scabies is transmitted from person to person with fertilized adult females.
Ticks are not active during the daytime. The female begins to “dig” the tunnel (2-3 mm per day) in the evening; At the same time, itching intensifies in patients with typical forms of scabies. At night, females come to the surface of the skin to mate and move to other parts of the body (on the surface of warm skin, mites move at a speed of 2.5 cm per minute. The most favorable situation for infection then arises.
The scabies mite can only live and reproduce on human skin. It is estimated that without treatment, six generations of ticks in the amount of 150,000,000 individuals can be born in just three months.
A fertilized female drills an itch duct in the upper layers of the epidermis - a gallery, where she lays eggs from which larvae hatch, they come to the surface and, together with the males who live on the skin, cause itching and scratching with their bites.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
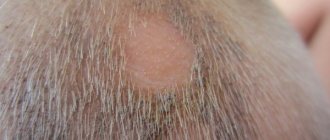
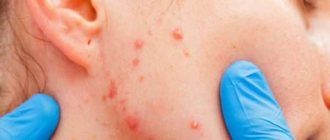
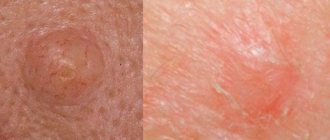
The first signs of scabies are the appearance of itching and pimples on the skin. As soon as infection occurs and the first symptoms appear, you should definitely consult a doctor for therapeutic treatment.
The scabies mite enters the human skin and begins to develop there. The female parasite lays eggs. This can only be done while in the epidermis. Outside the human body, ticks die after some time. A sexually mature female is capable of laying several eggs, after 3 days the larvae appear, and after 14 days they become adults. Therefore, within a few weeks from the moment of infection, a person begins to feel constant itching and burning.
Since scabies mites are predominantly nocturnal insects, symptoms are more active at this time of day. The parasite is viable only in the skin. Habitats where ticks spread most:
- palms,
- feet,
- wrists,
- male genital organs,
- elbow bends, their inner part.
In these areas of the skin there is no hair, there are many sweat glands in the epidermis, which together creates ideal conditions for the development of mites.
Symptoms of the disease are as follows:
- itching that gets worse at night,
- many small pimples,
- the appearance of moves between them,
- whitish scales.
In addition to larvae, eggs and scabies, there may be waste products of mites under the skin. Because of this, an infectious-inflammatory process very often develops. Excessive cleanliness and constant washing contribute to the rapid spread of the disease, since the protection of the skin in such people is impaired. There are several varieties of this disease. However, the causative agent of scabies in any of them is the same parasite.
Mechanism of scabies infection
Infection with scabies is possible in public places through door handles, stair railings, and telephone handsets. As a result, an epidemic focus is created and a person with scabies infects his environment of a domestic and professional nature. Infection with scabies can occur through sexual intercourse; more often, a man becomes infected from an infected woman. Scabies mites can remain on animals for a short time, so infection with scabies from animals is not excluded, although it is extremely rare. The scabies pathogen is most active from September to December, and it is during this time that the largest number of scabies outbreaks are diagnosed. Activity at night causes a high risk of infection within the family when the same bed is used. The interdigital folds and wrist areas are primarily affected, and already with the development of scabies, other areas of the body are affected, except for the scalp and armpit area.
Pathogenesis (what happens?) during Scabies
Symptoms of scabies are caused by an immune-allergic reaction of the host body to the waste products of the mite, so all symptoms develop only after the patient has been sensitized. This explains the long asymptomatic period (up to 4 weeks) preceding the appearance of the first signs of the disease during primary infection.
In cases of repeated infection, a reaction to the pathogen can develop within 24 hours. The development of protective immunity also explains the difficulty of re-infection in the experiment, as well as the fact that upon re-infection, a significantly smaller number of ticks are found on the patient’s body.
Itching with scabies is mainly caused by a type IV allergic reaction (delayed hypersensitivity) to saliva, eggs and mite excrement. Scratching caused by itching often leads to the addition of bacterial flora (staphylococci and streptococci) with the development of pustules (pyoderma). Thus, the scabies rash becomes polymorphic.
Interestingly, the same allergens were also found in household dust, inhabited by microscopic household mites, which also feed on human epithelium, which forms the basis of house dust.
With severe tick infestation, the level of interleukin-4 increases. Patients also have a Th2 type of immune response, which is associated with an increase in their serum IgE and IgG in combination with eosinophilia. However, this strong humoral immune response does not have a significant protective effect. With scabies, the cellular immune response, which has been studied at the histological level, is more significant: the mites are surrounded by an inflammatory infiltrate consisting of eosionophils, lymphocytes, histiocytes and a small number of neutrophils.
With the Norwegian form of scabies, pronounced hyperkeratosis is observed, and in areas of inflammatory infiltrate a large number of mites are found (up to several million on the body of one patient). Norwegian scabies occurs in patients who do not feel significant itching or are unable to scratch.
Such conditions occur in immunodeficiencies, when the immune reaction to ticks is sluggish (AIDS, regular use of glucocorticosteroids and other immunosuppressive drugs), in violation of peripheral sensitivity (leprosy, syringomyelia, paralysis, tabes dorsalis), constitutional abnormalities of keratinization, as well as in frail patients (senile dementia, dementia, limited mobility, etc.).
With the long-term existence of the infiltrate, the so-called scabious lymphoplasia is formed in the form of nodules (nodular scabies), when the infiltrates become very dense and are distributed around the subcutaneous vessels and in the fatty tissue, resembling elements of lymphoma or pseudolymphoma.
How does scabies appear on the skin?
The main symptoms are itching and skin rashes. However, itching can vary greatly in intensity (up to its complete absence), and “classic” skin rashes in the form of “itchy burrows” are rare.
Itching and skin rashes are accompanied by most other skin diseases, so diagnosing scabies is often a difficult task even for a dermatologist.
As an example, I can cite a case from my own practice, when a council of five dermatologists (!) examined and examined the patient repeatedly over the course of a month (!) and could not make a diagnosis of “scabies”, since the disease was “atypical.”
How to treat the disease
Scabies will not go away on its own. The disease needs to be treated urgently. In addition, the patient poses a danger to others. You can get rid of the disease at home. For these purposes, topical preparations are used.
It may also be interesting: How to quickly get rid of lice from a child?
The most effective remedy is Permethrin. You need to apply it at night and wash it off in the morning. Before each procedure, you should rinse the skin well, you can swim, and then dry the skin well. There are also other topical agents:
- Sulfuric ointment;
- Crotamiton;
- Lindane in lotion form.
Lindane has many side effects. This highly toxic drug is prescribed extremely rarely. Sulfur ointment gives a weak therapeutic effect and is not suitable for severe forms of the disease. To reduce allergic manifestations, antihistamines are prescribed. Check with your doctors for how long you will need to take the medicine. If 14 days have passed and there is no relief, you should consult a specialist for additional diagnostics.
Treatment of patients with local medications is supplemented with medications for external use. For this purpose, the doctor prescribes Ivermectin tablets. Pregnant women should not take this medicine. It is important that a woman takes all necessary preventive measures to avoid becoming infected with parasites during pregnancy. This may harm the baby.
Scabies does not last long if treatment is started on time. After two to four weeks the parasites should die. After treatment for scabies, re-infection is possible. A relapse indicates that one of the family members also became infected with scabies. If the disease is not treated, it will become more serious. A bacterial infection may accompany the underlying illness.
Ticks may not be sensitive to some drugs. In this case, the efficiency is significantly reduced. In this case, the course of treatment needs to be adjusted.
Some time after treating scabies, the course can be repeated to avoid the development of re-infection.
To prevent the spread of the disease, the infected person must follow safety measures. The patient's clothes and personal belongings are washed daily, separately from other linen. Ticks do not live long outside the human body; they die of starvation. Therefore, the infected person’s belongings can be packed and removed. The parasites will die of starvation after a while.
You may also be interested in: Symptoms of the presence of parasites: skin rash
Treatment of scabies should be entrusted to a dermatologist or dermatovenerologist. The specialist will tell you what to do and how to treat the disease, and will also determine whether the disease is in a complex form or not.
Types of scabies
There are several types of the disease:
- Typical scabies is a disease that occurs classically, that is, easily diagnosed (pronounced clinical picture)
Typical scabies is a disease that occurs classically, that is, it is easily diagnosed (a pronounced clinical picture). Specific skin lesions are characterized by the presence of scabies mite passages. A rare type of scabies is a disease without visible mite passages; the disease develops as a result of damage to the subcutaneous tissues by mite larvae (not adult individuals). This disease lasts no more than two weeks - this is the minimum time required for a tick larva to transform into an adult that can infect the skin and reproduce. During this period, typical signs of scabies appear.
- In 1848, it became known for the first time that a person was infected with Norwegian scabies. This case was recorded in medical sources.
- Norwegian scabies (other names: crusted or crustose scabies) is a disease that is quite rare.
The disease can affect people with weakened immune systems, patients with tuberculosis, AIDS, cancer patients, and also develops in people undergoing chemotherapy, taking hormonal drugs, and in those who suffer from vitamin deficiency. This is an aggressive form of scabies, which in most cases is very severe. A characteristic symptom of Norwegian scabies is a rash on the skin. The surface of weeping ulcers and erosions acquires a dirty yellow color and is covered with dark crusts that resemble a shell in appearance. It is in the lower layers of the cortical formation that the scabies tracts are located. In the intercortical space, when examining the material under a microscope, mites are found in various stages of development - a colony of 200 mites can be located on one square centimeter of skin. Also typical signs of Norwegian scabies are damage to the nails, soles, and skin of the palms. The patient exudes a heavy sour odor, and his temperature often rises. - There are facts when ticks are transmitted to humans from domestic animals - dogs, pigs, horses, rabbits and goats
There are facts when ticks are transmitted to humans from domestic animals - dogs, pigs, horses, rabbits and goats. This disease is called pseudoscabies, pseudosarcoptosis or tick-borne dermatitis. If contact with the source of infection is avoided, pseudoscabies goes away on its own, and this is explained by the fact that mites that cause diseases in animals cannot reproduce in human skin tissue. Pseudoscabies is transmitted from person to person.
- There is another type of typical form of the disease - low-symptomatic, or “incognito scabies”, “clean scabies”.
- The disease affects people who shower frequently; during this procedure, most of the scabies mite population is removed. That is why the disease occurs with mild symptoms. In this case, complications such as dermatitis, pyoderma or, in rare cases, microbial eczema and urticaria may occur. Thus, typical manifestations turn out to be blurred and not expressed.
Can one family member pass the disease on to another?
There are several ways of infection. The most common is close contact with a person diagnosed with the disease. Scabies is transmitted very easily and in two ways:
- direct contamination;
- indirect.
You can also become infected with this disease through contact with an infected animal, but this is quite rare and does not pose a particular threat to the patient. If the pathogen was transmitted to you from an animal, it will not harm you and will soon die on its own.
How can you get scabies?
Scabies infection occurs when a scabies mite is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person through direct contact or indirectly (through objects used by the patient).
Scabies is most often transmitted through sexual contact, through linen and bedding; infection is possible through mattresses and blankets in trains, hotels, hospitals, etc.
In children's groups, scabies can be transmitted through soft toys, writing instruments, and sports equipment.
How quickly does infection occur?
The limited number of methods of infection with scabies is due to the fact that close contact for 10 minutes is required for the mite to crawl.
Once on the body, the mite secretes substances that dissolve the microscopic upper skin cells and makes small passages in it. Its task is to lay eggs under the skin. Gnawing through a passage takes about 1 hour.
In place of the passages, white small elevations, stripes and scales appear, which can sometimes be felt or seen under a magnifying glass. The tick does not go deep because it breathes air. For the same reason, the tick makes additional holes.
Due to the way in which scabies is transmitted, examination and prevention are necessary, and often treatment, if someone in the group is diagnosed with the disease.
From the moment the tick penetrates the skin until the first symptoms appear, a little more than a week passes. This is how long the incubation period lasts. If the scabies mite has not been able to penetrate within 10 days, it will die.
Diagnosis and treatment
Symptoms of scabies are often similar to those of other diseases transmitted during sexual intercourse. Differential diagnosis with syphilis is carried out. To exclude a diagnosis of syphilis, serological tests should be performed. In children, it is necessary to differentiate the disease from urticaria or infantile prurigo. You should also distinguish scabies from dermatitis, eczema, pityriasis rosea, inflamed insect bites, and allergic rashes.
Scabies itself is a disease that a specialist can easily diagnose and prescribe treatment that will quickly relieve the patient of unpleasant symptoms. Skin irritation and itching cannot be ignored.