Description of the disease
Urticaria, or, as doctors also call it, nettle fever, is a dermatological disease of an allergic nature. The disease, which many also know as urticaria, is accompanied by the appearance of a vesicular rash on the skin, which occurs along with other unpleasant symptoms. It may be a full-fledged disease or a symptom of some other disease.
What is urticaria
Why does it occur
Since urticaria is allergic in nature, the main causative factor contributing to its development is an allergic reaction. The role of an allergen can be played by various irritants, including:
- Food;
- medications;
- ultraviolet radiation;
- severe stress;
- synthetic fibers;
- pet hair;
- pollen or road dust;
- chemicals.
Reasons for the development of urticaria
Sometimes urticaria develops against the background of other diseases or pathological conditions:
- chronic infection, such as infectious gastritis;
- dental caries or chronic tonsillitis;
- liver failure;
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract.
Etiology of urticaria
Note! If urticaria manifests itself as a concomitant symptom, it usually has a chronic course. The symptoms of the pathology are less pronounced, and periods of exacerbation practically do not occur.
Characteristic symptoms
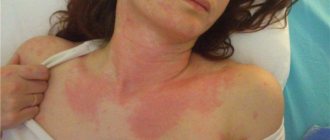
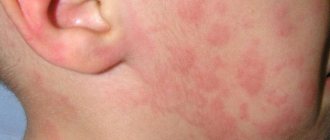
Urticaria is usually accompanied by pronounced symptoms. A pink or red rash suddenly appears on the skin. The blisters have a round shape, and in some cases they merge into one large blurry formation. The affected areas of the skin are very itchy, but after a certain time the rash goes away and appears in another place.
Signs of hives
The transition of nettle fever to a chronic form leads to the fact that the patient’s condition can alternate between exacerbation and improvement. The duration of such periods is always different. When urticaria worsens, additional symptoms appear:
- Strong headache;
- general weakness;
- diarrhea;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- increase in body temperature.
On a note! The most complex form of the disease is Quincke's edema or giant urticaria. This is an acute allergic reaction, accompanied by massive swelling of the mucous membranes or skin. This condition requires immediate medical intervention.
Dangerous symptoms of urticaria
All of the above signs refer to the external manifestations of urticaria, but there are changes that occur inside the patient’s body. Upon contact with an allergen, the cells of the body are gradually destroyed, resulting in the release of histamine (tissue hormone). It affects the body in such a way that liquid enters the cavity between the cells from small blood vessels. This leads to redness and swelling of the tissue.
Urticaria: contagious disease or not?
This disease poses a significant problem for humans. It not only creates considerable physical discomfort due to constant itching, but also spoils a person’s appearance. A particular nuisance is that rashes often appear in areas that are not covered by clothing.
Therefore, this illness can complicate a person’s relationship with his environment. This is especially acute for a child in a children's group.
Seeing such redness, rashes and blisters on the skin, as shown in the photo below, both the patient himself and the people around him wonder whether urticaria is contagious or not.
Really: is hives contagious? How dangerous is a person suffering from this disease to others? Is this disease a personal problem for the patient himself, or is there a possibility of infection spreading? How much precautions should be taken to prevent infecting other people? And how is urticaria transmitted if it is contagious?
So, is hives transmitted from person to person?
What is hives and is it contagious?
Among the various skin lesions, there are those that can be transmitted from a sick person to a healthy one.
Various types of lichen, infectious dermatitis and other skin diseases caused by viruses, bacteria and parasitic fungi can indeed be transmitted from an infected person to others. For this, sometimes direct contact between people is not even necessary.
For example, when shaking hands, infection can also occur through various objects that come into contact with the patient’s skin. Is urticaria transmitted in this case?
To begin with, urticaria is not an independent disease caused by any specific single factor. It may be an element of the overall clinical picture of any disease. This disease is a combination of the following symptoms (see photo):
- severe skin itching;
- lumpy rashes on different parts of the skin;
- blistering.
What is the reason for this clinical picture?
What causes hives and is it contagious or not?
As research by scientists has shown, the cause of rashes is an allergic reaction of the body. Allergies in this case can be caused by the following factors:
- side effects of antibiotics and other drugs;
- toxic effects of certain chemicals;
- intoxication of the body with waste products of parasites;
- the effect of allergens contained in a number of food products;
- exposure of the skin to sunlight, water, ambient temperature;
- mechanical effect on the skin;
- some infectious diseases;
- nervous tension, stress.
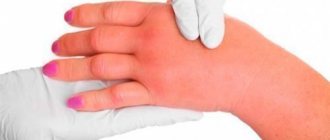
When the skin is directly exposed to factors that provoke pathology, allergy sufferers experience contact urticaria (see photo). The appearance of this type of disease can be caused by:
- skin contact with chemicals;
- contact with certain plants;
- wearing rubber gloves;
- contact with animals;
- use of cosmetics.
The cause of the skin reaction is an increase in the content of histamine in the blood, which makes blood vessels more permeable.
As a result, the skin turns red, becomes swollen, and blisters appear.
An increase in the amount of histamine occurs under certain external influences on the body or during internal intoxication caused by infectious diseases or parasitic infestations.
Different people have different susceptibility to certain agents that can cause allergies. This is determined by the state of the immune system, the presence of certain internal pathologies, hereditary predisposition, and so on. Therefore, it is impossible to say in advance what exactly can cause a corresponding skin reaction in a particular person.
Thus, urticaria itself is not transmitted either through direct contact of a sick person with a healthy person, or through objects.
How dangerous is hives?
This disease in itself does not lead to death or disability. However, the lack of timely treatment can lead to very unpleasant consequences.
Usually, the disease, even without taking any therapeutic measures, ends a few weeks after the first symptoms appear. However, chronic urticaria sometimes develops (see photo), which can last for years.
As a rule, the causes of this form of the disease are internal pathologies of the body, such as:
- internal secretion problems;
- oncological diseases;
- foci of various infections;
- helminthiases;
- chronic diseases of the nose and throat;
- cholecystitis;
- disorders of the digestive system.
Therefore, although the skin rashes themselves do not pose a serious danger, they can signal the presence of a serious illness, including a cancerous tumor. And if long-lasting rashes appear on the body, it is necessary to undergo a full examination of the body.
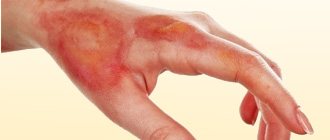
Despite the fact that skin problems do not pose a threat to life, if no measures are taken when itching and blisters appear, severe complications of the disease may develop. Thus, pathological processes in the skin can spread to the subcutaneous tissue, resulting in Quincke's edema, shown in the photo below.
The process can also spread to the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract and digestive organs. When the stomach and intestines are affected, vomiting and diarrhea appear. Damage to the upper respiratory tract is especially dangerous: the development of laryngeal edema in the absence of urgent measures leads to death from suffocation.
The appearance of rashes and papules on the skin indicates exposure to an allergen. If this effect is not eliminated in time, the result can be anaphylactic shock, which sometimes ends in death.
Therefore, the appearance of skin problems requires urgent elimination of the cause of the allergic reaction. So, if a skin rash occurs after taking any medication, then it is urgent to replace the drug used.
Is infectious urticaria transmitted?
Rashes with the formation of blisters can appear with some infectious diseases, such as:
- rubella and measles;
- herpes;
- diphtheria;
- cytomegalovirus infection;
- typhoid and typhus.
All of these infections can pass from person to person. But here it makes sense to talk not about the contagiousness of urticaria, but about the contagiousness of the corresponding diseases.
In addition, a skin reaction with a clinical picture in the form of blistering rashes does not always occur with these diseases.
This or that form of allergic reaction depends on the individual characteristics of the body, such as general health and hereditary predisposition.
Therefore, if one person has become infected from another person with a disease that can cause urticaria, this does not mean that he will necessarily develop the corresponding symptoms.
For example, the cause of a skin allergic reaction may be intoxication of the body due to helminthic infestation.
Some worms can pass directly from person to person, but the same helminthiasis can cause severe allergies in one person and be asymptomatic in another.
In some cases, it may seem that the skin rash may be transferable. For example, when a rash appears at the same time in several family members.
This can happen if these people have been exposed to the same thing, and not necessarily of an infectious nature.
If there is a genetic connection between people, then it is possible that they have the same predisposition to allergies.
That is why, if a nursing woman develops a rash, she should temporarily stop breastfeeding her baby. After all, the allergen that caused a skin reaction in the mother may be contained in her milk and enter the baby’s body with it. Due to heredity, a child may also be allergic to this type of irritant.
So, is hives contagious in adults and in children? It all depends on what caused it. If the causes of this disease are infectious, then one person can infect another. However, infection itself does not mean that the clinical picture of the developed disease will include urticaria.
In any case, the appearance of rashes and blisters requires urgent consultation with a doctor so that he can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Source: https://derms.ru/krapivnitsa/yavlyaetsya-zaraznoi-krapivnitsa-ili-net.html
Etiology and diagnosis
Another factor that raises doubts about whether urticaria is contagious or not is the lack of a general theory about the etiology of this disease. Unfortunately, even experts cannot name the exact cause of the development of urticaria and its origin. It is believed that some forms of nettle fever can be transmitted genetically. Therefore, within the family of the infected person there is a fear that the disease will spread to other members.
Differential diagnosis of urticaria
Despite the level of modern medicine, doctors cannot always find a connection with the patient’s pathology and the resulting skin rash. To clarify the etiology, it is necessary to carry out various diagnostic measures. But even this does not give a 100% result, so the origin of urticaria in some infected people cannot be determined.
Features of diagnosing urticaria
Diagnostic methods
You can diagnose cold urticaria at home using a simple procedure called the Duncan Test. Its essence is quite simple: you need to apply ice to the skin for 5 minutes and observe the body’s reaction. If there is a disease, a red bump will appear at the site of contact. If a more in-depth examination is required, then the patient is prescribed additional diagnostic measures, including laboratory blood tests and ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
Diagnosis of cold urticaria
If a cold allergy is suspected, doctors prescribe the following procedures:
- chest x-ray;
- electrocardiogram;
- gastroscopy;
- Ultrasound of internal organs;
- blood test for the presence of antibodies;
- stool coprogram for helminths;
- rheumatic tests;
- blood test for hepatitis and syphilis;
- Analysis of urine;
- general blood analysis.
Visual diagnosis for cold allergies
During diagnosis, it is important to differentiate cold allergies from other diseases. These include:
- Dühring's disease;
- erythema multiforme;
- bullous pemphigoid.
During diagnosis, female patients are prescribed a thyroid examination, especially if their close relatives have experienced autoimmune diseases. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the patient is prescribed an appropriate course of therapy.
When can you get hives?
Is urticaria contagious to others and is it transmitted by airborne droplets? These questions worry many people who have had to deal with itchy skin and rashes. As noted earlier, the disease can be triggered not only by infectious pathologies, but also by allergies to medications and various allergens, hormonal disorders and other disruptions in the body. But to encounter signs of urticaria, infection with an infectious pathology alone will not be enough.
Is hives contagious?
The causative factor against which the infectious form of urticaria develops is predominantly a viral disease. Such clinical cases are dangerous in terms of infection. But even here the key role is played by the state of immunity with the individual characteristics of the body.
Note! The process of producing special antibodies to allergens is not always activated in the body suffering from an infectious disease. Therefore, typical symptoms of urticaria in the form of a skin reaction will not develop.
Is it possible to get infected with urticaria?
The appearance of urticaria and, therefore, its contagiousness is influenced not by the infection itself, which can be contracted, but by the characteristics of the human body. The weaker its protective functions, the greater the chance of developing nettle fever.
Is hives contagious to others?
Red blisters on the skin all over the body, unbearable itching and general malaise are all symptoms of urticaria.
Whenever you see a skin rash, anyone will wonder if hives are contagious and if you can catch it from someone who is sick. Urticaria is an allergic reaction of the human body to unfavorable factors. These factors are infections, poisoning, chronic diseases and even stress.
An acute intolerance reaction occurs against the background of excessive production of histamine and other inflammatory mediators in the body, which increase vascular permeability, which causes rashes and blisters.
What causes hives
A tendency to allergies is an individual characteristic of the human body, which not everyone has. It is inherited from parents to children. It also occurs due to some serious problems:
- hormonal imbalances;
- endocrine disorders;
- chronic weakness of the immune system;
- intolerance to other irritants.
An attack of urticaria can only occur in a person with a predisposition to this disease after the influence of unfavorable factors causing intolerance. Such irritant factors include:
- stress and nervous disorders;
- acute viral and bacterial infections;
- hypothermia and overheating;
- contact with some plants, six animals, dust;
- contact with household and other chemicals;
- use of cosmetics;
- poisoning (food and others);
- infection with worms;
- injuries.
Is hives contagious? No. The manifestation of the rash depends on the characteristics of the human body at risk. Main symptoms:
- blisters and redness on the skin;
- itching;
- swelling;
- general malaise.
The appearance of rashes and blisters should be a reason to go to the hospital and see a therapist or dermatologist. Doctors will be able to determine the cause, which will determine whether it is contagious.
A predisposition to urticaria, which is not contagious in itself, is inherited from parents to children, but not the disease itself.
The answer to the question of whether urticaria is contagious or not is this: intolerance to something cannot be transmitted from person to person, so it cannot be considered dangerous.
But infectious diseases that can provoke this reaction are dangerous for the people around the patient.
How dangerous is the disease?
The danger of urticaria (another name is urticaria) is not that it can be “contagious.” Without treatment, the disease can develop into a generalized form and affect not only the skin, but also the mucous membranes. A severe attack of acute allergies can provoke Quincke's edema - severe swelling of the skin, mucous membranes and subcutaneous tissue, which is also not contagious, but can be fatal.
Is hives contagious in adults?
So, we found out whether urticaria in adults is contagious or not. In adults and children, urticaria is not contagious.
But if the rash is provoked by viral, bacterial infections or helminthiasis, these diseases are contagious.
The allergic reaction itself does not spread from person to person and is not dangerous to others. But diseases that provoke it in an adult can be dangerous.
Urticaria can be conditionally called contagious only if it is transmitted from parents to child (propensity to it). In other cases, urticaria cannot be considered contagious. It will not be transmitted to a person who is not prone to it, even through close contact with a sick person who has obvious signs of an acute allergic reaction.
If the rash is caused by an infection
If an acute allergy is provoked by bacterial or viral infections, then it is not the urticaria that is transmitted from a person to other people, but the infection itself. It is not 100% likely to manifest itself in an infected person.
It depends on the presence of a predisposition. But infections will definitely appear, but their symptoms have nothing to do with urticaria.
Diseases that are possible triggers of urticaria and are contagious include:
- viral infections (ARVI, HIV, herpes, chickenpox, etc.);
- bacterial infections (tonsillitis, diphtheria, scarlet fever, whooping cough, salmonellosis, tetanus);
- helminthiasis (infection with worms and other parasites).
Sometimes urticaria is confused with other diseases that are very contagious and dangerous, due to the fact that they have similar symptoms. Such diseases include:
- tuberculosis (transmitted to another person by airborne droplets);
- fungus (contagious through household items and personal belongings);
- chlamydia (infection possible through sexual contact);
- mycoplasmosis (similar to chlamydia, and also transmitted by airborne droplets and household);
- herpes (contagious and spread in a variety of ways).
These diseases can be contracted very easily. They are transmitted in the following ways: airborne, household, sexual, through personal belongings (clothes, shoes, combs, toothbrushes, cosmetics, underwear, etc.). If an infection has occurred, you can distinguish them by their symptoms.
With urticaria, the rash is randomly scattered throughout the body or concentrated at the site of contact with the irritant; it resembles red or pink dense blisters or swellings of various shapes and sizes (up to 10 cm). The spots itch and become even more inflamed due to mechanical trauma.
With tuberculosis there may be ulcers, the fungus causes severe peeling, chlamydia can cause small spots on the body, herpes can cause a small blistering rash in the area of the lips or genitals.
Is urticaria genetically transmitted from person to person?
Let's consider how allergies are transmitted at the genetic level and whether this is possible. The child will not always have a rash with blisters all over the body. Instead, an allergy to any irritant with other symptoms may appear, for example, nasal congestion and tearfulness or cough.
Only a predisposition to urticaria is transmitted at the genetic level from parents to children. The presence of the disease in parents does not guarantee its manifestation in the offspring, but it increases the likelihood.
The presence of intolerance symptoms in a pregnant woman does not affect the condition of the fetus. The baby is reliably protected from irritants and inflammatory mediators by the placenta.
But if urticaria has become a chronic disease, then certain complications for the child are possible, for example, developmental delay due to hypotension.
How to behave if you see characteristic rashes on a person
Knowing whether the disease is contagious or not, we can conclude: contact with a person with obvious signs of urticaria is allowed and it is absolutely safe. But only if these are symptoms of allergies, and not infections. It is difficult for the average person to distinguish the symptoms of infections from allergies. When in contact with a sick person, it is advisable to always keep your distance and be careful:
- try not to touch the rash with your hands or other parts of your naked body (especially if there are wounds);
- do not give away your personal belongings;
- wash your hands after touching a rash (for example, when a mother treats a child’s rash);
- do not communicate too closely;
- do not use the patient’s belongings (towels, clothes, dishes);
- do not have sexual intercourse.
Manifestations of allergies are similar to many contagious skin pathologies (herpes and others), so they are often confused. If a relative or loved one has a skin rash, you should persuade him to go to the hospital and get tested. Only in a hospital can you find out exactly what caused it and how to treat it. After successful treatment, to prevent relapses it is recommended:
- avoid contact with the irritant;
- change your lifestyle;
- maintain proper nutrition;
- treat infectious diseases (flu, acute respiratory viral infections and others) in a timely manner.
Not all pathologies are contagious. This should be remembered when contacting patients. Expressing your disgust can greatly offend. You need to react appropriately and calmly to a person with allergy symptoms.
Source: https://tden.ru/health/zarazna-li
In what cases is infection impossible?
Some internal factors that contribute to the development of urticaria provoke a non-contagious pathology. These factors include:
- formation of malignant tumors;
- hormonal imbalance;
- increased sensitivity of the patient's body to acetylcholine;
- consumption of certain foods;
- exposure to water, sunlight or cold;
- entry of various toxins into the body;
- consequences of taking certain medications.
When it is impossible to catch hives
If the causative factor is severe stress, then the blisters that appear on the skin will not be contagious. In such cases, the optimal method of therapy would be to maintain a calm lifestyle, avoid stressful situations and maintain a healthy diet. The appearance of skin symptoms under the influence of all of the above factors is nothing more than the reaction of the body, or rather the human dermis, to various negative processes.
Pathogenesis of urticaria
Symptoms
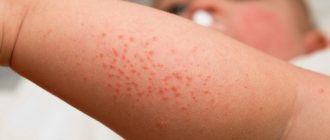
Acute childhood urticaria begins suddenly. The following symptoms of urticaria in children are distinguished:
- the appearance on the skin of ephemeral exudative elements - blisters of different sizes, from 0.5 to 15 cm, dense and swollen, rising above the skin, bright pink, with a blanching area often observed in the center; the shape of the blisters varies;
- in the chronic form – papules;
- Quincke's edema is characterized by limited swelling of the skin and subcutaneous fat;
- the patient complains of itching, burning, chills, arthralgia, suffocation;
- in some patients the voice becomes hoarse and shortness of breath occurs;
- in some cases, one of the symptoms is nettle fever;
- in young children, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea or constipation appear, and appetite disappears.
Acute limited angioedema, or giant urticaria, is indicated by the following signs:
- limited swelling of the skin or mucous membrane, subcutaneous fatty tissue, including on the face, genitals, etc., rapidly develops.
- the skin becomes white, sometimes pink, takes on a densely elastic appearance;
- there are no subjective sensations;
- swelling persists for several hours or days.
With Quincke's edema in the larynx, there is a high risk of stenosis or asphyxia. Often this form is combined with ordinary urticaria.
The onset of urticaria in an infant is acute, accompanied by a general deterioration in health and an increase in temperature to 39 degrees.
In a child, urticaria is differentiated from the following diseases:
| Disease | Symptoms |
| Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis | The appearance of erythematous rashes with a light center, intermittent fever. |
| Psoriasis | The rashes are characterized by stationary, scaly peeling, which is not the case with urticaria. |
| Exudative erythema (occurs more often in older children and adolescents) | The rash occurs first on the back of the extremities - feet, hands, as well as forearms, legs, and less often on the face, neck, and torso. Over time, the center of the papules sinks, and along the periphery they grow, forming a corolla, which does not happen with urticaria. Individual elements look like concentric figures, which are characterized by three color zones. In the center there is necrosis, covered with a crust. |
| Toxidermy | A maculopapular rash appears, the elements have different shapes. The surface of the affected area peels off. After the rash resolves, peeling remains, and persistent pigmentation occurs. |
| Mastocytosis (occurs from 3 months) | The rashes are multiple or single, nodular, red-brown in color, up to several centimeters in diameter. |
| Urticarial vasculitis | The rash lasts longer than 24 hours, pain is felt more than itching, antihistamines do not bring relief, skin lesions are accompanied by general malaise - fever rises, joint pain, etc. |
| Dermatitis herpetiformis | The rashes are polymorphic, grouped, symmetrically located, accompanied by severe itching. They evolve, vesicles and pustules develop, and secondary elements are formed. |
Urticaria and children
If we talk about preschool children, they rarely encounter signs of nettle fever. If the causative factor for the appearance of a red rash is an allergy, then the likelihood of infecting other people is minimal. But if parents identify blisters on their child’s skin, then they need to consult a doctor to determine the cause of such an allergic reaction.
Urticaria in children
Children are most often exposed to infectious diseases, including rubella, chickenpox, scarlet fever and others. All these pathologies do not pose any danger to adults, but for children whose bodies have not yet fully formed, they can lead to serious consequences.
Features of the development of urticaria in children
Consult a doctor
It is preferable to take a shower rather than a bath. Even if you are coping with allergy symptoms, consultation with an experienced doctor is required. It is necessary to find out the causes of the reaction, eliminate or reduce their influence. Basically, this range of problems is dealt with by an allergist and a dermatologist (skin specialist). The treatment will be complex.
This is a specific diet, internal antihistamines (tablets, injections), external (ointments, creams). The doctor prescribes specific medications. Of course, giving up some foods, such as sweets, can be a shock for a child. Try reducing your intake of the desired food as much as possible first before giving it up completely.
Sometimes the causes of allergies can be psychological in nature. The consequences of stress and quarrels in the family can provoke skin rashes in a child, and even an adult. If the allergist finds it difficult to determine the cause, consult a psychotherapist and neurologist. Many diseases are activated due to nervousness, in an unfavorable environment from a psychological point of view.
Can a child get infected from his mother?
During the process of passing through the birth canal, the child can become infected with certain types of pathologies from the mother. But if a pregnant woman suffers from allergic rashes, then infection cannot occur. During breastfeeding, the disease can pass to a small child through breast milk. If an endogenous irritant acts as an allergen, then it, being present in the circulatory system, can enter the mother’s breast milk.
Is urticaria transmitted from mother to child?
To determine the degree of danger of urticaria, you need to monitor how the disease manifests itself. In itself, it does not pose any threat to the patient’s life, but under certain factors anaphylactic shock or Quincke’s edema may occur. Such complications require emergency medical attention.
Quincke's edema is a dangerous complication of urticaria
Classification of cold urticaria
Most people experience the phenomenon of redness of the hands or cheeks in severe frost, but these manifestations disappear on their own after the person gets into a warm room. As a rule, it takes 10 to 15 minutes for the skin color to normalize. But if skin rash and itching are added to the redness, and after moving to a warm room the symptoms do not go away for several hours or days, then we are talking about cold urticaria.
Signs of urticaria can occur in different situations, for example:
- while walking in rainy, windy or damp weather;
- when swimming after being under the hot sun. You can swim in the sea, lake, river or even in an outdoor pool;
- when washing or washing limbs with cool water;
- when eating ice cream or other cold foods;
- after moving to a cold room from a hot room.
Allergy to cold
Sometimes signs of cold urticaria can appear even when you turn on the air conditioner, fan, or even when ventilating the room. People encounter this clinical feature in rare clinical cases.
In medicine, there are several types of pathology, each of which has its own characteristic differences. Below are the most common types of cold hives.
Types of cold urticaria
Table. Types of cold forms of urticaria.
| Name of variety, photo | Description |
| Acute | Symptoms of acute urticaria appear almost immediately after contact with cold. Sometimes patients experience severe reactions, but most often the pathology does not cause severe discomfort. |
| Recurrent | It appears seasonally, for example, in winter with the onset of frost. The disease may periodically subside and appear again after a few years. |
| Reflex | It is expressed mainly in the form of skin symptoms. Only those parts of the body that have been in contact with low temperatures are affected. Other areas of the body are not affected. |
| Family | The skin rash appears approximately 3 hours after contact with cold, and in some cases after 1-2 days. The disease is inherited and is rarely diagnosed. |
| Erythema | The disease is accompanied by redness of the epidermis and pain in the affected areas of the skin. Also, the above symptoms may be accompanied by itchy skin. |
| Dermatitis | Another type of cold urticaria. The disease is accompanied by severe peeling of the skin and itching. If left untreated, complications may occur in the form of tissue swelling. |
| Rhinitis | Nasal congestion with cold rhinitis occurs only when exposed to cold. As soon as the patient enters a warm room, the symptoms will disappear. |
| Conjunctivitis | When exposed to low temperatures, the patient begins to bleed profusely. There may also be a feeling of stinging in the eyes. As in the case of rhinitis, signs of cold conjunctivitis disappear in warmth. |
The body's reaction to cold may worsen over time, since allergies and their course are unpredictable. If initially a person develops a mild rash after contact with cold, then the next day the rash may be accompanied by other symptoms, for example, swelling of the soft tissues. Cold urticaria can be complicated by anaphylactic shock or Quincke's edema, which without timely medical care for the patient can be fatal.
Why is cold urticaria dangerous?
Incorrect therapy or its complete absence in some cases leads to the development of serious pathologies:
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis;
- systemic scleroderma;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- lupus erythematosus.
Hashimoto's thyroiditis as a consequence of cold allergy
General recommendations
Regardless of the type of urticaria that occurs, experts recommend following the following recommendations:
Diet for urticaria
- carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene, especially if you suspect the development of an infectious disease. This is an excellent preventive method;
- subject all products to thorough heat treatment during cooking;
- Monitor the general condition of your body. If even the slightest violations are detected, you need to contact a specialist for examination. You also need to follow all the doctor’s recommendations, since incompletely cured urticaria can lead to complications;
- take vitamin complexes to protect the body from the possibility of developing an allergic reaction. A properly selected course of vitamin therapy will improve immune barriers;
- try to avoid stressful situations, since along with an existing rash that has arisen as a reaction of the body to an external irritant, a rash may appear due to severe stress.
Principles of treating urticaria
Try to explain to people around you that a skin rash that appears is not a sign that they are contagious.
Ban on bathing
Therapeutic bathing for urticaria is part of traditional medicine. Many medicine recipes are based on various herbs. So why not treat your skin to a soothing herbal bath?
Not in all cases you can swim with hives. First of all, it is worth noting that water procedures are prohibited in case of illness that is accompanied by high body temperature.
Other prohibitions on swimming directly depend on the type of disease:
- Cold water temperatures can make cold urticaria worse.
- For cholinergic symptoms, only showering is recommended.
- For aquagenic urticaria, you need to minimize any contact with water. Household work must be carried out with gloves, and water procedures must be carried out for up to 2 minutes in filtered water. Babies should be bathed in boiled water without chlorine.
If a person feels worse after swimming, the itching and swelling intensify, or new blisters appear, then you should consult a doctor. He will find the best solution to the problem of daily hygiene procedures. You should not completely give up bathing, as this can lead to increased inflammation and infection of the skin.
How to get rid of hives
The key to successful treatment and quick recovery is a timely visit to a doctor and a correctly prescribed therapeutic course. Complex therapy for urticaria must include:
Preparations for urticaria
- correct diagnosis to identify and eliminate the causative factor;
- take antihistamines;
- the use of external agents that eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of nettle fever;
- desensitizing treatment;
- use of hormonal drugs (prescribed for severe disease);
- compliance with a therapeutic diet. A combination of drug treatment and diet therapy will speed up the recovery process.
Features of the treatment of nettle fever
On a note! Provided that all measures are taken in a timely manner, the symptoms of urticaria disappear literally after 1-2 days of treatment. But if adequate assistance is not provided to the patient, the pathology may accompany him for several weeks.
Medications
The doctor may prescribe both medications for oral use and medications for external use. The former help the body fight the allergen irritant from the inside, while the latter alleviate and eliminate the symptoms of the rash (itching, weeping eczema, infection of scratched wounds).
Self-medication is excluded, since many medications are contraindicated for young children and parents, through their own actions, can only worsen their condition.
External treatment
The first question that all parents ask is what to apply to a child’s hives to stop the rash from spreading throughout the body, how to relieve itching and prevent the appearance of weeping eczema and ulcers.
- Fenistil is a good ointment for urticaria, but is only allowed after 1 month.
- Hydrocortisone.
- We recommend Gistan cream, which is distinguished by its natural composition.
- Skin-Cap cream contains zinc, so it can be used to treat urticaria in a child only after consulting a doctor.
- Advantan cream.
- Elidel cream can be used to treat children from urticaria from 3 months of age.
It is not recommended to treat rashes with urticaria in children with green stuff, as it can burn the delicate tissues that are already damaged.
Injections
To combat allergies, a child diagnosed with urticaria may be prescribed intramuscular Prednisolone, which has excellent anti-inflammatory, antiallergic, antishock, and immunosuppressive effects.
For internal use
To treat urticaria, the child may be prescribed the following medications:
- histamines to eliminate an allergic reaction: Suprastin, Diazolin, Cetrin, Tavegil, Zyrtec, Erius;
- calcium preparations for increased capillary tone;
- immunostrengthening agents;
- cleansing the body in case of food allergies using sorbents: activated carbon, Smecta, Enterosgel.
In each case, medications are selected individually for the child. Those parents who prefer natural medicine can seek help from homeopaths.
Homeopathy
As medications for urticaria in children of different ages, homeopathy offers:
- Apis (for severe forms).
- Pulsatilla, Prymula (moderate and mild forms of the disease).
- Rhus toxicodendron (treatment of cold urticaria).
- Urtica urens (if the allergen is shellfish or crustaceans).
- Rescue Remedy (itch relief cream).
- Natrium muriaticum, Arsenicum album (for prevention).
Urticaria can be quickly and successfully treated if the cause of its occurrence is determined. If the allergen is not clear, recovery may be delayed, and the disease itself may develop into a more severe or chronic form. Sometimes folk remedies come to the rescue.
Treatment of urticaria in children
Statistics show that children suffer from urticaria quite often. The disease is accompanied by white or red skin rashes, as well as severe itching. The rash can appear on different parts of the body; it often appears on the child’s face. But how to fight a disease when you can’t use potent drugs? To do this, you need to follow the instructions below.
Step 1. Use antihistamines at the first onset of hives symptoms, without waiting for the symptoms to go away on their own. But medications can only be given to a child as prescribed by a doctor.
Give antihistamines
Step 2. Relieve the unpleasant symptoms of hives with oat lotion. This will help relieve burning and itching. Parents should also ensure that their child does not scratch the affected area of skin.
Make lotions from oats
Step 3. Treat the rash with a special herbal-based ointment. Local products containing aloe vera cope well with skin irritation. You can also relieve swelling and itching with a cold compress. Just wrap a few ice cubes in a handkerchief and apply to the sore spot.
Use external remedies
Step 4. Dress a child infected with hives in clothes made from cotton fabric. This will help the body to breathe, which will prevent the disease from spreading. Tight clothing should be avoided.
Use clothes made from natural fabrics
Step 5. If swelling occurs on the child's face during therapy, stop taking the medications and take the child to the doctor. Often, bloating leads to swelling of the throat, which is very dangerous for the child’s health.
Contact your doctor if complications develop
If an allergic reaction occurs after taking a medicine prescribed by a doctor, parents should contact the doctor immediately. Similar reactions can also occur after eating.
What is the disease
Urticaria is a common skin lesion caused by allergic reactions or malfunctions of the nervous system in children and adults. There are several types of disease, which differ in provoking factors - allergens. These include food, medications, sun, temperature changes, insect bites and other irritants. In some cases, urticaria develops due to nervous excitement.
OSTIOLucem traction orthopedic pillow is a unique product for women’s health
The most important thing is to establish the cause of urticaria, so as not to cause a worsening of the condition, and here you cannot do without consulting a doctor.
When an accurate diagnosis has been made, it is possible, and even necessary, to begin water procedures. If you have hives, you should bathe once daily.
Adults cannot always take a bath. They are not permitted in cases where there are pustules (under no circumstances!). Since urticaria causes inflammatory processes to form on the epithelial tissue, an excellent environment arises in which harmful microorganisms multiply well and quickly.
If you fit this description, it's best to just take a shower every now and then. And the areas of epithelial tissue where pus is located should be washed with a special washcloth (which will not be used for other parts of the body!), or not used at all.
Traditional medicine is very effective here, and not only for adult patients. Herbs are less likely to cause reactions than medications. Wipe the affected skin with a cloth soaked in a solution of string (outside of bathing), and after water procedures, rinse the skin with water and potato starch to reduce itching.
So, we found out that you can wash yourself if you have hives.
However, urticaria caused by an allergic reaction to water is very rare. This type of disease is very rare and is called “aquagenic urticaria”.
Irritation can be a response to basically all water, or only to a certain type of water: tap, sea or river.
Fortunately, this type of disease does not cause any pathological changes in the body. But at the same time it causes a lot of trouble in the form of dry and irritated skin.
Aquagenic urticaria appears in most cases 30-90 minutes after taking water procedures.
Having discovered such a disease, it is important to contact a dermatologist. At the reception specialist:
- conduct a mini-test by applying a compress soaked in water to an area of skin
- will give directions for the necessary tests
Depending on the results, treatment is prescribed.
In addition to traditional help, folk recipes are of great benefit:
- chamomile compresses;
- honey masks;
- violet decoction for washing.
Caution: in order to avoid an unwanted reaction, it is best to follow the advice and recommendations of specialists when choosing a folk remedy for the treatment and prevention of this disease.
Water allergy is highly treatable and in about seventy percent of patients the condition improves noticeably within a few days.
In order to mitigate the manifestation of an undesirable reaction upon contact with water, you can follow several preventive rules:
- try to use filtered or artesian water. If there are no such possibilities, you can get by with boiled water;
- replace all cleansers with hypoallergenic ones that contain a minimum of ingredients;
- adhere to the principles of healthy lifestyle.
The following forms of urticaria are considered non-contagious:
- medicinal – after using various medications (anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics), characteristic rashes occur;
- toxic - a rash develops as a result of the influence of toxic substances that enter the skin or inside the body;
- food - characteristic rashes occur after eating various foods;
- cholinergic – the development of blisters occurs under the influence of emotional overstrain and stress;
- demographic - the rash is localized at the site of mechanical irritation of the skin;
- rashes that appear under the influence of water, sun, heat, cold.
Summing up
Urticaria is not a contagious disease, but this does not make it any less dangerous to the patient’s health. In addition, urticaria in some cases is inherited. But if the cause is an infectious disease, then healthy people may well become infected by airborne droplets. Therefore, when diagnosing urticaria, it is important to determine the causative factor.
Difficulties in treating urticaria
Skin rashes, which appear depending on the state of immunity, can lead to serious complications in the absence of timely medical care. The most dangerous of them is Quincke's edema. But to summarize, we can say with confidence that urticaria is not transmitted to healthy people, so there is no need to be afraid of a skin rash on your loved ones or friends, knowing that it is urticaria fever.
Preventing the development of urticaria
Experts' opinion
In general, it would be fair to note that in almost any case, even quite difficult ones, bathing will be useful.
As a rule, the optimal permissible time for the procedure depends on the complexity of the disease and the area of the affected areas.
The average allowable interval is 15 minutes.
You also need to pay attention to the fact that a shower with urticaria will be preferable to taking a classic bath, since in the first case there is a greater chance of not leaving damage to the skin and thus not aggravating its general condition.
Allergic urticaria is rightfully considered the most common. It is not contagious and does not pose a danger to others. In this case, if you have hives, you can and even need to wash.
However, in order to avoid additional damage, you should remember how the hygiene procedure should be carried out. Let's consider the features of bathing with urticaria:
- swimming lasts no more than 20 minutes (ideally, it is better to keep it within a 15-minute period);
- the washcloth used for washing should be soft to the touch;
- It is good to use PH-neutral gels without fragrances as a detergent; regular baby soap can also be an alternative to these hygiene cosmetics;
- herbs help enhance the therapeutic effect of the procedure only if the patient is not allergic to them.
It is unacceptable to use hard washcloths, scrubs and other skin-damaging products, as in this case there is a risk of aggravating the disease. Shower gels with various additives can cause additional irritation on the skin, so their use at this time is also highly undesirable.
Good results in the treatment of urticaria can be achieved by taking a bath with decoctions of various herbs that have an antiseptic effect. But you need to keep in mind that herbal infusions can also cause allergic reactions. See recipes for medicinal baths and other folk remedies here.
Causes
The causes of the disease in adults depend on the exogenous and endogenous factors that cause it.
Environmental factors are considered exogenous, since the disease develops due to a person’s increased sensitivity to the rays of the sun and cold.
The occurrence of endogenous factors is associated with certain reasons: immunodeficiency, allergies, disorders of the nervous and digestive systems, metabolic diseases, dysbacteriosis, etc.
Medicines such as morphine, antipyrine, quinine provoke the occurrence of urticaria in adults with increased irritability. Subcutaneous injections cause a blister to form. This disease rarely occurs during donor blood transfusions.
For many people, mosquito bites, mosquito bites, and fleas cause deterioration in their health. Even larvae, when they get from a tree onto the skin, cause irritation.
The occurrence of pathology is explained by the synthesis and release of excess histamine into the circulatory system. At the same time, the capillaries expand, and at the same time the permeability of the vascular walls increases. A similar course is typical for diseases caused by an allergic nature. Such symptoms serve as evidence of an allergic reaction to external irritants affecting the human body.
Pathogenesis depends on the sensitivity of the body, the ability to accumulate the final products of dissimilation, for example, purine and pyrimidine components of polypeptides, which retain their characteristic specificity. Along with them, toxic compounds formed in expired products can become allergens.
Urticaria is especially acute in people with diseases of the digestive and excretory systems. Decay products accumulate in the large intestine, and manifestations of colitis and renal failure do not allow them to be quickly removed from the body.
One of the risk factors is latent foci of chronic infection. For example, streptococci and staphylococci, releasing metabolic products, can provoke bacterial allergies. It is transmitted to epithelial cells and provokes the appearance of acute edema in the papillary epidermis, leading to the formation of blisters.
The body exhibits an immune defense reaction, namely, produces antibodies in response to the introduction of specific food proteins into the body. Foreign nitrogen-containing compounds are considered as antigens.
The triggering factors for the manifestation of cholinergic urticaria can be stressful situations associated with strong feelings and nervous excitement. Functional disorders occur in the functioning of the nervous system, especially in the autonomic department, which regulates the functioning of internal organs.
The provoking agent leads to an increase in body temperature. Small bubbles appearing on the surface of the skin take on a swollen appearance and are located above healthy skin. The appearance of pustules is accompanied by burning and severe itching. Symptoms are aggravated by nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
In neuropeptides (proteins necessary for signaling pathways between the skin and neurons), as a result of high temperatures, the primary structure is destroyed, and nitrogen-containing biopolymers can fail. The trigger for heat urticaria can be eating hot food, taking a hot bath or shower, or sweating caused by intense physical activity.
Recurrent urticaria can accompany a person throughout his life and is practically untreatable. The use of medications only relieves obvious symptoms and only temporarily alleviates the patient’s condition.
Characteristic symptoms that suddenly appear and disappear within 24 hours lead to the misconception that urticaria is an infectious disease that can be transmitted from person to person. In fact, this disease is not transmitted either by airborne droplets or through household items.
You should not stop communicating with a person for fear of infection. This common disease is not life-threatening, except in cases leading to angioedema. True, there is a predisposition to this disease. It can be linked to genes and passed on from generation to generation.
Is it possible to walk if you have hives?
For a patient with this pathology, walking in the fresh air is very beneficial, except in cases where the person has solar urticaria or has Quincke's edema.
If the illness is associated with ultraviolet radiation, then it is advisable to go for a walk in the morning and evening, so as not to cause an exacerbation of the disease. Well, if a rash occurs in the larynx and near it, you should not think about walking, but carefully monitor your health. It is advisable that this be done under the supervision of doctors, since only in this case can unpleasant consequences be avoided.
Thus, the concern that urticaria is transmitted through contact is not only an unconfirmed fact. This is just speculation.
Hives are not a contagious disease! But it must be taken seriously. And if a rash appears, you should urgently rush to the doctor for a correct diagnosis and take appropriate measures.