Main symptoms
The appearance of a purulent formation on the gum is accompanied by quite specific symptoms.
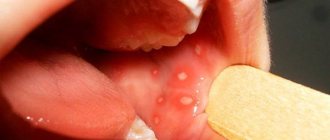
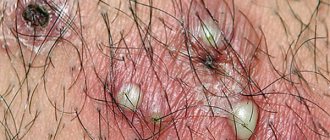
First, the child will notice a feeling of fullness in the gum, and a little later, a small reddish swelling will appear in the place he indicated. Gradually its size will increase, and a white dot will become noticeable in the center of the cone. It indicates the appearance of pus inside the gums. If you touch such a bump, you will see that it is soft, and the child will note that it is very painful. Increasing in size, the lump turns into a white abscess.
In addition to changes in the mouth, your child may experience other symptoms:
- Increased body temperature.
- Whims and restless behavior.
- Refusal of food.
What to do
The most correct tactic for parents when they discover an abscess on their child’s gum is to go to a dental clinic. The doctor will conduct an examination and determine his further actions, which will be influenced by the stage of the process (the abscess is just forming, has already formed or has ruptured) and the type of tooth (baby or permanent).
It is best if the child visits the dentist in the early stages of development, when the purulent lump has just appeared, but even after the abscess breaks through, the baby still needs to be taken to the doctor to eliminate the source of infection and prevent the abscess from re-forming in the same place or over adjacent teeth.
Types of pathologies
Depending on the source of the disease, there are:
| Fungal or candidal stomatitis. | Characteristic for weakened newborns and infants. The risk zone includes children undergoing treatment with antibacterial drugs. Initially, a whitish coating appears on the baby’s tongue and mucous membranes, which can be easily cleaned with a gauze cloth. After removing the plaque, foci of inflammation, hyperemia of the mucous membranes and their bleeding are detected. White sores are visible to the naked eye; after hygienic treatment, a new white, loose coating forms around them within a short time. |
| Herpes stomatitis. | Occurs after contact with a sick person or contaminated objects. Routes of transmission: household, airborne droplets. The pathology has an acute course. Suddenly the baby begins to complain of pain in the mouth, the mucous membranes swell, hyperemia, dryness, swelling, itching, and tingling appear. Along with the above symptoms, an increase in body temperature is observed. A few hours after the first clinical manifestations, small blisters filled with liquid appear on the mucous membranes. They can be single or multiple, located on the gums, the inside of the cheeks, and lips. After a few days, the formations open and in their place there remain ulcers - ulcers. The sores are very painful. Eating food leads to their irritation, and as a result, pain helps reduce the baby’s appetite. Some guys completely refuse to eat food and prefer to drink only water. Refusal of food in children of the first year of life is dangerous due to rapid loss of body weight. With adequate treatment, sores in the mouth can be successfully cured within 7–14 days |
| Allergic stomatitis. | It occurs as a result of exposure to a certain aggressive environmental factor on the body. Each person has their own allergen that can cause a negative reaction. In most cases, children who have atopic dermatitis are prone to rashes and dermatitis. Negative factors that cause pathological reactions: tablets, toothpastes, rinses, antiseptic, regenerating and painkillers (gels and ointments). After exposure to an allergen, a reaction may occur immediately or after some time. |
| Bacterial stomatitis. | It develops as a result of the simultaneous action of several factors: trauma to the mucous membrane, an allergic reaction, decreased local immunity, licking dirty objects. Symptoms: the baby complains of pain in the tongue and gums, signs of inflammation appear, after some time a white sore appears - a vesicle, which is called aphtha. The formation is painful, most often single, and can reach quite large sizes. Aphthous stomatitis most often affects adolescents and children of primary school age. The pathology is rarely accompanied by a change in general well-being or an increase in body temperature, but it makes the baby restless and capricious. With proper treatment, the disease is completely cured within 7 to 10 days. |
| Vesicular stomatitis. | It has an unusual and interesting name: hand - foot - mouth. The cause of the disease is Coxsackie viruses, enterovirus type 71. The route of transmission is airborne droplets. Outbreaks of the disease are observed in preschool institutions in the spring and summer. Symptoms: lethargy, irritability, sore throat, fever, rashes on the soles and palms. Small ulcers - pustules - form in the child's mouth. Despite the fact that the pathology brings many inconveniences, it rarely leads to complications. |
We suggest you read: In what cases is a dental x-ray indicated?
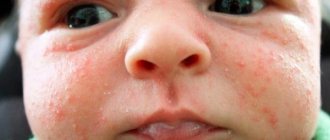
Reasons for the appearance of pustules on the face of a baby
There are several reasons for the appearance of inflammation on the baby’s face:
- Hormonal rash. Occurs in more than a third of babies. The medical name is neonatal pustulosis. Among the people - flowering of newborns, acne, whiteheads, milia. Pustules appear due to the formation of hormonal levels in the baby. Through breast milk, the baby receives maternal hormones. His body is not able to absorb them, red pimples appear that change the relief of the epidermis. Sometimes there are large ulcers with white dots. They are most often located on the baby's face - on the cheeks, nose, chin, around the eyes and occurs 2-3 weeks after birth.
- Allergic reaction. In breastfed children it appears due to poor nutrition of the mother. For example, a large number of children under one year of age suffer from an allergic reaction to the protein contained in cow's milk. It can enter the baby's body through breast milk. Be careful if your family has a history of allergies to any product or medication. An allergic rash looks like red spots with a rough surface; large pimples with white heads are possible.
- Prickly heat. The delicate skin of a baby reacts to overheating with rashes all over the body. They look like red pimples with blisters. Another reason for the appearance of prickly heat is unscrupulous adherence to the rules of hygiene for the baby.
- Too intense work of the sebaceous glands. This feature of the body does not pose a threat to health. Girls are mainly affected.
- Intestinal dysbiosis. Appears due to microflora disturbance.
- Staphylococcus, streptoderma are infectious diseases.
- Infections transmitted by airborne droplets - measles, chickenpox, rubella, scarlet fever.
Pustular rashes are divided into 2 types: pathological and toxic.
Pathological causes infection. There may be an increase in temperature, red pimples, and itching. Such skin diseases can only be treated by a doctor; independent treatment can threaten the baby’s life.
Toxic rashes are a consequence of hormonal imbalance or the functioning of the sebaceous glands. Most often, they do not require treatment and go away on their own with proper care.
If you find pustules on your baby's face, be sure to consult your pediatrician.
Types of rashes that do not require medical intervention
Medical intervention is not required for the following types of rashes:
- Neonatal pustulosis (hormonal acne) caused by yeast. It goes away on its own in the first months of a baby’s life with conscientious hygienic care.
- Miliaria is a small red rash. Localized in the groin folds, neck, armpits, and face. In this case, meticulous care is required: changing the diaper every 3 hours, washing with boiled water, air baths, regular washing, and not wiping with wet wipes. The main cause of prickly heat is overheating. Carefully monitor the compliance of your baby’s clothes with the temperature conditions.
- An allergy is a small rash that often weeps and causes itching. An allergic reaction is provoked by: improper nutrition of a nursing mother, hygiene and skin care products for the baby, synthetic fabric, medications prescribed to the newborn or his mother.
Allergic rash
Home treatment in these cases involves careful care. Wash your baby's face with boiled water twice a day. The skin of the face cannot be wiped; it is allowed to blot with a soft towel. Lubricate pimples with a decoction of string or chamomile.
Attention! Medicinal herbs can cause an allergic reaction! First you need to conduct a test - apply a couple of drops of the decoction to a small area of skin. The absence of redness and itching indicates that the herbs can be used.
Mild pathological pimples can be treated at home after consultation with a pediatrician. Usually the pediatrician prescribes antibacterial ointment. Among traditional methods, the use of Kalanchoe, rose hip, and sea buckthorn oils is allowed. If the pustules spread quickly, stop bathing for a while.
Other causes of pustules require drug treatment. If the baby has lost weight, become lethargic, or has a fever, you should call a doctor immediately. You may need a course of antibiotics. In advanced cases, treatment in a hospital.
Possible complications
If you do not consult a doctor when the abscess forms, it will increase in size and eventually burst. This will improve the child’s general condition (pain will decrease and the temperature will drop), but will lead to the formation of a fistula through which pus will escape into the oral cavity.
In some cases, the fistula heals on its own, but still represents a source of infection, which threatens to activate the inflammatory process under certain conditions (with decreased immunity).
If an abscess appears as a result of a disease in a baby tooth, it can cause infection of the permanent bud. In addition, bacteria from the abscess can enter the mucous membrane of the tonsils, provoking the development of chronic inflammation, as well as into the lymph nodes under the jaw, causing lymphadenitis.
Another danger of having a fistula in a child’s mouth is allergization of the body. In the most severe cases, pus can enter the bloodstream, after which it spreads throughout the child’s body and can cause suppuration in other organs and tissues. No less dangerous is the spread of infection into the deeper tissues of the jaws with the formation of phlegmon or inflammation of the bone.
Diagnostics
Some pathologies that cause ulcerative lesions are easy to diagnose, while others, on the contrary, are difficult to distinguish: the symptoms of allergy can be confused with chickenpox, and Bednar's aphtha is similar to aphthous stomatitis, oral tuberculosis, and syphilis.
Oral candidiasis should be distinguished from aphthous stomatitis, herpes, syphilis, and lichen planus.
At the first examination, the doctor interviews the parents and the child, records complaints, conducts an initial examination of the ulcers, makes a presumptive diagnosis and refers for further research, which, depending on the symptoms, may include:
- serodiagnosis;
- examination of a smear taken from the surface of the ulcer;
- clinical and biochemical blood tests;
- general urine analysis;
- culture for candidiasis to determine sensitivity to medications;
- collection of cerebrospinal fluid for suspected meningitis;
- examinations to identify autoimmune processes in the body;
- blood test to determine the concentration of immunoglobulin E;
- stool examination;
- skin prick tests;
- application tests.
Also, the pediatrician in almost all cases refers a child with mouth ulcers to the dentist. In some cases, the patient requires consultation with a neurologist, allergist, gastroenterologist, cardiologist and other specialists.
Is it necessary to treat caries of baby teeth in a child? Find out the answer right now.
How to treat the baby? The main remedies for the treatment of mouth ulcers, depending on the diagnosis:
- Anti-inflammatory medications. Reduce the severity of inflammatory reactions, lower body temperature. Examples: Ibuprofen, Paracetamol and drugs based on them.
- Antiseptics. Necessary for all types of ulcers, especially after eating, so that its remains do not cause discomfort to the child. Rinsing also reduces the likelihood of a bacterial infection. Examples: Furacilin, Chlorhexidine.
- Antihistamines. Prescribed if ulcers are symptoms of an allergic reaction. Examples: Zodak, Suprastin, Avil.
- Antiherpetic drugs. Affects herpes viruses. Examples: Acyclovir, Herperax.
- Antifungal medications. Prescribed if diagnostics have shown that the ulcers are associated with candidiasis. Examples: Fluconazole.
- Local anesthetics: Lidocaine, Benzocaine. They lubricate ulcers.
What treatment is prescribed?
Drugs
If the rash occurs as a result of the progression of any internal pathology in the body, first of all, therapy is prescribed to eliminate the cause of acne. For children, the treatment regimen is selected individually and often includes the following groups of drugs:
- antiviral;
- antimicrobial;
- antihistamines;
- antiseptics;
- vitamins, immunostimulants.
Desitin ointment performs well.
It is recommended to treat a flaky spot with Desitin and Bepanten ointments; soft baby creams, which should be prescribed by a doctor, also help to cope with rashes. If a child is not yet 1 year old, but already has rashes, it is forbidden to lubricate the pimples with iodine, brilliant green, or peroxide at your own discretion, as this can only worsen the situation. Sometimes drug therapy alone cannot get rid of the problem. Then the doctor will recommend laser cauterization, which increases the sensitivity of tissues to drug treatment, which will speed up recovery.
Among all types of rashes on the face or body, purulent acne is the most dangerous. They can appear at any age.
But if such rashes in adults require special care, then purulent acne in a child should not be ignored at all.
What reasons can influence their occurrence and how to treat these acne?
- All information on the site is for informational purposes only and is NOT a guide to action!
- can give you an ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS !
- We kindly ask you NOT to self-medicate, but to make an appointment with a specialist
! - Health to you and your loved ones!
Other causes of ulcers in a child’s mouth
Many factors contribute to the occurrence of white sores in the mouth of children, including vitamin deficiency.
Deficiency of vitamins B2 and B6 manifests itself in the form of cracks on the lips and white pustules on the mucous membrane of the palate, tongue, gums or cheeks. And a lack of ascorbic acid leads to blue and bleeding gums and the formation of aphthae.
To normalize the condition of the oral cavity, it is necessary to give the baby vitamin complexes or products containing elements the body lacks.
Factors leading to the formation of pustules on the oral mucosa are stressful conditions, excessive consumption of sour or starchy foods, malocclusion, and mouth breathing.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with Tablets for toothache – List of tablets for severe pain in teeth – dental portal
Before treating mouth ulcers in a child, it is necessary to establish the exact cause of their appearance and eliminate the provoking factor.
The source of the disease is identified by a specialist after examining the child’s oral cavity and analyzing severe symptoms.
Self-treatment of sores in a child’s mouth can cause the disease to progress and the infection to spread to internal organs.
Causes
Ulcers on the palate can appear for many reasons. The most likely ones are the following:
Infection of the wound surface.
In children, mucosal injuries are indeed very common. But this tissue has a high ability to regenerate, and damage to the mucous membrane caused by crackers or bread crust quickly heals without leaving a trace.
In cases where a child does not comply with personal hygiene requirements, brushes teeth irregularly or poorly, the surface of the wound becomes colonized with bacteria, which slows down healing and can lead to an increase in the affected area.
Avitaminosis.
If wounds in the oral cavity that appear after an accidental injury do not heal for a long time, but there are no signs of inflammation or infection (redness, loosening of the surface, plaque, etc.), the cause may be a deficiency of vitamin C, B2, B3 or B9.
Ascorbic acid, riboflavin, niacin and folic acid take part in cellular metabolism and are responsible for tissue regeneration. With a deficiency of these substances, the mucous membranes become more susceptible to inflammation, and the cycle of cell division and renewal is disrupted.
Allergy.
Contact allergy is a common disease in children. It develops due to hypersensitivity of the immune system to any substances. These can be pigments in food, components of medicinal substances, filling materials, etc.
During an allergic reaction, inflammation develops in the tissues, which destroys local immunity, leads to the formation of blisters or wounds, and the addition of an infection completes the process - ulcers that take a long time to heal are formed.
Stomatitis.
We wrote in detail about stomatitis here:
Herpetic, fungal and aphthous stomatitis are accompanied by the formation of ulcerated areas on the mucosa. But in the first two cases, such damage occurs after opening the vesicles or removing the films, and with aphthous stomatitis, ulcers form as an independent symptom.
In addition to the above reasons, a single ulcer on the hard palate in a child or multiple lesions can be the result of acute or chronic tonsillitis, endocrine disorders, or severe dysfunction of the immune system.
Treatment of oral diseases
Having noticed an abscess in a child’s mouth, parents should quickly show it to a pediatrician or dentist. The doctor will determine the cause and tell you how to treat the abscess at home (usually only infants are hospitalized).
READ IN DETAIL: treatment of stomatitis in children at home with photos
Having established the cause of ulcers in the baby’s mouth, doctors prescribe complex therapy. It usually includes treatment with dental gels, immunomodulators and other medications, as well as vitamin complexes. For severe lesions, local painkillers are prescribed.
Complications
The described symptoms of abscess in children can be attributed to a typical and uncomplicated course. But in children there are significant differences in the structure and function of the nasopharynx, which facilitate the spread of infection and its spread far beyond the limits of dental “powers”. Therefore, pay attention to the following signs, which, together with the appearance of an abscess, may indicate the development of complications;
- elevated body temperature persists even after the abscess has opened;
- the temperature does not return to normal after taking antipyretics, or decreases only slightly;
- the child complains of headache, pain in the ears or face;
- the pain intensifies when the child tries to tilt his head down and forward;
- the child experiences nausea, vomiting, and complains of pain throughout the body (signs of general intoxication);
- the child has enlarged and/or painful lymph nodes under the lower jaw or on the back of the head.
Be sure to read: Dental granuloma on the gum of a child - how to treat the problem?
Such symptoms may indicate the development of sinusitis, tonsillitis, lymphadenitis, otitis media, eustachitis, severe intoxication and other diseases, some of which require emergency medical care.
If even one of these signs appears, contact your doctor immediately and act according to his instructions.
Varieties
There are quite a few types of acne on the palate. Each of them is characterized by certain features.
Red
Such pimples usually affect the throat area and may indicate stomatitis, allergic reactions, or scarlet fever. The rash can also be a symptom of lupus erythematosus.
How to remove acne spots? More details here.
Solid
An internal pimple with a hard consistency often accompanies angioma. This dental disorder can have several types and is a benign tumor lesion of a blood vessel. It is associated with the expansion and appearance of new blood vessels.
The formation is called a true angioma and is accompanied by the appearance of a compaction on the palate. In addition, angioma is isolated that affects the lymph nodes. However, this form of the disease is observed much less frequently.
The appearance, location and accompanying signs of pimples on the mucous membrane depend on the cause of their occurrence and the advanced stage of the disease. This should include the general health of the baby. The same pathology is more pronounced in sick children than in children with high immunity.
Complications of purulent abscesses
If an abscess is left in a child’s mouth without diagnosis, treatment and observation, infection and residual pus remain, leading to serious consequences. They can also be caused by incorrect actions: eating hot food that injures the gums, warming compresses, lack of oral care during inflammation, or opening a purulent lump on your own.
The most common complications:
- if the pustule opens on its own, the infection can spread throughout the body, enter the blood and cause sepsis;
- bite pathologies;
- suppression of the child’s immune system due to constant infection;
- inflamed lymph nodes;
- chronic form of tonsillitis;
- pulpitis;
- the appearance of a fistula on the gum and the development of an abscess;
- phlegmon;
- disruption of the development of baby teeth and the appearance of permanent teeth;
- disturbed structure of tooth roots.
Features in newborns
If acne appears in a child in the first 2-3 months of life, then this is most likely a consequence of hormonal changes, which are typical for some babies immediately after birth. Hormonal imbalance in the body occurs due to an excess of maternal hormones in the baby’s blood. Such pimples do not hurt, do not itch and do not cause discomfort. They go away on their own without requiring treatment.
Children's pimples can also have an infectious etiology, causing the following diseases:
- epidemic pemphigus;
- toxic erythema;
- prickly heat.
Prevention of ulcer formation
To prevent pustules in infants and older children, preventive measures should be followed.
- Carry out daily oral care; in very young children it is not necessary to use toothpaste. The main thing is to remove food debris and prevent the appearance of pathogenic bacteria and their active activity. It is important to teach your child hygiene from an early age.
- Timely treatment of chronic diseases of the whole body, inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
- Strengthen the immune system, since a weak immune system is a high risk of the appearance of pathogenic microorganisms and suppuration.
- If dental problems or diseases appear, you cannot stop caring for your oral cavity.
- Excessive consumption of sweets and starchy foods contributes to the spread of pathogens and their active functioning. After moderate consumption of these products, it is important to rinse your mouth.
We invite you to read: The child’s teeth grow in the second row
Treatment of an abscess on a child’s gum must be qualified and timely. This will reduce the risk of complications and pathological conditions. It is important to follow preventive measures to prevent recurrence of a purulent abscess.
Symptoms of aphthous stomatitis
The course of acute aphthous stomatitis goes through three successive stages:
- Prodrome
- Stage of aft formation
- Healing of epithelial defect.
At the prodrome stage, there are still no specific signs of the disease. The symptoms are consistent with an acute respiratory tract infection. However, clinical signs gradually appear that make it possible to establish the correct diagnosis:
- General weakness
- Malaise
- High temperature (not a constant symptom)
- Refusal to eat
- A reddened area may be visible in the oral cavity
- Local enlargement of lymph nodes (cervical and occipital)
- Red ulcers that form in areas of hyperemia. Then they turn into white ulcers (sores) - redness remains only along their periphery, and the center is covered with a gray-white coating.
In some cases, aphthous stomatitis may also be accompanied by angular stomatitis, in which ulcerations appear in the corner of the mouth. Popularly this is called jamming. Typically, the combination of these two types of inflammatory process indicates a decrease in the child’s defenses. Sores around a child’s mouth can also be a sign of vitamin deficiency A, E and B12.
The combination of angular stomatitis with atrophic gastritis indicates a deficiency of cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) in the child’s body. Therefore, the only effective treatment method is replacement therapy in the form of intramuscular injections of the missing vitamin.
This disease is based on a deficiency of intrinsic Castle factor, which is necessary for the absorption of cyanocobalamin (extrinsic Castle factor) in the intestine. Deficiency develops due to atrophy of stomach cells, which normally should synthesize (form) it, and not due to the fact that this vitamin is not enough in food.
Video: “How to treat a boil”
It has long been known that beauty and health are interconnected. Skin is an indicator of the body's well-being. If it is smooth and velvety, then the person is healthy. Various rashes and changes in the color of the skin indicate malfunction of any of the body systems. In this case, treatment is not always required - sometimes lifestyle changes are enough. What to do if you find a rash?
A rash on the face of a child has various causes, so before starting treatment it is necessary to determine the etiology of the disease
What should you not do if you notice mouth ulcers?
Pustules in a child’s mouth require close attention. If white or red sores appear, you should not uncontrollably try all possible treatment methods. Dentists warn that if a child has ulcers in his mouth, he should not:
- apply brilliant green, blue, iodine, alcohol to problem areas until the diagnosis is clarified;
- warm the affected area to avoid suppuration;
- open and pick bubbles;
- Ignore the manifestations of the disease: you should make an appointment with the dentist as soon as possible.
Urgent professional help is required for a child in the following cases:
- high fever that cannot be brought down with traditional medications;
- pain that does not go away after taking painkillers;
- fever, general weakness, decreased blood pressure;
- bleeding from the gums that cannot be stopped.