be careful
People with psoriasis often try to eliminate the external symptoms of the disease on their own before going to the doctor, without thinking about the fact that the problem actually comes from within. Some patients manage to achieve an external positive result for some time. But inside the body at this time, psoriasis continues its attack on the autoimmune system, provoking the appearance of severe illnesses, in some cases fatal.
It should be noted that psoriasis can cause cancer. Therefore, in the case of this disease or suspicion of it, self-medication is unacceptable.
Psychosomatics of the disease
If among the causes of occurrence genetic predisposition is in the lead, then, as scientists around the world say, it is psychosomatics that starts the process, or, more precisely, stress. It is believed that the true causes of the disease lie in the mental and psychological state of the patient; it usually begins with dissatisfaction with one’s own appearance and body, environment, and society.
There is an assumption that even the localization of the rash may hint at a psychosomatic cause. It is believed that patients with manifestations in the head region suffer from downplaying their significance from the environment. Manifestations on the hands often symbolize misunderstandings with family and friends, and the impossibility of reconciliation.
To effectively treat psoriasis, it is necessary not only to use appropriate medications, but also to monitor your emotional background so that suppressed negative emotions do not manifest as psoriasis on the body.
Symptoms and diagnostic criteria
With the help of modern diagnostic tests, it is possible to determine psoriasis with maximum accuracy and find out the causes of its occurrence. At the same time, it is extremely important to conduct a competent examination and carry out the necessary tests, since psoriasis in its symptoms differs little from eczema and allergic manifestations, which require slightly different therapy.
Correct determination of the diagnosis, the nature of the disease and its cause is subject to only a qualified specialist.
Initially, the dermatologist examines the patient.
Among the external manifestations of psoriasis, the following signs are noted:
- The psoriatic triad is clearly visible, accompanied by stearin spots, psoriatic film and pinpoint bleeding after its removal.
- The skin is actively peeling off and itching a lot.
In addition, the doctor should pay attention to the following points:
- The patient’s lifestyle – his leisure time, nutrition, exercise, the amount of time allotted for rest.
- Presence of chronic diseases.
- Stage of development of the disease. Its progressive form is characterized by the formation of new papules, noticeable abrasions and scratches on the skin.
Basic methods for diagnosing psoriasis in adults and children
The main part of the diagnosis involves an external examination of the patient. In this case, a person with suspected psoriasis often needs to undergo a series of laboratory and instrumental tests. Sometimes histological examination of skin biopsy is used. In children, the diagnosis of psoriasis is also established based on a visual examination by a doctor. But the child may not have the “psoriatic triad.”
30-87% of patients develop nail psoriasis, sometimes even without accompanying psoriatic plaques on the body.
Instrumental diagnostics
If there is a suspicion of psoriasis and certain changes in well-being, the dermatologist may refer the patient to instrumental methods.
If psoriatic arthritis is suspected, the following diagnostic procedures are indicated:
- X-ray examination of joints;
- MRI in case of pain in the spine;
- joint puncture to collect synovial fluid.
If atypical skin symptoms are present, a histological examination of the biopsy (skin) is prescribed. Sowing for microflora is required if the mucous membranes of the oral cavity are involved in the pathological process, or the development of ulcers or pustules. Also, a person needs to undergo tests that will exclude the possibility of fungal infection of the skin. To do this, a referral is issued for a potassium test and scraping.
Clinical examinations
Psoriatic manifestations are not always clearly expressed, since the disease is characterized by a wave-like course. Often, psoriasis is determined by the presence of external skin symptoms. But such phenomena may vary depending on the current stage of the disease.
The progressive stage of psoriasis is characterized by the formation of individual or multiple papules of intense pink color, which tend to grow and unite.
Subsequently, they take the form of itchy and flaky plaques that rise above healthy areas of the skin.
At the stage of regression, papules, otherwise known as plaques, acquire a flatter appearance, itching and peeling become less intense. Sometimes they can disappear altogether, but more often they simply become less noticeable.
The stationary stage is characterized by the absence of new manifestations and any changes in existing affected areas.
Clinical diagnosis consists of analyzing current symptoms and studying complaints. But, based on the clinical picture, without obtaining information from laboratory and instrumental studies, it is difficult to establish an accurate diagnosis.
Differential methods
Differentiation in cases of suspected psoriasis can be performed subject to the following nuances of the pathology:
- The appearance of a stearin stain on the skin. This phenomenon is so called because the scales are similar to stearin. When the skin layers are scraped off, the scales peel off and their number increases.
- Terminal film - after removing the scales, a red, smooth surface appears on the skin. The skin in this area is extremely thin and easily injured.
- Bloody dew - when the film is damaged, small droplets of blood appear on its surface.
A characteristic manifestation of psoriasis is the Koebner phenomenon - in areas of healthy skin, spots can appear even in the case of minor injuries - scratches and abrasions.
Tests for psoriasis
It is worth noting that the above points are not enough to finally make the correct diagnosis. It is very important to carry out the necessary examinations and tests.
The picture of psoriasis can be clarified using the following research methods:
- General blood analysis. Basically, there are no major changes to the formula. In addition, there is an increase in ESR levels, which usually happens during inflammatory processes in the body. In addition, the doctor pays attention to the condition of leukocytes. In a blood test for psoriasis, especially in its complex forms, anemia is often visible.
- A biochemical blood test for psoriasis is characterized by a negative indicator for rheumatoid factor. In addition, there is an increase in protein levels.
- Liver tests for psoriasis show that there is a malfunction in this organ.
- Blood tests for cholesterol and glucose levels must be taken to see deviations from the norm.
- Analysis of stool for parasites, intestinal infections and dysbacteriosis.
- Urinalysis, which checks the water-salt balance.
- A blood test for HIV, since this disease can trigger the appearance of psoriasis.
With the help of a systematic examination and passing all the necessary tests, it is possible to find out not only the presence of pathology, but also the cause of its occurrence. Only after this the doctor prescribes the correct treatment with the optimal course. Only through consistency in actions can you speed up the healing process and achieve long-term remission of the disease.
In addition, with the help of these diagnostic measures it is possible to identify concomitant diseases, if any, and determine their treatment.
Treatment of psoriasis
Treatments for severe and moderate forms of psoriasis include phototherapy, systemic medications, combination therapy, and excimer laser therapy, which are often very effective.
TNF inhibitors reduce the activity of immune factors and help with severe forms of psoriasis, but complications may appear with other infections.
Ustekinumab. This product contains monoclonal antibodies. The remedy helps with severe and moderate forms of the disease. Research on the drug is still ongoing, and so far positive qualities have been identified.
Additional examination
A blood test for psoriasis does not always help determine this disease in adults and children.
In these cases, additional examinations are prescribed:
- Psoriatic arthritis is detected using x-rays. Thanks to her, it is possible to understand how badly the joints are affected by the disease.
- Spinal lesions are detected using MRI.
- To determine neutrophilic leukocytosis, it is necessary to examine the synovial fluid of the joints.
- Sometimes psoriasis occurs in an atypical form, which makes it difficult to diagnose. In this case, a skin biopsy from the affected areas is indicated. To carry it out, the epidermis of 6 mm of skin is examined.
- To exclude a fungal infection, a potassium oxide test is prescribed.
- Women expecting a child are tested for prolactin, which helps determine whether there is a genetic predisposition to psoriasis or whether hormonal imbalances are the cause of the disease.
- Psoriasis rashes can be confused with a syphilis rash. To exclude this venereal disease, a blood test is taken for the Wasserman reaction.
- Other diseases are excluded by taking a culture test for the microflora of the mucous membranes.
Treatment approaches
The treatment regimen for psoriasis is selected individually for each patient, taking into account the identified causes of the disease and the main symptoms. First of all, these are preparations for external use:
- based on tar: Antipsorin, Colloidin,
- based on solid oil: Cytopsor, Solipsor,
- petroleum based: Losterin, Naftaderm.
Medicines for internal use are divided into the following groups:
- retinoids: Soriatan, Acitretin,
- immunosuppressants: Methotrexate, Sandimmun Neoral,
- corticosteroids: Prednisolone, Betamethasone.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are indicated for patients: ultrasound therapy, electrosleep, UVB irradiation.
Mud and seaweed wraps, salt baths, and ozone therapy are also used. One of the conditions for effectively getting rid of the manifestations of psoriasis is following a diet that excludes foods that can provoke an exacerbation of the disease. The patient is also recommended to change his lifestyle, give up bad habits, and spend more time in the fresh air.
Complete blood test for psoriasis
With the help of laboratory tests, it is possible to quickly exclude many serious diseases, some of their symptoms reminiscent of psoriasis. Thus, dermatitis, eczema, and syphilis are excluded.
Thanks to blood and urine tests, the infectious type of psoriasis and its phase are determined.
A blood test alone is not enough to determine the disease. But with its help, the disease can be suspected.
In addition, a general blood test helps to exclude pathological and allergic diseases.
If the ESR levels are very elevated, this means that the body is experiencing a chronic course of an autoimmune disease.
A person suffering from psoriasis needs to take a blood test at least once a quarter.
Causes of scaly lichen
The true causes of the disease have not yet been established, but medicine identifies several versions that play a significant role in the diagnosis of psoriasis:
- Autoimmune failure. This is due to the increased concentration of T-lymphocytes in the blood. As a result of this, the immune system, which should fight foreign cells, attacks its own;
- Endocrine factor. It is based on dysfunction of the endocrine system and its regulatory function, resulting in disruptions in the functioning of the internal secretion systems, pituitary gland and thyroid gland;
- Disturbance of metabolic processes in the body. One of the reasons for the occurrence of scaly lichen may be a failure in lipid-nitrogen metabolism. This may also include elevated blood cholesterol levels and metabolic imbalances;
- Genetic predisposition. Unfortunately, the disease can be inherited. So if someone in your family has psoriasis, then you are at risk. However, if you protect yourself from provoking (trigger) factors, the development of the disease can be prevented.
Blood chemistry
This study is also not specific. Protein fractions resulting from the inflammatory process are usually increased in psoriasis.
There are certain rules that must be followed when taking a biochemical blood test:
- The analysis must be taken strictly on an empty stomach. The last meal should be at least 8 hours ago.
- Due to the fact that blood counts change throughout the day, almost all tests are scheduled for the morning.
- The day before the test, the patient should not undergo serious physical activity.
- It is important to avoid stressful situations and emotional tension.
- You should not drink alcohol the day before donating blood.
- Before taking the test, you should refrain from smoking for at least 2-3 hours.
- Taking medications should also be as organic as possible. If you still need to take the medicine, you should inform the laboratory assistant and doctor.
It is very important to take all blood and urine tests before ultrasound and x-ray.
The most reliable test for psoriasis is a skin biopsy from areas affected by plaques.
Every person who has experienced psoriasis knows firsthand how many tests they have to undergo. It is important to understand that all these activities are not the whim of doctors. With the help of these tests, it is possible to clarify the situation about the disease and the general condition of the patient. Therefore, you should not neglect doctors’ orders. This will help achieve stable and long-term remission of the disease.
How is a nail analysis performed?
A physician examines the condition of the nail plate to confirm or refute the presence of psoriatic onychodystrophy.
Nail analysis is performed by scraping the affected area of the nail plate.
The manipulation is painless.
The collected biomaterial undergoes special preparation and is subsequently examined under a microscope.
Nail analysis also makes it possible to distinguish psoriasis from paronychia and onychia of the infectious and fungal type.
How does psoriasis manifest?
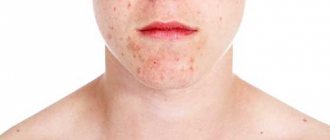
When the top layer is separated, the skin becomes thin and easily susceptible to injury, which leads to frequent bleeding. As the disease progresses, the rash can localize into large plaques covered with a rough skin crust.
In some patients, psoriasis can also affect the mucous membranes or genitals, which is quite rare. In addition to external symptoms, the disease affects internal organs and systems, and also has a negative impact on the condition of joints and bones. In extremely rare cases, patients experience redness in the area around the pupil of the eye.
One of the features of psoriasis can also be considered its recurrent nature. So, with proper treatment, external symptoms can completely disappear, and in the presence of negative factors, they can appear again. For patients with such an incurable disease, it is important to avoid stressful situations, decreased immunity, infectious diseases, hormonal imbalance and an unhealthy lifestyle.
Types of psoriasis
There are a number of forms of psoriasis, differing in their clinical manifestations. They can also have different localization and severity of symptoms. Main types:
- Simple or vulgar psoriasis. Most often it originates on the knee bends. The spots are covered with white-silver scales.
- Exudative. Affects the elbow and knee bends. The spots have a yellowish surface with crusts.
- Inverse. Develops against the background of problems with the endocrine system. It appears primarily on large folds of the body.
- Pustular. It can appear on the palms of the feet and throughout the body. Its characteristic difference is the formation of ulcers.
- Seborrheic psoriasis occurs in those who have seborrhea. The scales stick together into crusts, forming yellow spots.
- Psoriasis of the soles and palms most often occurs as a result of professional activities. A simultaneous rash on the arms and legs is typical.
- Nail psoriasis looks like thickening and deformation of the nail plate; upon examination, depressions are detected.
- Psoriatic erythroderma manifests itself as rashes all over the body.
- Arthropathic psoriasis is a consequence of the skin manifestation of pathological processes. Joints are affected.
- Guttate psoriasis forms on the trunk and lower extremities. Reminds me of small drops.
But even with such an abundance of types and their manifestations, only a qualified dermatologist can accurately diagnose psoriasis. It is especially important to undergo differentiated diagnostics in order to distinguish the disease from other diseases with similar symptoms.
Diagnosis of psoriasis
First of all, patients who notice the first signs of the disease should immediately consult a doctor. At the first stage of diagnosis, it is important for the dermatologist to conduct a detailed examination, as well as, based on the patient’s complaints, to draw up an anamnesis of the disease. Since psoriasis initially affects the skin, you should immediately consult a dermatologist, and if there is damage to the joints or mucous membranes, consult an orthopedist, rheumatologist or ophthalmologist.
Some forms of psoriasis are quite difficult to diagnose, since its symptoms are easily confused with other dermatological diseases. Only a qualified specialist in the localization of rashes can determine psoriasis during examination. At an early stage of the disease, treatment can be approached directly after examination, however, additional diagnostics may be necessary to exclude concomitant or similar diseases.
Type of psoriasis
There are several classifications of the disease. One of the most common classifications of psoriasis is the division into:
- Winter psoriasis, exacerbations in patients occur mainly in winter, while in summer symptoms are minimized. This form of psoriasis is believed to be the most common;
- Summer psoriasis, exacerbation occurs in the summer and subsides with the onset of more moderate temperatures;
- Indeterminate psoriasis does not have clearly defined seasonal changes.
In addition to this division, there is a classification according to the severity (area of the skin surface affected by the disease) of the disease. This classification is quite often used by doctors, since it gives a fairly clear idea of the degree of problem of the disease.
A specialist can diagnose psoriasis even during an external examination.
In medical practice, several types of disease are distinguished, which have their own characteristic signs.
According to the international classification of diseases, psoriasis is assigned the code L40. The forms of the disease depend on the clinical manifestations.
International classification of psoriasis:
- A simple form without complications. This form includes coin-like and plaque-like types.
- Generalized form. It includes impetigo herpetiformis and Zumbusch syndrome.
- Acrodermatitis Allopeau.
- Palmoplantar form.
- Drop-shaped.
- Arthropathic form.
Psoriasis appears as pink plaques that rise above the surface of the skin. The rashes have the appearance of frozen paraffin. Their surface is covered with peeling and numerous white scales. The classic localization of rashes is the scalp, extensor surfaces of the joints, buttocks, genitals, and umbilical area.
Depending on the form, psoriasis can be complicated or uncomplicated. The pustular variant is characterized by the appearance of papules and pustules with purulent contents, having a red rim. Joint damage (arthropathy) is characterized by painful symptoms. Arthropathy is irreversible, therefore, to prevent this complication it is necessary to adhere to treatment standards.
Differential diagnosis of psoriasis
Psoriasis is a complex autoimmune pathology. Therefore, before making this diagnosis, you need to be sure of it. To this end, every patient should be screened for psoriasis . It will help rule out other pathologies. Differential diagnosis of psoriasis is carried out according to the main syndrome of the disease – skin manifestations. Pathologies that have similar dermatological signs include:
- Various forms of dermatitis (seborrheic, atopic);
- Lichen planus;
- Syphilis;
- Reiter's disease;
- Athlete's groin;
- Neurodermatitis.
Psoriasis on the legs, which is rarely isolated, can be differentiated from vascular diseases. In addition to the main syndrome, attention should be paid to the nature of the pathology, the prevalence of skin rashes, and the general condition of the patient. Diff. Diagnosis of psoriasis should be carried out by a dermatologist. It is based on data from skin examination and laboratory tests. Diagnosis of psoriasis in children must be performed especially carefully. This pathology is rarely encountered in pediatric practice. In some cases, psoriasis develops during pregnancy, and special monitoring is required.
Conclusion
Each study prescribed by a doctor when diagnosing psoriasis is necessary - only a complete picture of the disease will allow us to determine at what stage the pathological process is. And this is necessary for drawing up the correct treatment regimen.
An obligatory point of research is differential diagnosis - psoriasis very often has similar symptoms to other skin diseases. In some cases, a visual inspection is sufficient for a specialist. However, it is better to take another blood test or conduct a special study than to start treatment incorrectly. Indeed, in this case, you can provoke a worsening of the disease.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
How to determine: psoriasis or not
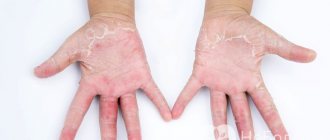
It is necessary to identify psoriasis on the patient’s skin or some other disease as early as possible. This affects treatment tactics and prognosis. Psoriasis can be recognized by specific skin manifestations - plaques (photo 2). They are pink papules that rise above the surface of the skin. The progressive stage is characterized by the spread of spots and the appearance of silvery scales on them. The diagnostic algorithm is a sequential execution of studies.
To recognize psoriasis in a child, the same methods are used for adult patients. First of all, the skin is examined. It is possible to determine psoriasis in a child only after performing dermatological diagnostic methods. Therefore, the pediatrician must refer the patient to a specialized dispensary. The examination plan for psoriasis includes the following points:
- Clarification of complaints and inspection;
- Special examination of the affected skin - dermoscopy;
- Laboratory tests - general and biochemical blood test, coagulogram, urine test;
- Skin biopsy for psoriasis.
Only after receiving the results can a conclusion be made. Diagnosis of nail psoriasis is based on laboratory methods and physical data. All examinations are important to identify the disease. The most important is a biopsy for psoriasis. It allows you to examine the affected areas of tissue.
Stages of the disease
The following stages of disease development are distinguished:
- Initial. The appearance of the first alarming plaque.
- Progressive. The formation of new elements that increase in size and merge with each other.
- Stationary. New plaques do not appear, old ones stop growing, but become covered with scales.
- Regressive. At the site of the rash, areas of excessive or insufficient pigmentation appear.
An individual treatment regimen is selected for each stage. Before starting therapy, a number of necessary tests are performed.
Differential diagnosis of psoriasis
Diagnosis of psoriasis is carried out in a hospital setting. This is necessary to monitor treatment and exclude infectious diseases. The differential diagnosis of psoriasis and lichen planus is based on physical examination. Dermoscopy is also performed. Rash with lichen has a lilac tint, the center of the pathological focus is pressed inward, the edges of the papules are elevated. Pathological foci are localized on the flexor surfaces, in the groin area. Peeling of the skin is not pronounced.
Diff. The diagnosis of psoriasis and syphilitic lesions is based on the medical history and a special laboratory test - the Wasserman reaction. Papules in this pathology are hemispherical in shape and identical in size. Differential diagnosis of arthropathic psoriasis is carried out with Reiter's disease. This pathological condition is characterized by damage to the joints, urinary tract, and eyes. Diagnostics in the clinic includes monitoring the patient's condition. With Reiter's disease, the rash goes away faster and is more often localized on the genitals and in the oral cavity.
In the literature on dermatology you can find a special table for the differential diagnosis of psoriasis (photo in gal). It is based on skin syndrome. The formulation of the diagnosis includes the phase of the pathological process, the severity and clinical form of the disease. A diagnosis of psoriasis can only be made after assessing all indicators and long-term observation. Symptoms of this pathology persist for several months.
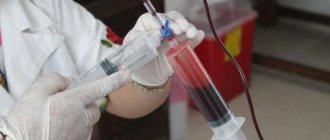
Blood test for psoriasis
Research into psoriasis begins with laboratory diagnostic methods. They help to quickly exclude diseases such as syphilis, dermatitis, and allergic skin pathologies. What tests need to be taken for psoriasis? For diagnosis, it is necessary to perform blood and urine tests. With their help, it is possible to determine the infectious nature of the pathological condition and the phase of the process. It is impossible to determine psoriasis using a blood test. However, it helps to suggest this diagnosis.
A general blood test indicates the presence of an inflammatory process of bacterial or viral etiology. These findings are nonspecific and therefore cannot be used to make a diagnosis. A blood test for psoriasis will show an increase in the number of leukocytes and an acceleration of ESR, in some cases there is a decrease in hemoglobin. It will help eliminate viral pathologies and allergic diseases. ESR in psoriasis can be greatly increased. This is due to the presence of chronic autoimmune inflammation. You should donate blood for psoriasis 2-4 times a year. The study allows you to monitor the activity of the inflammation process.
A biochemical blood test for psoriasis is also not specific. It will show an increase in protein fractions responsible for the inflammatory process. Rheumatoid factor must be negative. The most reliable test for psoriasis is a skin biopsy from the surface of the plaques. Histological examination allows us to make a final conclusion.
Is it possible to donate blood if you have psoriasis?
Tests are performed regularly for psoriasis. With the help of these studies, the doctor evaluates the dynamics of the pathological process and treatment. Some patients are interested in the question: is it possible to donate blood if you have psoriasis? Only the attending physician can answer this question. It all depends on the tests that the patient has at the moment. If no changes are observed, you should consult a transfusiologist.
Patients often wonder: is it possible to get psoriasis through blood? The likelihood of transmitting this pathology is low, but infection is possible. If the inflammatory process is in the active phase, donating blood is prohibited for psoriasis. The disease is characterized by the accumulation of immune complexes that are aimed at destroying one's own skin cells. In the active stage of the process, pathological antibodies can cause infection in a person who has not been sick before.
You should be especially careful when prescribing treatment for psoriasis in children, because the treatment of this disease uses hormones that are harmful to the growing body. A dermatologist, together with a pediatrician, should select and change the dosage of medications.
Specifics of the disease
However, the main identifying mark of any form of psoriasis is the eruptive elements that are unique to it - in medicine they are usually called “psoriatic plaques.” They are inflamed convex raised spots, painted in a reddish-pink color, the surface of which is abundantly strewn with small silver-gray flaky elements - scales. Such formations are easily removed with the slightest mechanical impact.
Despite the fact that more than one medical work has been devoted to the study of psoriasis, it has not been possible to definitively establish the cause of the appearance and development of this systemic disease.
Modern medicine has several main versions interpreting the etiology of the disease. The most common of these is the autoimmune theory. It is based on the postulate that the appearance of psoriatic plaques on the skin is the result of hypertrophied activity of the body's defenses (determined by various factors), which begin to intensively attack healthy cells of the epidermis. Those, in turn, begin to multiply faster and degenerate into abnormal rash elements localized in different parts of the body.
There are other approaches to explain the appearance and development of psoriasis. Here are examples of some of them:
- Neurogenic (stressful);
- Metabolic (exchange);
- Drug;
- Hormone;
- Viral;
- Allergic.
It has been scientifically proven that psoriasis is a genetically determined disease. This means that you can “inherit” not only the disease itself, but even the tendency to develop psoriatic plaques on the skin.
At any stage of life, a person whose relatives suffer from psoriasis may encounter unpleasant manifestations of this pathology. Medical statistics are disappointing: if both parents suffer from psoriasis, the risk of developing this disease in a child increases to 75%, when psoriatic plaques are found only in the mother or father - up to 65-70%. When other close blood relatives (grandparents, uncles, aunts) encountered this disease - up to 50-55%.
The ambiguity of the etiology of psoriasis entails that this disease is still on the list of incurables. This means that even properly selected complex treatment is not able to rid the patient of the hated rashes on the skin once and for all. Psoriasis is characterized by a chronic relapsing course with long periods of exacerbation and short stages of remission.
Relapses of the disease require medication (symptomatic correction) designed to eliminate discomfort and prevent the development of complications. Thus, patients are prescribed systemic and local drugs of various spectrums of action, physiotherapy, and a therapeutic diet.
A good symptomatic effect in relieving unpleasant sensations on the skin is demonstrated by proven folk remedies - decoctions, infusions, tinctures based on medicinal plants. They quickly relieve unpleasant sensations on the skin - itching, peeling, hyperemia, swelling, effectively combat pain and prevent further spread of psoriatic plaques throughout the body. It is worth considering that most of these products are potential allergens, so before starting treatment, you should consult a dermatologist.
Is it possible to donate blood if you have psoriasis?
Some people believe that you should not donate blood if you have this disease. However, this is an incorrect statement. Only a complete diagnosis and passing the necessary tests will allow you to find out an accurate diagnosis. Another question is when a person wants to donate blood.
The answer to this question depends on the attending physician and the tests. If the doctor has no complaints about the tests performed, then you can donate blood. But it is necessary to remember that there is still a possibility of contracting psoriasis. When donating blood, a person with psoriasis exposes another person to their disease. If he is in a progressive stage of the disease, then donating blood is strictly prohibited. If psoriasis does not currently manifest itself as acute symptoms, then this issue is discussed with the doctor.
Characteristics of rashes in psoriasis
In order to rule out a number of other skin diseases, dermatologists recommend undergoing a series of tests to clarify the diagnosis. Such analyzes include:
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- test for rheumatism;
- skin test.
Each analysis is extremely important for a dermatologist, since only with certain knowledge in hand can an absolutely accurate diagnosis be made and the correct treatment prescribed.
In order to rule out other problems, the dermatologist first conducts an examination, as a result of which he finds out the characteristics of the disease.
With psoriasis, plaques, peeling, and redness are found on the skin. The person experiences discomfort and itching. Cell division occurs for about one month in a healthy person, but in a patient this process lasts only five to seven days. During this time, the number of new plaques increases.
The color of the plaques varies from gray-silver to yellowish, depending on the type of disease. The process of plaque appearance is accompanied by itching, redness of the skin, peeling, and pain.
In order to exclude other pathologies, the dermatologist must prescribe certain tests.
Proper nutrition for psoriasis is very important. What you can and cannot eat, diet menu for psoriasis in a detailed table on the website. See here - what not to eat if you have psoriasis.
What is psoriasis and why does the disease occur? Why psoriasis is dangerous for children, for men, during pregnancy, for others, read here - the danger of psoriasis.
Does psoriasis itch at the initial stage, what causes itching? Read here - does psoriasis itchy?
Why does psoriasis occur?
An exact answer to this question has not yet been found, but there are some prerequisites for the development of this disease. These include:
- neurological abnormalities;
- stress and depression;
- problems with immunity and malfunctions of the immune system;
- metabolic disorders;
- too heavy physical activity;
- heredity.
Each of the factors influencing the development of psoriasis can affect its appearance together with others. Most scientists are inclined to believe that this disease is an autoimmune disease and appears as a result of malfunctions of the immune system. There is a theory that believes that psoriasis appears as a result of psychosomatic abnormalities. These include depressive states, frequent severe stress, neurological disorders and psychological problems in humans.
In addition, heredity plays a big role. There is a 30% chance that a child will have psoriasis if both or one of his parents has a history of the pathology.
Heredity
Scientists tend to argue that heredity is one of the important factors in the occurrence of the disease. Psoriasis appears if one of the relatives has a history of this disease. If none of the parents or close relatives has psoriasis, the child’s risk of getting the disease is much lower.
However, other factors have the same impact on the appearance of pathology, therefore, if a person did not develop psoriasis in childhood and does not have pathological heredity in this area, he can get the acquired disease in more mature years.
Psychosomatic state of a person
Psychosomatics implies the occurrence of psoriasis due to nervous conditions or due to existing psychological problems. A person who frequently experiences stress and has a history of neurological abnormalities is more likely to develop psoriasis than a healthy person.
This disease appears, according to psychosomatics, under conditions of experienced depression, severe conditions after or during stress, frequent and heavy physical activity. In addition, resentment, anger, aggression find their manifestation on a person’s skin. Anyone who cannot forgive their loved ones for long-standing grievances has a high probability of developing a skin disease.
All everyday problems experienced have an impact on human health. Each stress leaves a certain imprint on the condition of internal organs, as well as the skin. In order not to miss such a serious disease, you need to carefully monitor your health and diagnose it in time.
Climatic conditions
In European countries, people with this disease are most common. Whereas it is not found among South African peoples. This feature is associated with the climatic characteristics of the region in which a person lives.
Scientists have proven that in cold and humid climates the incidence of psoriasis is significantly higher than in those living in warm and dry climates. In addition, one of the factors that provokes the appearance of psoriasis is hypothermia, according to one version of scientists. In order to prevent the development of this disease, people living in countries with cold climates should be tested more often.
Frequent friction and skin injuries
The occurrence of psoriasis is also influenced by injuries to the skin. Frequent injury and contact of the skin with chemicals have a negative effect on the dermis, so people working with chemicals should carefully protect their skin from contact with components.
Often, after tests and even without them, psoriasis is discovered in people employed in the production of chemical dyes, cleaning products and other factories and factories associated with the production of household and non-household chemicals. Such people should be tested more often for signs of psoriasis.
Taking medications
One of the provoking factors for the appearance of this disease is taking certain types of medications. These include hormonal drugs that affect the functioning of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands. As a result of a malfunction of the thyroid gland, this disease may appear.
In addition, psoriasis can be provoked by incorrect and long-term use of certain other drugs, not only hormonal ones. Allergies to certain plants and medications provoke the onset of the disease. In order to protect yourself from many diseases, you should get tested regularly.
Transmission of infectious diseases
Infectious and viral diseases affect the appearance of plaques. For example, frequent colds and inflammatory diseases have a great impact on the human body, causing disruptions in the functioning of the thyroid gland, metabolic processes and other human systems.
A number of tests taken for sore throat, bronchitis and other diseases will help preserve the skin and protect against the appearance of many pathologies.
Diagnosis of psoriasis: types of tests and diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of psoriasis is the first step towards curing the disease. Modern research methods make it possible to make a very accurate diagnosis. In addition to visual examination and history taking, there are a number of instrumental and clinical methods for obtaining data on the causes of the disease and determining the stage of its development.
For differentiation, an additional analysis is carried out for psoriasis - the disease has an external similarity to other skin diseases. A specialist can sometimes make a diagnosis even by the appearance and location of the rash, but laboratory methods give an undoubted result.
Basic methods for diagnosing psoriasis
How to diagnose psoriasis? Currently there are no problems with this. The symptoms of the disease are so obvious that doctors have no doubts after a visual examination of the patient.
The main specific symptom is a rash on the skin, which is localized in various parts of the body. At the very beginning of the pathological process, it manifests itself in the form of small compactions that are pink in color. Their diameter is 1-2 mm. Gradually they become like tubercles. In the growth zone, the conglomerates become bright pink and are covered with loose white scales. The plaques increase to 7-8 cm. When examining the patient, the doctor makes a scraping. As a rule, these measures are sufficient. Additional research is used to understand what kind of disease we are talking about. There are many diseases that have similar symptoms. Differential diagnosis will help determine which pathology is progressing.
What tests need to be taken for psoriasis? First, a CBC (general blood test), UAM (general urine test) and, without fail, a stool test for I/worms.
If the clinical picture of psoriasis is unclear, then a skin biopsy becomes necessary. In this study, a small pinch of the affected tissue is performed. This makes it possible to distinguish lichen planus from similar diseases that have similar symptoms. This is the only way to obtain histological confirmation of the diagnosis.
Among the main diagnostic criteria, the following should be highlighted:
- Clinical manifestations and complaints of the patient;
- The presence of concomitant pathologies and the patient’s lifestyle;
- Collecting information about relatives in order to determine hereditary predisposition;
- Presence of psoriatic symptoms: terminal film, pronounced scales and pinpoint bleeding;
- Progression of the Koebner phenomenon.
The doctor prescribes a series of laboratory and instrumental tests to determine the cause of psoriasis. This approach eliminates the possibility of frequent relapses of the disease.
Instrumental diagnostics
Instrumental diagnostics is the most informative research method, prescribed mainly in advanced cases with the progression of lichen planus. This technique is widely used when specific symptoms occur. Tests for psoriasis such as a potassium oxide test and a biopsy are necessary. It is mandatory to do a culture to determine the microflora, conduct an examination for the presence of syphilide, and determine the level of prolactin.
To determine the level of neutrophilic leukocytes (Reete bodies), the thickness of the keratinocyte layer and their histological immaturity, it is necessary to examine a pinch taken from conglomerates. An increase in the number of macrophages and T-lymphocytes in the blood and other signs are a sure sign of the development of lichen planus.
A biopsy involves performing a histological analysis of the pinch under a microscope. If a number of signs are present, the result of the research will be positive:
- Lack of a protective layer of the epidermis, which protects the skin from dehydration;
- Swelling and elongation of the epidermal processes;
- An increase in the number of capillaries (blood vessels) in the affected area;
- The appearance of microabscesses - accumulations of neutrophilic leukocytes in the area of the stratum corneum;
- Infiltration around vascular structures (lymphohistiocytic).
Among the main diagnostic methods, scraping from the conglomerate using a special glass slide should be highlighted. In this case, an analysis of the signs of the so-called psoriatic triad is also carried out. They appear in a certain order: first - the phenomenon of stearin spots, then - peeling and the phenomenon of terminal film.
When removing the scaly layer, you can see the smooth pink surface of the skin, as if polished. With further scraping, the appearance of pinpoint bleeding is observed, which is otherwise called “blood dew.”
Particular attention is paid to the presence of the Koebner phenomenon. It is typical only for periods of exacerbation and represents the appearance of plaques on those areas of the skin that have been injured.
In order to clarify the diagnosis, you can use the UV radiation method (wavelength 308 nm). If you shine an excimer laser on a conglomerate or papules, the scaly areas begin to glow.
When plaques are localized in the area of articular structures, psoriatic arthritis is called into question. In this case, there is severe pain. To clarify the diagnosis, a blood test is taken and an x-ray or ultrasound is performed in the area where the lesion is located.
Clinical researches
Laboratory diagnosis of psoriasis allows you to obtain more accurate information. Among the main methods, the following should be highlighted:
- Complete blood count (CBC). It makes it possible to determine the general condition of the patient and identify pathologies such as anemia and leukocytosis. CBC shows ESR (leukocyte sedimentation rate) and other indicators;
- General urinalysis (UCA). Provides information on the water-salt balance of the body;
- Rheumatic tests. Necessary for determining the level of protein in the blood. When it increases, we are talking about the presence of a chronic inflammatory process. If we are talking about psoriasis, then these indicators remain normal.
The diagnosis of psoriasis cannot be made based on laboratory tests alone. Additional research is required. The patient is referred for consultation to specialists such as an immunologist, nephrologist, infectious disease specialist and dermatologist.
Differential methods
Many forms of psoriasis have similar symptoms to other skin diseases that need to be treated urgently. That is why the doctor prescribes additional studies to determine the true cause of the pathological change in the skin.
For psoriasis, differential diagnosis is carried out with the following diseases:
- Seborrheic eczema and various dermatoses;
- Lupus erythematosus, lichen (flat and pink);
- Reiter's disease and neurodermatitis;
- Papular form of syphilide.
Experienced dermatologists usually determine the type and form of the disease based on the clinical picture. Psoriatic rashes have a peculiar appearance, despite this, more in-depth studies are required to exclude any type of dermatosis.
1- Seborrheic eczema; 2- papular syphilide; 3- limited neurodermatitis.
With psoriasis, the color expression is brighter when compared with the papular form of syphilide. Conglomerates peel off over the entire surface, and with syphilis - only at the edges. In the first case, the lymphatic system does not undergo any changes. If a controversial issue arises, the patient is prescribed a serological blood test.
When it comes to scalp psoriasis, there is often confusion with a disease such as seborrheic eczema. Yellow flaking appears in the area of the scalp located at the border of the scalp. There is pronounced itching. To distinguish diseases, histological studies are prescribed.
Psoriatic plaques may appear on the back of the head. Most often this occurs in women during menopause. This form of the disease is similar to limited neurodermatitis. Distinctive features of neurodermatitis from psoriasis are the silvery tint of the scales and the absence of infiltration.
How to distinguish from lichen
Differential diagnosis of psoriasis also includes identification with lichen planus (LP). The main differences between pathologies:
- Location: lichen is characterized by rashes on the mucous membranes and in the folds of the skin, rarely in other areas.
- Character of the rash: lichen planus, unlike psoriasis, has a darker skin color on the rash - crimson, sometimes with a dark bluish tint.
- Other symptoms: if with psoriasis itching and burning occur in severe stages, then in the case of LP these signs are observed constantly.
Pityriasis rosea, unlike LP, is contagious and spreads throughout the body very quickly. However, you can recover from it just as easily as from LLP - you just need to see a doctor in time.
How to distinguish from dandruff
Dandruff is the exfoliation of dead skin particles, the nature of which depends on the general health and the care products used. Although sometimes severe dandruff causes itching, scratching does not have any painful consequences.
With psoriasis, the appearance of an inflamed spot on the head with a characteristic silvery sheen can be taken as a manifestation of dandruff only at the beginning. The skin is very thin and vulnerable; when scratched, microcracks appear and bleeding occurs.
Types of analyzes performed
Among the diagnostic measures for scaly lichen, standard and additional ones are distinguished. In the first case, we are talking about a blood test (general and biochemical), urine and feces examination. Studies do not confirm the fact that the patient is sick with this particular disease, but they make it possible to establish the cause of its development and the existing complications.
Additional techniques are required, such as skin biopsy, radiography of joints, and bacteriological culture. Through such studies, the degree of damage to the body is revealed and other diseases, if any, are established.
You should pay attention to such an informative study as a test using potassium hydroxide. This measure is taken when there is a suspicion of a fungal infection.
Pregnant women are prescribed a test to determine prolactin levels. The concentration of this hormone is key in making a diagnosis. The tests performed make it possible not only to confirm the diagnosis, but also to identify the true causes of the development of psoriasis.
Where to get tested for psoriasis
- in the skin and venereal disease clinic;
- in a private clinic;
- in special institutions.
You can also get tested for psoriasis in a private specialized laboratory Invitro:
Tel. 8 (800) 200-363-0. Medical offices in Moscow follow the link: https://www.invitro.ru/offices/moscow/.
Conclusion
Each study prescribed by a doctor when diagnosing psoriasis is necessary - only a complete picture of the disease will allow us to determine at what stage the pathological process is. And this is necessary for drawing up the correct treatment regimen.
An obligatory point of research is differential diagnosis - psoriasis very often has similar symptoms to other skin diseases. In some cases, a visual inspection is sufficient for a specialist. However, it is better to take another blood test or conduct a special study than to start treatment incorrectly. Indeed, in this case, you can provoke a worsening of the disease.
Visual diagnosis of skin disease
If you have skin rashes, itching and burning, you should consult a dermatologist. During the initial consultation, the doctor will examine the medical history, listen to the patient’s complaints and conduct a visual examination of lesions on the skin.
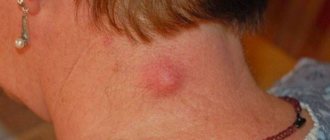
A medical specialist will determine the location of the disease. It can be absolutely anyone. The skin disease affects the scalp, facial skin, palms, soles, nail plates, abdomen, and neck.
Regardless of the location of the rash on the body, all pathological elements are red or pink, and peeling is present. Based on the size of the plaques, the form of the disease is determined - teardrop-shaped (up to 5 mm elements on the patient’s body), plaque-shaped (up to 8 mm) or coin-shaped.
Typically, a dermatologist examines the patient's entire body. It often happens that a patient complains of spots, for example, on the neck, but upon a careful examination, the doctor discovers other lesions that the patient did not even suspect about.
Depending on the location of the lesions and the nature of the rash, a preliminary diagnosis may be as follows:
- Von Zumbusch psoriasis is characterized by the rapid spread of rashes throughout the body.
- If there are erosions on the body, purulent crusts have formed, then this is a generalized Allopoly. It can be of a limited type - the lesion is in only one place.
- Impetigo herpetiformis is often diagnosed in pregnant women. The rash affects the armpits and groin area.
- Barber's disease affects the palms and feet.
- Against the background of vulgar psoriasis, the dermatologist notes thickening of the skin and the presence of white scales.
- With psoriatic erythroderma, the inflammatory process is clearly expressed and severe peeling is present. This disease is considered as a complication of a skin disease.
- When the scalp, ears, and neck are affected, seborrheic psoriasis is diagnosed.
- If pathological elements are localized on the flexor limbs, then this is inverse psoriasis.
Important information: What are papules and pustules: signs and treatment
As a rule, a visual examination and the presence of the psoriatic triad are enough to accurately diagnose and prescribe a course of therapy. Laboratory testing of blood, urine and feces is recommended to determine the individual characteristics of the patient’s body and associated pathologies.
In case of controversial clinical manifestations, the disease must be differentiated. For example, from diseases such as parapsoriasis, lichen planus, seborrhea, tuberculosis or syphilis of the skin, etc.
Psoriatic triad in psoriasis
A characteristic feature of psoriatic disease is the presence of the psoriatic triad - three symptoms that are always diagnosed together:
| Symptom | Description |
| Stearic stain | The very first sign in a triad of symptoms. It is accompanied by intense exfoliation after scraping the pathological element with a medical instrument. During scraping, many scales come off from the papules (they come off easily). After removal, the scales resemble “coconut flakes.” |
| Terminal film | The second sign in the triad. After scraping, the psoriatic plaque is covered with a shiny thin film. The film is the last layer that is easy to remove from the skin. |
| Pinpoint bleeding | After removing the film, pinpoint bleeding can be observed at the site of the lesion. |