About dermatitis Symptoms Types of dermatitis Treatment of dermatitis
When the skin peels off, and even accompanied by painful sensations, this greatly affects the general background, mood, and quality of life of the sick person. At the same time, it is equally painful to observe the suffering of both adult patients and small children. But exfoliative dermatitis, whose characteristic feature is a layered breakdown of the skin, can even affect newborns, whose skin is already delicate. Difficulties in healing open continuous wounds may lie in correctly identifying the causes, making a diagnosis and selecting one or another treatment method.
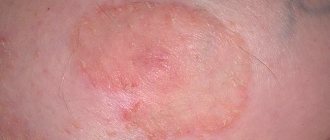
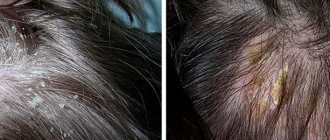
Exfoliative dermatitis, its photo and description
Before understanding the therapy methods and approaches, we need to understand more. What is this disease? All medical reference books and medical experts say that exfoliative dermatitis is a group of diseases in which the skin becomes very inflamed, red, and then blistering and peeling are noted in places where the swellings have burst. This disease can also be called “Ritter's dermatitis” and can often be mistakenly perceived as an infant disease.
The disease is quite common as it affects different age groups of people. Most often, this dermatitis occurs in infants and adults who are over 55 years old. Why in babies? Simply because the causative agent of this skin disorder is staphylococcus, which is often found in small children a few days old. Moreover, it is adult women who develop this pathology more often than men. Of all skin disorders, this type of dermatitis is recorded in 1% of all cases.
The skin of children is already delicate and requires a delicate approach to caring for it, and then there is the misfortune of a skin disease in which the layer of epithelium quickly peels off along with pain. Adults also get it, because the disease is characterized by the fact that it covers quite a wide area of the skin. And if the pimple can still be sealed with an adhesive bandage, then the places where the layer of epithelium has peeled off is very difficult to protect with anything. Not to mention wearing clothes, touching the bed during sleep and other contacts.
Basic diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of this disease most often does not pose a serious problem. Exfoliative dermatitis has a characteristic clinical picture. The high rate of development of the main symptoms convinces the doctor of the correctness of the diagnosis.
To accurately determine the nature of the pathological process, additional diagnostics are necessary. The following methods are used:
- bacterial seeding of discharge from blisters and other skin defects;
- PCR and RPR research;
- general blood and urine analysis;
- blood chemistry.
Sowing of the discharge is carried out on special nutrient media. After colonies of the pathogen grow on these media, it is clarified which microorganism caused the development of the disease. In the future, doctors are able to conduct special studies on the sensitivity of the identified pathogenic microflora to certain antibiotics.
Note. Treatment of exfoliative dermatitis with broad-spectrum antibacterial agents begins even before the sensitivity of the microflora to specific drugs is established.
Antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment for exfoliative dermatitis
For what reasons does the disease manifest itself?
In order to generally determine the causes of a disease such as Ritter’s exfoliative dermatitis in a person, it is still necessary to take into account the age gradation of patients and separately consider each age group - newborns and adults. The causes of the manifestations of the disease in infancy have been identified in the form of the following provoking factors:
- Infection of the baby's body with Staphylococcus aureus.
- The baby is infected with streptococci.
- Combined infection with both staphylococci and streptococci.
Streptococci and staphylococci are bacteria that can multiply very actively in the body and affect the internal organs of a person. Typically, for small newborns, the source of infection is the mother, unsterile instruments, linen, maternity hospital premises, medical staff, on whose skin these bacteria may be present. Staphylococci can also be located in the oral and nasal cavities and can spread to surrounding people when sneezing or coughing.
IMPORTANT! Premature babies, small children, and those who have experienced birth trauma are at particular risk. Therefore, weak children are very often exposed to this disease. Therefore, they should be kept in special chamber-boxes that ensure safety for their skin and the body as a whole.
Adults may be susceptible to the disease for the following reasons:
- Presence of an underlying skin disease. Such cases may be: psoriasis;
- ringworm;
- frequency;
- pemphigus foliaceus;
- toxic epidermal necrolysis;
- seborrheic, or contact, congestive or atopic dermatitis;
- ichthyosiform dermatosis;
- fungal infections of the skin and other diseases, the side symptoms of which are also exacerbation of the exfoliative type of inflammation.
- diabetes;
- sulfonamides;
NOTE! When establishing an accurate diagnosis, medical practice shows that in 47% of relapses the cause is very difficult to establish. Often there may be several reasons in reality, in combination.
What symptoms does exfoliative dermatitis show?
In addition to the fact that the skin exfoliates due to blistering and peels off, it also has the property with this disease to continue to peel further along the skin of the entire body. It is this feature that most often characterizes this disease, and also causes a lot of trouble for patients. The quality of life is so deteriorating that it is simply impossible to do without the help of doctors. Before connecting one or another therapy to the healing of an illness, a group of symptoms is identified in the patient.
The disease has its stages:
- Erythematous.
- Exfoliative.
- Regenerative.
During the first stage of the painful period, the skin simply turns red, swells and becomes blistered. At the second stage, peeling of the skin is already observed. Such manifestations are called by doctors - “Nikolsky’s symptom.” The epithelium exfoliates precisely because of the exudate (liquid) that accumulates during swelling under the bladder. At the third stage, the temperature drops, diarrhea that occurred in the second stage disappears, swelling subsides, redness decreases, and erosions gradually heal.
Symptoms of the disease
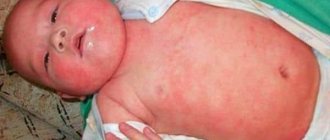
Ritter's dermatitis begins with the appearance of a red area around the mouth. The skin becomes swollen and inflamed. The pathology progresses rapidly. After some time, new territories are “captured”: inflammation spreads to the neck, navel area, genitals and covers the entire perineum. In severe cases, the entire body is affected within two to three days.
Large blisters with liquid inside form on the inflamed areas of the skin. They open easily and weeping erosions form in their place. If you grab the skin around them with tweezers, it will peel off easily. Healthy skin also peels off, exposing the deeper layers of the dermis.
The child experiences severe pain, refuses to eat, rapidly loses weight, sleeps poorly, and is constantly capricious. He may develop a high body temperature, vomiting and diarrhea.
Stages of development of exfoliative dermatitis
In its development, Ritter's dermatitis goes through three stages:
- In the first stage, the skin becomes red and swollen, and blisters appear on it.
- At the second stage, liquid (exudate) collects inside the blisters, which contributes to the peeling of large areas of the skin. In place of the opened blisters, constantly weeping erosions are formed, located nearby, they are able to merge with each other. Outwardly, it looks as if there are second-degree burns on the child’s body. The exfoliative stage leads to intestinal disorders.
- At the third stage, the intensity of the pathological process begins to decline: body temperature decreases, diarrhea and vomiting stop, erosions heal and gradually heal, swelling of the affected areas decreases, and signs of the inflammatory reaction disappear.
Experience in monitoring sick children shows that there is a relationship between the severity of the infection and the age of the baby. So, for example, if the pathology started in newborns in the second to sixth week from birth, the disease will be very severe with complications in the form of pneumonia, peritonitis, otitis media or even meningitis. If infection occurs in the second or third week, Ritter's dermatitis is always mild.
Development of the disease in adults
The development of Ritter's dermatitis in adults can be caused by long-term use of antibiotics or corticosteroids. A similar reaction can develop as a result of an infectious disease or the use of hard drugs. Often it acts as an additional symptom indicating the course of psoriasis, seborrhea, and atopic dermatitis.
Exfoliative dermatitis manifests itself in the same way as in infants, only the clinical picture in adults is more pronounced.
- Body temperature rises to 38 degrees and above.
- Large, relaxed bubbles form on the body.
- The skin around them itches, swells, and becomes red.
- Inside the rash elements there is a large amount of exudate.
- When the bubbles burst, the liquid pours out.
- In their place, red erosion is exposed.
- The skin remaining from the blister peels off.
- Externally, the affected area looks like a huge second-degree burn.
This whole picture develops against a background of general malaise, patients complain of local or total enlargement of lymph nodes, and the presence of signs of gastrointestinal disorders. If left untreated, the infection in adults does not go away on its own: huge red spots spread throughout the body, and the person experiences severe pain.
You can get Ritter's dermatitis at any age. At risk are people over forty years of age, patients who are forced to take antibiotics for a long time, or undergo radiation therapy. The disease is often diagnosed in pregnant women. Doctors explain this by saying that their body is experiencing strong changes due to hormonal changes, the immune system is noticeably weakening, so infection becomes possible.
Cases of exfoliative dermatitis in newborns
All experts agree in one opinion - small infants have a very difficult time with Ritter’s exfoliative dermatitis. And this is all due to the fact that the immune system of children, including the skin structure, its function as a protective barrier, has not yet stabilized and is not fully formed as adults under 55 years of age. In children, the disease manifests itself as follows:
- Regular diarrhea develops.
- Body temperature is consistently elevated.
- The child always sleeps poorly.
- Redness of the skin.
- Bloating in some places.
- Peeling of the epithelium.
- Wounds, erosions, ulcers.
The onset of the lesion in almost all cases occurs in the umbilical region, nose and mouth, including the inner mucous membrane, as well as on the genitals, in the anus, and in the folds of the skin. Sometimes in the second stage the temperature can jump to 40˚C. The child does not eat well and even refuses the mother’s breast. After two weeks, the disease subsides, all swelling, redness, and temperature decrease.
First signs
In most cases, like infantile pemphigus, Ritter's exfoliative dermatitis makes itself felt within 1-2 weeks of the child's development after birth. The disease has its own individual symptoms, which an experienced dermatologist cannot confuse with any other skin disease. The first signs of exfoliative dermatitis look like this:
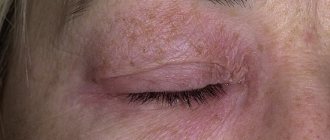
- Redness of the skin around the mouth and navel. Inflammation of the epidermis in this part of the body occurs simultaneously. On the first day of development of the disease, only red spots are observed. On the second day, the affected skin begins to peel off and keratinized scales separate from its surface.
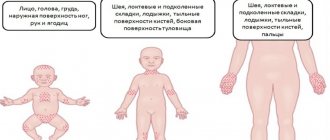
- Inflammation of the skin in folds. The infection spreads to other parts of the skin and covers the groin area, armpits, the space between the fingers and toes, and is localized around the neck. Also in the affected area are any folds of skin. The disease is especially severe in children who are overweight, when there is enough compaction of the skin for infection, where there is not enough sunlight and there is no air movement.
- Bubble formation. At the sites of inflammatory foci and red spots, white bubbles appear that contain clear liquid. They do not cause pain, and when mechanical pressure is applied to their surface, the integrity of the neoplasm is violated, it bursts, and colorless and odorless contents flow out of it. Such liquid always contains a large number of infectious microorganisms, which provoked a dermatological disease.
- Ulcerative surfaces. As the bubbles mature, they burst and a wound forms in their place. This is a sore, the size of which varies from 2 to 5 mm. The affected area of skin is inflamed and very painful. Without the use of medication, wound surfaces tend to increase in size and merge into one huge ulcerative formation. Externally, the clinical picture resembles a thermal or chemical burn of the 2nd degree.
- Swelling of the mucous membranes. The acute phase of skin damage spreads to the oral mucosa. An increase in epithelial tissue is observed with the further formation of ulcers on them, similar to those that spread throughout the patient’s body.
- Temperature increase. Violation of body heat metabolism is one of the key signs of the presence of Staphylococcus aureus or streptococcal infection in the body. The temperature rises to 40 degrees and above. The general condition of the child becomes extremely difficult.
- Weight loss and refusal to eat. Due to constant fever and high temperature, the newborn refuses to suckle the breast or take artificial formula. Against the background of increased sweating, sudden weight loss occurs, which in the first days of a child’s life negatively affects his entire further development.
If drug therapy was started in the first days of identifying Ritter’s exfoliative dermatitis, the disease does not last more than 2 weeks. After this period of time, all of the above symptoms begin to gradually subside, the ulcerative formations are covered with a thin layer of epithelium and gradually heal. Swelling and inflammation of both the epidermal tissues and the oral mucosa goes away. The disease ends with complete recovery and the child acquiring a stable immune response to microorganisms such as Staphylococcus aureus and streptococcal infection.
Exfoliative dermatitis in adults
Manifestations of Ritter's disease and exfoliative dermatitis in adults occur somewhat differently, not the same as in infants. Inflammation of the skin begins from the torso, head, perineum, and folds of the limbs. The redness is sparse at first, but then thickens to swelling and blistering. Common symptoms in adults include the following:
- Itchy skin.
- After scratching the blisters, liquid is released.
- The skin peels off where you scratched.
- In place of the peeled epithelium, ulcers form.
- The person has a fever and may feel chills.
- Lymph nodes may become enlarged.
Sometimes doctors note side effects such as baldness, peeling nails, increased heart rate, and a feeling of dry mouth. Regarding stool, it should be noted that the chemical composition of stool is such that it is difficult to wash off and has an oily consistency.
FOR REFERENCE: Older people, after 55 years, already have weakened immunity, which also affects the skin protective barrier.
Treatment method for exfoliative dermatitis
The specifics of treatment depend on the age of the patient, therefore, the method of therapy applicable to children will differ from the methods of healing for adult patients. Culture data helps to understand the texture of the fluid from the blisters in order to know what medicine to prescribe. It is imperative that specialists conduct a series of tests to maximally separate dermatitis from congenital syphilis.
For babies
Little patients are placed in a special box - an incubator made of organic plastic. Oxygen is supplied to the incubator so that the baby can breathe unhindered. It also ensures optimal temperature and humidity in the small chamber. Sterility inside the box is a must. Thanks to this chamber, erosions dry out well. Ritter's exfoliative dermatitis is treated with medication in newborns through an intravenous catheter. Medicines are administered - nutrient solutions, saline solutions, as well as light antibiotics, immunoglobulin and plasma (against staphylococci).
For adults
Adult patients are rarely hospitalized; they mostly undergo treatment at home. When it is necessary to treat exfoliative dermatitis in adults, photos of which can be viewed in this material, the following approaches are used:
- All provocative medications that can provoke this type of dermatitis are canceled.
- A bacterial culture is taken from the surface of the skin damaged by the disease.
- Local therapy consists of constant treatment of blisters, burst swellings, wounds, erosions, and dry reddened skin. Treatment is carried out with ointments (“Levomekol”, for example, or “Oflokain”), gels, creams and other drugs.
- For psoriatic dermatitis, PUVA - phototherapy can be prescribed.
- When prescribing a systemic method, the following may be included: antibiotics;
- antiviral drugs;
- antifungal;
- normalizing blood glucose (for diabetes mellitus);
- isotretinoin substances;
- Severe cases are treated with hormonal substances - glucocorticoids.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION: Local and systemic approaches to therapy differ in that they are used depending on the severity of the disease. The systemic option is often used to alleviate complex, severe stages. Local therapy is carried out for mild forms of the disease.
Local preparations
Local treatment for dermatitis is the most effective. In mild and moderate forms of the disease, it is often possible to achieve a cure with ointments, creams and lotions, without resorting to systemic therapy. Only a dermatologist can prescribe specific medications.
Typically used in the treatment of dermatitis:
- Anti-inflammatory ointments: Erythromycin ointment, Levomekol;
- Glucocorticosteroid drugs: Akriderm ointment, Lokoid cream and lotion;
- Ointments that restore the skin surface: Bepanten, Radevit;
- Anti-itch ointments: Fenistil;
- Keratolytic ointments: Lorinden, salicylic-zinc paste.
Systemic treatment
Systemic drugs are used to treat severe forms of dermatitis, as well as allergic skin inflammations. Drugs are selected based on the diagnosis and characteristics of the patient’s body.
A dermatologist, depending on the type of dermatitis, may prescribe:
- Detoxification therapy: activated carbon, Polysorb;
- Antihistamines: Kestin, Loratadine, Cetrin;
- Calcium preparations: calcium gluconate, calcium chloride;
- Sedatives: extracts of valerian, motherwort, Afobazol, Glycine.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are the most popular method of treatment, but there is always a danger of aggravating the disease and intensifying the problem. Therefore, it is worth using traditional methods of treatment only after consultation with your doctor and not instead of classical therapy, but together with it.
Traditional recipes for the treatment of dermatitis:
- Periwinkle. Make a decoction: pour about 300 grams of dry leaves of this plant with 1 liter of water, when it boils, wait another 10 minutes. When it cools, strain and add to the bath. Take a bath for at least 15 minutes. Apply the boiled cake to problem areas of the skin.
- Sophora japonica. The fruits of this tree can cope well with itchy skin. It is enough to boil 100 grams of fruit in 0.3 liters of water. Then wet the gauze or bandage and apply it to the itchy area of skin.
- A series. Take one tablespoon of powder from the string. Brew the herb with 150 milliliters of water. Leave for 4 hours.
Diet
Treatment of any dermatitis should begin with following a hypoallergenic diet, especially if the dermatitis is of an allergic nature.
Hypoallergenic products:
- poultry meat,
- veal,
- mutton,
- skim cheese,
- cucumbers,
- zucchini,
- fresh cabbage,
- vegetable oils,
- cereal porridges,
- fermented milk products without chemical additives,
- green apples,
- black bread.
You should not eat foods such as:
- chocolate,
- coffee,
- red vegetables and fruits,
- horsemeat,
- citrus,
- strawberries and strawberries,
- sauces and mayonnaise,
- industrial canned products,
- all types of tropical fruits.
Stories from our readers!
“I suffered from dermatitis. His hands and face were covered with small spots and cracks. No matter what I tried, the drugs only helped for a while. A colleague advised me to order this cream.
Finally, thanks to the cream, I completely got rid of the problem. After the third procedure, the burning and itching disappeared, and after 4 weeks the signs of dermatitis disappeared. I am very pleased and recommend using this cream to all people suffering from skin problems.”
What preventative measures can be taken?
When looking at one or another photo demonstrating this disease, you can immediately guess that the best way to avoid all this is to introduce preventive measures in the life of the baby, the mother of the newborn, medical staff or the adults themselves who are afraid of getting sick. There are several general points that sometimes keep people healthy:
- Avoid as much as possible any allergens that can get on the skin or inside the body.
- Do not start treatment for small, mild symptoms.
- Diet and its balance, healthy food should always be in a person’s life.
- Lead an active and healthy lifestyle, give up a number of bad habits.
In maternity hospitals, all wards should be regularly treated with quartz treatment. Medical staff must be tested from time to time to determine the presence or absence of bacteria and viruses in the blood of employees. If staphylococci or other harmful microorganisms are detected, personnel are removed from work until complete recovery. Women in labor should also undergo similar tests and undergo treatment if harmful bacteria are detected. When in contact with a baby who has just been born, all adults should have gauze bandages on their faces and gloves on their hands.
When you seek medical help in a timely manner when dermatitis with the effect of peeling skin is detected, then the pathology can actually be cured in literally 2 weeks. As for cases when help is not sought in time, especially when the patient is a newborn, a rapid onset of death is noted. Therefore, you should not delay diagnostic, therapy or prevention procedures, but it is better to do everything in due time.