Features of neoplasms in intimate places
Papilloma on the pubic part differs from other growths, the appearance of which is also caused by the papillomavirus.
- All information on the site is for informational purposes only and is NOT a guide to action!
- can give you an ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS !
- We kindly ask you NOT to self-medicate, but to make an appointment with a specialist !
- Health to you and your loved ones!
These are the following differences:
- this form of the disease is highly contagious. The risk of catching the virus from a partner infected with HPV is almost 100%;
- papillomas in intimate places tend to degenerate into malignant skin formations, which leads to cancer of the genital organs.
What types of HPV cause them?
The human papillomavirus is special; it provokes various problems. A genital wart is the most dangerous manifestation of this pathology.
Anogenital warts are caused by approximately 20 different strains of HPV. Visible growths – strains 6 and 11, anogenital – 16, 18, 33, . Genital warts can be represented by papillomas and condylomas.
Important!
It is possible to determine the HPV strain and assess its oncogenicity using modern research methods.
Papillomas
These anogenital warts appear on the genital areas that have skin. They are round and smooth, rise slightly above the skin and do not have a stalk.
There are also keratic papillomas. They appear relatively rarely and are characterized by a thicker surface. Dry skin areas are most often affected.
Condylomas
These are fibroepithelial neoplasms that appear on mucous surfaces. Condylomas have a thin stalk or a wide base; they can be single or merge into groups. In appearance, condylomas resemble a cockscomb or cauliflower.
Causes
You can catch the virus not only through sexual contact, but also if you do not follow the rules of personal hygiene.
- Infection can occur through skin contact with an object that was recently used by an infected person.
- In public places, such as a bathhouse, sauna or swimming pool, you must use only your own towel, washcloth, and disposable pads.
The skin in intimate areas is much thinner compared to other areas of the body. Thanks to this fact, the papilloma virus easily penetrates the layers of the epidermis.
Once in the body, the papillomavirus can “sleep” for some time. Factors such as:
- a sharp jump in weight;
- weakened immunity during pregnancy;
- long-term use of oral contraceptives;
- physical or mental stress;
- physical exhaustion;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- chemotherapy;
- prolonged use of an intrauterine device.
Differences from other formations on the genitals
Genital warts should be differentiated from Buschke-Levenshtein tumor, moles, genital herpes, and molluscum contagiosum.
Genital herpes is a group of vesicular neoplasms that have transparent contents. This disease, unlike genital warts, has a clear clinical picture - the patient experiences itching and burning, and when the blisters burst, the formation of large erosive foci may occur.
Molluscum contagiosum looks like an ordinary pimple, with a small depression in the center. Inside the bladder there is a mass in which there are rounded bodies that resemble mollusks in appearance.
Moles are most often small in size, dark in color and do not protrude above the surface of the skin. Easily confused with papilloma - a hanging nevus, which can be flesh-colored. Moles on intimate places are observed from birth.
Buschke-Levenshtein condyloma is a type of genital papilloma. At the initial stage, several papillomas are formed, which subsequently merge with each other into very large lesions.
Over time, the growth becomes covered with scales and becomes rough. The neoplasm is separated by grooves in which liquid contents with an unpleasant odor accumulate.
Important!
Neoplasms in the intimate organs should be distinguished from each other not by external signs, but by nature and etiology.
Symptoms
The main symptom of papillomavirus manifestation in the pubic area is the formation of growths.
Most often, the following types of papillomas occur in intimate places:
- genital warts;
- filamentous papillomas.
Photo: genital warts
These types of skin growths differ from each other in appearance and nature of occurrence.
- Genital condylomas are growths in the form of papillae, no more than a few millimeters in size.
- The color of the formation can be either pale gray or pink (with varying degrees of brightness).
Typically, the incubation period of the disease is 3 months; in some cases, symptoms may appear several years later.
The likelihood of developing genital warts on the pubic area in men is the same as in the opposite sex.
Thread-like papillomas (acroids) have a cone-shaped gray-yellow color.
Photo: filamentous wart
- The size of the growth is about 5 mm.
- In the early stages of the disease, several growths appear.
- In the absence of treatment, extensive proliferation of skin formations is observed.
Older people are most susceptible to infection with this type of papillomavirus.
- Most often, acne lesions appear on the pubic area of women.
- The highest risk of finding threadlike papillomas is in women approaching menopause.
- For girls who have abnormalities in the functioning of the ovaries, the likelihood of acrochodosis in the intimate area increases.
To prevent papilloma in the pubic area from becoming inflamed, it is necessary to avoid traumatizing it.
From the moment the growth appears, it is recommended to refrain from cosmetic procedures such as hair removal and depilation.
Symptoms
Due to gender differences between men and women, the clinical picture has similar and different symptoms. Common manifestations include the following:
- pain in the genital area, which is accompanied by severe burning and swelling of the soft tissues;
- the appearance of neoplasms in the form of genital warts and papillomas;
- weakening of general immunity, which is accompanied by frequent respiratory diseases;
- painful acts of defecation, accompanied by a slight discharge of blood.
In women, symptoms may have some features:
- painful menstruation, the duration of which increases by 3–4 days;
- deterioration in general health, frequent insomnia caused by pain and itching in the genital area;
- brown or scarlet discharge that appears after sexual intercourse;
- pain and irritation of the vagina during sexual intercourse;
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor from the vagina that is not related to nutrition.
Since women are more likely to contract the virus, it is important to pay attention to such manifestations. They may indicate the presence and progression of the virus in the body, which may precede the development of serious pathologies that cause infertility and cancer.
In the strong half of humanity, papillomas in the intimate area can provoke the development of symptoms such as:
- swelling of the penis;
- the appearance of neoplasms around the head of the penis and in the scrotum area;
- decreased sexual desire, which is associated with painful sexual intercourse and the appearance of unpleasant sensations during erection.
The structure of the papilloma is very loose, and the surface layer is delicate. Therefore, its integrity can be disrupted by ordinary scratching, wearing underwear, or during hygiene procedures. When the integrity of the papilloma is violated, blood appears in intimate places, and the resulting wound is an open gate for pathogenic microflora located on the skin. As a result, infections can be added to papillomatosis, which provoke decay of the neoplasm, which is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, severe itching and pain.
Diagnostics
Recognizing papillomas in the pubic area usually does not cause difficulties. The diagnosis is made by a doctor during an external examination of the patient.
Photo: external examination of the patient by a doctor
If there are doubts, to confirm the presence of papillomavirus infection and determine the nature of the formations, examinations such as:
- histological examination of material obtained by biopsy;
- cytological examination of biopsy samples;
- performing DNA testing to detect the HPV virus;
Blood tests and scrapings are necessary to determine the nature of the infection in order to prescribe the most effective treatment.
Diagnosis of papillomas
If papillomas appear, the doctor will recommend their removal.
This measure is connected not only with the fact that they can pose a danger.
First of all, they spoil the appearance and reduce the quality of life.
If a person has papillomas in the pubic area, he will need to undergo an examination to find out which viruses cause the formation of growths.
There are three types of viruses: with low, medium and high degrees of oncogenic activity.
If the tests show the presence of an oncogenic type of HPV, the patient will be under constant supervision of a specialist.
Degeneration into cancer is not excluded even after removal of all papillomas.
Removal of pubic papillomas
The same methods are used to eliminate condylomas and acrothomas in the pubic part. A qualified doctor will help you decide how to remove papilloma.
Modern clinics can offer excision of papillomas in the intimate area in the following ways:
- cryotherapy;
- laser therapy;
- diathermocoagulation;
- radio wave therapy;
- surgical excision.
During cryotherapy, the papilloma is exposed to liquid nitrogen.
- As a result, the growth dies, darkens and after some time disappears.
- Healing of the affected area takes about two weeks.
With laser therapy, a beam of rays is directed at a benign formation, designed to heat the surface of the growth.
Photo: laser therapy
- As a result, moisture evaporates from the papilloma, and the growth is noticeably reduced.
- A dry crust appears on the surface of the neoplasm.
- A week after the procedure, the crust disappears.
Diathermocoagulation is carried out using an electric knife or high-frequency radiation, which heats the tumor.
- After the procedure is completed, a scab appears on the resulting wound.
- The healing process lasts at least a week.
- This method is quite painful, so the treated area of skin must first be anesthetized.
- The procedure is used for minor manifestations of human papillomavirus infection.
Radio wave therapy involves the use of the Surgitron device.
Photo: using a radio knife
- The method is characterized by a minimal risk of inflammation of the growth after the procedure.
- The disadvantages of this therapy include scars formed at the site of skin lesions.
- Local anesthesia is recommended before removing papillomas.
How to distinguish a wart from a papilloma? Find out here.
Surgical removal is used in advanced stages of the disease, when tumors grow to impressive sizes.
- Also, an indication for removing papillomas in this way is the degeneration of papillomas into malignant formations.
- Surgical removal is very painful and local anesthesia is required.
Treatment
To date, there is no effective drug that can eliminate the virus from the human body. You can only get rid of the symptoms of genital warts. Physically, their removal is carried out using several methods. In addition, experts recommend means that slow down the process of further penetration and development of the pathogen inside the body.
Often, warts in intimate places disappear on their own, without any intervention. And although HPV remains with a person for the rest of his life, it may no longer bother the carrier. Thus, half of the infected who had such unpleasant skin defects did not relapse again. According to statistics, in 1 out of 4 patients they form again within 3 months after surgical removal.
The specialist chooses therapy for each patient diagnosed with genital warts on an individual basis. At the same time, the patient’s general well-being, the presence or absence of other infectious pathologies that are transmitted through sexual intercourse, and other factors are taken into account.
At the moment, complex therapy is predominantly used, when papillomas are eliminated not only surgically, but also using immunostimulating and antiviral agents.
The following surgical methods of elimination are known:
- Cryotherapy or exposure to liquid nitrogen using low temperatures. In this way, tumors on the penis or near the vagina are removed. Used to get rid of minor warts. The patient must avoid sexual intercourse until complete recovery, until the growths disappear.
- Surgical excision. Under local anesthesia, anogenital warts are cut off using a surgical scalpel. This technique is not suitable for large papillomas, since after the operation there is a possibility of scarring.
- Electrosurgical method. Used in situations where genital growths are of impressive size. New growths are eliminated using a heated device under local or general anesthesia.
- Laser. This technique uses a medical laser to remove large warts or those located in hard-to-reach places (urethra or inside the anus).
- Diathermocoagulation. Genital growths are cauterized with high-frequency current using a special device.
- Chemical method. Elimination is carried out with nitric or trichloroacetic acid; Feresol and Solcoderm are also used.
On this topic
- Warts
All about the radio wave method of wart removal
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- September 27, 2020
Medication methods are used along with surgical ones. In parallel with the removal of growths, the specialist prescribes immunomodulators and antiviral agents. Cytotoxic drugs:
- podophyllotoxin;
- podophyllin;
- 5-fluorouracil.
Medications are used (Cycloferon or Laferon), which serve to strengthen.
There are also certain hygiene requirements for those diagnosed with genital growths. It is necessary to avoid the use of soap and other substances with fragrances and fragrances.
After washing the genitals, you need to dry them thoroughly with a towel, since a damp environment is an ideal environment for the proliferation of microorganisms, viruses and fungi. It is required to wear clothes made of natural material and avoid mechanical and other friction. In addition, underwear should be changed regularly and washed separately from other clothes.
Folk remedies
How to get rid of papillomas in an intimate place at home?
Photo: using celandine juice for warts
To solve this problem, traditional medicine advises:
- celandine juice. To do this, the skin around the growth should be lubricated with fatty oil, and the juice should be applied pointwise to the growth. If it is not possible to obtain juice from a freshly cut stem, you can purchase the drug “Superclean” at the pharmacy;
- potato. Wipe the infected area with a peeled piece of root vegetable several times a day for a month;
- fir oil. This liquid should be applied to the skin lesion until it completely disappears;
- garlic ointment. To prepare such a medicine, you need to mix pressed garlic with baby cream in a 1:2 ratio. Make compresses with this ointment every day. But you should not keep the bandage on for more than 3 hours, otherwise burns cannot be avoided;
- Castor oil. Apply the product to the problem area at least 2 times a day. You won’t be able to get rid of papillomas quickly this way. Treatment with castor oil may take several weeks.
Photo: removing growths with garlic
Folk remedies for the treatment of benign skin formations do not provide a 100% guarantee.
If the fight against growths at home is prolonged, you need to consult a doctor to choose a more effective method.
Locations and symptoms
According to doctors, most often genital warts appear in places of maceration. These are areas of mucous membrane or skin in contact with moisture.
On the genitals of women
Possible areas where genital warts appear:
- vagina;
- labia minora;
- Cervix;
- urethral opening;
- anal area.
On the genitals of men
For men, the following risk areas are:
- anal area;
- head of the genital organ;
- foreskin.
Also find out how warts appear on the penis, diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
Drug treatment
Only a specialist should decide how to treat growths with medication.
Only a doctor can prescribe effective medications and outline a dosage regimen.
Treatment of papillomas with pharmaceuticals involves the prescription of immunostimulating drugs. Such medications are aimed at destroying the papillomavirus in the body.
Photo: remedy that improves immunity
The most commonly prescribed drugs for this purpose are:
To directly affect the skin formation, a specialist may prescribe a solution of trichloroacetic acid (90%).
The liquid is applied to the papilloma, avoiding contact with healthy skin. Usually one procedure is enough.
It is not recommended to choose a method of getting rid of papillomas on your own in order to avoid disastrous consequences.
Only a doctor will select treatment, taking into account all the characteristics of the body, and prescribe a study to identify the nature of the formations.
Photo: a doctor must prescribe medication
It is possible that the growths do not contain oncogenic components, but it is better not to take risks.
Causes and factors for the appearance of growths
The reason for the appearance of genital warts lies in the penetration of the papilloma virus into the human body. The aggressiveness of this infection is enhanced by the following factors:
- excessive sexual activity;
- sexual partner has anogenital warts or has cervical cancer;
- low immunity;
- the presence of sexually transmitted pathologies;
- tobacco smoking and drug addiction;
- alcoholism;
- pregnancy;
- avitaminosis;
- endometriosis and other diseases of the uterus.
Questions and answers
Is the appearance of growths dangerous for a pregnant woman?
The presence of papillomas in the pubic area during pregnancy does not in any way affect the intrauterine development of the fetus.
- The danger comes from benign formations located in the vaginal area.
- In this case, there is a risk of the baby developing growths in the respiratory tract.
Most often, the immune system, established from birth, suppresses the virus that the child encountered while passing through the birth canal.
How dangerous is the human papillomavirus during pregnancy? Find out here.
Can genital papilloma hurt when pressed? Read on.
Which doctor should I contact?
- To make an accurate diagnosis in men who have discovered pubic papillomas, a consultation with a urologist is required.
- A gynecologist will help a woman solve such a delicate problem.
- If growths are found on other parts of the body, you should consult a dermatovenerologist.
The effect of HPV on pregnancy
During pregnancy, a woman becomes most vulnerable, since her body is weakened due to bearing a child. In this case, the number of existing papillomas increases, their growth intensifies, and unpleasant discharge may appear from the vagina. In this case, neoplasms can appear even in women who have never complained of infection. Usually, after childbirth, the body returns to normal, and the rapid growth of papillomas stops.
During pregnancy, the unborn child is not at risk of contracting the virus, since it is not able to penetrate the placental barrier. However, infection can occur directly during childbirth, as the child passes through the birth canal. In this regard, treatment of papillomas should be carried out before pregnancy to eliminate possible risks.
If the pregnancy period has already begun, and the growths have just appeared, doctors do not recommend removing them immediately. If the neoplasms are not subjected to friction, trauma and do not cause discomfort to the patient, they are left until successful delivery. This is due to the fact that removal procedures carry certain risks even over a short period of time. To prevent complications, women are advised to delay removal.
During pregnancy, conservative therapy is usually prescribed to restore the immune system. This will help stop the uncontrolled growth of papillomas and prevent the appearance of new growths. This treatment is successful in most cases, but sometimes a relapse occurs after a few months, and tumors reappear. However, this time they may be localized in a different place.
Video: “How to treat papilloma virus”
Pubic papillomas are benign neoplasms caused by infection with the human papilloma virus. Growths localized in this area of the body may not cause any problems for a long time, but require special attention, because are likely to cause complications in the form of progression of HPV, the addition of other diseases or the development of cancer.
What is the danger
Genital papillomas themselves are benign neoplasms, but they can provoke a number of complications, which include:
- Papillomas in the groin are easily damaged, so there is a high probability of infection, which complicates the clinical picture and aggravates the treatment process.
- Neoplasms increase in size quite quickly, and in the absence of drug antiviral therapy, they can grow into the area of the urethra, which will lead to difficulty urinating.
- Papillomas on the pubis, which has thick hair, are most often accompanied by fungal diseases.
- There is a high probability of degeneration of pointed and flat papillomas into malignant tumors, which is facilitated by constant trauma and reduced immunity.
- The genital area is close to the anus, especially in women, so there is a high probability of infection that comes from the intestines.
- During pregnancy, the appearance of neoplasms is a reason for a ban on natural childbirth and an appointment for delivery by cesarean section.
The most terrible consequence for the female body is cervical cancer, as well as dysplasia, which does not allow a woman to become pregnant. In men, the virus can cause cancer of the penis and rectum. The virus is a real threat, so you should not take any growths in the genital area calmly. Early diagnosis and timely treatment will reduce the likelihood of cancer several times.
Causes of pubic papillomas
The appearance of pubic papilloma can only be caused by an infection such as HPV. This pathogen is highly contagious and has more than 100 varieties. When it comes to growths on the genitals and in the area of the pubic tubercle, it is believed that the disease is caused by human papillomavirus of increased oncogenic risk, for example, type 6, 11, 13, 16, 18, etc.
HPV is transmitted from person to person in many ways. The main route of transmission is sexual contact, genital, oral or anal. Using a condom only slightly reduces the risk of infection. Risk factors: early onset of sexual activity, promiscuous sexual behavior, frequent change of partners. In such cases, growths on intimate places, including pubic papillomas, are a common occurrence.
In second place is the contact and household method of transmission of infection. Sometimes just one kiss, handshake or close hug is enough for the pathogen to remain on the skin or mucous membranes of a healthy person and, over time, take root and multiply.
You can catch HPV by using any of the things of an infected person or by touching the surfaces that he touched. Not very often, but it is a fact, the virus that causes the appearance of pubic papillomas can be caught in a public bathhouse, solarium, locker room and in any other public place where the humidity level is high.
Over time, without proper treatment and if hygiene rules are not followed, HPV can be transferred from one part of the body to another - this is the so-called self-infection.
It is known that after prevention, the best protection against HPV is considered to be a strong immune system and a healthy lifestyle. On the contrary, people with weak immune systems are most susceptible to infection. Thus, having settled in human tissues, the microorganism does not immediately make itself felt and causes the appearance of symptoms of the disease only if the immune system is weakened and cannot suppress the activity of the virus. In this case, a rapid increase in the pathogen population occurs and the growth of pubic papilloma begins.
Constantly deteriorating environmental conditions, poor food quality and poor diet, alcohol consumption, smoking, and an inactive lifestyle lead to a decrease in the body's protective functions. An important role in weakening the body is played by acute infectious diseases, chronic forms of diseases (hepatitis, diabetes mellitus, depression, hormonal imbalance, etc.), untimely treatment of emerging pathologies and inadequate self-medication. All this provokes a deficiency of nutrients and the accumulation of toxins inside cells, which together disrupts the functioning of most organs and systems.
Provoking factors and causes of pubic papilloma:
- Insufficient hygiene culture . People who do not particularly care about their hygiene and do not sufficiently care for their skin are susceptible to the rapid development of HPV infection. The intimate area requires special attention, because there is a special microflora here, and sweating can often be increased due to constant wearing of underwear. Both women and men are recommended to use special hygiene products for intimate areas every day, and use only individual devices for depilation.
- Skin diseases . Any pathology of the skin can cause the development of HPV, as well as provoke the growth of papilloma on the pubis in women and men and the further spread of the disease to the mucous membranes of intimate places. Even the presence of small cracks, cuts, or slight irritation opens the way for the appearance of benign epithelial tumors.
- Sexually transmitted diseases . They play a significant role in weakening the immune system and the formation of special pathogenic microflora. Very often, in the presence of chlamydia, syphilis, HIV and other STDs, HPV is also diagnosed. In such cases, papillomatosis often occurs - multiple papillomas on the pubis, genitals and in the anal area.
- Pregnancy . Due to changes in a woman's hormonal background, the body weakens and becomes more vulnerable to HPV.
A pimple or bump popped up on the pubic area: why and what to do, methods of treating skin and subcutaneous inflammation
The appearance of painful pimples and bumps in intimate areas does not promise anything pleasant. In addition, lumps and pimples on the pubic area are common reasons for visiting specialists.
Do not panic when tumors appear and make diagnoses for yourself. Typically, such neoplasms turn out to be benign and are subject to conservative or surgical treatment.
In this article, I reviewed the possible causes of lumps, prevention and treatment methods available on the Internet.
A purulent lump on the pubis is an alarming symptom that should never be ignored. This neoplasm should not be taken only as an aesthetic defect, since the formation of lumps in the groin area can signal the development of certain pathologies in the body.
The first thing you need to do is visit a doctor who will help determine the cause of this phenomenon. If the formation arose as a result of any disease, then it will be possible to quickly get rid of it only by starting treatment in a timely manner.
Various lumps can form in the pubic area in women for a variety of reasons. These include the following:
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes, which forms during the development of inflammatory infections of the genitourinary tract.
- Abscesses (ulcers). When a lump with pus is found on the pubic part, this most often indicates an abscess. This phenomenon occurs due to the accumulation of excess contents of the sebaceous glands, or their inflammation. In such a situation, in addition to the formation of a seal on the skin, a woman experiences symptoms such as lethargy, chills, high fever, and general malaise.
- Cystic neoplasms. The most common localization of atheromas is the groin area. This cystic formation is benign. It is soft and mobile to the touch, has clear and even boundaries. The compaction is delimited from adjacent tissues by a fibrin capsule. Inside the cone there is a liquid consisting of intercellular elements and fibrin fibers.
- Bartholinitis. This disease occurs when the Bartholin glands become inflamed. In this case, a compaction forms in the vestibule of the vagina, to the left or right of it. It is filled with fluid and is quite painful - every touch to it causes severe pain. After some time, an abscess appears on the surface of the ball.
- Folliculitis. This phenomenon develops due to malfunctions of the hair follicles. In this case, we can say that the hair is not growing properly (hard pubic hairs have grown into the skin, which has led to the development of an infectious process in the tissues).
- Syphilitic neoplasms. Quite rarely, but it still happens that a ball forms on the pubis on the left or right side as a result of the development of syphilis. Such compactions are called chancre. They are characterized by small sizes (up to one centimeter in diameter) and smooth edges, painless to the touch. After a certain period of time, the structure begins to change, and a crater-shaped notch is formed on the skin.
- Oncological diseases (lymphoma).
Purulent bumps on the pubis - photos and symptoms
A lump under the skin on the pubis rarely occurs without symptoms. Usually this phenomenon is accompanied by certain clinical manifestations. The most pronounced of them is pain syndrome. Painful sensations vary depending on the reason for which disease the purulent lump appeared. The most painful lumps are those caused by folliculitis and lymphoma.
Another characteristic sign is hyperemia. It is characterized by redness of the skin in the affected area. Sometimes body temperature rises.
A pronounced clinical manifestation of this phenomenon is the release of the contents of the compaction. If we are talking about cysts, then it is transparent, with abscesses it is bloody with purulent impurities. If it is a syphilitic chancre, then the contents of the seal are bloody and have a pungent odor.
However, relying only on clinical manifestations, it is not possible to determine the nature of the neoplasm. You will need to undergo some examinations.
Diagnostics
- If the lump is painless and does not interfere with anything, then you should first go to a surgeon to rule out such a phenomenon as a benign formation.
- But if you experience any symptoms and a feeling of general malaise, it is recommended that you first go for a consultation with a dermatovenereologist and an infectious disease doctor.
Any diagnostic procedures are prescribed on an individual basis for each specific patient. In addition to the mandatory general urine and blood tests, a flora smear from the urethra or vagina is prescribed. More complex diagnostic methods may be required: ELISA and PCR.
If the development of a malignant tumor is suspected, a biopsy is performed.
Causes of pubic itching in women - https://ozude.ru/itching/cheshetsya-lobok/.
Lumps with pus on the pubis: treatment methods
It is extremely important not to forget that if any neoplasm appears, including on the pubis, you cannot self-treat. Even a small, harmless-looking bump on the pubic area can be a signal that a serious disease is developing in the body.
If the compaction appears due to inflammation of the lymph node, then therapeutic measures will be aimed at treating the underlying disease. When the source of infection is neutralized, the size of the lymph node will gradually decrease and normalize over time.
If, based on the results of the necessary studies, it is discovered that the pubic lump is a consequence of a malignant tumor, the patient will be prescribed a course of chemotherapy or radiation therapy. In some situations, for example, when the tumor progresses very quickly, surgery is performed.
If the outcome is favorable, a scar will remain in the bikini area, which will not look aesthetically pleasing. In the worst case, the wound becomes infected and the process of inflammation begins with all its clinical manifestations.
In the early stages, boils are successfully treated with levomekol and ichthyol ointments, which should be used in the form of compresses. They should be placed overnight. The course of treatment is 5-7 days.
Advanced forms are treated by surgical removal and cleansing of the affected area from purulent contents. Then the pubic area must be treated with chlorhexidine and levomekol for several days; in some cases, the doctor prescribes antibiotics.
Superficial folliculitis should be treated with antiseptics (for example, the same chlogexidine), as well as an antibiotic in the form of an ointment. Levomekol is used only if inflammation occurs. Until the affected area heals, it can be treated with ointments containing tetracycline or erythromycin.
- To remove lipomas and atheromas in the groin area, surgical intervention is performed largely due to an aesthetic defect.
- If the lump does not cause inconvenience and does not create obstacles to leading a normal lifestyle, it is recommended to monitor its density and structure, as well as the degree of its growth.
- You can avoid the appearance of bumps in the pubic area only by carefully observing the rules of personal hygiene - carefully use razors when depilating in the bikini area, then immediately treat the skin with antiseptic agents, use only good quality shower products.
Preventive measures
As a rule, it is quite possible to avoid the occurrence of a pathological process. To do this, you must adhere to several rules:
- use protective equipment during sexual intercourse;
- pay special attention to intimate hygiene - take a shower in the morning and evening, using soap or another antiseptic;
- Promptly disinfect any areas of possible infection.
The formation of purulent lumps can be caused by many factors. Basically, these formations do not pose a serious health hazard, but they often cause quite severe painful sensations that interfere with leading a normal lifestyle.
Therefore, it is extremely important to start treatment on time, as well as follow preventive measures to avoid their recurrence.
Source:
Pubic lump
The health of the intimate area is an important component of the normal life of a man and a woman. Any ailments or abnormalities make patients worry. A lump on the pubis is a common reason for visiting a doctor. When a tumor appears, you should not panic and make a dangerous diagnosis yourself.
Usually the lump turns out to be a benign neoplasm. Having diagnosed the disease, doctors prescribe treatment; it can be either conservative or surgical.
Causes of bumps
In medical practice, there are various factors that influence the formation of compactions. Symptoms in women and men are the same, depending on the disease. The ball may appear to the right or left of the pubis or in the middle of the intimate area.
Among the main seals and the reasons for their appearance are the following:
- Boils are an infectious and inflammatory process affecting the hair follicle. Through microtrauma on the skin, bacteria (staphylococci or streptococci) enter it. Bacteria cause the development of pus and inflammatory processes. A large red bump forms on the skin. The lump hurts a lot and pulsates. On palpation, a mobile and elastic ball is felt. Sometimes the patient’s general health worsens and body temperature rises. These are standard symptoms of furunculosis. Hypothermia, stressful situations, decreased immunity, and inflammatory processes in the body can cause the development of a boil.
- Hernia in the groin area - most often a hernia occurs in men. The main reasons are heavy lifting, frequent constipation, increased internal pressure in the abdominal area. When a hernia occurs, the abdominal organs prolapse into the scrotum or groin area. The ball is painless and is localized on the left or right side of the pubis. It doesn't cause any particular inconvenience. It is dangerous because it can pinch a loop of intestine. In this case, the patient feels severe pain, the intestines are pinched, the patient cannot empty the intestines, and intoxication of the body begins. The patient requires immediate surgery.
- Atheromas - they are also called cystic formations. These are benign tumors that often appear on the pubic area. Atheromas occur due to blockage of the sebaceous glands. The exudate has nowhere to go, as a result, it begins to accumulate inside the capsule in the sebaceous duct, expanding it. The cyst is a soft and mobile lump, with smooth and clear edges. The lump hurts due to inflammation and is chronic. Atheroma can periodically become inflamed (for example, during hypothermia or a stressful situation). You can get rid of it completely only surgically by removing the atheroma capsule.
- Lymphadenitis is an inflammation of the lymph node in the groin area. Lymph nodes become inflamed when immunity is reduced, during infectious and other diseases (sometimes with diseases of the pelvic organs or sexually transmitted infections). With lymphadenitis, bumps appear, fever and deterioration of health are possible. The seal on the pubis interferes with walking, causing discomfort.
- Lipoma is a benign tumor, like a lump in an intimate place, it is formed from adipose tissue. This is an absolutely painless neoplasm. On palpation, a soft and movable compaction is felt. Lipoma does not go away on its own, is not subject to regression, and can only be removed surgically.
Source: https://yarpol2.ru/diagnostika/vyskochil-pryshh-ili-shishka-na-lobke-pochemu-i-chto-delat.html
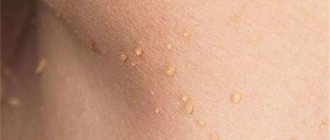
What do pubic papillomas look like?
Photo of pubic papillomas
HPV has no specific symptoms. The fact that the virus is present in the body can be judged if a papilloma has grown on the pubis or any other part of the body. Usually, with an uncomplicated course of the disease, patients do not complain of a general deterioration in health, fever or any other manifestations of an infectious disease.
In the area of the pubic tubercle there is a fatty layer and many nerve endings, so any mechanical effect on the pubic papillomas can cause sharp painful sensations. Although with careful palpation no pain occurs.
When the pathology is complicated, a secondary infection occurs, or against the background of injury to pubic papillomas, men and women may experience itching, burning, and bleeding.
Next, we will tell you what types of pubic papillomas there are and what they look like:
- Genital warts . This is a type of benign growth that very often affects the intimate parts of both men and women. If a papilloma of this type appears on the pubis, then there is a high probability that the same growths are present on the genitals, in the vagina, anal area and even in the urethra. The growth of such tumors is provoked by HPV with a high risk of malignancy, so their presence in women is a risk factor for the development of cervical cancer. Condylomas acuminata look like grouped small papillae, sometimes in appearance they are compared to the comb of a rooster. Protrude noticeably above the skin level. They grow very quickly. The color most often matches the skin color, although there are also light gray and pink.
- Hanging papillomas . They got this name because... literally hang from the skin, supported by a thin stalk. The shape of the process is either thread-like or spherical with irregular outlines. The sizes range from 1-2 mm to 5 mm. Most often flesh-colored or brownish in color. Without proper treatment and with weakened immunity, multiple hanging papillomas appear on the pubis.
- Flat papillomas . Located along the surface of the skin. They are flat on the outside, but they can be distinguished by touch, because... their structure is denser than that of the epidermis. Width - from 1 mm to 5-6 mm. Color - flesh-colored, grayish, yellowish, brown. Flat papilloma on the pubis appears much less frequently than pointed or thread-like growths.
Any type of growth that occurs in the intimate area, including on the pubic tubercle, is potentially dangerous in terms of damage during hygienic procedures and possible degeneration into malignant tumors. Do not forget that the genital form of HPV is extremely contagious, and the virus is actively transmitted during intimate intimacy.
Possible causes of lumps in the groin area in women and methods for diagnosing pathologies
Due to the fact that the female reproductive system has its own individual characteristics, small inguinal formations form in the fairer sex somewhat more often than in men. Their appearance may be the result of a malfunction of the body, the course of inflammatory processes or pathologies of a different nature that require careful diagnosis and timely therapy.
Types of seals and reasons for their appearance in women
A tumor that has arisen in the female intimate area can indicate the hidden course of pathological processes, so ignoring this signal is extremely dangerous.
Characteristic lumps can appear in the recess between the groin area and the inner surface of the thigh, on the pubis, in the perineum, or directly on the skin of the external genitalia. It is most often not possible to identify the cause on your own, and self-medication is fraught with the development of complications.
If a lump is detected during a visual examination or due to pain, do not panic. A woman should know, at least in general terms, the main causes of such pathologies.
Enlarged lymph nodes
The lymphatic system is a network of vessels that form a lymph node. The liquid contains important cells - lymphocytes, which destroy pathogenic agents that penetrate through various routes.
With low immunity, the system cannot cope with its functions, and as a result, lymphadenitis develops, accompanied by an increase in nodes.
The formation of lumps in the groin indicates the development of pathology in the genitourinary system.
Common causes of inflammation are:
- bacterial or viral infections of any origin;
- fungal infections of the genitourinary organs;
- sexually transmitted diseases – syphilis, chlamydia, gonorrhea;
- furunculosis;
- neoplasms of an evil or benign nature.
Lymphadenitis can be identified by the presence of the following manifestations:
- increased lymph node size and increased density;
- signs of intoxication - weakness, nausea;
- persistent hyperthermia, fever;
- redness of the skin in the lymph node area.
Inguinal hernia
This pathology is more typical for men, but in women it also protrudes. Experts identify a number of predisposing factors.
- Injuries of the anterior abdominal wall. Ligament damage reduces the ability of muscle structures to withstand any load.
- Increased intra-abdominal pressure caused by excessive physical exertion and heavy lifting.
- Weakening of muscles due to exhaustion or atrophy.
- Overweight, obesity.
If the seal increases in size and begins to hurt, you should undergo an examination, since strangulation of the hernia may occur, which leads to tissue necrosis and the development of peritonitis.
Bartholinitis
Blockage of the ducts of the Bartholin gland, which produces secretions, often causes a lump to appear in the intimate area. The main factors provoking pathology are:
- weakening of the body's immune defense;
- neglect of hygiene procedures;
- STD;
- severe consequences of abortion;
- colds, hypothermia;
- wearing clothes that restrict movement;
- surgical operations.
The seal appears in the vestibule of the vagina and causes discomfort. When accidentally touched or pressed, painful sensations occur. A few days after the lump appears, an abscess forms on its surface.
Inflammation of the sebaceous gland ducts
A lump on the pubis or groin appears due to the development of inflammation of the sebaceous glands. As a result of their increased work, the removal of secretions is disrupted, resulting in blockage of the ducts. This disorder usually occurs against the background of:
- hormonal disorders;
- dysfunction of the endocrine system;
- body changes during adolescence.
The process is accompanied by the formation of a focus of inflammation in the groin area and a small dense capsule filled with pus. Patients complain of weakness, fever, chills. Some of them show signs of general intoxication of the body.
Hidradenitis
A lump in the groin area in women may appear due to inflammation of the sweat glands, which is caused by the penetration of Staphylococcus aureus into the body. The etiological factors of the disease are recognized:
- age-related hormonal surge;
- metabolic disorders in the body;
- weakened immunity;
- hyperhidrosis – increased sweating;
- insufficient hygiene of the external genitalia;
- tissue trauma - shaving, combing.
Formation lasts on average 10-14 days, and the compaction gradually increases in size, causing tissue swelling. The course of the disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- increased body temperature, chills;
- weakness, fatigue;
- pain in the area of inflammation;
- swelling and hyperemia of tissues.
If phlegmon develops, the risk of developing an abscess increases. Spontaneous opening occurs, accompanied by the release of a purulent mass, and later scarring of the wound. When hidradenitis appears, frequent relapses are possible, which should be the reason for a visit to a specialist.
Allergies
The appearance of a small mobile formation in the groin in some cases is the result of the body’s reaction to the penetration of a specific allergen. Most often these are food products or medications of certain groups. There is an enlargement of the lymph nodes as a consequence of protection.
Oncological neoplasms
Attention! In recent years, complaints from patients about the formation of compactions have become more frequent, the cause of which lies in the development of the tumor process (which is revealed during diagnosis).
Most often it is a lipoma or atheroma.
In this case, the bumps increase to a significant size and cause discomfort when moving or wearing underwear. Since the nature of the formations is benign, there is no pain and other specific symptoms of oncology.
Women do not complain; they are much more concerned about cosmetic defects.
Malignant processes are accompanied by a clear clinical picture, and the neoplasms are small in size. Such lumps appear on the right or left, they are detected in the early stages, during this period they are better treated.
Associated symptoms
The formation of lumps in the groin in women can be painless and unnoticed, but in most cases it is accompanied by certain symptoms, allowing a specialist to assume the possible nature of the pathology and the degree of its potential danger to health. The most common manifestations:
- Painful sensations. They accompany most processes occurring in the body. They are considered characteristic of lymphadenitis, inguinal hernia, and oncology. Pain occurs when there is contact or pressure in the area of the lump.
- Bulging. Indicates inflammation with the formation of a purulent process or the formation of an inguinal hernia. As it increases, it begins to bulge, causing discomfort when moving or wearing underwear. In the future, it becomes the cause of serious complications and can lead to tissue necrosis or blood poisoning.
- Spontaneous opening. This phenomenon is typical for seals that look like a capsule with a purulent mass. It occurs in a number of diseases - inflammation of the sebaceous glands, hidradenitis, furunculosis, bartholinitis. The sac ruptures after 10-14 days and is accompanied by an outpouring of purulent contents. After the capsule is cleansed, scarring of the wound begins. Recurrence of the disease is possible.
- Asymptomatic. Characteristic for the development of formations of a benign nature. An increase in compaction is indicated only by emerging discomfort. The tumor interferes with movement, while wearing or changing underwear and is a cosmetic defect.
Diagnostic methods
The appearance of a small formation in the groin area is a serious reason to visit a specialist. Despite the fact that most cases of such disorders do not pose a threat to health or life, the possibility of the formation of a tumor or hernia cannot be excluded.
To determine a treatment regimen, it is necessary to conduct a thorough, comprehensive diagnosis. This event can be attended by specialists from various medical fields: gynecologist, infectious disease specialist, oncologist, dermatovenerologist, endocrinologist.
The main procedures include the following.
- Palpation. Seals caused by a purulent-inflammatory process have a soft, elastic structure and are highly mobile. Oncological formations, on the contrary, are easily palpated because they are hard.
- Biopsy. It is a microscopic examination of a sample of affected tissue. It is carried out if the development of oncology is suspected.
- Ultrasound. It is considered an auxiliary method for examining the abdominal and pelvic organs. Prescribed to confirm inguinal hernia and oncological pathology.
- MRI. is prescribed when other examination methods do not allow an accurate diagnosis to be made. Using tomography, you can confirm/exclude the presence of a benign tumor or cancer.
Features of treatment
The method of therapy is selected taking into account the diagnosis, stage of the disease, and size of the lump. Today such methods are used.
- Treatment with antibacterial drugs. Indicated for diseases of an infectious nature, when the causative agent is bacteria, fungi, viruses, including sexually transmitted ones.
- Local therapy. It is carried out for purulent-inflammatory processes, in particular, furunculosis, hidradenitis, bartholinitis. The lesion is treated with a solution of "Chlorhexidine", "Furacilin". Antimicrobial ointments can be used - Levomekol, Nystatin, Triderm.
- Hernia repair. If the protrusion is slight, wearing a bandage and exercises to strengthen the muscles of the groin area are recommended. If the disease is advanced, surgical treatment is performed.
- Oncology treatment. Involves radiation, radiotherapy or chemotherapy, and surgical methods of intervention. Maintenance therapy may be used.
- Surgery. If there is no effect from the use of medications or is considered insufficiently satisfactory, the lump is opened. The purulent contents are removed, after which the cavity is treated with an antiseptic and the wound is sutured. To prevent relapses, the tumor and a small area of surrounding healthy tissue are removed.
conclusions
The appearance of a small lump in a woman’s groin area is considered a fairly common condition, which can be caused by the development of infectious and inflammatory processes, the formation of tumor formations, or be a consequence of poor hygiene, reduced immunity, or allergies. Only a specialized specialist who can prescribe the appropriate treatment can determine the cause of its occurrence.
Source: https://UroMir.ru/andrologija/zabolevanija-testikuly/uplotneniya-v-oblasti-paha-u-zhenshchin.html
Methods for treating pubic papillomas
Before undergoing the procedure for removing pubic papilloma, blood tests are often prescribed for the HPV strain and viral load, for tumor markers, and for diseases of the reproductive system. Tissues are also taken to determine the risk of developing cancer. Other diagnostic procedures are performed at the discretion of the attending physician. Establishing an accurate diagnosis and determining the full picture of the disease allows you to prescribe a comprehensive comprehensive treatment that will help eliminate the manifestations of HPV in a short time and minimize the risks associated with it.
Removal of pubic papilloma
At the appointment, the attending physician will tell you how to remove pubic papillomas, list the methods that are suitable in a particular case, and give the patient the right to choose. The options differ in many respects, among which the ratio of cost, effectiveness and safety is significant for humans.
Currently, there are many ways to remove pubic papilloma within the walls of a medical institution, the most popular among them are:
- Cryotherapy . Exposure to liquid nitrogen provokes freezing of the pubic papilloma tissue, which leads to the death of the growth. The treated tissues immediately darken and fall off after a few days. With this technology, it is quite difficult to control the depth of freezing, so the procedure may be required 3 times so as not to affect healthy skin cells and not provoke the formation of a scar after healing. In terms of cost, it is one of the most inexpensive options - from 400 rubles or 220 hryvnia.
- Laser therapy . Pubic papillomas in women and men can be removed using a laser. Almost every specialized clinic offers the service. The laser heats the growth and evaporates moisture from it, which leads to a reduction in its size. Next, a thin crust forms, which disappears in 7-10 days. The initial cost is 1000 rubles, 400 hryvnia. Read how laser papillomas are removed?
- Diathermocoagulation . Before the procedure begins, local anesthesia is administered. High-frequency radiation generated by a special device heats the pubic papilloma, resulting in the formation of a scab. Tissue restoration takes place within 2-3 weeks. Prescribed for a small number of pubic papillomas. The price depends on the clinic providing the services and is calculated individually.
- Radio wave excision . The safest and most effective option for removing pubic papillomas in men and women. Works well with hanging papillomas and genital warts. It removes painlessly, while the vessels are sealed, and blood does not appear on the surface of the skin. Radio wave surgery minimizes the risk of infection and in most cases does not leave scars. It costs more than most other options - over 2000 rubles (700 hryvnia).
- Surgical excision . Not very popular, because... Using a scalpel it is quite difficult not to touch healthy skin. After removing large accumulations of growths, stitches must be applied. Scars often remain. Wounds take a long time to heal and require daily care. The minimum price for such a service is 500 rubles or 300 hryvnia.
- Plasma coagulation . During the procedure, alternating exposure to pulses of low and high temperatures occurs, which leads to the evaporation of pubic papilloma. In terms of safety, painlessness and effectiveness, the method is comparable to laser therapy and radio wave methods. Price - over 3000 rubles or 1800 hryvnia.
It is possible that after the procedure and for the entire recovery period, the doctor will advise you to refrain from intimacy. Visiting public baths, swimming pools, beaches, and solariums is also not recommended.
Treatment of pubic papilloma with medications
Photos of drugs for pubic papillomas
You can find a lot of information on the Internet about how to treat pubic papillomas, but you should not rely on the universality of the proposed methods. Each drug has a lot of contraindications and side effects, which is often quite difficult for a person without a medical education to take into account. In addition, each organism is individual, and the presence of concomitant diseases significantly complicates the selection of drugs. Therefore, it is not recommended to self-medicate, but rather visit a doctor’s office.
In general, to combat HPV and eliminate papillomas both on the pubis and in other places, medications are prescribed that can restore the functioning of the immune system and block the pathogen. Thus, immunomodulators and antiviral medications are prescribed, among which the most popular are the following:
- Imiquimod . Cream for eliminating genital warts and flat papillomas on the pubis and other intimate places. It stimulates the immune system at the local level, helping to produce interferon. Price - from 1900 rubles or 1000 hryvnia.
- Allokin-alpha . The action is aimed at inducing interferon, and, consequently, increasing the immune response. It is non-toxic and can be used during adolescence, because does not affect reproductive function. Sold in the form of a solution for intramuscular administration. The price for 3 ampoules is 3,700 rubles in Russia and 1,900 hryvnia in Ukraine.
- Lycopid . Inexpensive drug to improve immunity. Helps the body produce specific antibodies, provokes cell death of pointed, filamentous and flat papillomas on the pubis. Cost - from 320 rubles or 190 hryvnia.
- Ingaron . It supplies interferon to the body, which helps strengthen the body’s defenses, provokes a reduction in the number of pathogens and accelerates healing. Stimulates the death of skin tumor tissue. Price - from 1500 rubles in Russia and 800 hryvnia in Ukraine.
- Viferon . Sold in different dosage forms - ointment, gel, suppositories and tablets. It is actively used to treat papillomas on the pubis, genitals, face and other parts of the body. When used externally, it stimulates the restoration of the integrity of the skin, the removal of growths from the entire body, including pubic papillomas. The minimum price in Russia is 150 rubles, in Ukraine - 140 hryvnia.
- Immunomax . Strengthens the immune system, helping the body cope with various infections, including HPV. Cost - 1000 rubles (600 hryvnia).
Based on existing concomitant health problems, for men and women with pubic papilloma, the doctor may prescribe additional vitamin cocktails or special complexes that replenish the deficiency of vitamins and minerals. Currently, there are many options with a varied composition: Vitrum, AstrumVit, Centrum, etc. Separately, you can select drugs for men and women.
Folk remedies for treating pubic papillomas
In addition to traditional medicine, folk remedies can be used in the treatment of pubic papillomas. It is important that their action does not conflict with the therapy prescribed by the doctor, but, on the contrary, complements it.
The best option for supporting the body is to use homemade decoctions of medicinal herbs, as well as the use of antiseptic tinctures for external treatment.
Effective and safe folk remedies for treating pubic papilloma:
- Rosehip decoction . This remedy is often used to boost immunity. To prepare, you need to pour 200 g of rose hips into 600 ml of water and bring to a boil, then boil for another 10-15 minutes. After this, leave for half an hour and strain. Take 150 ml twice a day every 12 hours.
- Infusion of 3 herbs . Stimulates the immune system and replenishes vitamin deficiencies. Allows you to get rid of pubic papillomas at the initial stage of the disease. Take 20-30 g of St. John's wort, chamomile flowers and birch buds. All ingredients are crushed, pour 300 ml of boiling water, leave for half an hour. Take 100-150 ml orally before each meal.
- Infusion of 5 herbs . Replenishes the deficiency of nutrients and increases the body's defense in the presence of genital growths and pubic papillomas. For the infusion, equal amounts of horsetail, lemon balm, nettle, plantain and dandelion root are first crushed. Take 60 g of the resulting mixture and pour a liter of cool water, boil for 10 minutes and leave for 3-4 hours. After straining, consume 50-60 ml half an hour before meals.
- Infusion of 6 herbs . It serves as a source of many useful substances, therefore it normalizes the functioning of all organs and systems and strengthens the immune system. First, 10 g of clover flowers, St. John's wort, calamus root, dill seeds, as well as 5 g of violet and 15 g of plantain leaves are mixed and ground. Next, the resulting mixture is poured with 1-1.5 liters of boiling water and allowed to brew for 10-12 hours. After straining, take 1 glass in the morning, afternoon and evening. This infusion can be treated for a month, after which it is better to take a break.
- Wormwood tincture . It has antiviral properties, can significantly reduce the viral load, and also blocks the growth of pubic papillomas. Prepared from wormwood (100 g) and alcohol (500 ml). The ingredients are mixed and infused in a dark place for 2 weeks. After this, the cake is removed, and the alcohol tincture is taken 5 drops 3 times before meals and the new growths on the skin are treated with it. The course of treatment is 14 days.
- Green nut tincture . Used for external treatment of pubic papillomas in men and women as a strong antiseptic. To prepare, grind 200 g of green walnuts, add 400 ml of alcohol, leave for several days and filter.
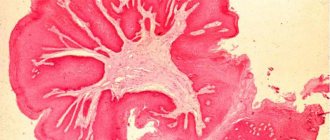
Histology and oncocytology for papillomas
Viral infection is dangerous not only for women, but also for men.
The formation of papillomas in women can provoke the development of a malignant process of the cervix.
In women and men, HPV can cause squamous cell carcinoma, since 29 types of the virus out of the known 180 are oncogenically active.
Therefore, if a woman has a papilloma on her pubis, she should urgently undergo examination.
As long as the virus is in the body, it poses a danger.
A woman should undergo smears for oncocytology at least once a year.
The laboratory will determine the presence of atypical cells in the biomaterial.
If the result is questionable or positive, an additional examination of the patient is carried out:
Colposcopy
The doctor uses a special device to examine the vaginal part of the cervix for the presence of dysplasia (precancerous changes in the epithelium).
The first and second degrees of dysplasia are reversible.
In most cases, the first degree can regress on its own, the second - only in 30% of cases.
The risk of degeneration into cancer is very high (up to 80%) - in the presence of third degree dysplasia.
In this regard, in the second and third degrees, surgical treatment (cauterization of the affected area) is recommended.
This approach will prevent the development of the oncological process.
Timely diagnosis of dysplasia helps to detect cancer at a very early stage of development.
Therefore, if a woman visits a gynecologist regularly, then the probability of preventing the development of cancer is 100%.
Papillomas may cause the doctor to doubt whether they are benign
In this case, after their removal, the resulting biomaterial is sent to the laboratory for histological examination for degeneration.
Histological examination of the formation is carried out if it is necessary to identify papilloma with other skin neoplasms.
If the analysis shows signs of malignancy, then the volume of tissue removed may go beyond the limits of the papilloma.
Distinctive features
Pubic warts are small formations that vaguely resemble moles. They are distinguished by their flesh color and convex shape. Sometimes their appearance is accompanied by itching, pain and bleeding.
When injured, the papilloma begins to secrete fluid and becomes crusty. Most often this happens after shaving the intimate area. The liquid that is inside the condyloma emits an unpleasant odor.
Papillomas in the pubic area not only do not look aesthetically pleasing, but also pose a health hazard. Therefore, they must be removed immediately. There are two types of warts - pointed and flat.
In the first case, the neoplasm has a thin base and small size. Flat warts can grow to the size of a coin. They are distinguished by a smooth and convex surface.
The danger of pubic condyloma is that it can develop into a malignant formation.
Warts on the pubic area in women photo
Papillomas on the pubis in men and women indicate penetration into the body, medically known as papillomavirus. More often, neoplasms are benign. Without treatment, papillomas in the pubic area can develop into malignant tumors.
General characteristics
Pubic warts resemble ordinary moles. But, if you pay attention to the color and shape of the formations, the differences are noticeable. Papillomas blend in color with the skin and have a convex shape. At the location of the growths, itching is felt, they are easily injured, pain and bleeding appear.
It is easy to injure a tumor. This happens as a result of wearing tight underwear, after shaving the pubic area, or carelessly washing the body. Inside the wart there is a liquid that is released when injured; it begins to bleed and hurt. When liquid leaks out, an unpleasant odor is felt.
Pubic condylomas in men and women do not look aesthetically pleasing. Patients with this pathology feel uncomfortable during sexual intercourse, and as a result, complexes develop. Doctors recommend removal of papillomas in the intimate area, since they have a tendency to malignant degeneration.
! The danger of papillomavirus in the intimate area lies in the long incubation period. From the moment the virus enters the body until its active action, it can take either a month or several years. A virus of an oncogenic strain that enters the body can lead to oncology in 5-30 years.
Where did the virus come from?
When papilloma appears on the pubis, the question arises - where and why? The main cause of the formation of growths in the genital area is considered to be intimate relations, but there are other ways of infection.
Once a virus enters the body, it can go undetected for a long time, being in a state of latency. The impetus for activity is a failure in the protective functioning of the immune system.
- a person suddenly gains or loses weight;
- visiting public baths, saunas, swimming pools, and other places with high humidity;
- neglect of hygiene procedures;
- papillomas in the vaginal walls;
- hormonal imbalance;
- frequent stress, nervousness, depression;
- papillomas on the labia in women;
- infectious pathologies that reduce the protective function of the immune system;
- diseases such as diabetes;
- sexual intercourse with a carrier of papillomavirus.
During pregnancy, the appearance of warts is caused by a decrease in the body's defenses as a result of changes in hormonal levels. For women, the period of menopause is dangerous, when the level of hormones in the body that are responsible for reproduction significantly decreases.
In men, a sharp decrease in immunity and the appearance of warts on the pubis are provoked by the following factors:
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking;
- drug addiction;
- papillomas on the penis;
- frequent infectious diseases;
- papillomas on and around the anus;
- stress and depression;
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract;
- taking hormonal drugs and other medications.
In some cases, the virus affects not only the pubic area of a man, but the penis, foreskin, frenulum, urethra, and urethra. Neoplasms in these places bring discomfort, constant pain, and threaten the life of the infected person.
Signs of defeat
The first symptom of infection is the appearance of warts in the pubic area. This mainly occurs through sexual intercourse, the virus is transmitted from an infected partner to a healthy one. A person becomes infected with one of the types of virus - pointed or filamentous papillomas, as in the photo. They differ in their natural origin, shape and color.
Pointed growths look like small flesh-colored or pink papillae and affect the pubic area in several places at the same time. They are particularly dangerous for women as they can lead to cervical cancer.
Thread-like, cone-shaped papillomas are pale yellow in color. They have the ability to grow, enlarge and merge with each other over time. This pathology is typical for women approaching menopause.
- warts appear on the inside of the genitals;
- formations inside the vagina, on the internal membranes;
- In case of injury, bleeding and pain are noted;
- strong growth;
- the growths acquire a flesh-colored, pale brown color;
- constant feeling of discomfort in the pubic and genital area;
- sexual intercourse causes pain;
- frequent infectious pathologies;
- unpleasant smell.
In women, against the background of papillomavirus, it is possible to develop pelvic cancer. Timely diagnosis and removal of warts will help prevent the further development of pathology.
Treatment
If a wart appears in the intimate area, contacting a specialist would be the right decision. Treatment is carried out with ointments and medications. A non-surgical method of getting rid of warts involves the use of a highly concentrated solution of formic or trichloroacetic acid. For these purposes, a lapis pencil containing silver ions is used.
The drugs provoke necrosis of affected tissues and have an antiviral and antiseptic effect.
! Lapis pencils are used carefully, applied only to papilloma, avoiding healthy areas of the skin. Products can cause chemical burns!
Therapeutic therapy allows the use of the following drugs:
Medicines will increase the body's protective functions. Laferobion in the form of injections is used for the natural rejection of warts.
Source: https://infomm.ru/borodavki-na-lobkovoj-chasti-u-zhenshhin-foto/
Reasons for appearance
A feature of the papilloma virus is the ability to remain in a latent state for a long time.
A person may not know they have the virus until their immune system is weakened. The appearance of warts on the genitals is preceded by unprotected sexual intercourse.
Factors influencing the occurrence of skin growths include the following:
- sudden change in weight;
- visiting public places with high humidity (reservoirs, baths, saunas, etc.);
- bearing a child;
- violation of hygiene;
- transmission of an infection, as a result of which immunity has decreased;
- hormonal disorders;
- depressive disorders;
- multiple unprotected sexual intercourse;
- diabetes.
The appearance of warts during pregnancy is due to the suppression of the body's defenses. This happens under the influence of hormones. If immunity remained at the same level, the body would reject the embryo, mistaking it for a foreign object.
Women approaching menopause are also at risk. It is characterized by a significant decrease in hormones responsible for reproduction. Against this background, papillomas often appear not only on the genitals, but throughout the body.
The danger level of condyloma is determined by a special analysis. To carry it out, a tissue sample of the neoplasm is taken.
Main symptoms
Warts on the penis in men
Often, a man develops warts on the penis, which, depending on the type, have special symptoms and require individual treatment. Mostly there are white growths on the head of the penis, in which a man experiences a number of unpleasant symptoms:
- burning sensation;
- itching;
- the formation of small cracks and injuries;
- painful sensations during sexual intercourse.
The latter symptom is not always present or may appear some time after infection. When growths on the penis begin to change structure, color or fester, you should immediately see a doctor. If you do not treat the formation in a timely manner, then many complications will arise in the male body, which will be more difficult to get rid of.
Warts on women's labia
Genital warts in women provoke pain, itching, and discomfort during sexual intercourse.
If a woman has a wart on her labia, then at first it will look like a small tubercle, which will eventually grow to a large size. For a long time it may not cause any discomfort and exist asymptomatically. Over time, the following signs appear:
- itching and burning on the female labia;
- rash and redness of the skin;
- painful sensations, especially during sex;
- unpleasant odor from the vagina;
- bleeding.
Blood discharge is observed if warts have formed in the area of the vagina or cervix. Formed warts near the anus are accompanied by a painful bowel movement. Warts on the labia of women require timely treatment, as they soon provoke complications, including cancer.
Removal methods
If a papilloma appears on the pubis, you should immediately consult a dermatologist or gynecologist. Previously, a fragment of a benign tumor is sent for PCR research, cytology and biopsy. Depending on the results obtained, measures are taken to eliminate the growth.
The following removal methods are used:
- Radio wave exposure is a painless method that involves the use of a radio knife. The advantages of the procedure include the fact that the device does not affect healthy skin cells. The risk of a scar appearing at the site of papilloma is reduced to a minimum.
- Cryodestruction is a common method of treatment using liquid nitrogen. During the procedure, the root of the wart freezes and then gradually falls off. Disadvantages include the possibility of scarring on the skin.
- Electrocoagulation is a procedure in which growths are removed using current. After this procedure, pigment spots may appear on the skin. The procedure is contraindicated for people with a low pain threshold, since it causes discomfort.
- Surgical removal of the growth is carried out if it is large.
- Laser therapy is the most expensive but effective method of eliminating condylomas. After it is performed, there are no scars or bruises left. This is due to the fact that the blood vessels are also cauterized by the laser.
Treatment at home is not advisable. The skin in the intimate area is particularly sensitive. By cauterizing condyloma with improvised means, you can cause a burn. In addition, home treatment is less effective than removing a pubic papilloma from a professional.
For pregnant women, the question is no less pressing: how to get rid of growths in the pubic area. The likelihood of their formation during pregnancy increases several times.
Doctors do not recommend resorting to painful methods, as they contribute to nervous tension. The most suitable solution to the problem is laser therapy. Sometimes treatment is delayed until after birth. But in this case, the risk of infection of the child during labor increases.
The rehabilitation period after removal of a tumor does not take much time. Providing proper care will speed up the healing of the wound.
Prevention
To prevent a wart from appearing on the pubic area, it is necessary to adhere to preventive measures.
The main principles are as follows:
- In order to strengthen the immune system, it is recommended to take vitamin supplements and give up bad habits.
- Having one sexual partner and having protected sex will reduce the risk of contracting the virus.
- If treatment with hormones and antibiotics is necessary, it is extremely important to monitor the state of immune defense.
- It is necessary to keep the genitals clean and not use other people's personal hygiene items.
- It is recommended to protect yourself from stressful situations and depression.
Warts tend to spread quickly throughout the body. Inaction leads to their occurrence in women in the vagina, labia and cervix.
Conclusion
Papillomas found in the intimate area should not be ignored. If suspicious formations are detected, it is advisable to compare them with photos posted on medical forums.
Doctors warn! Shocking statistics - it has been established that more than 74% of skin diseases are a sign of parasite infection (Accarida, Giardia, Toxocara). Worms cause enormous harm to the body, and the first to suffer is our immune system, which should protect the body from various diseases. The head of the Institute of Parasitology shared the secret of how to quickly get rid of them and cleanse your skin, it turns out that’s enough. Read more .
If there are similarities with papillomas, it is extremely important to consult a doctor as soon as possible. With the right approach, warts will not appear again.
Warts on the pubis: treatment of warts on the pubic area in men and women
A wart that appears on the pubic area can cause much more trouble than spoiling the appearance of the intimate area. If you don't want small papillomas to cause big problems, pay them a little more attention.
Warts on the pubis in men and women: where does the attack come from?
The cause of warts is the human papillomavirus (HPV), which can only be acquired through contact with the skin and mucous membranes of an infected person.
But this does not mean that growths appear instantly. You may not notice signs of infection until the time is right for infection.
Appearance of neoplasms
Warts that appear on the pubis and genitals are similar to small growths from 2 to 5 mm in height and approximately the same diameter. Color varies from flesh to dark brown. The growths can be single or form a large conglomerate.
Reasons for appearance
Genital warts have a long incubation period, so they may appear to occur for no reason. But the appearance of warts on the pubis and genitals always indicates infection with HPV, which occurs only from an infected person.
Most often, this problem appears in those who are promiscuous or forget about protection during sexual intercourse with an unfamiliar partner.
If you're just starting out in a relationship, it's a good idea to get tested for HPV before you stop using condoms.
Here are the main reasons for the appearance of papilloma on the pubis and genital area:
- Touching infected skin or mucous membranes.
- Sexual contact with an infected person. You can become infected through both vaginal and oral contact.
- If the mother is infected with the virus, it will be passed on to the child at the time of birth.
- Use of the patient’s personal hygiene products (towels, razors).
Symptoms and diagnosis
Even if a person becomes a carrier of HPV, this does not mean that the disease must manifest itself in the future. But if the virus is activated, this is expressed in the following symptoms:
- Burning and pain (typical for men).
- Itching (typical for women).
- Painful cracks in the genital mucosa.
- The appearance of papilloma.
- If the vagina is affected, discomfort appears during sexual intercourse.
- If papillomas appear in the urethral area, this can cause difficulty urinating.
To diagnose the disease, you need to see a doctor (for a woman, a gynecologist, for a man, a urologist). The doctor will conduct an initial examination and prescribe additional tests to establish an accurate diagnosis and to ensure that the detected formations are of good quality.
Types of additional examination:
- Histological examination. Necessary to obtain general information about the origin of papilloma. Using this analysis, you can determine whether the formation is benign or cancerous.
- PCR diagnostics. The most modern and effective method that allows you to accurately determine the type of virus.
Important!
Only additional tests will help the doctor prescribe the most effective treatment.
Types of genital formations
Two types of warts can appear on the pubis: filiform papillomas (acrochordas) and genital warts (or condylomas).
- Filiform . Their size does not exceed 5 mm and look like small papules. Sometimes they grow on a thin stalk. May be flesh-colored or brownish in color.
- Pointed . Usually their size does not exceed 2 mm. They have a lobed structure and outwardly resemble small papillae or a cockscomb growing on a thin stalk. They are pink or flesh-colored.
What diseases can growths indicate?
Genital papillomas appear only under favorable conditions for activation of the HPV virus. And this happens with a decrease in immunity and hormonal imbalance in the body, against the background of which these diseases develop:
- Metabolic disease.
- Diabetes.
- Atherosclerosis.
- Benign or malignant tumors.
- Osteoporosis.
- Various gynecological diseases.
- Infertility.
- Immunodeficiency.
- STIs that affect the genital mucosa.
It happens that HPV is activated when helminths appear. This leads to the following problems:
- Giardiasis.
- Enterobiasis.
- Ascariasis.
Are pubic growths dangerous?
Below we will separately consider each possible case in which warts may appear and the danger they may pose.
For men
Genital papillomas can lead to viral prostatitis and the appearance of malignant tumors. If warts grow in the urethral area, it may require surgery to remove them.
For women
The danger of HPV for women primarily lies in the fact that the virus can develop directly in the vaginal mucosa, which will allow it to remain invisible for a long time. This can lead to cancer of the uterus or ovaries, and, as a consequence, long-term treatment and surgery.
Important!
If papillomas appear on the genital mucosa, the risk of transmitting the HPV virus during sexual intercourse increases to 80%.
During pregnancy
Genital papillomas on the body of pregnant women are not anything special. Such warts are most often small in size and flesh-colored. Such formations do not harm the future baby.
If the papillomas are located directly in the vagina, there is a chance that the child may become infected with HPV at the time of birth. But more often than not, the newborn’s immune system is quite strong and can easily cope with the virus.
In rare cases, a baby who has received the HPV virus from his mother may develop tumors directly on the respiratory tract.
In what cases should you seek medical help?
If you find warts on the pubis or genitals, in any case you should consult a doctor who will carry out all the necessary tests. This will eliminate the possibility of dangerous consequences of the neoplasm.
Should they be removed?
Treatment of intimate warts is a whole complex of measures, part of which is their removal. But the most important thing in this process is the reduction of HPV activity. The process of getting rid of genital papillomas is divided into 3 stages:
- Preventing the virus from multiplying by taking antiviral drugs.
- Strengthening immunity with immunomodulatory drugs.
- Removal of papilloma.
Important!
Since the skin in the genital area is very thin and delicate, you should not resort to home methods for removing intimate warts. It is better to entrust this to a specialist.
No one is immune from the appearance of intimate warts. But since they can be a symptom of unpleasant diseases, you should not delay a visit to the doctor when they appear. The earlier treatment is started, the greater the chances of avoiding unpleasant consequences.
Source: https://vseopapillome.com/borodavki/na-lobkovoj-chasti-u-muzhchin-zhenshchin.html
How to treat them?
Medicine does not yet know how to destroy the papilloma virus in the human body. All treatment is aimed only at suppressing the activity of the virus and eliminating existing warts.
Treatment can be conservative or surgical, depending on the prevalence of tumors, their location and morphological features. Read also: wart on the penis, effective treatments
Use of medications
The following medications are used on an outpatient basis:
- Podophyllotoxin . The formation is lubricated with a solution or cream for 3 days. Several courses are required with breaks of 5–7 days. The cream is prescribed for neoplasms located on the skin, and the solution is used to treat the mucous membranes.
- Imiquimod . This is a cream that is used 3 times a week for 8-12 weeks.
- Preparations based on ascorbic acid and interferon - ointments Viferon, Altevir, Reaferon A. These drugs strengthen local immunity and are used several times a day for 1-2 months.
This treatment is prescribed for the treatment of genital warts at home, provided there are no signs of transformation into a malignant pathology, as well as in the presence of small lesions.
More severe forms of the disease are treated only in inpatient settings:
- 80% triacetic acid solution . Can be used once. The acid affects the growth, and its tissues become necrotic. After some time, the formation is rejected. Independent use of this product is prohibited, as it causes severe burns if it gets into healthy areas.
- Solcoderm . The drug contains oxalic, lactic and nitric acids, as well as copper nitrate. Removal of the tumor is achieved by burning out the growth. Several procedures are possible.
Along with local treatment, the patient is prescribed an injection of interferon into a vein, which has a blocking effect on the virus.
Chemical or surgical intervention
In case of extensive damage, hardware destruction methods are used:
- Radio wave treatment - tumor tissue is destroyed using a device that emits special ions. Used to remove growths that are dangerous due to their transformation into oncology.
- Laser removal - carbon dioxide laser vaporization is considered the most painless and safest operation for removing genital warts located in the cervix and urethra. This method reduces the possibility of re-developing pathology.
- Electrocoagulation is the removal of a tumor with an electric current passing through a metal loop.
Traditional methods of therapy
Modern medicine has different attitudes towards traditional treatments, but it would be wrong to categorically deny the benefits of such therapy. Of course, you should use traditional recipes only after consulting a doctor, and it is better to use them as additional therapy.
The most popular folk remedies for genital warts are:
- Celandine . Celandine juice is extremely poisonous, so it must be used very carefully, and only if the neoplasm is located on the skin. For the delicate mucous membrane, this remedy is quite aggressive. It is easy to use - you just need to apply the plant juice to the wart. This must be done every day until the tumor disappears. There have been no serious studies on the safety of using celandine to remove warts, and provoking the transformation of a benign neoplasm into a malignant one cannot be ruled out.
- Garlic . Garlic has antimicrobial and antiviral effects. To prepare the remedy, you need to chop a head of garlic and soak the mass in vodka. Leave in a dark place for 2 days, and then use for compresses.
- Rowan . It is necessary to cut the rowan berry in half and apply it to the papilloma until it disappears.
- Aloe . Cut along an aloe leaf, you need to tie it to the new growth 2-3 times a day.
Warts can also be treated with decoctions and infusions of the following medicinal plants; they should be taken orally:
- burdock;
- Melissa;
- St. John's wort;
- sage;
- calendula;
- blueberry leaves;
- burdock.
It is important to understand that treating malignant neoplasms with folk remedies is not only impractical, but also very dangerous.