Each of us has moles on our bodies. Big and ugly, or, conversely, small and inconspicuous, they are always with us. The term “mole” does not exist in medicine; it is a congenital or acquired pigmented formation on the skin, which can be benign or malignant. More often they are called neuruses. The most common term for moles is seborrheic keratosis. In aesthetic medicine, removal of moles
a fairly popular and quite affordable service, on a par with services such as face lift, collagen for the face or electrical stimulation using the Tranzion device.
What do moles look like?
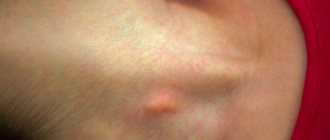
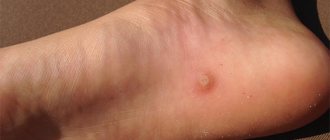
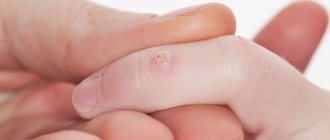
A mole is a pigmented, benign tumor on the skin that can be found on almost every person.
Small pigment formations can be aesthetically attractive and perceived as a “highlight” of the image. But large and convex ones can not only be a cosmetic, but also a medical problem.
The accumulation of pigment on the skin can have different sizes, shapes and colors:
- from 0.5 mm to several cm;
- flat, hanging on a thin base, in the shape of a semicircle on a wide base;
- yellow, brown, black, pink.
They occur on any part of the body, including the scalp and even the mucous membrane.
The types of formations are numerous. And not all of them are safe for their owner.
What are moles? What are they?
To answer this question, you must first clarify what we mean by the word “mole.” An ordinary person can easily find several types of skin formations. Brown, red, flesh-colored - all these can be called moles. In fact, the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of benign skin lesions includes about 150 names. And all this diversity can also be called moles. Read a little more about the most common types of moles here.
As we said above, there are a huge number of types of moles. Today we will talk about those that are most common and, theoretically, can pose the greatest danger - brown and flesh-colored moles.
Why moles appear on the face (4 reasons)
Moles arise from pigment cells that are located between the epidermis and dermis.
The most common causes of nevi:
- Genetic predisposition.
- Frequent exposure to UV treatment on the skin (sunlight provokes the production of melanin, which often causes moles).
- Hormonal imbalance (puberty, gestation, childbirth, endocrine diseases, etc.);
- Skin injuries, infectious diseases, pathologies of the epidermis.
Removal of moles on the face (TOP-5)
If the nevus gradually grows, changes shape, structure, causes inconvenience, is located in a vulnerable place or looks aesthetically unattractive, it is better to remove it.
But before doing this, the patient should undergo a thorough diagnosis to exclude malignancy of the cellular structures of the nevus.
To do this you may need:
- examination and history taking;
- taking a smear from the surface of the tumor;
- epiluminescence microscopy.
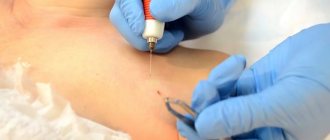
If cancer is suspected, it is recommended to remove the formation by surgical excision or electrocoagulation.
This is necessary in order to subsequently send the material for histological examination to confirm or refute the diagnosis.
In all other cases, either cryotherapy or laser removal of moles on the face are recommended. These methods are less traumatic and do not leave scars.
You cannot go to a beauty salon to have a mole removed. This procedure should not be performed by a cosmetologist, but by a plastic surgeon or dermatologist. Initially, it is better to visit an oncologist who will conduct a special study using a dermotoscope.
Dermatologist Jennifer Trent
What you need to know about moles:
Electrocoagulation
Excision of nevus tissue is carried out using thermal exposure to high-frequency current.
A special surgical coagulator produces a high-frequency current that simultaneously cuts and coagulates tissue.
After the procedure, a crust forms on the treated area, which disappears on its own after a few days.
The method is used primarily to remove medium-sized formations.
Advantages:
- the excised material can be sent for histology;
- the cosmetic effect is noticeable immediately after the procedure;
- There is no bleeding or risk of infection during the procedure.
Flaws:
- The method is painful, so anesthesia is required, and therefore it is not suitable for people intolerant to painkillers.
- Scarring is possible.
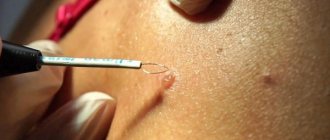
Surgical excision
This radical method involves the use of a scalpel. The method is suitable for removing large, hanging formations or those located in hard-to-reach areas (for example, on the eyelids).
It leaves behind scars, since the removal of the nevus involves the capture of adjacent skin. But it has almost no contraindications. Painful, so local anesthesia is required.
| pros | Minuses |
| Suitable for removing “dangerous” moles. | Anesthesia is required. |
| More effective on large lesions than any other method. | Traces after the operation are noticeable. |
| The result is noticeable immediately after the operation. | Possible infection. |
| The excised material can be sent for histological analysis. | Long-term postoperative wound care is required. |
Laser method
It is one of the most popular methods for removing moles on the face. Suitable for treating other areas of the body.
The essence of the method is to “evaporate” the liquid from the nevus cells to the level of normal skin. This is done using a laser beam.
For each patient, individual parameters of the laser beam (intensity, length) are set, since the depth and width of the mole is different in each case.
The duration of laser therapy does not exceed 5 minutes. Immediately after removal, the skin in the treatment area will be red, this is completely normal.
The session is painless, so doctors do not use anesthesia. Some people experience a slight tingling sensation on the skin.
Dermatologist Jason Emer
After a few days, a crust forms that cannot be removed so that no pigment spot remains on the skin. It will disappear on its own after a week.
The procedure provides excellent cosmetic results because it does not leave tissue scars. It has many positive reviews due to its reasonable cost and high efficiency.
Advantages:
- short and painless rehabilitation period;
- no marks on the skin after complete tissue healing;
- no need for pain relief;
- the likelihood of infection and bleeding is reduced to zero.
Flaws:
- Nevus tissue cannot be sent for histological analysis.
- More suitable for small formations.
Cryotherapy
This is another popular method for removing nevi. Destruction of the formation is carried out using exposure to low temperatures - liquid nitrogen.
- If the mole is flat, then the substance is applied using a special cotton swab with a small diameter.
- If on a thin stem - in the form of an aerosol jet.
- If the formation is deep and located on a wide base, an ultra-thin needle with a temperature sensor is inserted. It is cooled to the required temperature and removed almost immediately.
Low temperature freezes intracellular fluid. As a result, a scab forms, the mole shrinks, turns pale, loses sensitivity, and the affected cells are gradually rejected.
The time of exposure to cold lasts from several seconds to 3 minutes - depending on the size, shape and depth of germination of the neoplasm.
There are no unpleasant sensations during the procedure. After 3 days, a crust forms on the skin. It also goes away on its own after a week.
Advantages:
- effectively removes moles;
- reasonable cost;
- no anesthesia, suturing, or changing of dressings is required;
- no scars remain on the skin.
Flaws:
- Sometimes the effects of liquid nitrogen extend to healthy tissue.
- The result is not noticeable immediately, but after a week or two.
- There is a possibility of getting a cold burn (if the cosmetologist is insufficiently skilled).
- In some cases, it is not always possible to achieve the desired result the first time, so a repeat procedure is required.
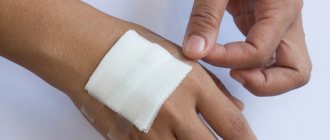
If you accidentally lose a mole (this can happen with hanging moles), wrap it in a napkin so that your doctor can check it later. Next, soak a cotton swab in hydrogen peroxide and cauterize the wound to disinfect it. Put a bandage on this place and go to the doctor as soon as possible.
Dermatologist Afshin Farzadmehr
Removal techniques and associated risks
The methods are effective when used correctly. A dermatologist or oncologist will accurately indicate the appropriate method of removal. In 2/3 of cases, loyal forms of mole removal are prescribed - laser therapy, electrocoagulation, radiosurgery. Surgery is appropriate when it comes to malignancy.
Each technique has its own characteristics. It is harmful to remove hanging moles using operative surgery. They indicate the presence of the papilloma virus in the body.
Dangers associated with the surgical method
The surgical method is radical. Direct skin incision and removal of the nevus is an exceptional method that entails a high risk of complications.
Consequences of surgery:
- Prolonged healing, accompanied by pain at the operation site.
- Subcutaneous hemorrhage is a consequence of any surgical intervention. Accompanied by redness and pain in the section area.
- High risk of infection.
- There is a possibility of relapse; part of the mole may remain in the body.
- A raised, colored scar.
- The likelihood of a keloid scar at the site of the scar.
If we are not talking about a malignant formation, surgical intervention can be replaced by other, loyal methods.
Dangers of electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation is the cutting of a birthmark using high-frequency current. The surface is burned so that the vessels are cauterized along with the nevus. Eliminates the possibility of hemorrhage.
The advantage of this method is that the likelihood of degeneration and relapse is minimal. The current deeply burns the tissue, leaving a small scar.
Dangers of Using Liquid Nitrogen
The cryodestruction method (cooling with liquid nitrogen) is effective for removing large moles. After applying nitrogen to an area of skin, the cold burns the tissue deeply. The nevus falls off and leaves no trace.
Consequences of using liquid nitrogen:
- burning pain throughout healing;
- high probability of relapse;
- it is impossible to accurately predict the depth of penetration of cold (there is a risk of damage to healthy skin);
- the likelihood of infection when the scab is torn off.
Using a laser
Laser nevus removal is an expensive, fast, safe method. Through a directed beam, the birthmark evaporates without harm to the dermis, leaving no scars or scars. Infection is unlikely, the skin is not cut or damaged during processing.
Adverse consequences when using a laser are caused by humans (poor care after surgery). The dermis heals within 2-5 days after treatment. But it is not recommended to sunbathe in the summer or get the operated area wet.
The laser has no strict contraindications. Not recommended when working with children under 15 years of age or during pregnancy.
Question answer
In addition to being a cosmetic problem, they can cause physical discomfort. Accidental injury can lead to damage to its surface and bleeding. Some types are prone to degeneration from benign to cancer.
No, it is impossible to know this for sure. To protect yourself from troubles, you should regularly visit a specialist if suspicious moles appear, begin to grow, or change their size.
The price of removing moles on the face depends on the type of procedure, the specific clinic, the characteristics of the nevus, the presence or absence of anesthesia, and the city. On average, the cost of laser removal of moles on the face in Samara, Krasnoyarsk, Novgorod, Simferopol, Moscow and other cities of Russia is about 1500-3000 rubles. The price of electrocoagulation is approximately 1500 rubles, cryotherapy - from 600 rubles, surgical intervention - from 400 rubles.
Removal methods
There are several ways to get rid of nevi on the face and body. These are radio wave surgery, cryodestruction, electrocoagulation and laser therapy. Classical cutting out of the growth with a scalpel is now performed in rare cases, only when there is a suspicion of malignant degeneration and if the size of the mole is very large.
Electrocoagulation
What is the best method for removing moles? One of the effective methods of treatment is the exposure of pathological tissue to high-frequency currents. The procedure lasts no more than 20 minutes, is practically painless, and sensitive patients are given local anesthesia. Since during the operation all small vessels of the skin are coagulated, bleeding does not occur.
Can I remove it at home?
Many products have been developed to remove lesions at home. But before using them, you need to make sure that the mole is not prone to malignancy (degeneration into cancer). Otherwise, tumor relapse and cancer cell metastasis are possible.
Some of the most effective drugs are:
- cryopharma;
- Wartner Cryo.
They operate on the principle of cryodestruction. The active ingredients are: dimethyl ether, propane.
A mixture of these components is contained in an aerosol can. A special holder with an applicator (included) should be placed on the latter. Then press for 3 seconds. and remove from the container.
During this period of time, the applicator will be saturated with refrigerant and after 20 seconds it should be applied to the problem area for 20 seconds.
Suitable only for removing flat, small moles (no more than 5 mm). If the formations are convex, hanging, or wide, then the method will not be effective enough, as a result, part of the mole will remain on the surface of the skin. The drug costs about the same as cryotherapy.
Also, if the mole is flat and small, it can be lightened. On sale you can find drugs that reduce the production of dark pigment and destroy it (expigment, Melalite forte, etc.).
Their active ingredient is hydroquinone. The result will not be noticeable immediately. It will take several weeks, or even months, to achieve lightening of the skin.
Creams have conflicting reviews and contraindications, so consultation with a dermatologist is required before use.
It is better not to self-medicate, do not remove moles yourself. There is a very high risk of encountering cancer as a result of incorrect actions.
Dermatologist Michael Rogers
Features of removal in children
Children may develop birthmarks from birth or after a couple of months. Nevi in young children are often harmless, but it is better to have them examined and, if possible, removed. If your child has pigmentation with a slight bulge, it is better to tell the dermatologist about it. Such formations are called vascular nevus and can be dangerous for the child. Sometimes it is worth removing large moles as early as possible, especially if there is a danger of their degeneration. There are no age restrictions. Nevi in infancy are removed in the same ways as for adults. Getting rid of tumors and pain relief during surgery is no different. The only problem is the risk of a keloid scar, which will have to be removed with plastic surgery.
Possible consequences
Judging by the reviews, the consequences of removing moles on the face can be unfavorable. The most serious is cancer, namely melanoma.
Pathology may occur due to incorrect depth of exposure to a laser beam or liquid nitrogen. And also, if nevus cells remain in the skin, with prolonged, regular exposure to the sun after the procedure.
Also among the negative consequences:
- A depression, a hole in the skin (during unprofessional work of a doctor).
- Inflammation, suppuration (due to improper care or non-compliance with sanitary and hygienic requirements during and after surgery).
- Recurrence of pigmented nevus (if nevus cells remain in the skin).
- Itching, pigmentation, peeling and pain (if healthy areas are damaged).
Types of neoplasms
The most common types of nevus include the following:
- melanocytic and dermal moles;
- specific and nonspecific formations;
- moles of mixed origin.
Epidermal melacytic spots are small in size and may rise slightly above the surface of the skin. They appear from birth and subsequently increase slightly in diameter. Most often, such neoplasms are localized on the male and female genital organs, hands, and in rare cases appear on the face. Moles of this type will require regular monitoring by a specialist, as they can develop into malignant cancer if damaged or changes in hormonal levels in the body.
Moles of the dermal-melacytic type are often localized on the face. Depending on their species, they can be black, gray or bright red bloody in color.
The most common moles of this type are the following formations:
- Nevus Oto;
- Nevus Ito;
- Mongolian spot.
Newborns often have Mongolian spots, which are an accumulation of melanocyte cells over a large area of skin. Such formations are blue or brown in color, in some cases they look like large hematomas. Mongolian spots fade as the child grows older and completely disappear by the age of five. Only in the case when a large formation does not disappear on its own, observation by an oncologist is required. An experienced doctor will be able to choose a completely safe and effective way to get rid of a birthmark on the face.
Nevus Oto is often localized on the face in the upper jaw area, on the cheeks and near the eyes. These are small dark blue formations that only increase in size as the child grows older.
Nevus Oto requires appropriate monitoring by an oncologist. You should consult a specialized doctor if a mole is damaged or bleeding, changes color, or increases the size of a pigment spot.
Reviews
MARIA, 25 YEARS OLD:
“For a long time I could not find a suitable method for removing moles on my face, I read reviews, consulted a doctor.
The specialist recommended the laser method, explained in detail all the nuances and why this particular method is suitable for me.
In general, thank you very much to my dermatologist, she did everything very quickly and painlessly. I’m happy with the result - there are no marks left on the skin.”
RIMMA, 32 YEARS OLD:
“I removed 3 large moles on my cheek using electrocoagulation.
It was quite unpleasant, plus the tissue took a long time to heal. But the procedure went quickly and took no more than 3 minutes. The results of my facial mole removal (before and after) can be seen in the photo.”
POLINA, 27 YEARS OLD:
“I went to a competent dermatologist.
I have had a large mole on my cheek for many years now. She grew for a long time, but constantly. The color was uneven, the edges were unclear and the shape was irregular. The doctor suspected a melanoma nevus and forced me to undergo several examinations.
The neoplasm was surgically removed. Now everything is fine, I’m glad that I turned to a specialist in time.”
Expert opinion
- Cosmetologist
- Surgeon
Michelle Ellern
practicing cosmetologist-dermatologist
The type of procedure for removing a mole should be chosen by the doctor, taking into account the clinical manifestations of the formation and its tendency to malignancy. In their practice, doctors most often use the laser method. The procedure takes a few minutes and does not cause tissue scarring.
Theda Contis
plastic surgeon
I consider cryotherapy more suitable for papillomas and warts, since often after it the nevus cells remain in the skin, requiring a repeat session.
I consider surgical treatment and electrocoagulation to be “heavy artillery” methods, since they are quite traumatic, painful, and leave a mark on the skin. And they are more suitable for large nevi that are prone to degenerating into cancer. In most cases, moles do not pose a danger to humans. But if they begin to manifest themselves differently, change sizes, then it is better to check with a doctor. After all, an ordinary mole can turn into cancer.
Beware of advertising!
sign up for removal in St. Petersburg . If there is no dermato-oncologist where you live, I will be happy to consult you online.
Other articles:
- Treatment of papillomas. Questions and answers
- Is it dangerous when a mole itches?
- Does your mole hurt? Inflamed? Blushing?
- The mole is growing. What to do?
Useful article? Repost on your social network!