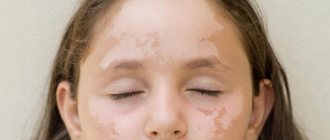
Dyshidrosis, or dyshidrotic eczema, is a skin disease that is localized primarily on the hands and feet.
Eczema is not considered a contagious disease and does not pose a danger to others, but it is symptomatic and extremely unpleasant.
The treatment tactics for the disease are selected comprehensively. This disease, unfortunately, occurs in phases with periods of relief and relapses (returns). Even competent and professional treatment does not guarantee periodic cases of the disease returning.
What it is
The mechanism of development of the disease, as well as the true cause of development, are not fully understood. Dyshidrosis or dropsy always indicates a problem in the body associated with hormonal levels, metabolism, and the functioning of the immune and nervous systems. Often the cause of skin damage is exposure to an allergen or a fungal infection.
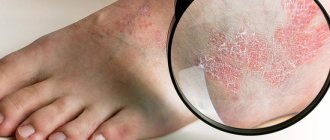
Dyshidrosis affects the hands, fingers, and feet. In most cases, it is seasonal in nature, manifesting itself in the autumn and spring, when the immune system weakens. Symptoms depend on the stage. Initially, this is a slight discomfort, itching, tightness of the skin, and a feeling of dryness. As the pathology progresses, cracks, eczema, and redness appear.
The disease is classified as dermatological, and you should initially seek help from a dermatologist. But it is systemic in nature. The cause of disruption of the sweat glands and their blockage may be associated with pathologies of the endocrine system, nervous, immune, digestive, therefore consultation with other specialists and a comprehensive examination is required.
Clinical picture of dyshidrosis
Dyshidrosis is considered a chronic skin disease. Exacerbation occurs in spring and autumn. Pathology usually appears unexpectedly, but with enviable regularity. Dyshidrosis is characterized by single or group small subcutaneous rashes ranging in size from 1 to 4 mm. Over time, they can increase to the size of a pea and merge into one large blister. The blisters have a dense shell and are filled with serous fluid. It is believed that they are a consequence of blockage of the sweat gland ducts.
Dyshidrosis is also called dyshidrotic eczema. The pathology is popularly known as dropsy.
The rashes are localized mainly on the palms and soles, less often on the fingers and the back of the limbs. They are often accompanied by increased sweating. Usually the patient discovers a new vesicle by accident: only after scratching the itchy spot does he feel a lump on the surface of the skin. The clinical picture is complemented by severe itching, redness, swelling and a slight burning sensation.
Dyshidrosis is not contagious, but it looks unsightly and causes discomfort to the patient. It can be diagnosed in a person at any age, including children. More common in women. The disease is independent in nature and acts as one of the symptoms of some dermatoses, such as mycoses and toxicoderma.
Is hand dyshidrosis contagious?
The external manifestations of the disease resemble mycosis, the causative agent of which is fungi. The infection is transmitted through household contact in public places if basic hygienic safety rules are not observed - walking barefoot in the gym, swimming pool, baths, saunas, showers, using other people's towels and slippers. As for dyshidrosis, the disease is not transmitted in this way and is not dangerous to others. Except in cases where the causative agent is fungi.
Causes
Dyshidrosis develops when metabolic processes are disrupted, resulting in clogging of the pores of the sweat glands. Internal and external factors contribute to the pathological process.
- Weakened immunity;
- Hormonal disbalance;
- Allergy;
- Drinking alcoholic beverages;
- Smoking;
- Addiction to coffee, chocolate;
- Nervous exhaustion;
- Stress;
- Depression;
- Pathologies of the endocrine system;
- Gastrointestinal diseases;
- Intestinal dysbiosis;
- Fungal infections;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Autoimmune processes;
- Hyperhidrosis or excessive sweating;
- Vegetovascular dystonia;
- The presence of parasites in the body.
In most cases, dyshidrosis develops under the simultaneous influence of several factors at once, with a weakened immune system being the trigger.
Causes of the disease
A person with dyshidrosis usually has a family history, impaired immunity, and disruptions in the hormonal system. Excessive emotional stress and frequent stress also contribute to the development of the disease. Other causes of the disease include:
- tendency to allergic reactions;
- impaired metabolism;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- increased sweating;
- old chronic infections;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- frequent consumption of coffee and alcohol;
- long-term treatment with certain medications;
- diseases of the vegetative-vascular system;
- any fungal infections on the skin.
It can be very difficult for doctors to determine the true causes of the disease. A person prone to excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis) is most likely to develop dyshidrosis. The average age of patients is from 12 to 45 years, susceptibility to the disease is characteristic of both men and women.
General symptoms
The first manifestations of the disease are subtle and do not cause significant discomfort. With further exposure to unfavorable factors, dyshidrosis begins to progress, and a more vivid clinical picture appears.
- Small transparent bubbles are visible under the top layer of the skin. When you press on them, nothing happens. There is slight itching, which most often intensifies in the evening. The skin is dry, wrinkled. The use of lotions and moisturizers does not provide the desired improvement.
- The blisters increase in size, protrude on the surface of the skin, and itch. When scratched, they burst, red eczema, microcracks, and peeling appear.
- The formation of eczema causes pain and burning. The scale of redness increases. Blisters with clear liquid appear on the fingers, palms, hands on the inside, as well as on the feet if dyshidrosis develops on the lower extremities.
- As the disease progresses and the wounds are scratched, swelling and swelling of the tissues occurs. The skin becomes rough and thickened.
- In the absence of proper therapy, the wounds become infected. Weeping eczema and pustules appear, the inflammatory process can extend beyond the foot and palm. All this is accompanied by severe itching, burning, and in some cases an unpleasant odor.
Symptoms depend on the stage of the disease, the causes of development, and complexity.
External signs
The disease can occur in two forms - acute and chronic with periodic exacerbation. At the very beginning, the patient feels a slight itching, tingling sensation, some areas of the skin (the site of future vesicles) become warmer, however, no redness is observed. Then, under the layer of skin, small (the size of millet grain) bubbles form, having a dense structure and filled with liquid.
As the disease progresses, the bubbles change, forming confluent foci, and begin to burst. Cracks appear on the surface of the palms, the top layer of skin is eroded, and the skin “falls off” from it. The whole process occurs accompanied by very painful sensations that harm the general well-being of the patient and his mood.
When infected blisters and cracks become infected, a complication may occur: local suppuration, enlargement of the lymph nodes in the armpits (lymphangitis). Cellulitis (subcutaneous ulcers) may form. With untimely and poor-quality treatment, the disease can progress to the next stage - dyshidrotic eczema. This form is characterized by a deterioration in general health with weakness, headache, lack of appetite, enlarged regional lymph nodes, and fever.
External signs of dyshidrosis in children are practically no different from the symptoms of an adult. However, they have a high probability of scratching and causing infection in the wounds on their hands. Parents should carefully monitor the cleanliness of their child's hands.
The danger of this condition requires mandatory monitoring by a dermatologist when treating a patient, who has the ability to adjust treatment measures in a timely manner.
What does the disease look like, photo
Characteristic signs are the appearance of transparent small bubbles on the fingertips and pads. When scratched, the bubbles increase in size and appear on the surface of the skin. Red spots remain where the bubbles burst. When a secondary infection occurs, there are clear signs of inflammation, redness, and pustules. You can see what a dermatological disease looks like in the photo.
Dyshidrosis of the hands and palms
The disease causes physical and aesthetic discomfort. Palms and hands itch, skin becomes inflamed, fingers swell. The condition is aggravated by exposure to irritating factors - hygiene products, products, detergents, as well as by ingestion of foods with a high content of allergens. If the root cause is not established, local treatment will not completely cure the disease. After some time, the blisters appear again.
Since dyshidrosis is often associated with a malfunction of the endocrine, nervous, digestive, and immune systems, determining the root cause is problematic, so the disease is often recurrent and sometimes disappears on its own.
Classification
Depending on the depth of the lesion, the severity of the pathological process, and the causes of development, several types of dyshidrosis are distinguished.
True
The cause of the pathological process is dysfunction of internal organs and systems. In particular, hormonal imbalance, weakened immunity, and digestive problems. The disease begins with the appearance of small transparent blisters under the skin on the fingertips and pads.
Accompanied by slight itching and dry skin. Since the bubbles are located under a dense layer of skin, it is impossible to crush them. The use of a moisturizing cosmetic product does not provide relief. The itching gets worse in the evening. After a few days, the bubbles begin to increase in size, protrude to the surface, and their skin ceases to be dense. When scratched, they burst and eczema appears.
A different course of events is possible when the blisters begin to disappear on their own after a few days, the itching decreases, and the skin becomes moderately moist again. This situation indicates the normalization of natural processes in the body; the immune system itself has coped with the pathology. Patients are often at a loss as to why dyshidrosis appeared and how it disappeared.
Dyshidrotic eczema
Appears as the disease progresses or initially has clear signs of eczema. It develops rapidly when exposed to unfavorable factors - stress, nervous exhaustion, physical fatigue, poor diet, alcohol consumption, skin irritation from household chemicals. Unlike the first case, dyshidrotic eczema begins with redness of the epidermis, swelling, and itching. After a while, small transparent bubbles appear.
The rash increases, the blisters burst, and in their place wet spots appear, and then crusts. The skin thickens and cracks. At this stage, a secondary infection often occurs. Inflammation and itching intensify, pustules appear, redness spreads to the outer side of the hands or leg in the case of foot dyshidrosis. In addition, general health worsens. There is weakness, malaise, irritability, fatigue, a slight increase in temperature, headache, sleep disturbance.
Dry lamellar dyshidrosis
There is no rash or blisters. The disease begins with redness, swelling, and peeling. As it progresses, cracks of varying depths appear, burning, itching, and secondary infection occurs.
Dyshidrotic eczema and dyshidrosis
Dyshidrotic eczema is a type of inflammatory skin disease that occurs in a chronic form. It is expressed in the formation of weeping serous-purulent blisters on the surface of the palms and soles, sometimes spreading to larger areas of the extremities. Dyshidrosis can transform into true eczema, and also affect the nail plates of the hands and feet.
The disease is most often observed in women at the age of 20-25 years, in men - after 40 years. In children, dyshidrosis appears mainly before the age of 3 with a tendency to diathesis and a hereditary predisposition to atopy.
Photo
Causes and factors of the disease
The cause of the development of the disease is most often a hereditary predisposition to increased sensitivity of the skin to the effects of allergens and irritants.
Often, dyshidrotic eczema develops in individuals with neuroendocrine diseases, immune changes, and a history of metabolic disorders.
Increased sweating and lung diseases also contribute to the development of this form of eczema.
When examining a patient with symptoms of dyshidrosis, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, allergic conditions, chronic infectious diseases, and mycoses are often discovered.
Among the external factors that can influence the development of dyshidrosis are nervous strain, stress, skin contact with chemical or physical irritants, and other allergens.
Symptoms and signs
The first sign of the disease is redness of the skin, itching, and then the sudden appearance of vesicles on the skin with a thin layer of cells covering them, filled with serous contents, ranging in size from 1 to 7 mm. Located on the inner surface of the hand or foot, the elements have the appearance of small round or oval grains, located both in groups and separately. Since the vesicles are located in the deep layers of the skin, they may not rise above its surface. Some bubbles increase in size. Closely located vesicles are able to merge with each other, forming large blisters.
As the disease progresses, the skin itching and burning sensation intensify.
The bubbles begin to burst spontaneously or when damaged, which leads to the appearance of erosive elements. Deep erosions formed from large vesicles can cause intense pain. Healing of the inflamed areas occurs slowly (2-3 weeks), with the formation of brownish or yellow scabs.
After the crusts disappear, hyperpigmented areas in the form of dark spots remain on the surface of the epidermis, different from healthy skin.
Within 2-3 months after the end of the acute phase, changes occur in the deep and superficial layers of the skin: increased skin pattern, thickening of the epidermis, formation of cracks, dryness and peeling, and in some cases (with eczematous lesions of the nail folds) - deformation of the nail plate.
Dyshidrotic eczema of the hands or feet often causes secondary infection with bacterial pathogens, which leads to the development of a purulent-inflammatory process on the skin. Pyoderma symptoms can occur with increased body temperature, lymphadenitis of regional nodes, erythematous symptoms, and severe tissue soreness.
In 70% of cases, eczema takes on a relapsing course with remissions within 1-6 months.
The chronic form of the disease is difficult to treat, and tends to worsen under the influence of provoking factors.
Dyshidrotic eczema on the hands is the most common manifestation of the disease. Symptoms of dyshidrosis can be detected not only on the palmar side of the hand, but also on the fingers and interdigital folds. If the process affects the lower extremities, then the inflammatory elements are localized on the soles and toes, especially often at the junction with the foot.
Consequences of the disease
An incomplete course of treatment, as well as an unattended disease, often lead to the transition of eczema to a chronic form. The result of damage to the skin with signs of eczema (trauma, scratching) can be the addition of a secondary bacterial or fungal infection, most often staphylostreptococcal. The phenomena of pyoderma, depending on the extent of the process, can cause serious complications - infection of tissues and organs. Blood poisoning is also possible.
Advanced forms of eczema in infants pose a great danger. Due to damage to a large area of skin and severe pain, death is possible, often due to anaphylactic shock.
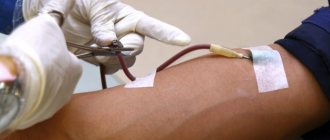
Diagnostics
The main criterion for diagnosing dyshidrotic eczema during visual examination is characteristic skin rashes, ulcers or scabs, as well as a specific area of localization of the inflammatory process. If fungal diseases of the skin of the feet are suspected, a microscopic analysis of the cells obtained by scraping is performed.
Differential diagnosis of eczema on the hands is carried out with psoriasis, allergic and contact dermatitis, and other pustular inflammatory diseases.
Treatment of dyshidrotic eczema on the hands
Treatment of the disease is complex and, above all, is based on compliance with a number of measures:
- Abstain from prolonged water procedures. Use only hypoallergenic pH-neutral hygiene products and cosmetics.
- Avoiding exposure of the skin to all irritating substances, physical factors, overheating or hypothermia.
- Diet with the absence of food allergens and junk food, abstinence from alcohol and smoking.
- Drink enough fluid, while limiting salt in the diet.
- Treatment of chronic diseases , especially internal organs, hormonal glands and the nervous system.
General therapy
General therapy may include:
- Antihistamines and desensitizing drugs to relieve itching and reduce inflammation (calcium gluconate, magnesium sulfate, Zodak, Telfast, Tavegil).
- Systemic glucocorticosteroids for severe and intense skin itching (prednisolone). At the same time, diuretics and hemodesis are prescribed.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, diclofenac) for severe swelling, redness, and tenderness of the affected areas.
- Sedative therapy (motherwort, peony tincture, valerian). In severe cases, the use of antidepressants is indicated.
- Antibacterial therapy (tetracyclines, macrolides) when pyoderma occurs.
- Vitamin complexes , immunocorrective therapy (decaris, diucifon, immunal).
- Autohemotherapy, course treatment with histoglobulin is recommended for chronic eczema.
Physiotherapeutic methods in the treatment of dyshidrotic eczema include reflexology, paraffin baths, application of therapeutic mud, magnetic therapy, UHF, and ultraviolet irradiation of the affected areas.
External therapy
External therapy for the disease may include:
- Solutions of aniline dyes (fucarcin, brilliant green, methylene blue), as well as potassium permanganate for severe weeping and at the stage of ulcer formation.
- Preparations to relieve itching (amidopyrine, Burov's liquid, furatsilin, tannin, silver nitrate solution).
- Local corticosteroids (elokom, advantan, dermozolon, triderm) in the absence of antipruritic effect from other drugs.
- Drying agents (talc, zinc paste, mash).
- Ointments with a keratolytic, anti-inflammatory effect (sulfur, tar, naphthalan).
- Ointments with a regenerating, moisturizing effect (Radevit, Vaseline, baby cream) are used in the chronic stage of the disease after acute symptoms have been relieved.
Treatment with folk remedies
Traditional methods of treatment can have a positive effect on the condition of the skin, especially during the chronic course of the disease:
- Mix 2 tablespoons of white cabbage, chopped into a pulp, and the same amount of raw potato pulp. Apply to affected areas, leave under a bandage for 10-15 minutes. The product promotes the healing of eczema ulcers.
- Itchy blisters on the hands or feet can be lubricated with the following lotion: lemon juice, egg white, shake 1 spoon of glycerin, then pour in 100 ml. cologne. You can wipe the skin as the itching intensifies, but not more than 3 times a day.
- Infusions of yarrow, string, and chamomile are used to speed up the healing of scabs on the hands.
- Sea buckthorn oil can be applied to affected areas of the skin daily, which promotes rapid tissue regeneration.
- Pharmacy tincture of eucalyptus is diluted with water in a 1:1 ratio, after which a bandage is moistened and applied in the form of applications to the hands; exposure time – 5-10 minutes.
- It is recommended to take infusions of St. John's wort internally (1 spoon of the plant per glass of boiling water), calendula flowers (1 teaspoon per 200 ml of boiling water), sage leaves (2 spoons per 250 ml of water), as well as a decoction of willow bark (1 tablespoon of bark per 400 ml water). Such products are consumed in 50-70 ml. 3 times a day to increase the body's resistance, improve blood circulation, and accelerate skin healing.
- Juice from burdock leaves is used to wipe the affected area, as well as to take 1 spoon orally 2 times a day.
- After scabs form, you can lubricate the skin with 100 ml of ointment daily. tar, 4 egg yolks, 50 ml. cream.
Prevention
The most important measures to prevent relapse of the disease are the following:
- Dietary food with a limit on over-salted, fried, canned foods, all possible food allergens, coffee, alcohol.
- Avoiding contact with allergens (household, industrial), irritating substances.
- If possible, it is recommended to wear underwear and clothing made from natural fabrics.
- Careful control of body hygiene, timely treatment of all infectious diseases and foci of skin inflammation, antiseptic treatment of any skin injuries.
- Preventive consultations with a dermatologist, regular examinations and preventive courses for the treatment of eczema.
Dyshidrosis in children
Often appears in infants and children under 5 years of age. The main reasons are weak immunity and unformed intestinal microflora. Any product, detergent, fabric can provoke a dermatological disease. In adolescents, the pathological process begins against the background of hormonal changes, poor nutrition, nervous tension, excessive physical activity, and weakened immunity.
There is a hereditary factor, a tendency to allergies, autoimmune disorders, abnormalities in the functioning of the endocrine system and nervous system. In this case, the frequency of relapses does not decrease with age. A rash or eczema appears after aggressive exposure to unfavorable factors, or against the background of a decrease in the body’s protective functions - after an illness, before and after menstruation, against a background of depression. Violation of sweating and metabolic processes occurs with poor nutrition, strict diets, overeating, and excess weight.
General recommendations
General recommendations for patients are:
- limit the consumption of alcohol, sweets, smoked and spicy foods;
- the inclusion of vegetables, fruits, and natural fermented milk products in the diet is approved;
if the disease affects the feet, it is necessary to change socks often;
- carefully adhere to the rules of personal hygiene for body care;
- wear rubber seals when doing housework;
- in acute forms of the disease, avoid direct contact with water and detergents;
- patients should not wear clothes made of wool and synthetic fabric;
- Dyshidrosis can be effectively treated only after complete recovery from existing chronic infectious diseases (sinusitis, caries, tonsillitis).
Dyshidrosis in pregnant women
Develops against the background of hormonal changes. During pregnancy, the immune system weakens, the vegetative-vascular system suffers, and the digestive system works under load. All this together leads to the development of dyshidrosis of the hands and feet. Symptoms intensify when exposed to external factors - foods high in allergens, smoking, alcohol, synthetic clothing, poor hygiene, detergents, cosmetics.
After childbirth, the condition returns to normal on its own as the body recovers and hormonal levels stabilize. Or it happens, on the contrary, nothing happened during pregnancy, and dyshidrosis appears during breastfeeding. To improve the condition of the skin, it is recommended to use traditional medicine, since most professional drugs are not used during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
What pathologies should the dyshidrosis clinic be compared with?
If a clinical picture similar to dyshidrosis appears, you must first contact a dermatologist to rule out a number of conditions:
- contact (allergic) dermatitis in the acute stage . First of all, it appears on the hands; other areas are not typical, given the mechanism of development of the allergic process. This form of dermatitis is much more easily treated with an antihistamine, which can help determine the disease. Bubbles in allergic dermatitis are possible, but even in the acute period their characteristics are different - there is no such transparency, the location and resolution of the bubbles are somewhat different;
- if the process affects the skin of the feet , a differential diagnosis is made with the dyshidrotic form of dermatophytosis. In this case, microscopy helps to detect mycelium or fungal spores, and cultural testing - inoculation on a nutrient medium. For examination, skin flakes are taken from suspicious areas;
- for pustular psoriasis of the palms and soles , we look for other foci of psoriasis. The fact is that isolated psoriasis of only the palms or soles is extremely rare. If we find signs of psoriasis on the outer surfaces of the elbow and knee joints, dyshidrosis can be excluded;
- scabies - we check the surface of the skin for the presence of passages and the mite itself.
Diagnostics
Dyshidrosis is treated by a dermatologist. However, to find out the root cause, other specialists are involved - an allergist, therapist, hepatologist, venereologist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, psychotherapist, neurologist, etc. To exclude relapses or reduce the number of exacerbations, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive comprehensive examination. They usually start with an endocrinologist.
When examining the skin, the specialist’s main task is to determine the stage and nature of the disease. To exclude a fungal infection, scrapings from the affected areas are taken for analysis. But distinguishing dyshidrosis from allergies is problematic, since the symptoms are identical.
How is diagnosis carried out?
At present, no methodologies have been created that could be used to determine dyshidrotic eczema. The doctor will be able to make a diagnosis based on an analysis of the clinical picture and course of the disease.
The rashes are compared with signs of other skin diseases (fungal infections of the fingers, psoriasis) and unlikely options are excluded.
For a more accurate medical conclusion, additional studies are prescribed:
- scrapings for the presence of pathogenic fungi;
- seeding the contents of the vesicles for microorganisms.
Treatment
Therapy must be comprehensive. Efforts are aimed at eliminating local symptoms, eliminating the influence of negative factors, and preventing relapses. However, recovery is complicated by the fact that it is not always possible to establish the root cause or to competently influence it.
Pills
To eliminate the inflammatory process and reduce the amount of histamines in the blood that cause an allergic reaction, antihistamines are prescribed. The new generation tablets are well tolerated and do not cause drowsiness or side effects. It should be taken in a course according to the instructions for at least 10 days. Effective drugs - L-Cet, Suprastin, Diazolin, Eden. Taking antihistamines improves the condition of the skin.
If there are problems in the functioning of blood vessels, the heart, against the background of vegetative-vascular dystonia, it is advisable to undergo a course of therapy with vasodilating drugs. The tablets activate metabolic processes, improve the condition of the nervous system, improve blood circulation, and cleanse the body of toxins. Take a course - up to 2 months. Phezam, Piracetam, Aminalon are prescribed.
If the cause of dyshidrosis is the unsatisfactory state of the nervous system, sedatives and antidepressants are prescribed. The drugs are prescribed by a neurologist depending on the general condition. For drowsiness, weakness, lack of energy, tearfulness, antidepressants are recommended; excessive agitation, sleep disturbance, hysteria - sedatives. Stimulant drugs - Fluvoxamine, Paroxetine, Sertraline. Sedatives – Nova-Passit, Glycine, Glycised, Afobazole, Valerian, Motherwort.
In some cases, diuretics are indicated. In the case of dyshidrosis, it is recommended to drink tinctures, decoctions based on medicinal herbs, extracts, and juices. An effective remedy is rosehip decoction and tinctures containing this component.
In case of pathologies in the functioning of the endocrine system, hormonal imbalance, hormonal drugs are prescribed. Selected individually in each case.
Drug treatment
There are no special medications for dyshidrosis. Tablets that stop inflammation and rashes are selected depending on the cause of the disease, the individual characteristics of the body, and age. An important role is played by strengthening the immune system, since in a normal state the immune system is able to independently overcome the problem. Vitamins, probiotics, Echinacea tincture, rose hip decoction, Imupret, etc. strengthen the immune system. To cleanse the body of toxins that weaken the immune system, sorbents are recommended - Enterol, Atoxil, Enterosgel, Smecta, Activated carbon.
Preparations for topical use
Used to eliminate local symptoms. In some cases, to restore the skin, it is enough to avoid contact with irritants, change your diet, use moisturizers, and take a course of antihistamines. Other situations require long-term use of special ointments.
In case of severe damage to the epidermis, products containing sulfur, tar, naphthalene, as well as glucocoricosteroid hormones and antihistamines are used. The appropriateness of using drugs is determined by a specialist. This can be Vishnevsky ointment, Sulfuric, Zinc, Fenistil-gel, Psilo-balm, Advantan, Dermovate, Sinaflan.
If there are signs of a secondary infection, dyshidrosis is treated with local antibiotics or combined agents - Triacutan, Elokom S, Levomekol, Tetracycline ointment. The duration of therapy should not exceed 14 days; in parallel, antihistamine tablets and drops are taken - Fenistil, Claritin, L-Cet, and others.
Botox
The procedure is used to treat dyshidrosis due to excessive sweating. It is one of the most effective methods of combating sweaty palms. A Botox injection is made through a small incision, and the sematic nerve nodes are compressed, preventing the release of sweat. The effect appears almost immediately and lasts for an average of six months. If necessary, I repeat the procedure after 6 months. The procedure has contraindications and a possible side effect in the form of an allergic reaction to the drug.
Ultraviolet
Problem areas are exposed to ultraviolet rays. The procedure is indicated in case of severe damage to the skin, in the absence of a therapeutic effect from other methods.
In addition, magnetic therapy, laser cauterization, diadynamic therapy, acupuncture, electrophoresis, cryotherapy, and paraffin therapy are often prescribed. The cost of one procedure is from 400 rubles. Up to 11,000 rub.
Treatment of hand dyshidrosis
Various means and methods are used in the treatment of the disease. Treatment should be comprehensive and include not only getting rid of external symptoms, but also actions aimed at strengthening the body. Symptomatic treatment consists of eliminating inflammation, itching, relieving swelling and preventing the addition of a bacterial infection. These are drug therapy, traditional methods and physiotherapy.
Additional treatment is based on increasing immunity, strengthening the nervous system, and restoring physical and psychological balance. This is facilitated by physiotherapeutic methods, hardening, changes in rest and diet. Non-traditional methods are also widely used: hirudotherapy, apitherapy, acupuncture.
Drug treatment
For dyshidrosis, antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamins (A, E, C, P, PP) are prescribed internally. Sometimes the use of sedatives and tranquilizers is required. In severe cases - corticosteroids.
The dosage form for external use is selected according to the stage of the disease. If the weeping stage predominates, use baths, lotions or wet-drying dressings. When the inflammatory process subsides, creams and ointments are used (as prescribed by the doctor).
Wet dressings and lotions
At the bubble stage, wet dressings with Burov's liquid are used. Large bubbles must be pierced and the liquid blotted with a napkin. The skin covering of the bladder should not be removed.
For lotions, you can also take lead water or resorcinol. Make the solution and keep the bandages according to the instructions.
Hand baths against dyshidrosis
Baths with potassium permanganate or soda dry the skin well. You can use folk remedies. Decoctions of chamomile, celandine, and string relieve itching and inflammation. You can also brew some herbs by adding oak bark or sage. Keep your hands in the warm broth for at least 15 minutes. Then lubricate with oil infused with the same herbs or use medicinal ointment.
Keep your hands in the warm broth for at least 15 minutes.
Making herbal butter is not difficult. Take the required amount of any vegetable oil, add herbs (any of those listed above) into it at the rate of 100 ml/1 tbsp. l. respectively. Keep the mixture in the “bath” for about 40–60 minutes. The oil needs to sit for another 2-3 days in the dark before it can be used. It will eliminate flaking and soften the skin.
Folk remedies
They are used as independent remedies for minor damage to the epidermis or as part of complex therapy. They make medicinal baths or wipe the skin.
- Baking soda. Is a powerful antiseptic. Quickly relieves itching and stops the inflammatory process. For 500 ml of warm water, 2 teaspoons of the product are required. Place your arms and legs in the water and hold for 20 minutes. Wipe with napkins, apply ointment, cream.
- Herbal collection. Mix oak bark, string, and sage in equal proportions. Fill with water, boil for 10 minutes over low heat, allow to cool to a comfortable temperature.
- Lemon. Squeeze the juice of one lemon into 500 ml of warm water or add 0.5 teaspoons of acid. Used for wiping, making a bath.
Laundry soap, tar soap, and olive oil will help relieve itching, irritation, and redness.
Treatment of exacerbation (or primary process) of dyshidrosis
- dehydration therapy : both loop and potassium-sparing diuretics are used. In the first case, saline solution is prescribed at the same time;
- sedatives are used to partially relieve the symptoms of the disease to avoid scratching and suppuration;
- antihistamines also help reduce itching and limit inflammation;
- Zinc ointment, a solution of ethacridine lactate, resorcinol, and lead water are applied topically to the skin.
Diet
During the treatment process, it is recommended to exclude foods that provoke intestinal irritation and increase histamine levels. In this case we are talking about allergens, spicy, fatty, fried foods. Drinking alcohol and smoking are prohibited.
Excluded:
- Fruits, vegetables red, orange;
- Carbonated drinks;
- Products containing preservatives, flavor enhancers, chemical additives;
- Whole milk;
- Chicken meat, beef;
- Wheat bakery products;
- Chocolate;
- Cocoa;
- Eggs;
- Honey;
- Nuts;
- Sweets;
- Sauces, seasonings.
It is allowed to eat porridge, fermented milk products, vegetables, fruits, yellow, green, blue berries, mineral water, compote, tea, dried fruits, jam, Lenten cookies, black bread, crackers. Lean pork, turkey, and rabbit are allowed.
The role of nutrition
Nutrition is of paramount importance in the treatment of this disease, since it determines how quickly a person will recover.
For severe dyshidrosis, doctors recommend adhering to a hypoallergenic diet. They also recommend taking a multivitamin.
Foods that can be eaten with this pathology:
- durum wheat pasta;
- oat bread;
- boiled turkey, chicken and beef;
- porridge;
- biscuits;
- vegetable stew;
- apples;
- low-fat cottage cheese;
- yogurt;
- kefir.
Products (possible allergens) that should be avoided:
- fatty food;
- fried food;
- alcohol;
- citrus fruit;
- strawberry;
- nuts;
- canned food;
- marinades;
- spicy food;
- spices;
- mayonnaise and ketchup;
- semi-finished products;
- fish;
- milk;
- honey;
- shrimps;
- eggs
- candies;
- release;
- semolina porridge;
- chocolate.
By adhering to such a diet, a person will be able to cure dyshidrosis much faster and minimize the risk of its secondary manifestation.
Find out how microbial eczema manifests itself on the hands. What do the symptoms of weeping eczema look like? Details in the article.
What are the causes of dry eczema on the hands? See below.
Lifestyle
For a quick recovery and to prevent relapses, it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle.
- Monitor the state of the nervous system, avoid exhaustion, overstrain, avoid problematic situations and scandals. Know how to relax.
- Rest, get enough sleep.
- Have sex.
- Monitor your menstrual cycle.
- Do not abuse alcohol, do not smoke.
- Play sports or do gymnastics.
- Strengthen the immune system in every possible way - decoctions, tinctures, walks in the fresh air, swimming, contrast showers.
- Normalize physical activity.
Proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle are the main methods of prevention. Strong immunity, normal hormonal levels, active metabolism are the basis of the health of every person.
Prevention
In order to protect yourself from this disease, you need to adhere to the following preventive measures:
- strengthen the immune system (take vitamin complexes, exercise, exercise);
- give up bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol);
- eat right and avoid eating foods that contain dyes or emulsifiers;
- do not come into contact with various household substances and allergens without rubber gloves;
- wear high-quality clothes and linen (only from natural materials);
- consult a doctor in time if the first symptoms of the disease occur;
- do not self-treat with antibiotics and other medications;
- treat diseases of the digestive and endocrine systems;
- avoid stress and overwork;
- maintain hygiene;
- Do wet cleaning in the house regularly.
Read whether toxicerma is dangerous in children. What does hand dyshidrosis mean? The answer is here.
Forecast
Dyshidrosis can disappear forever or recur periodically when the immune system is weakened or hormonal imbalance occurs. The result depends on the strength of the immune system, the causes of the disease, and the qualifications of the specialist. Symptoms can be eliminated in a few days with hormonal drugs, but it is problematic to achieve stable remission. In this case, the efforts of the person himself also play an important role. If you follow proper nutrition, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and have a favorable psycho-emotional environment, dyshidrosis does not manifest itself.
Video about dyshidrosis
- Author: Julia
I decided to follow in the footsteps of my mother, who works in a rural clinic, and become a doctor. She graduated from school with a gold medal, was the best student, but when she came to the city to enter medical school, she failed the exam. Rate this article:
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(0 votes, average: 0 out of 5)
Share with your friends!
Treatment of dyshidrosis with traditional and folk remedies. Prevention of dyshidrosis
Hand dyshidrosis - what is the cause of the problem and how to solve it?
Reviews
Dear readers, your opinion is very important to us - therefore, we will be glad to hear your feedback about dyshidrosis of the hands and feet in the comments, this will also be useful to other users of the site.
Alina:
“Dyshidrosis appeared after childbirth, when the child was breastfed. Especially on that finger where the gold ring was. Nothing helped. I went to the dermatologist, he prescribed me Triacutan ointment. I apply it, the next day it goes away, then it appears again. I eat something red, it sprinkles again. It was like this for almost six months. Then she took off the ring and began to recover. There has never been anything like this in my life.”
Ksenia:
“I sent my husband on a business trip for 2 months. By the end of the fourth week, I began to notice strange things about myself. Mood swings, pain in the lower abdomen, constant thoughts about sex. And then my palms and fingers began to itch. I noticed small transparent bubbles. Clearly signs of dyshidrosis, clearly from hormonal imbalance. Didn't treat it with anything. My husband arrived and everything went away.”
Symptoms of dyshidrosis and dyshidrotic eczema
Symptoms of dyshidrosis and dyshidrotic eczema
The following clinical picture is typical for dyshidrosis:
- paroxysmal appearance of blisters on the lateral surface of the fingers and toes;
- the rash is transparent, as if embedded in the skin, visible through the stratum corneum;
- swelling and hyperemia in the affected areas increases;
- rashes are accompanied by burning and itching;
- when scratched and infection occurs, the blisters become cloudy and yellowish in color.
Be sure to read:
What is Rescuer ointment (balm) used for: indications and instructions for proper use
There is also an abortive form of dyshidrosis. It is characterized by peeling in the form of rings and is not accompanied by itching.
Symptoms of dyshidrotic eczema include:
- rashes in the form of vesicles 1-5 mm, distributed over the entire surface of the hands and feet;
- hyperemia, itching are mild or absent;
- the bubbles either burst or dry out, forming yellowish crusts;
- sometimes the vesicles merge, forming small erosions, scales and crusts.
The chronic course of eczema is characterized by excessive keratinization.