Dermatovenerologist
Khasanova
Alina Rashidovna
7 years experience
Make an appointment
Hyperkeratosis is a general name for a group of pathologies, the main symptom of which is excessive keratinization of the skin. Cells of the outer, stratum corneum, under the influence of a certain factor, activate the process of division, while the desquamation of dead cells slows down. As a result, the skin is covered with a stratum corneum, the thickness of which varies from fractions of a millimeter to several centimeters. Any part of the body can undergo keratinization, depending on the causes of the pathology.
Pathogenesis and types of hyperkeratosis
Throughout life, a programmed process of division (mitosis), growth and death of keratinocytes - germ cells - occurs in human skin. They form in the basal layer of the skin, gradually moving to the top.
During migration, the cells lose water and organs, become flat and turn into corneocytes. These are dead cells, which are 80% keratin and form the basis of the stratum corneum of the skin. Gradually, the corneocytes slough off, giving way to new cells.
Under the influence of internal or external causes, a failure may occur in the process of mitosis. Cell division begins to occur in an enhanced mode. Corneocytes do not have time to exfoliate and stick together with newly arriving cells.
Another mechanism for the development of hyperkeratosis is based on a disruption in the process of desquamation of horny scales. Regardless of the cause, a thickening is formed on the surface of the skin, consisting of corneocytes, the layer of which can reach up to 4 cm.
Hyperkeratoses are divided by origin:
- congenital;
- acquired.
Clinical course:
- Follicular. With this form of hyperkeratosis, the pathological process affects the hair follicles. This leads to blockage of the follicular ducts by horny scales and the formation of small purulent-inflammatory foci in the affected area.
- Lenticular. This hyperkeratosis occurs in a chronic form, which most often worsens after prolonged sun exposure.
- Disseminated. In this form of pathology, dead cells form polymorphic elements that resemble short hairs. Rarely seen.
Hyperkeratosis itself does not pose a threat to human health. However, in advanced cases with the follicular form, purulent-inflammatory processes - pyoderma - can join the symptom complex.
Causes of hyperkeratosis on the face
Hyperkeratosis is not considered as an independent disease. It mainly manifests itself as a symptom in various pathologies. However, there are cases of independent formation of keratinization disorders, which mainly occur under the influence of external factors.
External factors, as a rule, cause local formation of keratinization of the skin. Main reasons:
- poor hygiene;
- long-term insolation;
- constant chapping of the skin;
- regular exposure to hard water;
- contacts with reagents and chemicals.
The causes of damage to large areas of the skin are internal causes:
- ichthyosis (genetic disorder of keratinization of the epithelium);
- psoriasis, lichens of various origins;
- dermatitis, erythroderma;
- fungal diseases;
- diabetes;
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract;
- deficiency of vitamins A, C;
- psycho-emotional stress.
Regardless of the cause, hyperkeratosis can be eliminated or long-term remission achieved. The success of treatment depends entirely on quick diagnosis and adequate therapy.
Are there external risk factors?
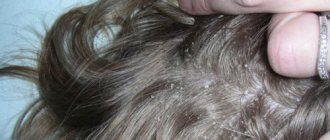
Of course, internal disorders can cause hyperkeratosis of the scalp. The reasons, however, can also be external. In particular, thickening of the stratum corneum is observed if a person ignores the rules of personal hygiene and does not provide the scalp with appropriate care.
In addition, experts consider the incorrect selection of cosmetics to be a risk factor. Some shampoos, masks and hair conditioners cause increased dryness of the skin or an allergic reaction. In some patients, hyperkeratosis develops as a result of strong compression of the scalp for a long time - this is observed with constant wearing of headbands, hairpins, hairpins and even too tight hats.
It is almost impossible to determine the cause of the development of such a pathology on your own. That is why, at the slightest suspicion of the presence of hyperkeratosis, you should seek help from a specialist.
Symptoms of hyperkeratosis on the skin
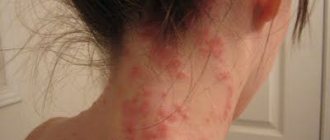
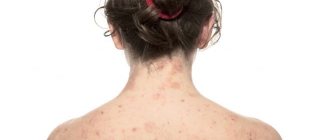
Follicular hyperkeratosis appears as small bumps located around the hairs on the facial skin. These are dense red formations that peel and itch. The external signs of the formations resemble the “goose bumps” that occur during a chill.
With the lenticular form of hyperkeratosis, papules of horny tissue ranging in size from 1 mm to 5 mm are formed. The formations are reddish-brown or yellow-orange in color.
After removal, a weeping surface prone to bleeding can be found under the papule. Papules are single and do not tend to merge. They do not cause much discomfort to the patient except for moderate itching, which rarely occurs.
In the disseminated form of hyperkeratosis, various elements are formed on the skin that resemble short and thick hairs. In some cases, they unite several follicles, taking the shape of a brush. They are characterized by active peeling.
Regardless of the form of hyperkeratosis, the patient’s skin is dry and pigmented. With tactile contact, distinct seals can be seen. Most often, elements of hyperkeratosis are localized in the space between the eyebrows, wings and sinuses of the nose. This is due to the abundance of sebaceous and sweat glands in these areas, which are susceptible to various types of infections.
Symptoms
The main symptom of hyperkeratosis is the appearance on any part of the body of thickened skin with reduced sensitivity, often with a changed color that differs from the main shade. In the initial stage, the skin gives the impression of being rough, then the thickness of the stratum corneum increases, sometimes to such an extent that it begins to cause discomfort. In particular, advanced hyperkeratosis of the feet can lead to changes in gait. The keratinized skin flakes off or partially peels off; painful cracks may appear in the thickest and driest areas, which take a long time to heal and become sites of infection. Often the pathology is accompanied by dry skin and decreased function of the sebaceous glands.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of hyperkeratosis is based on physical examination and medical history. The examination is carried out by a dermatologist. He clarifies the presence of somatic pathologies, hereditary predisposition to hyperkeratosis, possible use of hormonal drugs, dietary features and lifestyle.
In doubtful cases, a general blood test (determination of hypovitaminosis) and histological examination of tissues may be needed. The main diagnostic criterion is the nature of the formations on the skin.
In cases where hyperkeratosis is a symptom of internal pathologies, additional examination and etiotropic treatment are prescribed.
Diagnostic methods
As a rule, with hyperkeratosis, diagnosis consists of identifying the disease that led to the formation of keratinized areas. The dermatologist conducts an external examination and interviews the patient, checking for signs of skin diseases. As a rule, a qualified specialist can recognize the disease by external signs. For clarification, differential diagnosis may be necessary, which is necessary if the manifestations of the pathology are similar to other skin diseases, which are also characterized by peeling and dry skin. If there are difficulties in determining the diagnosis, a biopsy of the affected area of skin is performed with histological examination of the tissue.
Complex for the treatment of hyperkeratosis
To cope with hyperkeratosis that appears without underlying diseases, going to a cosmetology clinic will help. Here, dermatocosmetologists will select a complex of treatment, which includes the use of salon procedures, pharmacological drugs, a special diet and lifestyle correction.
Cosmetic procedures
To eliminate dead skin layers and deeply nourish facial skin tissues, cosmetologists select the most suitable cleaning methods.
Effective procedures:
- Chemical peeling.
This is a burn of certain layers of facial skin controlled by a cosmetologist, performed using various active substances. Depending on the skin type, degree of keratinization and age characteristics, it can be superficial, medium or deep.
- Brossage.
This is a hardware-based skin cleansing with special rotating attachments using an antiseptic gel or fine scrub.
- Ultrasonic cleaning.
The advantage of this method is the absence of mechanical impact on the skin. Cleaning is carried out using ultrasonic waves, which create acoustic pressure, ensuring easy removal of horn cells.
- Cryotherapy.
Exposure of the skin to ultra-low temperatures, which results in the death of surface tissues.
After these procedures, the face is cleansed of the stratum corneum, local metabolism and blood circulation are improved, and the natural hydration of cells is increased. This collectively suppresses the active processes of hyperkeratosis and prevents the development of inflammatory processes.
Pharmacological agents
A course of treatment with oral and local drugs helps regulate the division of keratinocytes and desquamation of horny scales, which allows for long-term remission.
Preparations:
- Corticosteroids.
The drugs are indicated for severe forms of hyperkeratosis accompanied by inflammatory processes. Ointments used: Prednisolone, Beloderm, Flucinar, Celestoderm, Dermovate, Hydrocortisone.
- Retinoids.
Derivatives and synthetic analogues of vitamin A. These are dermatoprotective agents that stimulate skin regeneration and suppress keratinization processes. They are used externally, intramuscularly and orally. Preparations: retinol palmitate and acetate (Videstim, Sanvit A); tretinoin (Lokacid, Retin-A, Vesanoid); acitretin (Neotigazon); etretinate (Tigazon).
- Salicylic acid.
These are drugs that cause active exfoliation of dead cells from the surface of the skin. For hyperkeratosis, ointments and pastes (1-10%), alcohol solutions (1-2%) are used.
- Vitamin complexes.
For hyperkeratosis, a course of vitamin therapy is recommended. For this purpose, complexes with a high content of vitamin A and C are used.
The process of treating hyperkeratosis is long and difficult. Any violations in treatment tactics can lead to a more intense process of cell division or the appearance of outbreaks of inflammation. Therefore, treatment is carried out only under the supervision of a dermatocosmetologist.
Cosmetology products
When treating hyperkeratosis, it is important to choose the right cosmetics. Many cosmeceutical concerns have a special line of skin care products for hyperkeratosis.
Used for skin care:
- facial cleansing using gommage, soft scrubs;
- rubbing with lotions;
- protective equipment;
- moisturizing creams and gels.
To do this, select products containing one of the components: vitamins A and C, lactic, fruit or glycolic acids, allantoin, urea, Shea butter, salicylic acid. It is better to buy products in pharmacies, where you can additionally get advice from a pharmacist.
Folk remedies
During treatment with pharmacological drugs, non-traditional methods should not be used without consulting a cosmetologist.
Recipes:
- Potato.
The product is used to soften the stratum corneum of the skin. The raw vegetable is grated on a fine grater, placed in a gauze cloth and applied to problem areas for 1 hour before bedtime before applying moisturizers.
- Aloe.
The plant contains vitamins A, E, C, and has anti-inflammatory, softening and antipruritic effects. To prepare a compress, the leaves of the plant are kept in the refrigerator for 15 minutes, crushed in a blender, placed in gauze and applied to the affected areas. Leave for 1-2 hours. The procedure is repeated 3-4 times a week.
- Propolis.
The product has antibacterial properties, so it will be useful in the development of foci of inflammation. Propolis tincture (2 tsp) is mixed with egg yolk (1 pc) and liquid honey (1 tsp). The mixture is distributed over the face, left for 20 minutes and washed off with warm water. The procedure is carried out 2 times a week.
- Beet.
The vegetable contains provitamin A, vitamin C, fruit and lactic acids. Peeled beets are ground on a fine grater and left for 2-3 hours. Distribute the mixture over the face and leave for 1 hour. The procedure is repeated every other day.
- Onion peel.
The crushed raw materials (4 tablespoons) are washed and scalded with boiling water. The husk is placed in a dark glass container and filled with 9% table vinegar (200 ml). The remedy is infused in a dark room for 14 days, filtered and used as a lotion. The duration of the procedure is 30 minutes, frequency 2-3 times a week. The procedure has a moderate keratolytic and antimicrobial effect.
- Burdock.
Dry raw materials (2 tbsp) are poured with water (0.5 l) and boiled for 10 minutes. The broth is filtered and poured into a glass container. Use to wipe the skin 2-3 times a day. The product helps exfoliate horny scales.
The effect of folk remedies will increase if you take a steam bath before using them. To do this, heat up a 1-3% solution of baking soda and hold your face over the steam for 3-5 minutes.
Nutrition and hygiene
People prone to skin hyperkeratosis should review their diet, switch to fractional meals and improve their drinking regime.
The diet includes products:
- vegetables and fruits;
- red fish, caviar, seafood;
- lean meats;
- milk, cottage cheese, natural yoghurts;
- egg;
- unrefined vegetable oils;
- nuts, dried fruits;
- whole grain bread, cereals.
You should avoid refined foods (preservatives, flavor enhancers, flavorings, chemical additives), fatty, hot, smoked and spicy foods. It is recommended to drink the optimal amount of fluid (30 ml X 1 kg of body weight). The best sources: filtered water, decoctions, compotes, juices and herbal teas.
The formation of multilayer scales with hyperkeratosis is attractive for the accumulation of dirt and dust particles. Therefore, it is important to monitor the cleanliness of the skin with special attention.
When washing your face, use special gels and soaps with moisturizing ingredients. The skin of the face is rinsed with gentle movements, avoiding rough friction. For wiping, use soft towels made of natural fabrics. After each water procedure, moisturizing and protective creams are used. Mechanical squeezing of blackheads and comedones is not allowed.
You can learn about ways to combat hyperkeratosis depending on the degree of damage by watching the video.
Care
Basic hygiene rules and a healthy lifestyle are one of the main conditions for recovery from hyperkeratosis. Without them, successful and effective treatment of the disease is almost impossible. You can regularly go to salon treatments and use the strongest medications, but still not move one step towards recovery. Therefore, it is so important to be able to properly care for the epidermis of the scalp affected by hyperkeratosis and lead a healthy lifestyle.
- Follow a dietary diet.
- Improve the functioning of the liver and gastrointestinal tract.
- Treat dysbacteriosis.
- Strengthen your immune system.
- Maintain normal body weight at all times.
- Be sure to treat all concomitant diseases.
- Maintain a drinking regime - from 1.5 to 2.5 liters of fluid per day.
- Use only high-quality cosmetics.
In addition to following these recommendations, treatment of hyperkeratosis involves various procedures for the scalp and the use of medications. Their independent use is contraindicated, as it can lead to complications and unforeseen side effects.
Some stages of hyperkeratosis treatment can even be pleasant - for example, mild salon peeling of the scalp
Prevention of hyperkeratosis
The basis for the prevention of hyperkeratosis is adequate skin care, a constant supply of vitamins and macroelements from food.
The following will help to avoid recurrence of hyperkeratosis:
- regulation of hormonal and emotional levels;
- absence of prolonged sun exposure, overheating and hypothermia of the skin;
- application of protective measures when in contact with chemicals;
- use of protective cosmetics, regular facial cleansing;
- vitamin therapy courses:
- rational nutrition and hygiene;
Constant contact with a cosmetologist will help you keep abreast of cosmetic innovations and select products depending on the season and the problem that has arisen.
Despite the frequency of the problem, the phenomenon of hyperkeratosis is not fully understood. All forms of hyperkeratosis are quite difficult to correct and can quickly appear under favorable conditions. This suggests a chronic course of the disorder. Therefore, it is important for people prone to hyperkeratosis to get used to a new lifestyle and treat possible discomfort as positively as possible.
Troubleshooting
You need to understand that in order to obtain and consolidate the desired result, treatment for goose bumps should be carried out comprehensively.
It is also worth considering that there is no ideal way that would help you forget about this problem once and for all. It is possible that goose bumps may appear periodically from time to time.
Therefore, in order to encounter such unpleasant manifestations as rarely as possible, it is necessary:
- First of all, consult a doctor for diagnostics to identify the cause of goose bumps. If the culprits are malfunctions in the functioning of internal organs, then there will be no effect from any kind of wraps and masks. It is necessary to fight the root cause, and not its consequences.
- Have a clear desire to get rid of the disease and be persistent in this matter.
- Be sure to change your diet and organize proper nutrition.
- Take proper care of your body and do not violate the rules of personal hygiene.
- Use only high-quality medicinal and cosmetic products with natural ingredients.