Causes of intradermal nevi
Such a mole can be either congenital or acquired during life. Most often, intradermal nevi appear during puberty , which is associated with hormonal changes in the body.
Pregnancy, menopause, diseases of the gonads and adrenal cortex (especially hormone-producing tumors) also entail a strong change in the hormonal levels of the body, which can lead to the appearance of such formations on the skin.
What is such a mole?
Moles of this type are mainly measured in millimeters. But there are times when they reach several centimeters in diameter. The color can be anything from light shades to black. The main characteristic is homogeneity. There is also a depigmented nevus, when the mole is colorless or whitish. This indicates the absence of any pigment.
The intradermal nevus is soft to the touch and has a clear outline. The appearance resembles a wart, as it protrudes above the skin and most often has a rounded shape.
Intradermal nevus can often be detected only by touch
Symptoms
The appearance of such a mole does not entail the development of any characteristic symptoms .
When making a diagnosis, attention is paid to the features of the clinical picture, namely: localization, color, consistency, size, shape, pain and the presence of hair in the pigmented formation under study.
The final conclusion is made taking into account histological data (in case of removal of a nevus), dermoscopic examination and the general clinical picture.
Note! Intradermal nevi almost never appear on the extremities and are not dark in color.
Causes and symptoms
The exact cause of the appearance of intradermal pimples has not been established. However, experts identify some factors that can provoke the appearance of growths.
Factors:
- Heredity. This reason comes first. In newborn children, intradermal growths are almost always absent; they begin to appear later, most often during hormonal changes in the body.
- Exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Prolonged exposure to the sun and abuse of solariums lead to the formation of many moles.
- Increased sensitivity of the skin, frequent allergic manifestations.
- Disorders of fetal development in the womb.
In certain cases, the occurrence of intradermal formations is possible as a result of severe intoxication of the body.
The evolution of this type of nevus occurs in several stages. During development in the mother's womb, the unborn baby develops nevus cells - melanoblasts. Some of them accumulate deep in the skin before the birth of a child. In children, intradermal pezhins are invisible. With age, they gradually rise above the surface of the skin, becoming more pigmented and clearly defined. Intradermal nevus is characterized by certain signs.
Symptoms:
- When pressed, the softness of the formation is felt,
- The color is uniform throughout the birthmark,
- The boundaries of the growth are smooth, clearly defined,
- There is no redness or inflammation on the skin around the nevus.
Often such a mole looks like a black or dark brown wart, sometimes reaching a size of two centimeters.
Mechanism of disease development
The epidermis, the outer layer of the skin, contains melanocytes that produce the pigment melanin in response to exposure to ultraviolet radiation .
For unknown reasons, melanocytes may move into the middle layer of the skin , where they begin to multiply and synthesize melanin, which is externally recognized as the appearance of an intradermal nevus.
Changes in hormone levels , namely puberty, pregnancy, menopause, diseases of the endocrine system, provoke a similar migration of melanocytes and contribute to their reproduction .
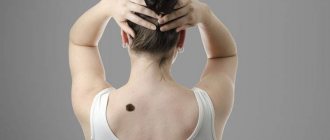
Photo 2. Nevi do not pose a danger to the body until they begin to change. It is recommended that you check your moles regularly. Source: Flickr (Julia)
Papillomatous skin nevus: types
There are several classifications of moles of this type.
By origin:
- Congenital . It occurs in utero as a result of an abnormal development of a certain area of the skin, that is, an increased accumulation of melanocytes in a certain place (hence its second name - papillomatous intradermal melanocytic pigment nevus).
- Purchased . Appears after birth, the causes of its occurrence have not been studied.
Note. Congenital nevus tends to grow. The growth process stops when a person reaches 20–30 years of age.
Based on the number of plaques there are:
- Organic nevus is a small single formation, consisting of many papillary processes covered with a single stratum corneum. The most common form.
A mole of this type is located on a broad base. Color can vary from light brown to black.
- Disseminated nevus - multiple formations dispersed throughout the body. Sometimes they may indicate the presence of some organic brain damage.
Multiple plaques of disseminated nevus. They tend to gradually increase in size.
By appearance they distinguish:
- pigmented papillomatous nevus;
- hairy
Types of intradermal nevi
The group of melanoform nevi, which also include intradermal nevi, contains several more common forms of moles with which differential diagnosis should be carried out during diagnosis. All of them are benign melanocyte tumors.
Papillomatous nevus
In its shape, such a formation resembles a round wart on a stalk, but is colored with pigment. Papillomatous nevus is usually located on the neck, face, chest or back. May contain hair follicles from which long hair grows. It has a rough surface and fairly large dimensions (from 10 mm).
Pigmented or melanocytic
Here, melanocytes are located not in the dermis, but in the epidermis. The formation is round or oval in shape, 4 - 5 mm, does not contain hair, has a smooth surface and dark color . Melanocytic nevus can be located on any part of the body.
Noncellular nevus
Such a mole is located on the border of the epidermis and dermis, that is, it is something between a melanocytic and intradermal nevus. It is dark in color, rises above the skin level, has a flat or spherical shape, and often contains bristly hair .
general characteristics
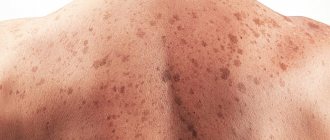
Intradermal moles form on the surface of the skin and initially look like elastic palipules or nodules, which usually change their shape and size over time. They can be flat or convex, small (diameter up to 6 mm) or large (diameter more than 1 cm). Each person can have a large number of moles on their body, which in most cases manifest themselves during adolescence or after about 40 years. For some, the number of tumors is in the dozens, for others it can reach more than a hundred.
Typically, intradermal skin nevi form in the neck, armpits, under the mammary glands in women, or in the intimate area. Less commonly, they can be found on the scalp, face, back, stomach, arms or legs. In this case, moles can be located singly or in entire clusters. Distinctive features of growths of this type are:
- homogeneous shade that does not change over time;
- clearly defined edges;
- soft, painless surface;
- absence of inflammation and other negative processes.
Intradermal melanocytic nevus transforms into melanoma in only 16% of cases.
Removal of intradermal nevi
Intradermal nevi do not pose a particular danger due to the fact that they are not prone to malignancy and degeneration into melanoma. However, such moles can be removed if they cause a cosmetic defect and the patient does not like (for example, if they are located on the cheek, forehead, neck).
If it is necessary to determine the nature of the formation, but diagnosis is difficult for some reason, then surgical removal followed by histological examination of the sample.
The disadvantage of this method is the frequent formation of a scar.
radio wave removal are more acceptable . They are carried out when the diagnosis is clearly established and do not leave scars, which is especially important when nevi are localized in open areas of the body.
Diagnostics
Only an experienced specialist can make the correct diagnosis. Diagnosis is carried out using various techniques.
First of all, an external inspection is carried out. The location, appearance, and shape of the nevus are analyzed.
If necessary, additional studies may be prescribed.
Methods:
- A smear of discharge from a nevus,
- Examination under a microscope using special staining substances.
- Dermatoscopy. Using a special device, the structure of the nevus is examined.
- Siascopy. The procedure allows you to examine the birthmark in quite detail and detail.
- Biopsy. Carried out after removal, it allows you to determine oncology.
Preventive methods to prevent disease
Medicine cannot yet provide specific preventive measures on this issue. It is currently considered impossible to prevent the occurrence of intradermal nevus. But it is possible to prevent a mole from degenerating into a poor-quality formation. The usual preventative measures will help here.
You should avoid visiting the solarium and avoid intense sunlight from 12 to 16 hours. It is advisable to visit spa treatments as little as possible. It is necessary to be especially careful with the sun for those people who have fair skin, due to the fact that it is more susceptible to the appearance of moles and melanomas. You should treat the tumors as carefully as possible and try not to injure them.
Let us remind you that if a mole is damaged, you must immediately go to a specialist. When any neoplasm occurs, you need to notice the smallest changes in the shape, structure or color shade of the mole. This will help diagnose skin cancer at the initial stages of the disease and promptly develop and begin a course of treatment.
Today you can find a huge number of folk methods for getting rid of unwanted skin formations. But the best effect of this healing will be countless scars and scars or no effect at all. You should be aware that it is impossible to treat intradermal nevi with non-traditional means. The course of treatment can only be carried out in specialized clinics under the supervision of professionals.
Features of treatment in the clinic
Surgeons at the Bilyak Clinic use gentle methods for excision of skin tumors. This allows you to carry out the operation as carefully as possible, without leaving a trace. Before prescribing your treatment, our doctors will conduct a thorough examination. This will help you understand whether you can remove the nevus, or whether it is better not to touch it. If a risk of degeneration into cancer is detected, surgeons will remove the intradermal skin nevus and then send the removed tissue for histology.
For advice about a suspicious mole, make an appointment now!
Why do deviations appear?
At the moment, medical practice cannot give an unambiguous answer to this question. It is clear that this kind of anomaly appears due to the improper functioning of the human skin. There are circumstances that can cause intradermal nevus, factors that provoke the appearance of such neoplasms:
- allergic skin diseases (and in general a tendency to allergies, increased skin sensitivity);
- intrauterine disorders of fetal maturation;
- unfavorable heredity;
- deviations at the hormonal level, for example, reorganization of the functioning of the body during pregnancy or menopause in women.
It is also worth noting that intradermal papillomatous nevus can develop as a result of severe toxic poisoning of the body.
Moles. Nevi.
It is vitally important to recognize the malignancy of a mole in time and distinguish it from a benign nevus. A timely diagnosis and accurate determination of the stage of melanoma development is the key to successful treatment.
In a conversation with the patient, it is clarified when the pigment formation arose (whether it is congenital or acquired), whether the type of nevus, its size, shape, color has changed. If changes occurred, what caused them (trauma, burns, scratching, removal attempts), how long ago the changes were noticed. It also turns out whether the nevus was treated and what plan this treatment was. During the examination of a mole or spot, its size, color, shape, and other visible characteristics are specified.
It is visually impossible to distinguish benign and malignant neoplasms with sufficient reliability; special studies are required for a more accurate diagnosis. It should be remembered that a biopsy (partial removal of a nevus) for histological examination is strictly unacceptable.
It has been established that any traumatic impact (mechanical, chemical, radiation) can cause the degeneration of some types of melanoma-dangerous nevi, especially borderline ones, into a malignant form. Therefore, a biopsy, as well as such types of cosmetic treatment as electrocoagulation, cryotherapy (cryodestruction), and removal of moles using chemicals are a threat to the development of a malignant tumor.
Material for histological examination of nevi is obtained by taking a smear from the surface of the neoplasm if there are cracks and bleeding on it. The next day, you can already have the finished result of tissue examination, which is carried out under a microscope.
Such a study should be carried out only in specialized oncological institutions, where it is possible, immediately after receiving the results under local anesthesia, to completely remove the neoplasm (with 3-5 mm from the edges) for further histological examination. In a few days the result will be ready.
Currently, a new diagnostic method has emerged - epiluminescent microscopy. The study is carried out using an optical device with artificial illumination (dermatoscope) directly on the surface of the body. A few drops of vegetable oil are applied to the pigment formation to create an epiluminescence effect (an oily environment appears between the object of study and the dermatoscope), then the device is placed at the site of study. This research method does not damage the nevus and is the most accurate in determining the structure of the pigmented neoplasm.
The computer diagnostic method is also one of the advanced research methods. Using a digital video camera, an image of the pigment formation is recorded and stored in the computer memory. A special computer program processes the received data, compares it with a database and issues an accurate conclusion.
The disadvantage of computer diagnostics and epiluminescent microscopy is their high cost, which prevents their widespread use in our country.