Causes of athlete's foot
Athlete's feet occurs due to infection with the pathogen Trichophyton mentagrophytes, which can also cause diseases such as athlete's foot in the groin area and athlete's foot nails. Healthy people can become infected with the fungus from sick people through contact in gyms, showers, public saunas, baths and swimming pools through objects of common use. Mycelium and fungal spores are present in scales exfoliated from the stratum corneum of the skin, which the patient quite often loses with athlete's foot. The fungus that gets onto rugs in shower stalls, rugs, washcloths and shoe insoles in this way can persist there for a long time, especially if the environment is warm and humid.
Not all people infected with the fungus Trichophyton mentagrophytes will develop athlete's foot. Favorable conditions for the disease are trophic disorders of the legs, which can manifest themselves in varicose diseases with chronic venous insufficiency, diabetes mellitus, deep thrombosis of peripheral vessels, atherosclerosis, polyneuropathy, vegetative-vascular dysfunction. The occurrence of a fungal disease can be facilitated by increased sweating of the feet, alkaline sweat reaction, narrow spaces between the toes, and flat feet.
STATUTE BEHIND THE TOPIC
Finger's pseudofurunculosis symptoms and treatment in newborns and children
In the journal “Neurology and Neurosurgery. Eastern Europe" (2018; Vol. 8, No. 2), an article by colleagues from Belarus was published, which presented research data assessing the impact of an original comprehensive rehabilitation system on the quality of life in patients who had suffered a cerebral stroke (MI) with a history of cardiac pathology . The negative impact of concomitant heart diseases on the quality of life of patients after MI has been established. It has been proven that the developed comprehensive system of new approaches to the rehabilitation of such patients is safe, does not have a negative impact on the level of quality of life, and for a number of parameters there is a more pronounced tendency to improve a number of indicators compared to previously generally accepted measures.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN) are rare secondary pathological conditions that a small number of clinicians experience over the course of their professional lives, and the successful results of treatment You can write even less. The practice of managing such illnesses among doctors in many specialties and health care settings varies greatly. This is explained by the limited evidence base based on the results of therapy for these nosologies. Thus, in many explicit recommendations, the term SSD/TEN covers a new spectrum of manifestations of illness, so that SSD, TEN and SSD/TEN (overlap syndrome) are avoided and the same principles of treatment are lost.
At the 9th scientific and practical conference of the Association of Arrhythmologists of Ukraine, which took place on the 16th-17th in Kiev, the problems of arrhythmias, the complexity of this pathology and current treatment strategies were thoroughly considered . Among the many current reports, master classes, and discussions, the lecture of Yuri Mikolayovich Sirenko, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Cardiology and Functional Diagnostics, attracted the attention of the listeners. from the Medical Academy of Postgraduate Studies named after P.L. Shupik, head of the department of symptomatic hypertension at the Institute of Cardiology named after Academician M.D. Strazhesk NAMS of Ukraine (m. Kiev).
The IX scientific and practical conference of the Association of Arrhythmologists of Ukraine was held in Kyiv on May 16-17. Among the many reports, lectures, and discussions presented at the event, the symposium “New opportunities of NOACs in stroke prevention: from patients with atrial fibrillation to patients with sinus rhythm” aroused interest, in particular. As part of the exchange of scientific opinions, two reports were made - Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Oleg Sergeevich Sychev and Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elena Akindinovna Koval.
01 Aug 2020 12
Athlete's squamous
Athlete's foot appears as red plaques with grayish-white peeling or flat papules that appear on the skin of the arch or on the sides of the foot. The lesions may resemble plaques typical of psoriasis and have clear boundaries. Along the circumference of the plaques there is a border consisting of peeling skin with single small bubbles. Peeling is often combined with symptoms of plantar hyperkeratosis in the form of cracks and yellow calluses on the surface, which resemble manifestations of mechanical dermatitis. Characterized by intermittent and moderate itching sensations.
Types of calluses on the feet
Vasculitis - what kind of disease is it Photos, symptoms and treatment in adults
Corns affect the sides of the foot, the heel area, the pads of the toes, and the areas located under and between the toes. At the first stage, a small painless spot appears, which over time becomes yellow and becomes denser. As the callus develops, it becomes larger and may take root. The rod penetrates deep into the skin and reaches the nerve endings, causing pain.
Dry calluses are most common on the feet, since the skin in this area is quite rough and dry.
Dry callus on the foot
As a result of constant rubbing in certain areas of the foot, blood circulation is disrupted and the natural keratinization of the epidermis increases. This is how a dense growth of dead tissue appears, so at the formation stage it rarely causes pain.
Core calluses
Over time, the dry tumor increases in size, grows into soft tissue, reaches the nerve roots and becomes a source of severe pain. The presence of a rod can be determined even by visual inspection: a grayish-white spot forms inside the callus. This subspecies is the most dangerous. It is very difficult to get rid of deep roots at home.
Water calluses on the sole of the foot
Wet callus is also called watery callus or simply dropsy. In structure, it is a leather pouch filled with a clear liquid (lymph). If small capillaries are damaged, blood spots inside the formation can be seen. Such a callus can burst on its own or with outside help (for example, during a puncture with a needle). If infection occurs, a rotting process will begin inside the seal.
Dyshidrotic athlete's foot
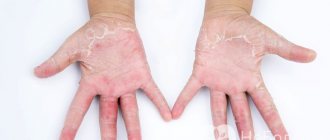
Dyshidrotic athlete's foot manifests itself in the form of small rashes of blisters on the skin. Most often they are located on the arches of the feet, but at the same time the skin of the soles, folds between the toes and the toes themselves can be affected. Having previously increased, the bubbles merge and form multi-chamber formations, after the resolution of which erosive elements of a pink-red hue form on the skin. Patients report itching and pain. With a pronounced inflammatory element, swelling and skin redness occur, which resemble dyshidrotic eczema in clinical manifestations.
Drug therapy
Fungicides are highly effective against epidermophyton floccosum. Before the appearance of vesicles - terbinafine ointment 2 times a day for up to 14 days; on nails up to 28 days.
Oral forms:
- Itraconazole 50 mg once a day for 7 days, the cycle is repeated after 21 days;
- On the nails - itraconazole 500 mg 3 times a week with a break of 14 days, terbinafine 150 mg once a day for 14 days with a break of 21 days.
Average duration of therapy: on the skin 28 days; on the feet – 90 days; on nails – 120 days. If there are several pathogens, the doctor may prescribe fluconazole as an additional drug.
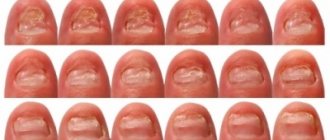
Diagnosis of athlete's foot
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out by a dermatologist or a specialist in the field of mycology. As a rule, diagnosis consists of conducting a luminescent study, determining the pH balance of the skin and examining the lesions using a dermoscopic examination. Scrapings from the affected nail and skin are examined under a microscope to identify fungal spores and mycelial filaments, which must be distinguished from the loop-shaped or mesh structures of the mosaic fungus, which is a product of the breakdown of cholesterol in the skin.
Examination under a microscope will not reveal which type of fungus caused the disease. For differential diagnosis of the fungus Trichophyton mentagrophytes from other pathogens of fungal diseases (rubromycosis, trichophytosis, pityriasis versicolor, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis), bacterial culture of scrapings is also carried out on nutrient media.
When diagnosing parallel diseases, additional examination may be required by specialists such as an orthopedist, podiatrist, vascular surgeon, endocrinologist or phlebologist.
Diagnostic measures
With such problems, the patient should seek professional medical help from a mycologist. During the appointment, the doctor will conduct tests such as:
- Dermoscopic examination
- Scanning a surface using a special type of luminescent equipment.
- Skin pH assessment.
- Scraping test.
- Sowing to check the nutrient medium.
In addition, the expert can refer the patient for a consultation with colleagues in the orthopedic, phlebological, endocrinological and other departments.
Treatment of athlete's foot
Treatment of fungal foot disease is a two-stage process. At the initial stage, in the squamous form of athlete's foot, hyperkeratotic layers and scales are removed; in the dyshidrotic and intergriginous form, the acute inflammatory process is relieved. In the first case, when treating athlete's foot, drugs with a keratolytic effect are used (salicylic acid and lactic acid, baths with soap and soda solution for the feet), in the second case, the use of antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs). In case of athlete's foot, the nail affected by the fungus is surgically removed.
The main stage of treatment of the disease consists of treating fungal-affected areas of the skin and/or the removed nail bed with drugs with antimycotic effects (Castellani liquid, Mikoseptin, nitrofungin, Mikozolon ointments). If the course of athlete's foot is long-term, persistently untreated, and accompanied by damage to the nail plate, experts prescribe systemic therapy with antifungal agents to patients: Diflucan, Orungal, Nizoral, Lamisil, etc.
Generalized rubromycosis
Rhinophyma of the nose: types, causes, symptoms and treatment
Generalized rubromycosis in most patients develops after long-term existence of mycosis of the feet, hands and nail plates, which greatly facilitates diagnosis. Pathology of the endocrine system, immunodeficiency states, metabolic disorders, long-term use of antibiotics, cytostatics and glucocorticoids contribute to the development of the disease.
Fungi spread through blood and lymphatic vessels. A large number of pathogens accumulate in the lymph nodes. The disease affects the smooth skin of the chest, back, abdomen, groin area, buttocks, thighs, legs and upper extremities, often in places of friction, bruises and burns.
There are 3 types of smooth skin lesions: erythematosquamous, follicular-nodular and infiltrative-suppurative. Each of the three types of inflammation can manifest itself independently or in combination in the same patient.
Rice. 29. Rubrophytosis of smooth skin. Erythematosquamous form.
Erythematosquamous type of inflammation
Against the background of hyperemia, foci of peeling appear, which over time acquire a bluish tint, increase in size due to peripheral growth, merging, forming large areas of inflammation. Along the periphery there is an intermittent ridge consisting of papules, pustules and crusts. Vellus hair is often affected. The disease lasts a long time with periodic exacerbations in the warm season, and is resistant to treatment.
Rice. 30. Rubrophytosis of the skin of the back.
Follicular nodular form of rubrophytosis
This type of lesion is often localized in the forearms, legs and buttocks. Foci of inflammation are prone to peripheral growth and fusion. The process forms in the dermis and affects the hair follicles. Infiltrates form on the affected areas of the skin, which over time become deep, similar to boil-like nodes. This form of the disease should be distinguished from erythema nodosum, erythema induratum of Bazin, nodular vasculitis, and papulonecrotic tuberculosis. When the pathological process is localized on the face, the disease should be differentiated from tuberculous lupus and erythromatosis.
Rice. 31. Follicular nodular form of rubromycosis of the leg.
Rice. 32. Rubromycosis of the legs.
Infectious agents
Foot rubromycosis is a type of dermatomycosis. The main causative agent of the disease is red trichophyton (Trichophyton rubrum, Epidermophyton rubrum, pathogenic fungus-dermatophyte, anthropophil). The incubation period of infection can be several days or weeks.
Varieties of polymorphic trichophyton red:
- Velvety;
- Fluffy;
- Plaster-like;
- Mealy;
- Coriaceous.
Trichophytons have a red or bright crimson color, are prone to mutations, and affect the surface layer of the epidermis and subcutaneous fatty tissue. No immunity is developed to rubromycosis.
Prevention
In order to prevent infection with epidermophytosis, it is recommended to follow a number of rules. First of all, it is necessary to ensure good microcirculation of air in the area of the external genitalia. It is important to regularly carry out hygiene procedures, at least 2 times a day. This is especially true for women suffering from excessive sweating.
Following precautions will also help prevent infection. You should not allow others, even close relatives, to use personal belongings, especially hygiene products.
Underwear should be selected from natural materials of anatomical shape, avoiding tight or lace underwear. It is important not to forget to change clean linen daily.
Types of fungal skin lesions
Mycosis caused by yeast-like organisms is a consequence of improper use of antibacterial drugs and the result of infection from a source of infection. There are many types of fungus on the body. The most common are:
- Dermatophytosis (dermatomycosis). Deep skin lesions caused by yeast or mold fungi (favus, trichophytosis, rubromycosis, microsporia). This disease provokes an inflammatory process. May be accompanied by the appearance of spots or plaques of any size from pink to red.
- Keratomycosis. Flexible affects the top layer of skin. This category includes erythrasma, pityriasis versicolor, axillary trichomycosis, and nodular trichosporia. With this type of disease, inflammation may be absent. The fungus forms hard small nodules with purulent contents on the skin.
- Deep mycosis. It is characterized by damage to the subcutaneous tissue, musculoskeletal system, internal organs, mucous membranes, and nervous system. The skin is often covered with fistulas and warts.
- Candidiasis. Pathological damage to the mucous membranes by yeast fungi. Often such an infection can be found in women under the breasts, in the armpits, and groin area.