People infected with herpes should know that once the virus has entered the body, it cannot be removed. No medicine can do this. With the help of drugs, you can only reduce the intensity of symptoms, shorten the intervals between exacerbations, and improve overall well-being. And the most important fighter against infection is immunity. If it is strong, then relapses of herpes are not scary for a person. Frequent exacerbations, or chronic herpes, indicate that the ability to resist, the activity of the immune response, and the degree of adaptation of the body are insufficient. And we need to fight this.
Key Facts
Of the 8 types of herpes simplex virus, the most common are 1 and 2. In medicine, they are designated HSV-1 and HSV-2. The following are the features based on which the infection was classified:
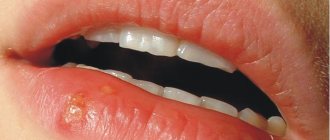
- Type 1 virus is most often oral herpes (less often genital), and is characterized by the appearance of a rash on the lips. The disease is transmitted from person to person through oral contact (kissing), as well as through household means (using other people's dishes, hygiene products).
- Type 2 virus is an infection that causes rashes on the human genitals and is transmitted through sexual contact.
- Both types of HSV are incurable; a person becomes a carrier of the infection for the rest of his life.
- Both types of infection are often asymptomatic.
Note! Herpes simplex virus type 2 often causes HIV infection, which destroys the human immune system. Therefore, it is very important to diagnose herpes in a timely manner and take all measures to introduce the virus during the dormant period.
Epidemiology
HSV is widespread, since antibodies to it have been isolated from 90% of the world's population over 40 years of age. Primary infections with HSV-1 occur mainly in childhood, namely during the first years of life (6 months - 3 years).
The source of the first strain is people whose disease is in the period of exacerbation, because it is in this case that the pathogen is released into the external environment in the largest possible quantity.
Symptoms and signs of HSV-1
Most often, infection with herpes simplex type 1 occurs in early childhood (usually between the ages of 6 months and 5 years), and it manifests itself in the form of acute herpetic gingivostomatitis.
Herpes is a viral disease. Therefore, it is very often transmitted from mother to child. What to do if your baby has herpes, how to treat it and how dangerous is it? You will find all the information in this article.
Clinical features of the disease:
- Acute onset of the disease accompanied by fever (fever, chills).
- The child is irritable, it hurts him to drink and eat.
- The occurrence of gingivitis (the tongue and gums become noticeably swollen, red and sometimes bleed).
- Increased saliva production (due to pain when swallowing).
- Vesicular eruptions on the tongue, oral mucosa and palate, sometimes affecting the lips and face (blisters may rupture and stick together to form large ulcerated areas).
- Inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes.
Note! Once the virus has entered the child’s body, it remains there forever. It makes itself felt again with rashes as soon as the child’s immunity decreases.
Such lesions are quite painful. The described symptoms may persist for 10 to 14 days. Primary HSV-1 infection of the oral and pharyngeal mucosa in adolescents and adults usually manifests itself not as gingivostomatitis, but as acute pharyngotonsillitis (upper respiratory tract infection). The disease is accompanied by an increase in temperature to 37 - 38°C, malaise, discomfort when swallowing and headache, as well as vesicular lesions of the tonsils.
But most often, type 1 herpes is asymptomatic, and most infected people do not suspect that they are sick. They consider a rash on the lips, which is preceded by a slight burning, itching and tingling, to be a sign of a cold. After the initial infection, such a rash always occurs again, and each person has their own frequency of its occurrence.
Herpes on the lips is common, so it is important to know how quickly you can get rid of it.
Genital herpes type 1 occurs with barely noticeable signs of the disease (several ulcers or blisters in the genital area) or is completely asymptomatic. The frequency of recurrence of rashes is less than with oral herpes.
You can learn more about the existing types of genital herpes and methods of its prevention from the following video:
Virus danger
The danger of herpes for adults lies in the possibility of the following complications:
- conjunctivitis;
- eczema;
- psoriasis;
- prostatitis (in men);
- cervical erosion (in women);
- infertility;
- oncology;
- pathology of the gastrointestinal tract.
The danger of HSV for children is:
- early development of psoriasis;
- neurological abnormalities;
- damage to the respiratory system.
Symptoms and signs of HSV-2
When infected with herpes simplex virus type 2 (genital infection), there are no symptoms at all, or the disease makes itself felt by the appearance of a rash in the form of ulcers or blisters with liquid contents on the genitals and anal area. The rash is often accompanied by body aches, fever and enlarged lymph nodes in the groin area.
Note! Of all people with HSV type 2, only 10 - 20% of people are suspected of being infected in a medical facility. Therefore, in order to avoid infection with genital herpes, which is sexually transmitted, doctors recommend refraining from casual sexual intercourse. Herpes type 2 cannot be cured; the virus remains in the human body for life.
After the initial appearance of a genital rash caused by type 2 herpes, repeated rashes do not appear as often as with type 1 herpes. A warning sign that blisters or sores may soon appear on the genitals is a sensation of shooting pain or barely perceptible tingling in the legs, buttocks and thighs.
Complications
Considering that the HSV-1 strain develops very quickly, some of the pathogens may move into the eyes, which will cause a complication such as ophthalmoherpes, and in the future this may cause a decrease in visual acuity, up to complete blindness.
Because of herpes, the central nervous system and PNS are affected, which can cause paralysis. During the disease, the kidneys, adrenal glands and genitourinary system experience considerable stress.
How to recognize infection in newborns?
Signs of a child being infected with herpes types 1 and 2 can be noticed at 1-2 weeks of the baby’s life. There are 3 clinical forms in which the infection can manifest itself: localized, generalized, herpetic lesion of the central nervous system.
Localized (limited) infection
The infection spreads throughout the skin and mucous membranes (mouth, eyes) in individual or multiple blisters (1.5 to 2 mm in diameter) with transparent contents. This rash appears from 5 to 14 days of the baby’s life. In this case, systemic inflammation syndrome (general inflammation of all body systems as a response to the action of the virus) is absent. The skin under the blisters is swollen and red. After opening the blisters, ulcers with a smooth bottom remain in their place. The wounds heal within 2 weeks.
Note. Against the background of herpes infection, newborns may develop inflammation of the eyes (cornea, sclera, conjunctiva, choroid), as well as the optic nerve. In the absence of adequate treatment, localized herpes becomes a generalized form or leads to complications in the form of infection of the central nervous system.
Generalized (spreading) form
This type of herpes is most often a neonatal infection, which is characterized by the appearance of symptoms in the period from 5 to 11 days of a newborn’s life. Sometimes generalized herpes manifests itself in the first day of a baby’s life, which means that its infection could occur in the womb (about 5% of cases), during the passage of the birth canal (85% of cases) or immediately after birth (15% of cases) .
Symptoms of generalized herpes in an infant:
- Constant lethargy, frequent regurgitation.
- Increase or decrease in temperature.
- Microcirculation disorder (damage to capillaries) is the cause of ischemic diseases.
- Apnea (stopping breathing during sleep for more than 10 seconds).
- Signs of pneumonia (fever, heavy sweating, chest pain, frequent coughing).
Note. Against the background of infection, an infant's spleen may become enlarged, blood sugar may decrease significantly, and bilirubin in the blood serum may increase (destroys red blood cells). Pathological changes may affect the liver and adrenal glands. Signs of infectious-toxic shock (nausea, vomiting, fever) are likely to appear.
Approximately 5% of patients with HF (generalized form) of the disease show signs of herpetic meningoencephalitis (infection of the brain). In this case, the rash appears on the mucous membrane of the nose and mouth from the 2nd to the 8th day after infection. Sometimes, with HF, there are no specific rashes in newborns.
Herpes CNS
From the 12th to the 17th day of life, an infant may show signs of infection of the central nervous system (CNS - consists of the brain and spinal cord) in the form of encephalitis and meningoencephalitis (inflammation of the lining of the brain, which is a consequence of asymptomatic encephalitis and meningitis).
Signs of herpetic lesions of the central nervous system:
- Increase in body temperature to 39 - 40°C.
- Lethargy alternates with excitability.
- Uncontrolled and impulsive contraction of the muscles of the limbs and body.
- Poor appetite, against the background of which difficult-to-relieve cramps develop.
Note. In 40% of those infected with this type of herpes, there are no rashes on the body and mucous membranes.
If the baby's central nervous system was infected in the womb, he may be born with microcephaly (small brain mass, small skull size), hydrocele, or intracranial calcification (salt deposits).
A specialist will tell you in the following video how to prevent this problem from occurring, as well as what to do for a pregnant woman who has genital herpes:
How does infection occur?
Primary infection with herpes occurs in several ways:
- Contact and household. The virus is transmitted through unsterile instruments, dirty dishes, unprotected sex, and kissing. Infection can occur through objects on which biological material of the carrier remains. However, herpes infection is transmitted less frequently through the personal belongings of an infected person. The virus does not live long outside the human body.
- Airborne. When leaving the body, type 1 herpes can become airborne. You can become infected at a distance of a few centimeters from the carrier.
- Less common methods of infection include organ transplantation. Infection can occur in utero. The virus is transmitted from a carrier mother to her child through the placenta or during the baby's passage through the birth canal.
The principle of virus penetration into the body
After a healthy person comes into contact with a person infected with herpes simplex, a large number of pathogenic microbes enter the mucous membrane or skin of the first person. As a result of the collision of viral agents with epithelial cells, some of them attach to the epithelium due to glycoproteins (spikes made of adhesive protein molecules, attachment proteins).
Note! During the first hours after infection, the reversible adhesion stage operates, during which microbes can detach from epithelial cells. This means that a person can still have time to rid his body of the herpes virus. For this purpose, the skin or mucous membrane can be treated with an antiseptic solution (chlorhexidine) and take an antiviral drug recommended by a doctor (Zovirax, Acyclovir).
After the virus envelope has fused with the basement membrane (the outer wall of the cell), changes occur in its surface structure. After which the pathogenic microbe leaves its protective shell, penetrates inside the cell and settles in its nucleus. The latter can be destroyed and begins to produce not its own DNA but the DNA of the virus.
The herpes virus is as dangerous as the papilloma virus. In this article, you will learn everything you need to know about the papilloma virus, as well as how you can cure it.
9 hours after infection, viral agents leave the cell nucleus into its liquid environment, where they acquire a new shell. A day later, microbes in a new form enter the blood, where they stick to red blood cells and spread throughout the body. A cell that has produced millions of viruses dies.
Prevention
Although not all people experience the clinical symptoms of the herpes virus, everyone should have an idea of how to prevent a flare-up. The main thing is to adhere to a number of conditions provided by experts:
- To begin with, it is important to strictly adhere to the basic rules of personal hygiene, since the virus can be transmitted through personal contact.
- Eat exclusively from separate and clean food.
- Do not use general cosmetics.
- Use barrier methods of contraception during sexual intercourse, refusing them at the moment when the partner has obvious herpetic lesions on the lips or genitals.
- It is very important to adhere to proper nutrition. Products must contain a sufficient amount of useful substances so that the immune system is constantly strengthened and the disease cannot become more complicated.
- Stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle and engage in active sports.
- Maintain a rational sleep schedule.
- If you have cold symptoms, start treatment as soon as possible. Patients who are not treated have weak immunity, which means that the virus has all the prerequisites for reproduction.
Diagnosis of herpes types 1 and 2
Asymptomatic herpes types 1 and 2 can be reliably diagnosed by ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) based on the presence of protective antibodies in the blood, which, when foreign agents appear in the body, the human immune system begins to produce:
- Ig G - appears as a result of primary infection of the body with herpes, as well as as a result of relapses.
- Ig M - antibodies begin to circulate in the blood within a few hours after infection.
After the initial infection of a person with herpes simplex occurs, the virus permanently settles in his nerve cells, and at the acute stage, its particles appear in the blood.
As a result of enzyme immunoassay, two types of reactions can be obtained:
- Qualitative - allows you to determine the presence of immunoglobulins Ig G and Ig M in the blood, the type of herpes (1, 2), and the resistance of immunity to the virus.
- Quantitative - helps to find out the amount of antibodies in the blood and assess the stability of the immune system.
Table of possible results (qualitative reaction):
| Ig G | Ig M | Meaning |
| — | — | High risk of herpes infection. |
| + | — | There is immunity to the virus. An exacerbation is possible when a cold or other illness occurs that reduces the level of general immunity of the body. |
| — | + | Sign of primary infection (urgent treatment required). |
| + | + | Recurrence of herpes (renewal of the disease). Treatment is prescribed in the presence of clinical symptoms. |
Note! The results of quantitative reactions are interpreted differently by attending physicians, because Different clinical diagnostic laboratories use consumables from different manufacturers.
During pregnancy
A woman should undergo testing if she is planning a pregnancy. If herpes is detected, including in the intimate area, it is necessary to undergo a course of treatment prescribed by a doctor. If this is not done, then the woman risks not carrying the baby to term.
Infection with herpes type 1 during pregnancy is dangerous, since the mother’s body will not be able to produce antibodies that could protect the fetus.
All doctor’s prescriptions must be followed in order to cause as little harm as possible to the unborn baby.
Drug treatment
Herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 cannot be completely cured. There are no prophylactic agents that could prevent infection. Moreover, the infection cannot be suppressed with antibiotics.
Herpes therapy in adults
- HSV type 1 - the use of direct-acting medications is recommended. Today, the most prescribed drug is considered to be: “Acyclovir” (ointment, tablets, solution for intravenous injection). The use of an antiherpetic drug in accordance with the instructions can reduce the duration of the disease and the number of its relapses.
- HSV type 2 is a more serious type of disease, therefore, in addition to acyclovir, patients are prescribed immunocorrective drugs “Viferon”, “Anaferon”, as well as drugs that help strengthen the body’s defenses (“Amiksin”, “Cycloferon”) and droppers with saline solution. The latter reduce the concentration of the virus in the blood.
Treatment of newborns
If the child is infected in the womb or during the passage of the birth canal (neonatal herpes), then for any form of infection (localized, generalized, meningoencephalitis), treatment with antiviral drugs is practiced:
- Intravenous administration of acyclovir (dose from 45 to 60 mg/kg - determined by the doctor, taking into account the type and form of the virus). Enteral (through the stomach) administration of the drug is not considered effective. The course of treatment is 10 - 21 days (the duration depends on the form and type of the virus).
- Herpetic lesions of the eye mucosa are treated with a 3% solution of vidarabine and a 1% solution of iododeoxyuridine.
- The skin of newborns is treated 3 times a day with Acyclovir or Zovirax ointment.
- In conditions of immunodeficiency, newborns can be prescribed intravenous immunoglobulins (antibodies Ig G and Ig M), the list of such drugs includes “Intraglobin” and “Pentaglobin”.
- For herpetic meningoencephalitis, anticonvulsant therapy is practiced.
Note! During the period of treatment of the newborn, breastfeeding is not stopped (unless the herpetic eruptions have spread to the mother’s breast), since the likelihood of HSV penetrating into milk is very low.
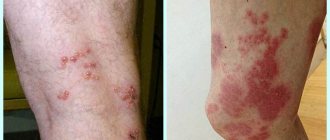
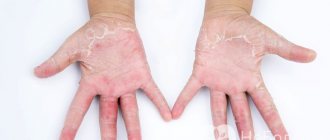
Signs of the disease
Despite the division of herpes types into viruses of different localizations, the general symptoms of the disease are defined in a single key:
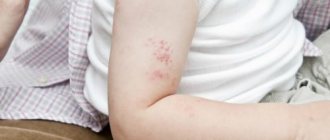
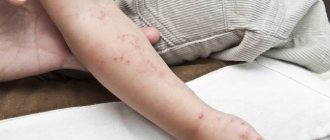
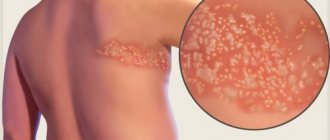
- Redness and itching of the skin.
- Formation of a group of watery pimples.
- Irritation of the mucous membranes of the eyes.
- Swelling of the nasal mucosa.
- Loss of strength, lethargy.
- Increased body temperature.
- Fever.
If you notice some of these symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Traditional methods
In addition to medications, for the treatment of herpes infections in adults and children, herbal preparations with a strong antiviral effect are recommended. Licorice root and St. John's wort have this property. You should also pay attention to the medicinal properties of echinacea, which acts as an antibiotic and at the same time improves immunity.
Licorice root tea
Ingredients:
- Licorice root - 2 tsp.
- Cool boiling water - 1 tbsp.
How to prepare: pour a glass of boiling water over the plant material, cover, and let steep for 30 - 45 minutes.
How to use: drink 3 glasses of this tea a day, no more, since licorice is a poisonous plant.
Result: due to toxicity, the medicinal properties of the plant are also manifested; licorice root tea suppresses the growth and development of the herpes virus.
Note. The drug is contraindicated for pregnant women, hypertensive patients and people with renal failure.
St. John's wort compress
Ingredients:
- St. John's wort - 2 tbsp.
- Boiling water - 2 tbsp.
How to prepare: pour boiling water over the herb, simmer over low heat for 5 minutes, once the broth has cooled, strain it through cheesecloth .
How to use: moisten a tampon in the broth, apply it to the skin affected by herpes ( do such compresses 4-5 times a day until complete recovery).
Result: a compress with a decoction of St. John's wort kills the herpes virus, relieves inflammation, and relieves pain.
Echinacea alcohol tincture
Ingredients:
- Medical alcohol or strong moonshine - 1 l (70°).
- Freshly picked echinacea flowers - 1 tbsp.
How to prepare: rinse the flowers, place them on a towel to remove moisture. Transfer the raw materials into a glass jar and fill with alcohol, close the lid. Place in a dark place for 14 days. Strain. Store in a dark glass container, always in a cool place.
How to use: 2 tsp. add tinctures to 1 tbsp. water, drink during the day. Moisten a cotton swab with undiluted tincture and apply it to the herpes.
Result: when taking medicine from echinacea internally, it is possible to suppress the reproduction of the herpes virus and prevent its spread throughout the body. External use helps clear the skin of rashes.
Preventive measures
Following good personal hygiene will help you avoid getting infected with herpes. After visiting public places, you must wash your hands with soap. Even members of the same family are recommended to have separate dishes. A person who has discovered that he has a herpetic infection must temporarily refuse tactile contact with others.
Protected sex reduces the risk of contracting herpes. However, it is not recommended to enter into casual relationships or frequently change partners. If symptoms of the disease appear, sexual activity should be avoided for the period of treatment. Sexual relations can be resumed after signs of herpes are eliminated. If the virus is in a passive state, its transmission is virtually impossible.
Carriers of herpes can reduce the number of relapses of the disease if they avoid stress and hypothermia. Strengthening the immune system is the main preventive measure. Proper nutrition and giving up bad habits will help support the immune system. Playing sports has a positive effect on the body. The patient is recommended to take vitamin complexes twice a year.
Question answer
Is the herpes virus inherited?
Scientists have proven that HSV is not a hereditary disease. In order for the virus to be inherited by a child, its genome must be integrated into the DNA of the parents after entering the body. This doesn't happen.
Can you get herpes by using the same household items as an infected person? How long can the herpes virus survive on household items?
The likelihood of becoming infected with HSV through household items is low, but still exists. The herpes virus, without the conditions provided by the human body, cannot exist for more than 4 hours in the environment.
Why does one of the spouses show signs of genital herpes several times a year (husband/wife), while the other does not?
This means that the second spouse has a strong immune system, which does not allow the herpes virus to become active and thereby prevents its exacerbation.
What is the danger of genital HSV for pregnant women?
Intensive development of the infection and the lack of treatment can lead to fetal death, the birth of a premature baby, and the impossibility of secondary conception.
Laboratory tests show that there is no herpes virus in the blood, but why then do herpetic rashes appear from time to time?
If HSV of any type enters the human body, it is impossible to completely destroy it. Thanks to antiviral and immunostimulating drugs (see section “Drug treatment”), it is possible to eliminate the exacerbation of the disease and significantly reduce the concentration of the virus in the blood. In this case, the virus will continue its inactive existence in nerve cells until the body is subjected to, for example, stress, hypothermia or re-infection.
Causes of exacerbations of herpes
Recurrent herpes occurs for one reason - a weakened state of the body. Immunity may decline due to:
- mental and emotional overload;
- frequent stress;
- hypothermia, overheating;
- failure to maintain proper nutrition;
- vitamin deficiency;
- constant overwork;
- acute respiratory viral infections;
- severe infections (HIV, tuberculosis, diabetes, hepatitis, etc.);
- the presence of malignant tumors;
- taking antibiotics and glucocorticosteroid drugs;
- hormonal changes (pregnancy, menopause, puberty, hypothyroidism, etc.);
- overweight and underweight.
What to remember:
- Herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 are the most common infections.
- A herpetic infection can affect a child while still in the womb.
- HSV cannot be completely cured; the virus remains in the body forever.
- Often, type 1 and 2 infections are asymptomatic; an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay allows us to clarify its presence in the body.
- Exacerbation of herpes is relieved with the help of antiviral, immunostimulating and immunocorrective medications. (see section “Drug treatment”).
In children
Do not think that herpes does not pose a danger to a child. The rash will go away, but traces will remain in the body. The virus can infect internal organs, the nervous system and cause many more complications.
In the first months of life, the body of a newborn baby is protected by the mother’s immunity.
Along with breast milk, he also takes in antibodies produced by the mother’s body. But if a woman is infected with herpes, then the presence of herpes virus in the baby is possible.
Herpes is often diagnosed in children at 2 years of age. By this time, the mother’s protection is no longer there, and the body has not yet produced its own antibodies. But by the age of 5, the body is able to resist the virus, as it begins to produce substances necessary for protection.
Interpretation of results
- Negative/Normal – no herpes virus is detected, but HSV infection may be present in the body. This means that the sample does not contain enough cells to be detected. If there are signs of illness, you must undergo a re-examination.
- Positive/Abnormal – HSV was found in the biomaterial. The infection is active or has been in the past.
Cell culture and PCR tests may give a false negative result if the ulcers have turned into sores and have begun to heal, or if there is a recent infection. This indicates that the virus is present in the body, but has not been detected. False-positive results are also possible. They involve repeated screening.
A blood test determines whether a person has ever been exposed to the virus and the type of infection. Such a test cannot determine the presence of herpes at the moment. The blood test is carried out for more than a week so that antibodies to the virus have time to form.
Video
You can also watch a video where they will tell you what herpes is and how you can get rid of it.
Visceral herpes is the most dangerous form of the disease, which can lead to the death of the patient. It is possible to prevent the development of serious pathology if the virus is detected at an early stage and treatment is started in a timely manner. Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely remove herpes from the body. Currently, active developments are underway in the field of gene therapy, but these methods have not yet received widespread use.
Diagnostics
First of all, doctors focus on anamnesis (collection of complaints) and external manifestations. If there are doubts or if the patient wants to undergo preventive diagnostics (when planning pregnancy, for example), then a blood test is prescribed.
Basic laboratory methods:
- Serological study . With its help, specific antibodies are searched for in the blood - immunoglobulins M. The method does not allow determining the exact type of virus.
- Culture method . The patient's blood is placed in an environment in which the virus can actively multiply. When it “grows up”, the laboratory assistant recognizes its type. The method gives reliable results, but you have to wait several weeks for these results.
- ELISA . Using this method, specific immunoglobulins M and G are found, which indicate an exacerbation of the disease.
- Blood for herpes PCR, RIF . The latest generation methods allow you to quickly determine the type of virus and the severity of the exacerbation. Disadvantage: high cost of research.
What is PCR diagnostics, how accurate is it and how to donate blood for herpes for more accurate results, you will learn in this article.
Where is blood taken for herpes? In all cases, blood is taken from a vein. It must be taken on an empty stomach. Research can be carried out both in the acute phase and during remission.