Papillomavirus is a disease that has recently become known, but doctors say that it can lead to cancer. At the same time, according to statistics, most of the population is infected. Are these viruses really that dangerous and what are the differences between the strains? These are the questions that every person who suspects a virus asks himself. The papillomavirus group includes more than 170 strains. Some of them are oncogenic, while others are not. They cause various types of papillomas, which differ in appearance - genital warts, papillomas, warts and others.
What are papillomas?
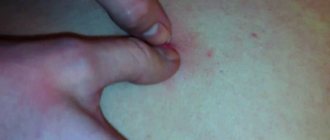
Papilloma, warts and condyloma are all a consequence of the activity of the papillomavirus or HPV. The virus enters the human body and is inactive for a long time. Under the influence of provoking factors, HPV activation occurs. This is manifested by the formation of soft growths on the skin and mucous membranes.
Factors that provoke activation of the virus:
- decreased immunity;
- stress;
- lack of vitamins;
- weakening of the body after long-term treatment;
- skin injuries.
Infection with the virus occurs mainly through sexual contact. However, transmission of HPV in everyday life is possible under the condition of a severe decrease in immunity or the presence of lesions on areas of the skin that have been in contact with the carrier of the virus.
Papillomas are a manifestation of the activation of the human papillomavirus
HPV is equally common in men and women. Transmission of the virus to a child is possible during childbirth, when passing through the birth canal.
As a rule, in most cases the virus manifests itself against the background of decreased immunity. This occurs after infectious diseases, long-term treatment with antibacterial drugs, or vitamin deficiency.
The presence of HPV in the body is indicated by the appearance of soft growths. They can be localized on various parts of the body, including mucous membranes. The formation of warts on the feet is often associated with a decrease in local skin immunity due to damage from hyperhidrosis or fungal infection.
Flat papillomas on the face
Formations of this type can appear on the face of both adults and children. They come in small and large ones. The latter cause severe discomfort because they cannot be disguised with cosmetics.
Infection with HPV, which leads to the appearance of papillomas, occurs in several ways:
- during unprotected sexual intercourse;
- ignoring the rules of personal hygiene, using the personal belongings of other people;
- through wounds and abrasions on the skin;
- during hair removal (applies to women).
The provoking factors in this case are:
- hormonal imbalances;
- chronic diseases;
- diabetes;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- period of bearing a child;
- unmotivated use of hormonal drugs and antibiotics.
Correctly selected treatment will help eliminate the manifestations of the virus, but will not get rid of it itself. An infected person will be a carrier of HPV for life.
Types of papillomas
It is important to be able to determine the type of papillomas on the body. The type of neoplasm depends on the strain of the virus. Once in the body, the virus provokes excessive division of skin cells, which leads to the formation of a growth. There are dangerous and safe strains of HPV. In most cases, people encounter non-dangerous forms of infection that do not cause harm to health and cause only aesthetic discomfort. It is enough to remove such a wart to forget about discomfort.
An alarming signal is the appearance of neoplasms on the mucous membranes. Such papillomas are often caused by oncogenic strains of the virus and can cause the development of cervical cancer in women. The danger is also increased because the virus is transmitted sexually. These types of neoplasms require complex antiviral therapy aimed at suppressing HPV.
It is quite easy to distinguish different types of warts on the body by comparing different photos. Each type of formation is characterized by a number of features, knowing which it is easy to suspect one or another form of the disease.
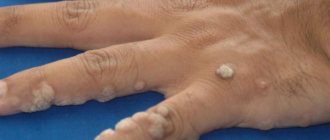
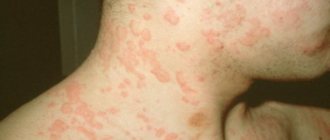
Common papillomas or vulgar warts
The most common form of manifestation of papillomavirus is ordinary papillomas, popularly called warts. They are caused by several strains of the virus, which are easily transmitted through household contact and sexual contact. According to statistics, approximately every third person on the planet has encountered the appearance of ordinary papillomas at least once in their life.
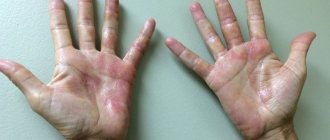
Vulgar warts most often occur on the hands
The localization of such growths is the skin of the body, soles and feet, palms and fingers. The peculiarity of common warts is that they quickly appear in areas of skin damage against the background of a decrease in local immunity. Factors that provoke the appearance of papillomas on the soles and palms:
- contact with household chemicals;
- profuse sweating;
- skin damage;
- fungal or bacterial infection (dermatitis).
Vulgar warts (another name for ordinary papillomas) are small papillary neoplasms on the skin, the size of which at the beginning of development does not exceed a few millimeters in diameter. The head of the wart rises above the skin, it has a soft, uniform structure, is poorly pigmented, and the color of the wart rarely differs from the color of the skin. The root of the growth goes deep under the skin and is fed by blood vessels, which causes the growth to increase over time.
These warts may darken as they grow. Hair growth in the center of the papilloma is normal. As a rule, such warts are caused by non-oncogenic strains of the virus.
Thread-like growths
This form of skin tumors gets its name due to the thin stalk on which the head of the papilloma rises. Such growths are easily diagnosed from photographs due to their elongated shape. They appear predominantly in people over 45 years of age and are localized in areas with thin skin (chest, armpits, neck).
Thread-like papillomas can increase in size, stretching even further. Usually the head of such neoplasms is colored yellowish or pinkish; they are almost never highly pigmented.
This type of papillomas has a peculiarity - a thin stalk
Flat warts
This form of skin tumors looks like small flat yellowish plaques that rise slightly above the skin. The structure of flat warts is quite dense, the root of the growth goes under the skin, which can be accompanied by pain when pressing or damaging the wart in everyday life.
Such growths are localized on the face and skin of the hands. They often appear around the anus, on the labia majora in women and on the scrotum in men.
They tend to rapidly increase in size due to the abundant blood supply. The peculiarity of growths of this form is the difficulty of treatment. After removal of flat papillomas, scars often remain on the skin.
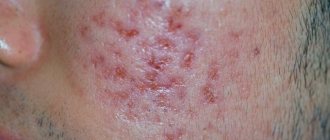
Condylomas acuminata
This form of growths appears in the groin area and on the mucous membranes. They resemble small thin papillary neoplasms, the size of which does not exceed 2-3 mm. The peculiarity of condylomas is their rapid progression. Quite often, just one growth appears on the skin, which over time progresses into a large papillary growth on the skin, shaped like a rooster's comb or cauliflower.
Genital warts are dangerous due to the risk of infection. They often become inflamed, especially if located in the vagina or on the labia minora. Such growths are easily injured, which subsequently leads to infection.
The problem with genital warts is the high risk of relapse, even after antiviral therapy and removal of growths. This form of skin neoplasm is caused by several strains of the virus, some of which are dangerous to women’s health.
This type of papillomas affects the genitals
Lewandowski-Lutz papillomas
This type of growth is very rare. Papillomas appear on the hands and feet. A characteristic feature is the brown color and uneven edges of the neoplasm. Lutz papillomas can be colored red and purple. This is a dangerous form of the disease; in a third of patients with this diagnosis, over time, the process of degeneration of papilloma cells into malignant ones begins.
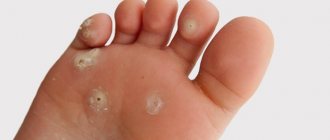
Plantar warts
A plantar wart or plantar wart is a common type of growth on the skin of the feet. In most cases, spines are encountered in childhood and adolescence. The reason for the appearance of such warts is a decrease in local immunity as a result of wearing tight shoes, injuries to the soles, excessive sweating and poor personal hygiene.
The peculiarity of this papilloma is that it grows inward. On the surface of the skin, only a small rough spot is visible, rarely distinguished by color. The root of the wart goes deep under the skin. The growth compresses and irritates the pain receptors of nearby healthy tissues, causing discomfort when walking.
The spines are difficult to remove due to their deep location. After removing a wart, it is often necessary to apply stitches - such a deep wound forms at the site of the growth. Often a scar remains after removal.
The spine does not rise much above the surface, but affects the deep layers of the skin
Juvenile warts
Infection of a child most often occurs at the time of birth. In this case, juvenile warts appear. They may be harmless if localized on the skin, but laryngeal papillomatosis is more often diagnosed in infants. Despite the fact that this form of the disease is quite rare, it is important to be able to promptly suspect the development of a disorder in a child.
Juvenile warts on mucous membranes are difficult to identify on your own. In older children, the voice may suddenly change, indicating damage to the vocal cords. If papillomas are damaged, breathing may be impaired, even completely stopping. If you suspect something is wrong, you should visit a doctor as soon as possible.
Papillomatosis
A dangerous form of HPV is papillomatosis. With this disorder, a large number of warts suddenly appear on the skin. They can completely cover a person's arms, body or face. Papillomatosis of the mucous membranes and internal organs is life-threatening. Damage to the wart can lead to bleeding of internal organs. If warts in the mouth and larynx are damaged, breathing may be impaired.
For pregnant women, the danger is posed by a generalized form of human papillomavirus infection, in which neoplasms appear in the vagina and cervical canal.
Structural features
On the surface of the epidermis, the structure of the wart can take various forms. It all depends on their type:
- flat;
- threadlike;
- cone-shaped;
- coralliformes.
The color range ranges from flesh to dark brown. The structure is dense, hard, scaly. They can appear in a single version or in several pieces. This is what we see on the surface. General structure of a wart:
- reinforced top;
- skin covering;
- dermis;
- root system of infectious neoplasm;
- fatty tissue.
When examining a wart under a microscope, attention is drawn to its roots.
What is the root
The root base is the microscopic cells that make up the granular layer. The system is equipped with blood vessels that give the dark color to the root. The blood flow to the lower part of the tumor allows it to receive nutrition for cell growth.
The rod, if we look at the wart in cross-section, is healthy blood vessels that have died from blockage due to compression. The more intensively the root grows, the stronger the negative impact on the vascular system, as a result, the appearance of more rods.
Localization and type of papillomas
Most often, people encounter vulgar, filiform and genital papillomas. These types of papillomas on the face appear quite often, especially thread-like growths.
Vulgar warts “prefer” the skin of the feet and hands, but can appear on any part of the body. Despite the fact that it is quite simple to remove such growths with modern means, over time they reappear due to a decrease in immunity.
Condylomas appear only on the mucous membranes. They can affect the glans penis, foreskin, vagina and labia minora. There are known cases of the formation of genital warts in the urethra in men. This form of the virus carries a dangerous risk of developing cervical cancer.
Plantar warts appear on the rough skin of the feet and on the balls of the toes. In rare cases, it is possible to develop a spine on the thumb after damage to the skin.
Papillomatosis is a generalized form of the disease, manifested by the formation of growths throughout the body. Having seen a photo once, it is impossible to confuse papillomatosis with other neoplasms.
Types of HPV, what they are and their characteristics
Each type of virus has a serial number and can contribute to the development of various diseases. You should not think that HPV always poses a big threat; only types that can cause cancer are considered dangerous. These include 16 and 18, which provoke the appearance of warts in the intimate area. At the same time, the most common forms, manifested by warts on open areas of the body, are not oncogenic.
Although many types of HPV are now described in the medical literature, you should not try to make a diagnosis yourself. The appearance of warts on the body may indicate serious disorders in the body. Therefore, when prescribing treatment, it is important to take into account not only the type of HPV, but also the individual characteristics of the patient.
Considering the types of virus that cause human papillomas, it is worth noting that there are 27 of them in total. Some types may include one or more strains. People who are sexually active usually become infected, and the virus is often combined with infections. Now one of the methods of combating the disease is vaccination, but if a person is already infected, getting vaccinated is useless.
Different HPV groups can affect different areas. This can be the skin, mucous membrane of the genital or non-genital area. Non-oncogenic viruses in women, including HPV 14, cause the formation of papillomas. In rare cases, they can provoke the development of verruciform epidermodysplasia. With this disease, multiple growths appear that can degenerate into cancer, but only if there is a hereditary predisposition. The disease is autosomal recessive; if a person is not predisposed, the human papillomavirus will not lead to such manifestations.
Patients often ask about HPV type 54 in women, what it is and how dangerous it is for the reproductive system. This form is oncogenic; it can cause cervical cancer, like type 56. It is expressed by the formation of condylomas in the vagina and genital area. If you notice such symptoms, you should make an appointment with a gynecologist.
It is useful to know how many forms of this disease there are, that is, how many types of HPV are known to modern medicine. More than 170 types have now been studied, but about 80 are the most studied. Therefore, it is impossible to say exactly how many types of HPV exist in nature. In 90% of cases, the disease goes away on its own after 1-2 years, when the immune system is restored and suppresses pathogenic organisms.
There are known cases of warts degenerating into cancer, but most often they are observed in the presence of sexually transmitted infections. To learn how to distinguish which form is oncogenic and which is less dangerous, a table that describes all types of human papillomavirus will help. Also, you can often find information in tables about which body systems are affected by one or another strain.
Some strains, causing HPV in humans, provoke the formation of tumors in the prostate in men; these include all oncogenic types. Often, form 16 is transmitted after unprotected contacts. Although the virus cannot be completely eliminated from the body, if a man undergoes treatment in a timely manner, he can avoid dangerous complications.
It is worth highlighting HPV 13, which, when infected, can cause focal hyperplasia of the mouth, known as Heck's disease. As a result, formations resembling the shape of raspberries are formed that affect the oral cavity. Warts are often damaged and the patient feels pain, so although this form is not the most dangerous, it significantly reduces the quality of life.
In most cases, people learn about the disease by finding a wart on the body. Often, visitors to websites on medical topics are interested in what virus causes papilloma on the arch, and how to deal with this type of HPV. To distinguish HPV from other formations, the characteristics of HPV, types and their descriptions can always be found on the Internet, since the virus was registered back in 1971, it has been sufficiently studied, and the information is widespread. But you should consult a doctor for a diagnosis.
How to determine the type of papilloma?
Having figured out what types of papillomas a person has, it is important to be able to recognize the disease in a timely manner. For diagnosis, you should contact a venereologist or dermatologist. We can talk about the presence of the virus in the body after an external examination of the growth, but to determine the strain, a PCR analysis should be done.
Many types of skin growths look similar, and only a doctor will determine the specific type
Depending on the type of papilloma on the skin, the doctor will suggest a removal method. As a rule, if a wart causes any discomfort, it is customary to get rid of it using radical methods.
Knowing what types of growths there are, it is important not only to be able to distinguish between them, but also not to confuse papillomas with a mole. The main feature is the color. Papillomas and warts are rarely highly pigmented, their color ranges from light pink to yellow.
Classification according to oncogenicity
Since research has proven that this disease provokes the development of cervical cancer, HPV viruses have been divided into different types. Those that cause the formation of warts on the skin are considered not dangerous, but condylomas localized in the urogenital region pose a threat. Depending on the ability to influence the human body, the following types of papillomavirus that exist today are distinguished:
- Non-oncogenic - not capable of causing cancer; these include more than ten types, including 1, 2, 10, 55.
- Low oncological activity - the likelihood that cancer will develop at the site of the papilloma is low.
- Moderate degree of danger - identification of such strains must be taken carefully, not only remove the growths, but take a course of immunomodulatory and antiviral drugs.
- High-risk strains that can lead to cervical and skin cancer.
Low and medium
Strains of average risk of degeneration into a malignant formation have numbers 30, 35, 45, 52, 53, 56, 58. For low risk, doctors define modifications 3, 6, 13, 11 32, 34, 40 – 44, 51, 61, 73, 72. It is worth remembering that any form is contagious, so if you have symptoms, you should not postpone your visit to the clinic.
High oncological activity was found in strains 16, 18, 31, 33, 39, 50, 59, 64, 68, 70. A medically proven connection with breast and cervical cancer; almost all patients with these diagnoses had one or more HPV viruses. However, according to statistics, no more than one percent of those infected develop these forms of cancer.
In the overwhelming majority of cases, cancer is caused by forms of the HPV virus 16, 31, 33 and 18. Therefore, those who care about their health, if they detect HPV that causes further stages of the development of dangerous formations, need to think about complex therapy. The doctor will prescribe tests that will also help identify concomitant infections, if any.
Removal methods
To remove growths, they practice the use of nitrogen, destruction of the wart root with electric current, and laser burning. Such methods guarantee quick results due to the complete removal of the tumor. During the procedure, the blood vessels feeding the wart are cauterized, thereby minimizing the risk of spreading the virus through the bloodstream.
Quite often, laser burning is chosen as a method of removing papillomas. This allows you to get rid of a skin defect in a matter of minutes, and there is no scar left after removing the wart.
At home, it is practiced to use alkaline and acidic solutions to burn out warts. This method is only permissible for ordinary warts; to remove any other growths, you must consult a doctor.
It is strictly forbidden for children to remove growths at home. Their skin is thin and delicate, there is a high risk of formation of rough scars after burning out the papilloma.
In addition to radical measures, it is necessary to consult a doctor about prescribing antiviral therapy. Without drug treatment, removal of papillomas cannot guarantee a lasting result, since the next time immunity drops, there is a possibility of re-formation of papillomas due to the activity of the virus.
Why do papillomas turn brown?
It happens that papillomas of a flesh-colored or pinkish hue change sharply and become brown, even dark tones. This is also often accompanied by a change in the shape and size of the tumor. Such transformations require mandatory consultation with a doctor.
Only a specialist will be able to identify the cause of the changes and prescribe the correct treatment to avoid the degeneration of benign growths into malignant ones. If the papilloma has changed color to brown, this may mean that the following contributing factors have taken place:
- The growth was regularly damaged. This often happens when tumors are localized on the head, armpits, neck, or groin. In these places it can be very difficult to avoid injury;
- The injury was complicated by a bacterial infection. In this case, redness of adjacent tissues, inflammation, and swelling in the area of the tumor are noted. The papilloma also becomes painful and may bleed.
- Strengthening the body's protective functions. In this case, the papilloma spontaneously darkens and disappears over time. This indicates that the immune system has activated and is fighting HPV. This case of papilloma turning brown is not dangerous
- Medicines or traditional medicine were used. Most external means for eliminating papillomas cause tissue burns and subsequent drying out of the growth. This process is accompanied by darkening of the tumor as a normal skin reaction to cauterization.
Changes in the shade of neoplasms can also be caused by hormonal fluctuations, stressful situations, and exacerbations of chronic diseases.
You should immediately consult a doctor if dark brown papillomas appear, even black. Especially if their occurrence is accompanied by pain, itching, inflammation, the formation of bleeding ulcers, and dry crusts.
This may indicate that the process of malignancy has begun. In this case, treatment and removal of dangerous tumors should be urgent.
Flat papillomas on the chest
Such growths form on different parts of the mammary glands.
- Under the chest. Appear more often than other species. The cause is excessive sweating. Most often, this phenomenon is encountered by people who are overweight or have diabetes. This pathology also applies to pregnant women.
- On the nipple. They appear quite rarely. In most cases, they are a consequence of microtrauma of the nipples, which are formed, for example, during breastfeeding.
- Warts. The result of wearing tight clothing.
Most often, papillomas in the chest area appear when the immune system is weakened. By their number one can judge the state of the body’s defenses.
How to remove flat papillomas
There are several ways to get rid of flat papillomas. There are two types of treatment:
- conservative;
- operational.
The first type of therapy involves the use of medications: ointments, tablets, etc. Each product has its own properties and application features.
- Isoprinosine. An antiviral drug whose main active ingredient is inosis pranobex. It normalizes the activity of the immune system and improves the process of interferon production. Helps cope with growths on the larynx, body and genital area.
- Viferon. It is a gel for external use. It has a lot of advantages, including an absolutely natural composition, fast action, hypoallergenic, and can be used by pregnant and lactating women. The drug will be most effective in the initial stages of HPV development.
- Genferon. A beneficial effect on the body is possible due to its special composition. It contains interferon alpha-2, benzocaine and taurine. These substances relieve inflammation, restore the body and promote the removal of toxins. Suitable for treating pregnant women and even children. In some cases, side effects occur, such as itchy skin.
- Allokin-alpha. This product is available in powder form. Its main active ingredient, alloferon, provokes the production of cells that destroy viruses. The use of the drug has a number of features. For example, it is contraindicated for persons under 18 years of age, pregnant and lactating women. Also, Allokin-alpha often has side effects. It manifests itself in the form of general weakness, dizziness, rashes and allergies.
- Lycopid. These are broad-spectrum tablets. They, like the previous drug, promote the production of so-called killer cells, cells that take an active part in the fight against viruses. Not used in the treatment of children and pregnant women.
Important! None of the above medications should be taken without a doctor's prescription. Self-medication is dangerous and can lead to tragic consequences.
To eliminate flat papillomas, you can use other pharmaceutical products.
- Super clean. This is a liquid that should be applied directly to the growth, while avoiding its contact with healthy skin. Repeat the procedure until the papillomas are completely eliminated.
- Cryopharma. Freezes papillomas and warts. Flat formations are removed with just one application. The solution is applied with a special applicator.
- A mixture of salicylic acid and cream. The proportions of the ingredients are 1 to 10. The resulting ointment should be applied to damaged skin using a small cotton swab or cotton swab. This is a fairly effective and at the same time long-lasting method of treatment. The first results will appear approximately 20 days after starting to use the product.
- Patch. Helps in eliminating single growths. The patch contains sulfur and salicylic acid. They effectively soften and then dry papillomas. Before applying the patch, the neoplasm must be thoroughly steamed.
If the above remedies do not help, you will most likely have to resort to removing papillomas during one of the cosmetic procedures.
- Laser therapy. A painful but very effective treatment method. The growth is evaporated by a beam of laser beams. If the procedure is carried out in accordance with all the rules and precautions, no scars or scars remain on the skin.
- Cryodestruction. The papilloma is frozen under the influence of liquid nitrogen. The substance is applied using a cotton swab. A couple of days after the procedure, a blister appears in this place. It dries up and falls off. Clean skin remains. Cryodestruction is painless and completely safe.
- Electrocoagulation. The papilloma is cut off by a loop of electric current. This treatment method is suitable for removing only flat tumors. After the procedure, a crust remains in their place, which will fall off on its own after a few days.
- Plasma coagulation. The growths are removed using a plasma beam. This is a non-contact treatment method that completely eliminates the possibility of infection or inflammation.
You can get rid of such defects on the skin using folk remedies. There are several examples.
- A decoction based on pine needles will help strengthen the immune system and reduce HPV activity. You need to take it 2 times a day, 100 ml. You can top the drink with honey or jam.
- Garlic helps remove formations. It can be applied either in pieces or in the form of a paste. You can mix garlic with rendered lard, apple cider vinegar, rye flour, etc.
- Regular laundry soap also has a good effect. They need to rub the papillomas for 4 days.
- New growths can also be lubricated with a solution of aspirin, iodine, boric acid and alcohol.
As in the case of medications, folk remedies can only be used after consultation with a doctor.
So, flat papillomas are the result of the manifestation of HPV. Like other types of such neoplasms, for the time being they do not cause discomfort. But under certain circumstances they begin to grow and become inflamed. To avoid these unpleasant consequences, it is necessary to start treatment on time.