Jellyfish, often found on sea coasts, can cause a lot of trouble for vacationers, namely causing burns. A burn from a jellyfish, which occurs during tactile contact with this representative of the aquatic world, is not only accompanied by physical discomfort and damage to the skin, but also causes disruption of the functioning of internal organs and can be hazardous to health. It is best to avoid contact with these marine creatures. But if this fails, it is important to know what to do if you receive a burn: how to provide first aid and how to treat the injury.
Why are jellyfish dangerous?
About two thousand species of jellyfish have been well studied, but only seventy of them can pose a danger to human health or life. Medusa does not attack people first, so it uses its stinging abilities solely for the purpose of self-defense. However, often an invertebrate representative of the aquatic world regards even a chance meeting with a person as an attack, and uses toxic stinging cells. The sea animal inflicts injuries by striking the human body with a sharp “spear” connected to a special capsule that is filled with toxic substances .
Note! Burn injuries received by a person from contact with a jellyfish vary in severity and symptoms, and sometimes even cause death.
What is the danger
The body and tentacles of the jellyfish are covered with stinging cells that produce a paralyzing poisonous substance. Inside these cells there are capsules with threads twisted into a spiral. With their help, jellyfish hunt and get food. When a jellyfish touches prey or an enemy, threads are released from the stinging cells, with the help of which a poisonous, burning substance is injected into the victim.
Upon contact with a jellyfish, a person immediately gets burned, and the toxic substance that gets into the skin harms the entire body. Some species of coelenterates are especially dangerous. For example, after being bitten by a Sea Wasp (found off the coast of Australia), a person dies from its poison within three minutes. Other representatives are no less dangerous:
- Physalia (causes respiratory paralysis);
- Cross (the bite is accompanied by unbearable burning pain, loss of coordination);
- Irukandji (provokes vomiting, paralysis);
- Cyanea (the bite is accompanied by a strong burning sensation, swelling of the mucous membranes occurs, and the temperature rises).
On the Black Sea coast you can encounter the Cornerot and Aurelia jellyfish. The first type is considered more dangerous, although this jellyfish has no tentacles and stinging cells are located throughout the body. Aurelia rarely stings, and after its bite only local symptoms occur - burning, redness, swelling.
The seasonal activity of these animals depends on the month and water temperature, most often they can be found in July and August. Jellyfish are dangerous not only in the sea: on land they retain the ability to sting for up to 3-4 hours.
Which jellyfish are dangerous?
The effectiveness of action and the composition of toxins in different types of jellyfish have significant differences. The safest species are characterized by the production of weakly active poisons, the contact of which with human skin does not provoke a significant negative impact. There are also known types of jellyfish that are deadly to humans:
- The sea wasp (Chironex flaskeri) is a deadly species for humans, a representative of the order of box jellyfish, which have a bell-shaped cubic dome and a very powerful toxin. Even with timely and competent first aid, the result of a “burn” is the appearance of poorly healing, long-lasting ulcers;
- Irukandji (Сarukia barnesi) is a small, umbrella-shaped species with four rather long tentacles. The first signs of a burn are manifested by lumbar pain and muscle cramps, headache and increased blood pressure, a burning sensation on the skin and nausea. In conditions of a weakened body, death may occur;
- The Portuguese Man of War (Physalia Physalis) is one of the most beautiful species with a blue, violet or purple dome. Numerous stinging cells contain a very strong toxin, so the “burn” is accompanied by excruciating pain, damage to the nervous system and failure of the respiratory function, as well as increased body temperature and general malaise.
No less dangerous to humans are the clinging cross jellyfish, Nomura species and Giant Cyanea , as well as planulas or larvae .
Note! Often, the victim, having experienced the first signs of a burn from the stinging cells of a jellyfish, quickly loses orientation in the water space, and therefore needs immediate first aid.
Actions after a bite
Often, if a jellyfish stings, it is not life-threatening to the victim, and first aid, as well as further therapy, is carried out independently.
At the same time, there is a list of circumstances in the development of which you need to immediately contact a medical institution.
- A man was bitten by a box jellyfish. To maintain his life, it may be necessary to use special serums.
- A severe allergic syndrome developed.
- The bite occurred on a large area of the body or on closely located large vessels on the head, neck, and chest.
When attacked by a marine species, it is important to have an idea of what to do if a jellyfish bites
First aid
The intensity of the effects of the toxic substance depends on the coelenterate individual. The bite of a Black Sea marine life is painful, especially if the lesion is huge, but not fatal. Individuals in tropical climates can burn fatally. An attack by coelenterates in Vietnam will be severe and will cause the death of the victim.
jellyfish burn
First aid for a jellyfish sting is carried out as follows:
- To prevent the possibility of a bite when encountering a jellyfish, you must calmly leave the body of water. In case of fear or hysteria, the speed of blood flow increases and the absorption of toxic elements increases;
- The bite area must be thoroughly washed with sea water, using regular salt water or shaving foam. These procedures will reduce the spread of the toxin. When poison passes into the mucous membrane of the eye, it is required to rinse it with tap water;
- using the blunt part of the knife, the remaining tentacles are lifted and carefully removed from the bitten area;
- to reduce swelling and pain, apply cold to the wound;
- a Ketanov, Ibuprofen or other analgesic pill is drunk;
- in case of probable development of an allergy, it is necessary to take an antihistamine - Diazolin, Suprastin;
- Plenty of fluid intake is indicated, which allows you to immediately eliminate poison.
Prohibited actions
There are a number of misconceptions associated with providing first aid after a jellyfish attack. The use of such methods in practice becomes meaningless or will lead to consequences.
prohibited actions
What not to do if you are stung by a jellyfish.
- Fresh water that is used for drinking should not be used to clean a wound. This is due to the fact that the remaining tentacles can quickly collapse in liquid, its salinity is somewhat less than the salinity of sea water. As a result of the use of such an action, a large amount of toxic substance will be immediately injected into the epithelium of the victim. Use fresh water only after the tentacles have been completely removed from the skin.
- Ambiguous folk remedies - compresses made from vinegar, using alcohol, ammonia. They can reduce the feeling of pain in not very poisonous individuals - cornet, aurelia, but when the drugs influence box jellyfish, they will accelerate the introduction of the toxin by 50%.
- Rub the affected area. This way it is possible to injure the epithelium and provoke an increase in the toxic substance.
- Touch the burned area with your bare hands to avoid burning your hands.
- Wipe your eyes from the poison with dirty hands.
- Sunbathe until the wound passes.
Treatment
Only a doctor will correctly assess the situation and tell you what to do after a jellyfish sting. A combined approach using external and internal medications will eliminate the burn in 5-10 days. It is recommended to use folk remedies together with pharmaceutical drugs.
To relieve the rash and itching after a bite, ointments and gels that contain antihistamines are prescribed.
- Bepanten.
- Trimistin.
- Panthenol.
Trimistin
Corticosteroids used:
- Advantan;
- Citrine;
- Fenistil.
The local therapeutic course is strengthened with medications that relieve inflammation.
- Voltaren.
- Baneocin.
In case of a serious burn, when Quincke's edema and anaphylactic processes develop, Medopred and Dexamethasone are prescribed. Muscle cramps are eliminated with No-shpa. If there are violations, use antibacterial drugs - Neosporin.
If you are bitten by a jellyfish, but there are no pharmaceuticals at hand, you can relieve the symptoms and make you feel better with the help of folk recipes.
- Mix baking soda with salt to form a paste. The mixture is applied to the bite until it dries.
- A tomato or lemon is cut into rings and applied to the wound.
- The egg white is beaten and the bite is coated with it.
- The carrots are grated and fixed on the wound. Carrots will soothe the burn and eliminate the burning sensation.
soda with salt
Signs of a burn
Unpleasant but non-life-threatening symptoms may include:
- itching and burning of varying intensity at the burn site;
- pain;
- increased body temperature;
- weakness and lethargy;
- headache.
A fairly strong allergic reaction to a burn is most often represented by:
- shortness of breath;
- allergic cough and suffocation;
- difficulty breathing;
- spasms and convulsions;
- pain on the mucous membrane of the eyes;
- a sharp increase in blood pressure.
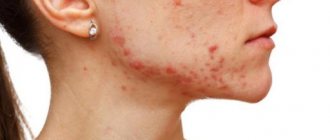
A mild injury in the form of a burn is accompanied by the appearance of redness and swelling on the skin. More severe damage may cause blistering.
It is important! A burn received in contact with a dangerous type of jellyfish requires special attention, since in this case the victim experiences symptoms, represented by a sharp deterioration in health or fainting.
Symptoms
The very first thing a person experiences after a jellyfish burn is severe pain and severe burning at the site of the lesion. This injury is usually characterized by skin redness, rashes, and scarring. Sometimes the bite is noticeable only after a while. The severity of the symptoms depends on the intensity of the exposure and the size of the burn. The following symptoms of a jellyfish burn usually appear:
- pain and severe redness of the affected area;
- feeling of nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness and sometimes fainting;
- spasms of the upper and lower extremities;
- muscle paralysis;
- numbness of some parts of the body.
If you do not provide assistance to the victim in a timely manner and do not begin treatment, the victim’s condition may worsen. These complications include: panic attack, tachycardia, swelling of the tongue and difficulty breathing. Sometimes the victim may experience a complete absence of discomfort due to the development of a state of shock.
First aid and rules of action
The following measures are considered as first aid to be provided to a victim of a jellyfish burn:
- leave the body of water;
- remove particles from the injured area using a sterile object;
- wash the wound surface with a soda solution;
- neutralize toxins with an alcohol compress;
- take an antihistamine.
The victim needs to ensure optimal drinking regimen , and the total volume of liquid drunk should be approximately one and a half to two liters.
The presence of symptoms in a victim indicating a severe burn will require qualified medical care at a nearby medical facility.
Preventive measures
Burns are not only unpleasant, but also dangerous. Therefore, it is better to avoid encounters with jellyfish than to treat a burn later. There are several preventative measures that will help avoid burns :
- Choose the right places for swimming, where meeting with marine life is unlikely;
- When swimming in the sea, keep an eye on children and do not leave them alone in the water;
- Don't swim too far. The deeper you go, the greater the likelihood of encountering jellyfish;
- Do not swim in the sea after a storm. At this time, they can accumulate off the coast;
- Do not touch jellyfish, even if the person is wearing a wetsuit;
- You should not touch dead jellyfish that have washed ashore. Even in this state, their sting cells are active;
- If you notice jellyfish in the water near the shore, leave the sea immediately.
Treatment of burns from jellyfish
Treatment measures are prescribed depending on the severity of the patient’s general condition. The individual susceptibility of a person to the toxins contained in the stinging glands is also important, so the treatment regimen is prescribed only by a doctor, based on the collected medical history, diagnostic measures and examination results.
Medicines
External medications, as well as medications in the form of tablets and injections, can be used as medication. External remedies to combat skin rashes, pain, itching and burning:
- " Bepanten ", which relieves signs of inflammation, reduces pain and itching;
- " Panthenol ", which is a clinical analogue of the drug "Bepanten";
- " Dermovate ", based on corticosteroids that block the production of histamine;
- " Trimistin ", which blocks the action of toxins, eliminates swelling and hyperemia;
- " Afloderm ", which reduces the risk of blistering and shock;
- " Belogent ", which quickly eliminates pain and reduces the risk of wound suppuration.
Drugs that eliminate the symptoms of allergic rhinitis and bronchitis, as well as alleviate the general well-being of the victim, are represented by the antihistamines “ Fenistil ”, “ Diazolin ”, “ Eden ”, “ Citrine ” and “ Suprastin ”.
In severe cases, intramuscular administration of the glucocorticosteroid drug “Diprospan”, the corticosteroid “Medopred”, as well as the use of “No-shpa” injections to eliminate muscle spasms are indicated.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine is usually used in the treatment of mild skin lesions. In this case, a good result is given:
- tomato juice or half a tomato, fixed at the burn site with a regular bandage;
- freshly squeezed lemon juice or a solution with citric acid and adding a small amount of oily vitamin “E”;
- self-prepared paste based on milk and potato starch .
Goose fat , which is applied to the affected surface immediately after providing first aid to the victim, allows you to eliminate redness and damaged epidermis
It is important to remember that folk remedies are acceptable and relatively effective only if the affected area is not very large or there is no severe allergic reaction to the burn.
How to treat a jellyfish sting
Only a specialist can correctly assess the situation and tell you how and how to treat a jellyfish burn. Complex therapy using external and internal drugs will solve the problem, and after 5-10 days you will forget about the trouble that happened to you. In parallel with pharmaceutical products, traditional medicine can be used to treat a bite.
Drug treatment
Topical creams, gels, ointments containing antihistamines, such as Bepanten, Trimistin, Dermovate, Panthenol, as well as corticosteroids - Hydrocortisone, will help relieve external symptoms of jellyfish stings in the form of rash and itching. , "Advantan", "Akriderm". Allergic reactions are treated with Citrine, Fenistil, and Eden. Local therapy is supported by anti-inflammatory drugs - Voltaren, Baneocin.
In severe cases, when angioedema and anaphylactic manifestations occur, Medopred or Dexamethasone are prescribed. Muscle spasms are eliminated by injections with No-shpa. If there are complications, you will have to take antibiotics, for example, Neosporin.
Traditional medicine, what to do if you are stung by a jellyfish and there is no medicine
You have been bitten by a jellyfish, and there are no doctors or pharmacies nearby. How to eliminate a jellyfish burn and how to treat it in such cases? You can relieve symptoms and alleviate the condition using traditional medicine.
- Paste of salt and soda. Mix them in equal quantities and add water to form a paste consistency. Apply a thick layer to the affected area and leave until completely dry. After this, remove the dried mixture with a napkin. Do this procedure once a day for three days.
- Mix flour and fine salt in a ratio of 5:1, add a spoonful of water and knead into a stiff dough. Form a cake out of it, apply it to the burned area and secure with a band-aid. Leave the bandage on for 2 hours then remove. Continue to apply the mixture daily after a jellyfish sting, symptoms should subside within a week. Before each procedure, make a fresh cake.
- Prepare an ointment for jellyfish stings from ground carrot root, aloe leaves, egg white, lemon and tomato juice. Mix everything well until smooth and apply to the stung area. You need to change the composition as it dries. After two days of such lotions, the symptoms should disappear.
If you see that self-medication does not bring results and, moreover, complications arise, immediately consult a doctor.
Complications and consequences of jellyfish burns
Severe burns resulting from tactile contact with dangerous species of jellyfish cause serious complications:
- complex or combined allergic reactions ;
- repeated and debilitating vomiting ;
- numerous large blisters .
With the development of anaphylactic shock, respiratory arrest occurs, which is preceded by swelling of the throat and severe tachycardia.
The consequences of burns caused by exposure to jellyfish toxins are represented by scars and cicatrices , which, with the proper use of medicines and folk remedies, quickly become unnoticeable.
Photo 2. A jellyfish sting can cause a severe allergic reaction. Source: Flickr (Joshua P. Light)
Folk remedies
For minor injuries, you can use remedies prepared according to traditional medicine recipes:
- mix a teaspoon of soda and salt with 2 tablespoons of water, apply the resulting mixture to the damaged area, leave until dry (the product reduces swelling of damaged tissues, neutralizes toxins);
- dilute a mixture of 20 g of flour and 5 g of salt with water, make a compress with the resulting mass, keep for 3 hours (like the previous remedy, the compress helps neutralize toxins);
- make a compress from finely grated carrots (reduces swelling and redness, stimulates regeneration);
- Apply a tomato ring to the bite site (neutralizes the toxic substance) or a slice of lemon (reduces pain and redness).
A burn from a jellyfish can ruin your entire vacation, because even minor damage takes a long time to heal. But the main danger is that a jellyfish sting can lead to the development of severe dysfunction of internal organs.
To avoid encounters with dangerous inhabitants of the deep sea, during your vacation you need to follow basic safety rules: do not swim too far into the depths, avoid areas where jellyfish accumulate, be careful in the water, look around and do not touch anything while diving, do not touch jellyfish, washed ashore by a storm. By following these simple recommendations, you can ensure yourself a pleasant and relaxing holiday without incident. If a burn occurs, it is better to seek medical help.
FAQ
Jellyfish are unusual and beautiful. That is why people show special interest in them. However, it should be remembered that these marine inhabitants are dangerous. People are often interested in whether all jellyfish are dangerous, why burns occur from contact with them, and which representatives of this species live in different seas. Let's look into it and answer the most frequently asked questions.
Which jellyfish burn?
Various types of jellyfish live in the seas. Some of them are very dangerous for humans, as they sting with strong poison, others almost never burn or their poison is weak. In any case, it is better to avoid these unusual marine inhabitants.
The following species are considered the most dangerous to humans:
- Cornerot;
- Sea wasp;
- Cross;
- Portuguese man-of-war (Fisalia).
Cornerot
sea wasp
Cross
Portuguese man of war
Contact with the above jellyfish leads to extensive burns and severe intoxication. Their poison has a negative effect on the central and peripheral nervous system (paresis and paralysis, including paralysis of the respiratory system).
Why do jellyfish burn?
Jellyfish have a jelly-like body and tentacles. They are not able to defend themselves from enemies, which is why nature has endowed them with a defense mechanism. The body of a jellyfish has special cells called stinging cells. They contain toxins of varying degrees of danger.
The defense mechanism is always triggered when the jellyfish comes into contact with the “enemy” . If the jellyfish touches something or someone, the stinging cells are released and release poison. This mechanism is necessary to protect marine life from death (predators), and humans are perceived as a potential danger. That's why jellyfish sting everyone who touches them.
Dangerous jellyfish of the Black and Azov Seas
Having decided to relax on the Black or Azov Sea, you need to remember the danger that they pose. In the waters of these seas you can most often find 2 types of jellyfish:
- Aurelia .
Aurelia This species is practically not fraught with danger, because they sting extremely rarely. They are transparent, making them almost invisible in the water. The dome of the jellyfish is large, its diameter can be 35 - 40 centimeters; - Cornerot. This species is the most dangerous. Their appearance is bright, they are purple in color. Which indicates their danger (the brighter the jellyfish, the more dangerous and poisonous it is). Its bite is most dangerous for young children.
Strictly prohibited
Despite the notorious folk wisdom, some recommendations can cause serious harm to the body. It is necessary to remember the list of recommendations that are not applicable for cases of coelenterate bites:
- It is strictly forbidden to lubricate the affected areas of the body with oils, tonics, lotions and other oil-based products.
- disinfection with alcohol or other chemicals is also prohibited.
- treating the wound with iodine and brilliant green is prohibited.