( 1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Home » Fungal diseases
A dermatologist can determine why the skin on your palms is peeling. The reasons are different: from a lack of vitamins, the harmful effects of chemicals, allergic manifestations to serious infectious and dermatological diseases. Examination of scales from the affected areas will help make an accurate diagnosis.
Causes
The reasons why the skin on the palms and fingers peels are varied, as are the diseases that cause these symptoms:
- Avitaminosis. Epidermal tissue damage occurs when there is a deficiency of vitamins A and C.
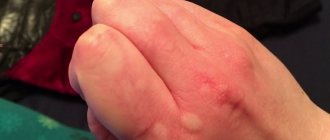
- Allergies to chemical detergents, latex products and other cosmetics. In response to irritation, the top layer on the hands peels and cracks.
- Contact dermatitis is a disease of chemical industry workers and anyone who has direct contact with household chemicals, latex gloves (cleaners, housekeepers and all women who clean the house using chemicals).
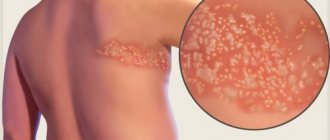
- Fungal infections are the most common dermatological disease. Girls (dishwashers, saleswomen in meat departments), male construction workers, workers in hot shops and chemical plants often suffer. It appears as weeping lesions, the surface of which is covered with bubbles, spots, and a whitish coating. The epidermis in them peels off and cracks.
- Eczema. There are many varieties, manifesting in different areas with the same symptoms. During an exacerbation, blisters and cracks appear, the skin of the affected areas itches and burns. Scratching leads to secondary infection.
- Psoriasis. The disease is known to be incurable. The appearance of plaques, scales and crusts on the hands and between the fingers is characteristic. The skin becomes rough and causes severe itching.
How is keratoderma of the palms and soles treated?
Therapy is based on the use of Niotigazone, the active ingredient of which is acitretin. The drug has an antipsoriatic effect by regulating the processes of skin cell differentiation, their renewal and keratinization. The dosage is selected taking into account the severity of symptoms and the severity of the pathological process. The patient's body weight also matters.
Niotigazone is the main drug for the treatment of palmoplantar keratoderma.
In cases where, for one reason or another, the patient cannot take Neotigazon, large doses of vitamin A are prescribed over a long course.
External therapy is also carried out, the essence of which is the use of the following drugs:
- Keratolytic agents - for active exfoliation of dead cells from the surface of the skin.
- Ointments containing retinoids - to normalize the process of keratinization, inhibiting the reproduction (proliferation) of epithelial cells. The basis of such ointments are glucocorticosteroids, which have an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Physiotherapy: laser therapy, cryotherapy, diathermocoagulation, salt baths.
Other causes of peeling
- Peeling of the hands and feet may be associated with endocrine disorders, manifested by increased sweating of the palms and interdigital folds, and roughness. Patients with diabetes have flaky and itchy feet.
- A common cause of dry and red hands is chapping in cold weather, the appearance of peeling, and the same changes under the influence of bright sunlight.
- Some infectious diseases are accompanied by detachment of the upper epidermis: lupus erythematosus, syphilis, scabies, lichen, hyperkeratosis (increased cell division).
- There are causes of dryness and flaking associated with uncontrolled use of antibiotics and antihistamines.
- Age-related changes are added: hormonal imbalance, metabolic disorders, reduced immunity.
- Some people periodically experience dry and peeling skin on their hands. The reason is bad heredity. No treatment is required, but constant care is required.
- If you notice that the epidermis is drying or flaking, apply cream, observe and wait. If other symptoms are added, you should consult a dermatologist.
Hand lesions in children
In teenagers, the top layer on the palms of the hands dries out and peels off due to hormonal changes, and not vitamin deficiency, as is often assumed.
! To diagnose peeling skin on the hands of a teenager, it needs to be shown to an immunologist or pediatrician.
The reason for the decrease in the protective functions of the epidermis on the hands of a child may be childhood infectious diseases: measles, scarlet fever, staphylococcus. Often a rash, irritation, itching appears on one hand of a child (usually on the right hand), the cause being a fungus.
Children most often become infected with it because they touch dirty objects on the street. Such diseases are difficult to treat and recur (either disappear or reappear). The photo shows features of fungal infection of the hands.
Summary
Palmoplantar keratoderma is a chronic skin disease of a predominantly hereditary nature. The main symptom is excessive peeling of the skin on the soles and palms of the hands. In many cases, signs of pathology begin to appear from the first months of a child’s life, but it can also develop in adolescence, and sometimes later. In some types of keratoderma, the pathological process also affects nails, teeth, and possibly even the development of mental retardation and the occurrence of a number of other symptoms.
Treatment
Spring vitamin deficiency is identified as a separate disease. For treatment, a course of vitamin complexes and the consumption of fresh vegetables, fruits and dairy products are prescribed. Allergy treatment is carried out with Bepanten, Elocom, Fenistil, the course is supplemented with folk remedies and avoidance of foods such as chocolate, honey, carbonated drinks and others.
When treating contact dermatitis, you should remove all aggressive chemicals, use moisturizers, emollients, ointments and creams, use antibiotics and antiviral medications. Dermatitis and eczema are treated with anti-inflammatory and antiallergic drugs. It is necessary to find out the cause of the exacerbation and follow a diet during such periods.
Fungal diseases are diagnosed after examining the scales under a microscope. Drugs for the treatment of candidiasis: Ketocanazole, Candide, Clotremizan, Fluconazole and others. They are taken for a long time (up to 1 month) until the symptoms disappear. Antifungal ointments are used externally for another week after recovery for prevention.
For mycosis, in addition to pharmaceutical medications, treatment with folk remedies is used in the form of infusions, decoctions, herbal baths (celandine, lavender extract, chamomile), various oils (almond, flaxseed, sage oil). A potato mask moisturizes well and makes your hands soft and tender (raw grated potatoes are applied to the damaged areas, a glove is put on your hand for two hours).
Hand masks are prepared from fermented milk products (sour cream or kefir is applied to the dry surfaces of the palms and covered with a napkin). It is good to wipe the outer side of the brush dehydrated in the sun with cucumber juice. Use an oatmeal scrub to remove the stratum corneum.
Hyperkeratosis in psoriasis
Hyperkeratosis often develops against the background of systemic chronic diseases. Especially often, keratinization and peeling of the epidermis is observed in psoriasis (a pathology in which the immune system begins to attack skin cells, causing inflammation and the appearance of ulcers). Psoriatic lesions heal when the disease goes into remission. But skin cells are unable to shed quickly. This leads to the formation of thickened plaques, characteristic of hyperkeratosis. In case of severe exudative type of psoriasis, the patient is often diagnosed with subungual hyperkeratosis, which provokes deformation of the nail plate.
Prevention
To avoid unpleasant symptoms on the skin of the palms and fingers (itching, peeling, cracks), you need to: moisturize them daily, exfoliate dead cells, wash your hands with cosmetics containing glycerin, take baths with herbal infusions, give preference to hypoallergenic cosmetics. It is necessary to include the following components in the diet: greens, nuts, cereals, cereals, vegetable oil, and take complexes of vitamins and minerals.
Remember! Hands, our main helpers, need constant care, perhaps even more than the face and other parts of the body.
Hands should be protected from temperature changes. In cold weather, be sure to wear warm gloves or mittens, avoid contact with the ground and cement during construction work, and if necessary, wear protective gloves. Dishwashing detergents should be gentle, do not forget rubber gloves (if you are not allergic to them!).
Severely irritate the skin of the hands and feet, mechanical injuries lead to cracks, as well as burns and hypothermia. If dryness on the inside of your palms appears as a result of dehydration, you should increase the amount of water you drink to cope with it.
Folk remedies
You can get rid of rough, rough and cracked skin and make it soft and attractive with the help of special folk recipes.
Baths
Baths to normalize the condition of the skin on the surface of the hands can be carried out using the following products:
- Camomile tea. Two tablespoons of medicinal plant flowers should be poured with a glass of boiling water. The mixture should sit for 20 minutes. The liquid is filtered and diluted with a small amount of clean water. It is recommended to take a chamomile bath before bed. The duration of the procedure is 20 minutes. After the bath, dry your hands with a soft towel and apply olive oil to their surface. Chamomile has an anti-inflammatory, antibacterial effect, moisturizes the skin and relieves irritation.
- Saline and soda solutions. This procedure helps get rid of dry skin and strengthens it. In a liter of warm purified water, you need to dissolve 70 g of soda and 15 g of regular or sea salt. Place your hands in the resulting mixture and hold for 20 minutes, after which they are washed under the tap.
Masks
You can treat chapped hand skin using special homemade masks:
- Honey. Has a pronounced moisturizing and wound-healing effect. To prepare it, you need to mix a tablespoon of honey and oatmeal. After about 15 minutes, the mask is applied to the skin of the hands and kept for 30 minutes. After this, hands are washed and additionally lubricated with rich cream.
- Cucumber mask. Has a softening and moisturizing effect. Grate fresh cucumber on a fine grater and add 120 ml of milk. Place your hands in the resulting mixture and hold for 13 minutes, then wash them with plain water.
- Carrot. To prepare the medicinal mixture, take one root vegetable and grate it on a fine grater. Add two tablespoons of milk and one tablespoon of oatmeal to the resulting puree. The thoroughly mixed mixture is applied to problem areas and left for 20 minutes. After the procedure, it is recommended to apply olive oil.
- Sour cream. Helps moisturize the skin and relieve irritation. To prepare it, mix a glass of sour cream with the juice of one lemon and raw yolk. The resulting mixture is applied to a piece of gauze and applied to the problem skin. Hands are additionally wrapped in cellophane and cloth. Keep this mask for half an hour, after which it is washed off with plain water.
Ointments
If deep cracks appear on your hands caused by increased sensitivity and dry skin, you can use a special homemade ointment to improve their condition. The medicine consists of several simple ingredients - a teaspoon of vinegar, yolk, a tablespoon of any vegetable oil.
These components are combined with each other, and the ointment is ready. It is applied to the hands, after which cotton gloves are put on. This compress should be kept overnight. In the morning, wash your hands with warm water.
Diagnostic methods
To diagnose keratoderma, the doctor interviews the patient. The dermatologist asks when the keratinized areas appeared, whether their area increases over time, what kind of discomfort bothers you, and whether there are cases of keratosis in the family history.
The doctor then examines the affected areas using a dermatoscope.
A biopsy is also performed - a part of the keratinized epidermal layer is taken and sent to the laboratory for histological examination.
Since the manifestations of keratosis are similar to other pathologies, the doctor differentiates hyperkeratosis from psoriasis and dyshidrotic eczema.
The doctor refers patients with autosomal recessive types of keratoderma to an additional consultation with a dentist for the purpose of timely diagnosis and treatment of periodontal disease.
Forms
Clinical manifestations depend on the type of dermatosis. Depending on the symptoms, keratoderma is divided into diffuse and focal.
It is worth highlighting Haxthausen's keratoderma separately. This is a chronic keratodermatitis that develops during menopause due to a lack of estrogen in the body.
Menopausal keratoderma occurs in 20% of women over 45 years of age.
Doctors associate the appearance of this disease with age-related ovarian depletion, so keratoderma is considered one of the symptoms of menopause. Papular rashes appear on the sole and palms of the woman, which merge into one large lesions, forming a keratinized area over the entire surface. Papules are covered with scales. The skin is dry, so it peels and cracks appear.
Women are tormented not only by painful sensations, but also by severe itching. Scratching areas can become infected. The clinical picture is similar to dry eczema.
Diffuse
There are such diffuse forms:
- Tosta-Unna (congenital ichthyosis of the soles and palms). This is a hereditary disease, so the first symptoms can appear from an early age, in the first 2 years of a child’s life. The skin turns red, and after a while yellow horny layers appear. Small and deep cracks may appear in the lesion. Nails are involved in the pathological process.
- Meleda. Other names for the disease are palmoplantar progradient keratosis of Kogoya or transgradient keratosis of Siemens. This form is also hereditary. Symptoms appear by the age of 16-20; they rarely appear in childhood. The keratinized areas are yellow-brown in color, along the edge there is a purple border 2-4 mm thick. The cracks are deep, foot sweating increases.
- Werner. A hereditary form, the symptoms of which appear in the first 2-3 months of life. The nail plate is affected.
- Mutilating. Other names are hereditary keratoma or Vonwinkel syndrome. The first symptoms appear at the age of 2 years. The skin of the feet and palms becomes keratinized, grooves appear on the fingers, which impairs their mobility, and spontaneous amputation of the fingers may occur.
- Papillon-Lefebvre. The symptoms are similar to Melad's disease. Not only the feet and palms are affected, but also nearby skin and teeth.
Focal
There are 4 focal forms:
- Disseminated macular keratoderma Fischer-Buschke. Numerous brown horny seals appear, up to 10 mm in size. The formations have crater-shaped edges.
- Limited Brunauer-Franzeschetti keratoderma. Horny areas appear on the skin where the cover is subjected to increased pressure and the nail plate is destroyed.
- Costa's acrokeratoelastoidosis. The origin of this form is unknown. It is diagnosed in women aged 18-20 years. Horny tubercles up to 3 mm in diameter, oval or irregular in shape, appear. The disease is accompanied by increased sweating.
.
Linear keratinized areas appear on the feet and palms. Symptoms appear in the first 2 months of a child’s life.