The beauty of a woman's skin opens up like a flower over time. At first it is a delicate bud that captivates with its freshness at every touch. Then it blooms and captivates with its amazing splendor. The flower needs abundant watering, and our skin needs active care from early childhood. If you take good care of it, it will look healthy and fresh for a long time. But the beauty of skin, like a flower, is not eternal. The skin is a kind of mirror, reflecting many internal processes in the body. Without proper attention, it begins to fade.
Signs of aging appear to varying degrees in all areas, but age-related changes are most noticeable on the skin of the face and neck. There are certain patterns of changes in the skin over time, which we bring to your attention.
AGE CHANGES: INFANT (0-2 YEARS)
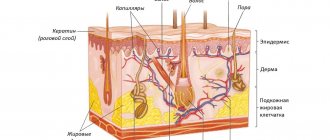
The skin of newborns is very soft and elastic, like velvet. This is due to the fact that for a long time it was covered with a special curdled lubricant, which consists of fat, glycogen, salt, cholesterol, various acids and vitamins. In the womb, it helped prevent maceration (soaking) and performed a bactericidal function. Children's skin has a delicate and thin layer of epidermis - the surface layer of the skin - from 0.5 to 0.25 mm, only 3-4 rows of germ layer cells (in an adult there are 5-6), stratum corneum cells lie in 2-3 rows and are loosely connected to each other and easily peel off. And although the ability of children's skin to regenerate (recovery) is much higher than that of an adult, the epidermis is loosely connected to the underlying layers of the skin, collagen fibers are still defective (they mature by 4 months), and local immunity is weak. Therefore, the skin of a newborn is very vulnerable and prone to redness, peeling and inflammation.
The dermis is 1.5-3 times thinner than in adults, the subcutaneous fatty tissue is very well developed. Per unit surface and mass in newborns it is 5 times greater than in adults. Sweat glands in babies are not yet formed and do not function (imperfect sweating will begin at 1 month), so children easily overheat. The easy occurrence of prickly heat is explained by the still wide ducts of sweat jelly, into which infection easily penetrates. The sebaceous glands in newborns are large and produce sebum much more intensely than in adults, and their number per 1 cm2 is 4-8 times greater than in adults, which ensures that children of this age are prone to milia, gneiss and newborn acne. By the age of 7, the sebaceous glands decrease in size and a significant part of them atrophies. By puberty, their size increases again. The number of fat cells increases at 1 year of life, and the size increases from birth to 6 years. Fat at an early age is more dense, because contains more saturated fatty acids.
How to soften the aponeurosis?
Initially, it is important for us to learn to feel the work of the muscles, to do this, soften the aponeurosis:
We massage the head with our palms and fingers, knead the tendon helmet over the entire head, go through spirals, pinches, and rubbing along vectors from the periphery upwards.
Since hair is a vector continuation of the aponeurosis, with its help we can perfectly massage the entire surface. We grab small strands of hair at the very roots, lightly stretch and hold in tension for 3-5 seconds. You can grab with both hands at once, moving slightly from side to side.
We set the tissues in the correct direction of movement and lift them up: we place our hands with “rakes” and slowly, with good pressure, “stretch” from bottom to top along the following vectors: forehead - crown, temples - crown, corner of the eye - crown, zygomatic bone - crown, back of the head - crown. Mentally follow the movements, imagining that, following your hands, your forehead, temples, eyelids, and cheekbones are being pulled up.
After some time, having thoroughly stretched the muscles of the cranial vault, you will be able to feel and control them. Then you can move on to the lifting exercise “circular lifting”
To do this, you need to learn to pull all the muscles of the cranial vault towards the top of the head. Without using your hands, you will already be able to feel how the frontal and occipital muscles shift upward, how the tendon helmet contracts, how the temporal and ear muscles strive upward.
It feels like you are wearing a knitted cap on your head, which softly shrinks right on your head and pulls the fabric up. It is good to maintain this state for 10 to 20 seconds, you can do several repetitions.
AGE CHANGES: ALICE'S AGE (2-10 YEARS)
At this age, the child's skin is still very vulnerable. It is not yet so well protected from microbes and the external environment. Children's skin will be fully formed by the age of 7 and will acquire all the properties and structure of adult skin.
The skin of babies at this age has increased hydrophilicity, as a result of which it is abundantly saturated with water: the water content in the skin of a child of this age is 80–90%, while in an adult it is only 65–67%. This moisture content in the leather must be maintained at all times, however, because it is very thin, moisture is easily lost when the ambient temperature rises, and the leather dries out.
Children's skin has unique regenerative abilities. There is faster epithelization and more rapid formation of granulations when the integrity of the skin is damaged.
The subcutaneous fat layer is thin, but the density of sweat glands is high. As a result, the child's skin does not provide the necessary thermoregulation, and children very quickly become hypothermic or overheated. This is also facilitated by the abundance of blood vessels, which, although they give the skin a wonderful pink color, at the same time create increased heat transfer. For the same reason, children's skin has a high absorption capacity. In addition, in young skin, melanin-producing cells are contained in small quantities, which explains increased sensitivity to ultraviolet rays and rapid sunburn.
AGE CHANGES: JULIET'S AGE (PUBERTY)
During adolescence, the skin has the ability to quickly regenerate and is very elastic. During puberty, the structure of the skin changes. This is due to hormonal changes in the body. The amount of sex hormones in the blood increases, which ensures the appearance of secondary sexual characteristics. During this period, the body experiences enormous stress on all systems; functional disorders and exacerbation of chronic diseases may occur. But the skin reacts most clearly: the pores of the sebaceous glands enlarge and begin to secrete more secretion, which in turn mixes with dirt and dust. As a result, the skin becomes unpleasantly shiny, pores become clogged and the main problem becomes acne, which is especially susceptible to those with oily skin. Teenagers' skin needs especially careful care, cleansing and moisturizing. There is an opinion that after puberty ends, acne will go away, but it is better not to start the acne process. Firstly, acne can persist for many years, and secondly, after acne heals, post-acne scars may appear on the skin, which are difficult to correct.
The difference between premature aging and natural aging
The age at which the body’s natural aging processes begin is determined by nature at the genetic level and is individual for each person. This type of aging is called chronoaging or natural aging. It is not possible to slow down this process - the program will work at the appointed time, regardless of the person’s wishes.
But another type of aging - premature or photoaging, each of us is able to correct, because its development is influenced by external factors:
UV rays, free radicals, lifestyle, bad habits, dietary principles.
AGE CHANGES: TURGENEV GIRL (25-30 YEARS OLD)
The period when a girl turns from an angular teenager into a young woman. At this time, the skin is still smooth and elastic. There are no more problems with acne, but the first wrinkles appear. Due to facial movements, the skin is subject to constant mechanical deformation, and by the age of 25, shallow facial wrinkles appear in the corners of the mouth, eyes and forehead. The so-called laugh lines become noticeable. The skin still retains the ability to recover, but already needs more thorough and comprehensive care. It needs to be nourished and moisturized. In addition, the skin needs special vitamins and nutrients that promote collagen formation. It is important not to miss the first expression lines.
AGE CHANGES: CHEKHOV'S HEROINE (30-40 YEARS OLD)
After 30-35 years, small superficial wrinkles very slowly, gradually become noticeable, and a so-called “plateau” state occurs, characterized by moderate changes in the depth of all wrinkles.
During this period, fading processes are launched in the epidermis and dermis, which will actively progress in the following age intervals. These changes occur unnoticed at first, gradually, gradually, accumulating and becoming obvious (suddenly!) by the age of 40-45 and reach a peak by the age of 50-55:
- the rate of cell division of the basal layer decreases, and its thickness decreases.
- the thickness of the stratum corneum, on the contrary, gradually increases, although the horny scales themselves also become thinner, but they peel off more slowly.
- The functional abilities of epidermal cells gradually decrease, which leads to thinning of the lipid (fatty) membrane of the skin and a decrease in the number of protein bonds between corneocytes. As a result, there is a large loss of water, as well as dryness and flaking, and over time, thinned skin becomes like parchment.
- the thickness of the dermis decreases, the number and size of dermal cells (fibroblasts, macrophages, tissue basophils) and their functional activity decreases, and therefore the volume of the ground substance, collagen and elastic fibers decreases. On average, the synthesis of collagen and elastin decreases by 1% annually from the age of 25.
- elastin and collagen fibers thicken, their structure is disrupted, and their arrangement becomes less ordered. All this causes the skin to relax and lose its former elasticity when stretched.
- the content of glycosaminoglycans in the dermis also decreases. A decrease in the level of hyaluronic acid in the skin leads to disruption of its hydration, turgor and elasticity, contributing to the appearance of dry skin and the formation of wrinkles.
- external signs of skin aging in people are expressed in its relaxation, thinning, dryness, deepening of facial folds, the formation of a network of fine wrinkles, the appearance of pigmentation and other changes.
- microcirculation of the skin decreases, which leads to deterioration of nutrition (trophism) and deterioration of complexion.
- muscle dystonia: muscle tone is no longer as high as before. This primarily concerns the muscles of the neck and face. In the area of the chin and forehead, muscles contract - longitudinal and transverse wrinkles appear, and in the cheek area they sag, which leads to a slight deformation of the facial contour and drooping of the corners of the mouth.
Floating oval
A clear jaw angle is one of the main indicators of youth. With age, subcutaneous fat shifts downwards, as a result the cheeks become less elastic, jowls, nasolabial folds, and a double chin appear. The face becomes pasty, blood circulation slows down, and swelling is observed. The changes are especially noticeable on the side.
In youth, the face looks like a triangle with the apex on the chin; this arrangement of tissues is called the “triangle of youth.” With age, the architecture of the face changes - the cheeks slide down and become the base of the triangle, the eyebrows lowered down emphasize the picture.
To restore the “triangle of youth”, fillers and mesothreads are used. You can perform face fitness exercises. As a result, the volume of the cheeks increases, the tissues are stretched, jowls and nasolabial lines disappear - the face looks much younger.
AGE CHANGES: BALZAC AGE (40-50 YEARS)
At this age, women experience a process of involution - age-related dystrophy. The thickness of the epidermis and dermis decreases, and atrophy of the subcutaneous fatty tissue and small sebaceous glands begins. Collagen fibers thicken, some of them stick together or fall apart. Another feature of this period is progressive lipoatrophy (reduction of fatty tissue on the face). According to modern data, changes in the fat layer do not occur evenly: there is a decrease in the volume of deep-lying fat packets, as well as thinning and downward displacement (ptosis) of subcutaneous fat tissue. In women over 40 years old, wrinkles begin to actively appear all over the face: around the eyes, on the forehead, near the nose, and facial features become outlined and become angular. The skin becomes drier, denser and tougher, prone to peeling, and pigment spots can often be seen. The cheeks begin to sag a little, the first wrinkles on the neck and a hint of a double chin are visible (this is especially noticeable in overweight women). After 40 years, the skin of the eyelids also changes. It becomes heavier, folds appear, and the eyelid itself droops. Dark circles under the eyes are already noticeable, and there are “crow’s feet” in the corners of the eyes. This is due to the fact that the skin in these areas is much thinner than in other areas and has few sebaceous glands. In addition, many women experience problems related to hormonal status, for example, hair growth on the upper lip.
Progressive microcirculation disorders lead to vascular appearances - rosacea, spider veins and telangiectasias.
Is it possible to prolong youth
Extending youth and stopping age-related changes in the skin on a woman’s face is a rather long and labor-intensive process, but it is quite feasible. Proper care appropriate to your appearance type, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, regular cleansing of the body, proper facial exercises, facial taping, vacuum massage, regular courses of environmentally friendly hardware therapy in the form of biomechanical stimulation will help control the skin condition and avoid significant changes.
Significant changes in appearance with age can be prevented and stopped using the above methods only after consultation with a competent specialist in each area of eco-rejuvenation. The required level of knowledge, fairly narrow specialization and an integrated approach will ensure a sustainable effect of preserving youth despite adulthood.
Tags: rejuvenation, aging
- Related Posts
- Varicose veins on the legs: symptoms, causes, consequences, treatment options, prevention
- How to get rid of pigmentation on the face and body at home
- Couperosis on the face: causes, treatment methods, methods of care and strengthening of blood vessels
« Previous entry
AGE CHANGES: WOMEN OF ELEGANT AGE (OVER 50 YEARS OLD)
At this age, hormonal changes usually occur - menopause. Progressive formation of wrinkles and their deepening are observed after 50 years, which is mainly due to the active loss of collagen and elastin, especially in the first 5 years of postmenopause, as estrogen levels sharply decrease. As a result, the body lacks vitamins and nutrients. The skin rapidly loses its natural strength and begins to change dramatically, losing its barrier properties. It becomes thinner, the subcutaneous fat layer on the face decreases, regeneration processes slow down and blood supply worsens even more (vascular sclerosis progresses) and, as a result, oxygen starvation of tissues increases. Due to the lack of estrogen, the oiliness of the skin and the activity of the sebaceous glands in the skin decrease, the amount of hyaluronic acid and collagen decreases, lipoatrophy of the face and neck progresses (reduction of subcutaneous fat), and a selective decrease in the volume of the skull bones is added: expansion of the orbit leads to a rise in the head of the eyebrow, bulging fatty hernias and deepening of the nasolabial furrow; resorption of the upper jaw leads to flattening of the midface, drooping of the tip of the nose, flattening and lengthening of the upper lip.
The skin becomes very pale, dry and thin, like parchment, and often peels off, which leads to disruption of the barrier and regenerative properties of the skin, so aging skin is more easily injured and more difficult to recover. Its turgor (hydration) and elasticity decrease, and deep wrinkles appear. In people over 65 years of age, the thickness of the dermis usually decreases by approximately 20%. Pronounced pigment spots, senile keratomas and other benign neoplasms, growth of vellus hair on the cheeks, chin and above the upper lip appear. Along with the appearance of pastiness and edema, there is a sharpening and change in facial features, which is associated with a reduction in subcutaneous fatty tissue and changes in the skull. Bags and circles appear under the eyes, and horizontal and interbrow wrinkles appear on the forehead.
After 60 years, another “leap” occurs in the dynamics of age-related changes, caused by increasing ptosis of soft tissues, which leads to noticeable deformation of the external contours of the face. The skin at the chin and around the jaws becomes flabby, the skin of the cheeks sags, the nasolacrimal and nasolabial furrows deepen, marionette wrinkles give a mournful, eternally sad expression, jowls appear, a double chin, the face becomes swollen against the background of many small wrinkles.
Why does the face age?
Externally, the effort of the face is expressed by the appearance of wrinkles and distortion of its features. When studying the issue globally, it becomes clear that the main cause is deformation of the muscles under the skin. They come in two types: mimic and chewing. In different situations (sleep, work, expression of emotions), the behavior of these muscles is quite individual, which serves as the basis for age-related changes in the skin.
The struggle for youth is doomed to failure if you approach the problem superficially or with insufficient knowledge. Having studied in detail the anatomy of the facial muscles, you can target a specific problem. The main difference is the mounting methods. The mimic ones are attached to the bone on one side, and the other flows directly into the skin; the chewing ones are in contact with the bones of the skull with both ends. The appearance of the skin depends on their condition.
Facial changes with age
Diagnosis of age-related changes
You can check for the presence of muscle blocks that affect facial aging using self-diagnosis using the following video: