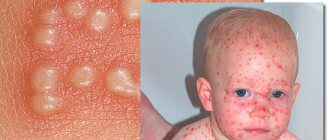
Genital herpes is a chronic recurrent viral disease caused by herpesvirus infections type 1 and 2. This type of genital damage is one of the most common and is transmitted during sexual intercourse.
In more than 60% of cases, transmission of infection occurs in the absence of any characteristic severe symptoms in the infected person.
Medicine for herpes in intimate places can only be selected by an experienced, qualified dermatovenerologist after a comprehensive diagnosis.
The disease is accompanied by the formation of painful rashes in the genital and perianal area, itching, increased pain during sexual intercourse and during urination, and the formation of mucopurulent discharge from the vagina.
Additionally, there may be an increase in body temperature, the development of nausea, myalgia, and sleep disturbances.
- The main indication for episodic therapy is the presence of the described symptoms.
- Suppressive therapy is prescribed for severe disease, exacerbations more often than 5-7 times every 12 months, and the development of complications.
If specific antibodies are detected in the patient’s body, there is no need to use drugs for genital herpes.
Causes of genital herpes
The genital form of the disease has tended to increase in incidence over the past decades. According to one version, in European countries this was facilitated by an increase in the number of sexual partners for the average person, as well as the widespread practice of oral sex. Also, this disease is more common in areas with high population density, in families with a low socio-economic standard of living and in cases of poor personal hygiene.
Read more
Primary infection with the herpes simplex virus in childhood occurs through airborne droplets - as statistics show, among children 6-7 years old, almost half are infected with herpes. Secondary infection most often occurs through genital, oral-genital and anal-genital contact. The virus that causes genital herpes enters the human body through intact mucous membranes or damaged areas of the skin during sexual intercourse. The highest incidence rate is observed among people aged 20-30 years. In many cases, the infected partner is unaware that he is infected, is an asymptomatic carrier of the virus, and transmits the virus to his sexual partners. A number of scientists believe that about 90% of adults are carriers of the herpes virus, but only 10-20% of them experience its clinical manifestations, including rashes on the genitals. This is due to a decrease in immune defense and the presence of other diseases that further weaken the body. It has been established that women suffer from genital herpes more often than men, which is due to their anatomical and physiological characteristics. Also, according to one version, the risk of HSV infection is increased by surgical termination of pregnancy and the use of intrauterine devices.
The virus is also transmitted vertically - from a sick mother to the fetus and through the use of household items together with an infected person. Also, if there are rashes on the lips and nose, there is a possibility of transferring the virus to the genitals. In addition, HSV is often detected in combination with ureaplasma, other STDs and cytomegalovirus.
Features and rules for applying ointment
Before using ointments for genital herpes, a mandatory consultation with your doctor is required. The disease is localized in different places, so the application has its own specifics. It is carried out 4-6 times a day, and recommendations for use are similar for all types of medications:
- Carrying out intimate hygiene procedures. The affected area is thoroughly washed with warm water and an antibacterial agent and dried with paper towels. However, they must be strictly individual to eliminate the risk of infecting family members.
- Herpetic ointment is applied not only to the site of the disease, but also around it. If blisters appear on the uterus, fallopian tubes, or vaginal walls, the medicine should be applied using a tampon or vaginal applicator.
- The herpes virus is expressed in the appearance of rashes, after opening which it comes out. During this period, it is forbidden to apply the cream with bare hands, as this risks spreading the infection to other parts of the body or person through close contact. It is also necessary to use personal protective equipment (rubber gloves) if the drug is applied by a loved one. It is equally convenient to treat areas of the skin with cotton pads or swabs.
The course of treatment for herpes lasts for a week, depending on the condition of the patient’s body and the stage of the disease.
Treatment of the intimate area should be carried out regularly to achieve maximum effect and rapid healing.
If treatment is suspended, there is a high probability of sudden activation of the virus with deterioration of the immune system. As a result, therapy may take a long time.
Treatment with antiherpes ointments should not exceed 10 days. If their use does not produce results, then they are not suitable. Then you should consult your doctor again to select an effective drug.
Application rules
For herpes, the ointment should be applied following certain recommendations. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Before the procedure, hands should be thoroughly washed with soap. It is best to treat them using a special skin antiseptic.
- Before using the ointment, a skin test is performed to determine sensitivity to the drug. A small amount of liniment is applied to the elbow or wrist. The results are assessed after half an hour. If there is no redness or other unpleasant symptoms, then you can safely use it.
- The medicine is applied with a cotton swab or cotton swab to avoid direct contact of hands with the rash elements.
Types of genital herpes
Primary genital herpes: symptoms and localization
The first stage of the disease is manifested by the appearance of vesicular elements on the skin and mucous membranes. Initially, swelling, redness, itching and discomfort appear in the area where the virus has been introduced. Sometimes this is accompanied by weakness, lethargy, headaches, enlarged inguinal lymph nodes and increased body temperature. After a few days, rashes appear - small blisters filled with clear liquid, which soon burst open and form weeping erosions. Complete healing of the ulcers occurs in approximately 10-14 days.
The localization of rashes on the genitals is determined by the place where the virus enters the body. In women, clinical manifestations of herpes in the intimate area are observed on the labia majora and minora, in the vagina, in the cervix and perineum. In men, vesicles with transparent contents appear on the head and body of the penis, as well as on the scrotum.
The virus can also infect the urethra, bladder, anus, rectum, ovaries, cervical canal, fallopian tubes, uterus in women and prostate and seminal vesicles in men.
Recurrent genital herpes
50-70% of those infected with HSV experience a recurrent form. It makes itself felt by repeated blistering rashes that periodically appear in the same place. In the mild form, exacerbations occur no more than three times a year, the moderate form is characterized by exacerbations up to six times a year, and in the severe form, the patient suffers from monthly rashes and accompanying symptoms, which can significantly reduce the quality of life.
The arrhythmic course of HSV in the genital area is characterized by the presence of remissions, which can reach several months. According to observations, rare outbreaks of the disease are more intense in clinical manifestations than frequent ones. The monotonous course of the infectious disease most often manifests itself depending on the monthly cycle in women. And with HSV of the subsiding type, there is both a decrease in the intensity of symptoms and an increase in periods of remission.
FAMCICLOVIR
PHARMACY
Antiviral agent. Prodrug; is a 6-deoxydiacetyl analogue of the active antiviral substance penciclovir. Transforming in the body into an active compound - penciclovir, it acts on Herpes simplex viruses (types 1 and 2), Varicella zoster, Epstein-Barr virus.
Penetrating into virus-infected cells, penciclovir is phosphorylated by viral thymidine kinase to penciclovir monophosphate, which is then converted into penciclovir triphosphate under the action of cellular kinases. Penciclovir triphosphate is retained in the infected cell for more than 12 hours and suppresses viral DNA replication. Has no effect on uninfected cells. Active against some acyclovir-resistant strains of the Herpes simplex virus that have an altered DNA polymerase.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, it is quickly and almost completely absorbed and quickly converted into active penciclovir. Bioavailability – 77%. TCmax – 45 min, Cmax after taking a single dose of 500 mg – 3.3-4.2 mcg/ml. Volume of distribution – 1 l/kg. Communication with plasma proteins – 20%. T1/2 – 2.1-3 hours T1/2 of penciclovir triphosphate from cells infected with herpes simplex virus type 1 – 10 hours, from cells infected with herpes simplex virus type 2 – 20 hours, from cells infected with Varicella zoster virus – 7 hours T1/2 with CC less than 30 ml/min – 10-13 hours. Excreted by the kidneys by glomerular filtration and tubular secretion; with urine (60-65% in the form of penciclovir), 27% with feces. Does not accumulate. Excreted during hemodialysis.
INDICATIONS
Infections caused by Herpes simplex (types I and II): primary infection, exacerbation of chronic infection, prevention; herpes zoster (Varicella zoster), postherpetic neuralgia, recurrent genital herpes.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity, pregnancy, lactation, childhood. Carefully. Kidney failure.
DOSING
Orally, for adults with acute herpetic infection - 250 mg 3 times a day for 7 days. For herpes zoster (Varicella zoster) and a high risk of developing postherpetic neuralgia - 250 mg 3 times a day for 7 days. Treatment should begin immediately after diagnosis. For genital herpes caused by Herpes simplex (type II): for primary infection - 250 mg 3 times a day for 5 days, for relapses of chronic infection - 125 mg 2 times a day for 5 days. Treatment should begin immediately after the first symptoms of the disease appear. For prevention – 250 mg 2 times a day. It is recommended to periodically discontinue the drug at intervals of 6-12 months to assess possible changes in the course of the disease. In patients with impaired renal excretory function, dose adjustment is required: for CC 30-59 ml/min – 250 mg 2 times a day; with CC less than 30 ml/min – 125 mg 3 times a day. For patients on hemodialysis, 250 mg (for patients with Varicella zoster) and 125 mg (for patients with genital herpes), the dose should be taken immediately after the procedure, because after 4 hours of hemodialysis, the plasma concentration of penciclovir decreases by approximately 75%.
SIDE EFFECTS
Headache, nausea, dizziness, vomiting, diarrhea, allergic reactions; in the elderly – confusion, hallucinations; with reduced immunity - abdominal pain, fever and rarely - granulocytopenia and thrombocytopenia. Overdose. Symptoms: if recommendations for dose reduction are not followed taking into account renal function, acute renal failure occurs. Treatment: symptomatic, hemodialysis.
INTERACTION
Drugs that block tubular secretion increase plasma concentrations.
SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONS
Penetrates into breast milk; nursing mothers are advised to stop breastfeeding. If there are clinical manifestations of genital herpes, patients should avoid sexual intercourse during antiviral treatment.
Manifestations and symptoms of herpes in the intimate area in women and men
Herpetic cystitis of women
Herpetic cystitis is a pathology characterized by inflammatory processes in the bladder caused by the herpes virus. This disease manifests itself as discomfort when urinating and hyperemia of the skin and mucous membranes. Women are especially often bothered by the urge to urinate at night. If left untreated, herpetic cystitis can lead to complications, including herpetic salpingoophoritis. In this case, the inflammation affects the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
Herpes of the urethra and bladder
The disease makes itself felt by painful sensations and pain when urinating. There is a frequent urge to go to the toilet, there may be blood in the urine and discomfort in the bladder area. In men, detection of the herpes simplex virus in the urine may indicate inflammation of the prostate gland.
If you suspect herpetic prostatitis, which is characterized by frequent relapses, the patient must undergo a special examination for sexually transmitted infections of a viral nature.
Herpetic lesions of the anal area and rectum
The disease manifests itself with itching, burning and pain in the affected area. Bleeding may occur during bowel movements. As the disease develops, erosions and cracks form on the mucous membrane, which are often attempted to be treated only surgically, without the use of drug antiviral treatment.
Herpes on the pubic area
The disease causes not only pain, but also significant discomfort. Herpes on the pubic region in women (photo 3) and in men appears against the background of the same prodromal symptoms of redness, itching and burning. Herpes pubis in men affects not only the skin itself, but also the hair follicles. You can often notice an abscess with a hair sticking out of it. The risk of infection of the subcutaneous layers in this case increases.
The appearance of herpes on the pubis is red spots, in the center of which there are blisters with liquid. Herpes on the pubis causes inconvenience because constant friction against clothing leads to early bursting of the contents of the blisters, weeping areas remain in their place, and when the hair follicles suppurate, the recovery of the skin is significantly delayed. After the integrity of the vesicles is damaged, spots with dried contents and sometimes a slight admixture of blood remain in their place. During the healing process, the crusts come off, revealing a thin, healthy epithelium underneath. On average, the recovery process ends by the end of the first week.
Treatment of genital herpes during pregnancy
The greatest danger of this disease is that the virus can infect the nervous tissue of the fetus, which can lead to the development of intrauterine pathologies. It is especially dangerous if the disease develops in early pregnancy. It can interfere with the normal development of fetal organs and tissues and even lead to spontaneous miscarriage and premature birth. Herpes viruses occupy second place after the rubella virus in terms of teratogenicity - disruption of the process of embryogenesis, leading to developmental abnormalities. More than 60% of children infected with herpes develop encephalitis.
To prevent infection of the fetus as it passes through the birth canal, the expectant mother is most often recommended to have a cesarean section.
How to use the medicine correctly
The ointment must be applied with clean hands. The affected skin should also be cleaned and gently blotted with paper towels (so as not to further injure the tissue).
Before using the drug, you need to test for allergic reactions. Apply a little ointment to the inner surface of the forearm and wait half an hour. It can be used if redness, itching, burning, and rashes have not appeared over the past period of time.
The rash should not be handled with unprotected hands. Therefore, the ointment is distributed over the affected areas using a cotton swab or swab. The devices used for processing are disposed of to avoid a new wave of rashes.
The product should be used at the first warning signs of the disease, when a feeling of swelling and itching appears in the areas of the future rash.
Treatment of herpes in the intimate area with folk remedies: will traditional medicine help?
Traditional medicine existed in all periods of human history, and the experience of traditional healers multiplied over the millennia and was passed on from generation to generation. True, one cannot help but admit that today many of the recipes that our ancestors used have been lost and forgotten, and the assessment of traditional medicine by specialists is still ambiguous. What happens when treated with traditional medicine methods
Today, traditional medicine offers both rational methods, which, under certain conditions, can really help cope with various diseases, and irrational ones, which deserve critical evaluation by doctors. But this does not stop those who, instead of turning to a specialist, decided to help themselves on their own by testing the effectiveness of traditional medicine recipes. As a rule, such people will be disappointed - no decoctions, infusions, applications of medicinal herbs and other drugs prepared at home can help get rid of the manifestations of herpes in the intimate area. It must be remembered that refusal to see a doctor and lack of adequate treatment can lead to unpredictable consequences and the development of life-threatening complications.
Only antiviral drugs that not only relieve symptoms, but also fight the root cause of the disease can help reduce the severity and shorten the course of the disease.
General recommendations
To get rid of intimate herpes, procedures alone are not enough. Don't forget about nutritional therapy.
The patient is advised to give up fast food and simple carbohydrates. The main food should be vegetables and fruits (preferably raw, since heat treatment reduces the value of the product). The protein necessary for humans can be replenished with fermented milk products and lean poultry meat.
To boost immunity and prevent genital rashes, it is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle. Exercising and morning douches with cold water will also help strengthen the body.
Antiviral drug VIFERON for genital herpes
To combat herpes in the intimate area, it is recommended to use antiviral agents containing interferon. According to experts, interferon has a powerful antiviral effect, and its deficiency is one of the main causes of relapse of the disease. One of the drugs used to treat herpes is VIFERON - an antiviral and immunomodulatory drug with an indirect antibacterial effect, which has a number of unique pharmacological properties.
The drug contains interferon alpha-2b, which blocks the reproduction of viruses and also corrects the body’s own immunity. VIFERON is available in the form of suppositories, ointments and gels. To treat herpesvirus infections in children, suppositories are used in a dosage of 150,000 IU once every twelve hours, for adults - 1,000,000 IU, for pregnant women - 500,000 IU. Gel and ointment are also used to combat herpes in the intimate area. The gel has a hydrophobic base and is better absorbed on the skin, and the ointment has a hydrophilic base and is better absorbed on mucous membranes. The gel in the form of a strip no more than 0.5 cm is applied to the previously dried affected surface 3-5 times a day for 5-6 days. The ointment is applied to the affected surface 3-4 times a day for 5-7 days.
The drug VIFERON Suppositories (suppositories) suppresses the activity of viruses and increases the effectiveness of the body’s own immune response to pathogenic microorganisms. And VIFERON Gel and VIFERON Ointment, when applied to the skin and mucous membranes, form a thin protective layer, which allows you to fight viruses and also strengthens local immunity.
Treatment
The process of treating genital herpes in women is quite complex. Antiviral drugs can only suppress symptoms for a while, but do not completely get rid of the virus. To obtain advice on treatment, a woman should contact a gynecologist or dermatovenerologist.
General rules
Genital herpes in women is treated comprehensively using various antiviral drugs. Drug therapy is the main method of treating type 2 herpes in women. No special diet is required for herpes infection. A healthy diet is recommended; the diet should be enriched with vitamins. Alcoholic drinks, strong tea and coffee, preservatives, and spices are excluded.
It is important to avoid sexual intercourse during treatment. A woman’s sexual partner should also take antiviral drugs, even if he has no external manifestations of infection.
During treatment, personal hygiene should be carefully observed. It is recommended for a woman to wash herself using plain boiled water, without hygiene creams and gels. Linen should be made from natural fabrics and should be changed daily.
Antiviral drugs
These are agents that directly affect the herpes virus. They are divided into drugs with systemic and local action. Both options are used to treat genital herpes in women.
The main medicine used for herpes infection is Acyclovir. It is prescribed 200 mg 5 times a day. The duration of use is 10 days. The dose may be doubled if the rash is widespread. The effectiveness of the drug will be significantly higher if you start taking it immediately when the first symptoms appear.
A more effective and modern drug is Famciclovir. It is a derivative of acyclovir. It is prescribed in a dosage of 500 mg 2 times a day. Duration of treatment: 7 days. Also derivatives of acyclovir are drugs such as Valtrex, Valvir.
In the presence of frequent relapses, maintenance therapy with acyclovir and its derivatives is prescribed. Acyclovir in this case is prescribed 800 mg daily. The duration of treatment is several months. Thanks to this, the frequency of recurrence of infection is reduced by a third. The drugs can cause allergic reactions, nausea, and digestive disorders. With long-term use, liver and kidney function is impaired, so during preventive treatment you should regularly take control blood tests.
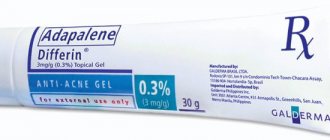
Local preparations include ointments and gels containing antiviral components. They help dry out rashes, eliminate itching and burning. They use drugs such as:
- "Fenistil Pentsivir".
- "Viru-Merz Serol".
- "Viferon".
- "Panavir".
The products are applied in a thin layer to the affected areas twice a day. The effectiveness of local treatment is higher in the first days of the disease.
Immunostimulants
These drugs stimulate the body's own interferon production. Thanks to this, the body copes with the infection itself. Immunostimulants are usually prescribed for chronic herpetic infections with frequent relapses. Herpes can be treated with such drugs only if there are no disturbances in the functioning of the immune system.
Immunostimulants include:
- "Cycloferon".
- "Galavit."
- "Polyoxidonium".
- "Isoprinosine."
- "Viferon".
- "Genferon."
Doctors consider it more effective to treat genital herpes with local administration of interferon stimulants - in the form of suppositories and gels.
Prevention of genital herpes virus infection
To prevent infection, you must remember to use a condom during casual sexual intercourse, as well as the use of antiseptics to treat areas of the skin where the virus can get. Relapses of the disease are observed with a decrease in immune defense, various diseases, stress, and even with frequent overheating and hypothermia. Therefore, in order for the clinical signs of herpes to make themselves felt as rarely as possible or not to appear at all, you must try to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat well and get enough rest, as well as regularly take vitamin supplements recommended by your doctor.
To prevent self-infection, in order to prevent the virus from being transferred from the face in the presence of rashes on the lips to the genital area, it is necessary to adhere to the rules of personal hygiene and wash your hands more often. Each family member should have separate towels for different parts of the body.
After unprotected sexual intercourse, during sexual relations with a carrier of the herpes simplex virus, and when planning pregnancy, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations with a doctor.
Reference and information material
Author of the article
Belyaev Dmitry Alexandrovich
General doctor
Loading...
Take other surveys
Preventive actions
To prevent the formation and exacerbation of herpes in intimate places, it is necessary to exclude casual sexual contacts, use barrier contraception, and promptly examine and treat the sexual partner.
If the virus worsens, use medications in strict accordance with the doctor, and in the future use medications according to a special regimen aimed at preventing the disease.
To prevent infection of a sexual partner, a doctor may recommend the use of a number of antiviral and immunomodulatory medications intended for long-term use.
Author: Antonova Elena Mikhailovna, pharmacist
Pros and cons of drugs
Therapy is not complete without herpes ointment applied in the intimate area. The advantages of using such drugs:
- Ointments have a light oily consistency that is easy to apply and further softens the skin.
- The likelihood of developing negative reactions is minimal, although prolonged use may cause peeling.
- There are relatively few contraindications and side effects.
- The products prevent the spread of the rash to adjacent tissues and the reappearance of vesicles.
- Ointments act quickly enough, reducing the period of disability.
- There are drugs that are approved for use during gestation and breastfeeding.
However, it is impossible to cure herpes with ointment alone. In addition, its use does not protect against infection of the patient's partner. During a relapse, it is recommended to exclude sexual contact or use barrier methods of contraception.