Herpetic pathology caused by the herpes zoster virus (family of herpes viruses) manifests itself in two forms: chicken pox and herpes zoster.
Chickenpox is a childhood infection familiar to most parents, associated with a specific skin rash and perceived as quite harmless.
Shingles is an adult disease that occurs in people who have had chickenpox. With this pathology, in a person with an immunodeficiency state, herpetic eruptions appear in the form of small blisters along the course of individual nerves.
Doctors know well how to diagnose and how to treat shingles. Therapy is based on the use of antiherpetic drugs, immunomodulators and a number of other medications aimed at eliminating unpleasant itching and pain.
Pathogenesis
Infection is possible from a person who has herpes zoster or chickenpox. The routes of transmission of the virus are airborne droplets, contact, and the transplacental route is also possible. The virus is neurodermatotropic, that is, it can infect cells of the nervous system and skin epithelium. Initially or after chickenpox, the virus penetrates through the skin and mucous membranes, then through the circulatory and lymphatic systems into the intervertebral nodes and dorsal roots of the spinal cord, where it can remain latent for a long time, like the related herpes simplex virus.
Activation of the infection occurs when the immunological resistance of the body decreases. The most common causes of the onset of the disease:
- taking drugs that reduce immunity;
- chronic stress and exhausting work;
- local hypothermia;
- oncological diseases (lymphogranulomatosis, malignant tumors);
- consequences of radiation therapy;
- patients with HIV infection in the stage of transition to acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS);
- organ and bone marrow transplantation.
Predisposing factors:
- persons over 55 years of age;
- pregnant women;
- after long-term treatment with antibiotics, cytostatics, glucocorticosteroids.
An obligatory component of the activation of infection is a kind of viral ganglioneuritis with damage to the intervertebral ganglia (or ganglia of the cranial nerves) and damage to the dorsal roots. The virus can involve the autonomic ganglia in the process and cause meningoencephalitis. Internal organs may also be affected. Thus, in the picture of herpes zoster, in contrast to chickenpox, mainly the neurotropic properties of the virus come to the fore.
Causes
There are several types of this virus, so you should consult a doctor to determine the exact picture of the disease. The dermatologist will conduct an examination, make an initial diagnosis and take a scraping of the scales. Such simple but most necessary actions will help determine the exact cause of the skin disease.
Main reasons:
- Weak immune system.
- Contact with microscopic spores of the fungus – canis – on the face. Most often this happens after contact with the pet's fur.
- Mental problems, long-term depression.
- Allergic reactions.
- Anthropophilic fungi - with animal hair or saliva.
- Lack of vitamins and minerals in the body.
- Constant colds.
- Insect bites.
- Fungal infection – Malassezia.
- Residual infected cells after the disease – chickenpox.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Gastrointestinal problems.
- Helminthiasis.
To quickly and easily cure lichen on the face, you need to carefully examine the diseased cells under a microscope, as well as understand the cause of what is happening.
Symptoms of herpes zoster
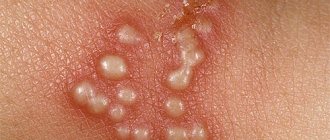
Rash and pain are the main symptoms of shingles (see photo). When the disease occurs, the patient always experiences pain, the intensity of which ranges from barely perceptible to excruciating, debilitating pain, which stops for a short period under the influence of drugs. Most often, pain appears in the area of skin rashes corresponding to the affected nerves. The intensity of the pain does not always correspond to the severity of the skin rash.
The prodromal period of herpes zoster has its own special color. The main symptoms during this period: weakness, malaise, low-grade body temperature, headache, tingling, itching and burning in areas of future rashes (dermatome). Prodrome lasts from 2 days to a week or more.
Rash with herpes zoster:
- 1st period. The appearance of redness (erythema) in the area of future rashes. Erythematous spots are swollen, round in shape, with raised edges. If you run your finger over such a spot, you can feel the roughness, which consists of many tiny papules. However, this symptom is often absent.
- 2nd period. After 1 - 2 days and in the next 3 - 4 days, the papules turn into vesicles - bubbles filled with clear liquid. Bubbles come in different sizes, can be located separately, or less often merge with each other.
- 3rd period. After 5 - 7 days from the moment the first vesicles appear, pustulization begins, when the transparent contents of the vesicles become purulent. The pustules open quickly. In their place, crusts form. If the patient has significant immunodeficiency, new rashes appear during this period.
- 4th period. At the 4th week, the crusts disappear. In their place, peeling and pigmentation of varying degrees of severity and color appear. Pigmentation can remain for a long time. Skin rashes are located in areas corresponding to the innervation of the craniospinal ganglia.
Most often, herpes zoster affects the skin of the torso, and a little less often - the extremities. The rashes are accompanied by pain, which is often girdling in nature. The rash is localized on one side.
After the exacerbation stops, 10-20% of patients develop postherpetic neuralgia, in which pain persists for a long time - from several months to several years. Pain is associated with viruses affecting the intervertebral ganglia of the cranial spinal nerves and dorsal roots of the spinal cord. A severe course of the disease is recorded when the spinal cord, brain, and its membranes are damaged. When the autonomic ganglia are damaged, the function of internal organs is disrupted.
Pain from herpes zoster is a painful manifestation of the disease. Sleep is disturbed, appetite is lost, weight decreases, chronic fatigue develops, and depression appears. All this leads the patient to social isolation.
Medications
No drug can completely destroy the herpesvirus; treatment is aimed at suppressing viral activity and achieving stable remission.
- Antiviral Acyclovir - stops reproduction, inhibits the vital activity of the virus by introducing into the DNA of the viral cell. The combined use of Acyclovir tablets and ointment quickly reduces the appearance of the rash, improves skin regeneration, thereby accelerating recovery. Application – 1 tablet every 4 hours during the day, at night the interval between doses is 6-8 hours. In case of a complicated form of the disease, the dosage is doubled. The course of therapy for uncomplicated disease is 5 days (can be extended to 10 days).
- Antiviral Valacyclovir - intended for oral use. Once inside, it is quickly converted to Acyclovir and acts similarly. Application – 1 tablet (500 mg) twice a day. The usual therapeutic course is 5 days (can be extended to 10 days).
- Antiviral Famciclovir (Famvir) - tablets for oral use of 125, 250 and 500 mg. After administration, it is converted into penciclovir and acts selectively without inhibiting healthy cells. By introducing itself into the DNA of the virus, it inhibits reproduction, inhibits activity and stops the spread of infection. Application – 1 tablet (250 mg) three times a day, for a course of 5-10 days (depending on the course of the disease).
It is recommended to take sedative drugs for protracted, complicated forms of the disease, 1 tablet three times a day (last dose half an hour before bedtime). Course 2 weeks.
Along with systemic drugs, you can use drugs for external use with antiviral and immunostimulating activity - Viferon, Panavir, Cycloferon, Virolex.
To improve immune protection, human interferon preparations for intramuscular injections are recommended - Ridostin, Immunofan, Immunomax.
Without adequate treatment, herpes zoster can cause serious complications.
Atypical forms
There are forms of herpes zoster, in which the symptoms may be atypical for this disease. These include:
- Abortive form - occurs without severe pain, inflamed spots appear on the skin, but a rash does not form. Treatment is quick and without complications;
- Hemorrhagic - this form is characterized by blistering rashes filled with blood. In the affected area of the epidermis, sensitivity decreases, numbness and tingling occurs, the skin is very itchy;
- Bullous form - clinical manifestations of this form are manifested by large blisters with jagged edges;
- Gangrenous (necrotic) - in place of the papules, purulent ulcers are formed, covered with a black scab. Deep tissue damage occurs, necrotic processes develop when a bacterial infection is attached;
- Generalized (disseminated) form - occurs in patients with immunodeficiency and cancer. In this form of the disease, the rash covers the entire body on both sides, affecting the mucous membranes, internal organs and brain.
About 40% of patients with cancer of the lymphatic system suffer from a generalized form of the disease, in 10% of cases they develop meningoencephalitis, hepatitis, viral pneumonia and other severe complications.
With any form of this disease, damage to the ganglia of the autonomic nervous system can occur, which can cause atypical symptoms:
- bowel dysfunction;
- urinary retention;
- chilliness of the limbs;
- pronounced venous pattern;
- drooping eyelids;
- sunken eyeball;
- constriction of the pupil.
Varieties and symptoms
To cope with an unpleasant problem on the face, you should study the true nature of lichen, and for this it is important to establish its type. The treatment process will depend on the species predisposition. A large number of types of such an obvious problem have been identified:
Weeping appearance, or eczema of the skin. A variety of eczema has one of the most striking types of lichen, as can be seen from the structure and sensation of swollen bumps. They are quite small in size, but can be dangerous. If the bubbles burst, erosion with internal fluid will appear on the skin. The formation itself is very itchy and brings an unpleasant burning sensation. Later we will look at what and how to treat lichen on the face.
Viral herpes zoster. Complex symptoms accompany this disease:
- temperature increase.
- painful feelings.
- deteriorated condition.
- swollen blisters and spots.
- bubbles with liquid.
- crust on formations.
A flat, red appearance occurs on the skin of the lips, inside and outside. The color of the lichen depends on the virus itself and can have shades of pink and purple. In the presence of irritation, small ulcers appear on the surfaces of the species.
Colored pityriasis. The color of this species varies from beige to brown, and the boundaries of the tubercles are quite blurred. Signs of scaly skin may appear.
Trichophytosis is a fungal infection. The most common places to appear are the chin and forehead. The spots are rather blurry at the edges, pink in color with a white edge.
Psoriasis. Symptoms of the disease:
- small red nodules on the skin.
- Over time, the spots grow together and become crusty.
- slight bleeding - in case of complications.
Pitiriasis. The favorite place for pityriasis is the body, but sometimes it is localized on the face. That is why this disease is difficult to immediately identify in this place, because it looks like an allergic reaction. The spots have a pink color and uneven edges, and the sensations from them are quite unpleasant. Flat bumps itch, itch and flake.
Microsporia - localized directly to the face, neck and temples. The spots gather in a whole bunch and form small blisters with a rare rash. Sometimes itching or irritation appears.
Each form of lichen carries with it a variety of problems that a doctor can solve. And only a dermatologist can correctly determine the nature of a fungal infection. It is important to remember that any type of lichen can be on the face, regardless of a person’s health.
Diagnostics
The answer to the question of how to treat herpes zoster is determined by the attending physician. In medicine, an algorithm is used that allows one to identify characteristic changes in the disease and carry out differential diagnosis with diseases of internal organs (angina pectoris, pleurisy, etc.) and other infectious pathologies (erysipelas, herpes types 1 and 2, eczema, etc.).
For all patients, the examination is carried out as follows:
- Careful collection of complaints and history of symptoms. The doctor must establish that a person has had chickenpox in childhood, since only in this case is the patient likely to develop shingles. In addition, it is necessary to determine how long ago the rash appeared and the characteristics of its localization on the skin.
- During clinical and biochemical blood tests, signs of inflammatory changes are noted: an increase in the number of lymphocytes, an increase in the concentration of C-reactive protein and fibrinogen.
- In severe diagnostic cases, when it is not possible to immediately make a diagnosis of herpes zoster, i.e. herpes zoster, doctors use molecular analysis methods: polymerase chain reaction, immunofluorescent methods, etc.
Additional diagnostic procedures are used to detect pathology in children in infancy, in immunodeficiency states, as well as in atypical forms of infection that make it difficult to make a correct diagnosis.
It should be noted that only a doctor should deal with diagnostic issues, since if the disease is incorrectly identified, an ineffective treatment for herpes zoster may be prescribed.
Reviews of injections for herpes
Herpes is present in the body of almost every person, so the use of drugs against such an infection is very important today. There are a lot of reviews about injection drugs for herpes, and most patients prefer the drug Panavir. They note that after a course of treatment with this medicine, the incidence of herpetic eruptions in them decreased significantly, the disease began to recur much less frequently or ceased to manifest itself in any way.
As for other antiviral medications, as well as immunomodulators, Acyclovir, Cycloferon and Galavit are recognized as the best injections for herpes. Many positive reviews have been left about these medications.
How and with what to treat herpes zoster
In the treatment of herpes zoster in adults, several points must be taken into account:
- severity of pain syndrome;
- number of rashes and their prevalence;
- presence or absence of complications;
- body temperature;
- duration of rashes.
Most cases of shingles resolve on their own, even without treatment. However, effective treatment exists and can significantly relieve the symptoms of the disease and also prevent complications.
The goals of treatment for Herpes zoster are:
- Speed up recovery;
- Reduce pain;
- Prevent complications;
- Reduce the likelihood of developing postherpetic neuralgia.
To treat herpes zoster, several groups of drugs are used:
- pathogenetic drugs;
- painkillers;
- antipyretic medications;
- antihistamines.
Antiviral drugs are the basis for the treatment of herpes zoster in adults; they should be started from the appearance of the first signs of the disease, which will significantly speed up the healing of skin lesions and reduce the incidence of postherpetic neuritis.
"Vitagerpavak"
This medication is an antiherpetic vaccine and is used in the treatment and prevention of exacerbation of herpes simplex.
Despite the fact that this medicine is not able to permanently eliminate this disease, it has many advantages:
- promotes cellular immunity;
- protects against relapses;
- has no toxic effect.
The drug is administered subcutaneously on the forearm in a volume of 0.2 ml. The course of injections for herpes should be 5 injections - once every 7 days.
Shingles treatment in adults: tablets and ointments
To relieve pain and discomfort, your doctor may prescribe painkillers such as Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, Naproxen or lidocaine gel. If the pain is more intense, then strong painkillers such as Gabapentin and Oxycodone will be prescribed along with antiviral drugs. It is also possible to use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (see list of all NSAID injections for back pain).
To treat shingles in adults, a doctor may prescribe antiherpetic drugs in injections, tablets, creams or ointments:
- Acyclovir preparations - Acyclovir, Zovirax, Virolex.
- Valacyclovir preparations - Valciclovir, Valtrex. Acyclovir ester, which is transformed after absorption into acyclovir.
- Penciclovir drugs - in the form of triphosphate, penciclovir also blocks the synthesis of viral deoxyribonucleic acid.
- Famciclovir drugs. A prodrug that is converted to penciclovir in liver cells
Antiviral therapy is necessary, since without adequate treatment, herpes zoster can cause complications, and antiherpetic treatment promotes rapid healing of ulcers, reduces pain and improves general condition. Both the dosage and course of therapy are determined by a specialist, taking into account the individual course of the inflammatory process, concomitant diseases and on average lasts no more than 10 days.
In 2020, Epigen antiviral cream, which contains glycyrrhizic acid, is considered to be a fairly effective drug for the treatment of herpes. It has local anti-inflammatory, antiviral, immunomodulatory, antipruritic effects.
In the gangrenous form, when a bacterial infection occurs, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed. Also, if necessary, a specialist can prescribe immunomodulators, such as Cycloferon, Genferon, physiotherapy and vitamin therapy.
There are also several opposing opinions regarding the treatment of rashes. One thing is that you can use brilliant green - a solution of brilliant green, boric acid - Castellani liquid, fucorcin, a strong solution of potassium permanganate. All of these products have a drying effect and should be used with caution to avoid the formation of burns, which worsens the condition of the skin. Another opinion is that you should not treat rashes with these agents, but rather use antiviral, antiherpetic creams, ointments, and sprays.
Corticosteroid medications should not be used, either orally or in the form of creams and ointments, as this will only worsen the situation. Hormonal agents have a suppressive effect on the immune system, which must itself cope with viral agents.
Treatment of postherpetic neuralgia with chronic pain in older people is not always successful, since antiviral drugs are powerless. Neurologists can prescribe plasmapheresis, acupuncture, physiotherapy, tricyclic antidepressants, Pregabalin, Gabapentin.
In what cases are they prescribed?
The use of injections against herpes may be required in the following cases:
- when adequate treatment was not used at the acute stage of the disease;
- with severe immunodeficiency;
- when the patient is undergoing surgery;
- when there are extensive infectious processes that affect the skin, mucous membranes, respiratory tract, digestive organs, brain and hepatobiliary area;
- cases of relapse of the disease are increasingly repeated;
- in cases of infection of a sexual partner;
- with degenerative-destructive lesions of peripheral nerves;
- in case of disturbances or delays in urination processes;
- in women with herpes virus in combination with HPV.
Injections for herpes infection have a serious effect on the body. Therapy can be carried out using immunostimulating or antiviral drugs, and can also be combined with the use of several pharmacological agents simultaneously. Properly organized therapy is the key to a long period when the virus will remain in a “dormant” state and will not manifest itself in the form of pathological symptoms.
So, what injections are effective for herpes?
Vitamins and diet
For shingles, it is recommended to consume the following foods:
- dairy products (milk, kefir, butter, cottage cheese);
- vegetables (beets, broccoli, carrots, eggplants, zucchini, pumpkin, tomatoes, peppers, onions);
- white meat;
- seafood (salmon, pike perch, herring);
- nuts (peanuts, pistachios, almonds, walnuts, cashews);
- fruits (grapes, apricots, apples, kiwis, plums, citrus fruits);
- cereals (oatmeal, wheat, barley);
- legumes (peas, beans);
- green tea, tea with rosehip or raspberry.
Also, for shingles, it is recommended to take the following vitamins to strengthen the immune system:
- Vitamin A;
- Vitamin E;
- Vitamin C.
These vitamins, being antioxidants, reduce the ability of cells to respond to inflammation and also help increase the body's defenses.
- B vitamins.
Vitamins from this group improve epithelial regeneration, participate in the formation of antibodies, as well as in all metabolic processes.
It should also be taken into account that during treatment, a patient with herpes zoster is recommended to have a gentle diet rich in nutrients, vitamins and microelements. It is recommended to boil or steam food, and you should also reduce the consumption of salty, fatty and fried foods.
Immunomodulatory medications
Immunity protects the body from the aggressive influence of external pathogens and internal aggression (autoimmune processes). One way to improve immunity is the use of immunomodulators. With herpes, the level of T and B lymphocytes in the body decreases, their functional activity decreases, the work of mature monocytes and the processes of interferon production change.
In addition to antiviral therapy, treatment of pathology involves correction of antibody production and the process of phagocytosis. Immunoglobulin and interferon are widely used as injections for herpes.
The names of the drugs are as follows:
- "Vitagerpavak";
- "Tactivin";
- "Immunoglobulin";
- "Timogen";
- "Imunofan";
- "Galavit";
- "Polyoxidonium";
- "Cycloferon";
- "Ferrovir."
What else can I do for treatment at home?
When treating shingles at home, it is important to pay attention to the treatment of the rash. However, the use of ointments is not recommended. Antiseptics must be applied in liquid form. Chlorhexedine is best suited for this. It can be used in any period of the disease. The product does not cause any discomfort.
In addition to treating rashes, we must not forget about personal hygiene measures. It is necessary to take a shower daily. However, detergents and washcloths should not be used on the affected areas of the body. It is better to simply rinse the affected areas with running water at room temperature. It is not recommended to use cold or hot water.
Healing of shingles in a person and its treatment with medications will not be effective without selecting the right clothing. It is best to choose natural materials - cotton or linen. Do not wear tight or tight-fitting underwear - it can cause irritation and lead to the appearance of blisters on adjacent areas of the skin.
Which doctor should I contact?
Since shingles is a manifestation of an exacerbation of a herpetic infection, if it occurs, you can contact an infectious disease specialist. In addition, a dermatologist will help with treatment. If complications develop, the patient is consulted by a neurologist or ophthalmologist.
Traditional methods
As they say, “In wrestling, all means are good!”, so there is an opportunity to use proven grandmother’s methods.
Folk remedies and recipes for the treatment of lichen have always saved people when modern medicines were unavailable.
- Propolis infusion. 200 grams of the product must be poured into ¼ glass of water and left for a week.
- Film from a raw egg. You need to crack the egg and remove the raw film from it, which contains useful vitamins for future chickens. This mucus should be lubricated on the affected parts.
- Cranberry juice. It is necessary to lubricate the stains with freshly squeezed juice.
To avoid complications, you should contact a specialist in time for professional help. Ringworm can develop into complex forms of the disease and cause irreparable problems to a person.
Consequences and complications
At a young age, a person who is faced with herpes zoster most often will not experience any consequences or complications of the disease. It will end with complete recovery for the patient and the disappearance of all symptoms.
However, if the functioning of the immune system is impaired, then serious health problems may develop:
- Meningoencephalitis is another possible complication of herpes zoster. If the patient does not die as a result of meningoencephalitis, then he becomes disabled.
- There is a possibility of developing dysfunction of the duodenum, abdominal muscles, genitourinary system (bladder sphincter), lungs (pneumonia).
- The disease can affect the functioning of the spinal cord and brain, since the virus has the ability to actively multiply there. If a transition occurs to brain tissue, they are subject to destruction, which can lead to paralysis of the lower and upper extremities, and paralysis of the facial nerve. In addition, there is a threat of respiratory failure and death of the patient.
- If the virus affects the organs of vision, optic neuritis may develop. This threatens the formation of glaucoma, damage to the cornea and complete blindness of the patient.
- If the disease is accompanied by a bacterial infection, the person’s condition worsens and the recovery process is significantly delayed.
As a rule, complications occur only in people with weakened immune systems. If the disease is mild, it does not threaten relapses and passes quickly.
"Panavir"
This antiviral medicine contains a biologically active element - hexose glycoside, extracted from Solanum tuberosum. It is a high-molecular polysaccharide that increases the level of general resistance of the body to a variety of viral pathogens and increases the production of its own interferon by white blood cells. In addition, it has a slight anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect.
When this medication is administered parenterally, its active substance in high concentration is detected in the plasma after 5 minutes. Removal of the medication begins after about half an hour. It leaves the body through the urinary system and respiratory tract. The drug "Panavir" is recommended for use in the following situations:
- With the development of pathologies caused by herpesvirus (including oral, ocular and genital), HPV (including the occurrence of genital warts), as well as other DNA and RNA enteroviruses.
- For cytomegalovirus infection in women.
- When the functions of the immune system are impaired against the background of infectious diseases or after them.
- For local defects in the mucous membrane of the gastroduodenal zone, natural focal viral infections transmitted by ticks, inflammatory processes in the prostate of bacterial origin and autoimmune diseases of the joints and adjacent tissues in combination with recurrent herpesvirus.
When infected with herpesviruses of the first and second types, as a rule, 2 injections of Panavir solution (5 ml) are prescribed with an interval of 24 hours or two days. If such a need arises, the therapy is repeated after another month.
The pharmacological agent "Panavir" is administered intravenously. This medicine cannot be taken into the same syringe with others. The administration of the medication should be a stream and very slow.
What other injections for herpes are used?
Prevention
A live vaccine known as Zostavax has been proposed against the occurrence of the disease.
This vaccine rarely causes side effects but is contraindicated in immunocompromised patients and may not be effective in patients taking antiviral drugs active against Varicella zoster virus. From an economic point of view, it is advisable to use it for patients over 60 years of age.
A Cochrane Library systematic review of eight randomized placebo-controlled trials that included 52,269 participants found that the Zostavax vaccine in older adults prevented one episode of herpes zoster in every 70 people vaccinated, meaning it was effective in reducing the risk of herpes zoster by almost 50%. Side effects caused by the vaccine were mainly mild to moderate symptoms at the injection site.
Treatment with traditional methods
To cure ringworm on the face, you can use proven medications and ointments for ringworm.
Each medicine listed below is sold in pharmacies and hospitals:
- Effective drugs against fungi: Ketaconazole, Exoderil, Clotrimazole.
- Agents with an antifungal effect, for oral administration: Griseofulvin, Acyclovir.
- Vitamin preparations: oily retinol solution.
- Sulfur-salicylic ointment.
- Ethyl alcohol - for severe rashes. For small and non-spread rashes - Sinaflan.
What is not recommended to do
Herpes zoster is a contagious disease, so until crusts form on the erosions, those around you should limit contact with a sick person. During the entire course of treatment, you should not visit swimming pools, saunas and other public places.
Some traditional methods of treating shingles can be harmful to health if compresses, powders, ointments, etc. are used irrationally. To prevent complications, you need to consider the following recommendations:
- a blistering rash should not be treated with locally irritating and warming agents;
- It is undesirable to treat the entire lesion with iodine, as this can lead to burns and the spread of the rash;
- Vesicles and ulcerations should not be wetted until light brown crusts form on them;
- during an exacerbation of herpes zoster, you should not take a bath, you can quickly rinse in the shower, without a washcloth;
- It is impossible to squeeze liquid out of the blisters and rip off dried crusts, as this can lead to infection in the wound.
The development of the disease is accompanied by severe pain, so some people use mustard plasters to alleviate the condition. Doctors categorically do not recommend applying mustard plasters to areas of inflammation, which is associated with a high risk of spreading infection and the formation of new blistering rashes.
Treatment approaches
People need to know which doctor treats shingles. A therapist or pediatrician deals with issues of therapy, however, in some cases (atypical course, severe health condition of the patient), an infectious disease specialist is involved in the therapy.
When treating herpes zoster in older people, therapy is carried out only in the infectious diseases department to prevent damage to internal organs.
The herpes zoster virus does not cause serious health threats in most people at a young age and goes away on its own with symptomatic treatment that eliminates pain, itching and signs of the inflammatory process.
In addition, treatment regimens for herpes zoster should always be aimed at preventing the patient from developing postherpetic neuralgia, which is characterized by severe pain.
At the same time, carrying out such treatment at home is welcomed by doctors after consultation with them, since the person does not need hospitalization.
Placing a patient in a medical hospital is carried out in certain cases when therapy at home can quickly lead to the progression of the disease or the development of complications, even the death of the patient. These conditions include:
- a generalized version of the pathology with multiple lesions of the skin and internal organs;
- development of herpetic encephalitis or damage to the organ of vision;
- the patient's age is more than 70 years due to the risk of rapid progression of the disease against the background of age-related immunodeficiency;
- severe immunodeficiency state, including HIV infection;
- concomitant renal or liver failure, affecting the effectiveness of the medications used.