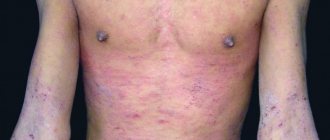
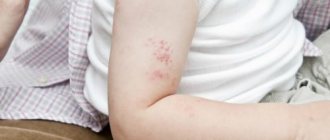
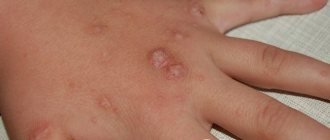
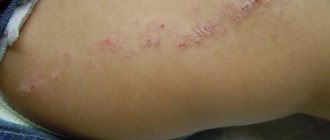
We will look at what the obvious external signs of hepatitis C look like in this article, because with such a serious illness, not only the color of the skin changes, but also the condition of the liver, the color of the whites of the eyes and the general appearance of the patient.
Treatment of spider veins
To remove stars as a cosmetic defect, different techniques are used:
- Therapeutic. Wearing compression clothing, massages, using masks that strengthen facial blood vessels.
- Medicinal. Taking medications aimed at strengthening vascular walls - ascorutin.
- Surgical. Removing stars. Electrocoagulation is used - cauterization of localization sites. Radio wave surgery – removal using high frequency radio waves. Sclerotherapy is the introduction of a sclerosant into the vessels, a gluing agent that stops blood flow in the vessel. Ozone therapy is an injection of an oxygen-ozone mixture. Laser photocoagulation – burning with a laser beam.
- Traditional methods.
| Compound | Mode of application |
| Green tomatoes. | Cut off the peel and apply to the affected area for ten minutes to expose the juice. Remove, rinse, apply emollient cream. |
| Apple vinegar. | Spot lubricate the star area up to four times daily. |
| Cabbage, carrot, plum juices. | Take orally, alternate. |
| Yarrow, egg yolk, cream, honey, a teaspoon of lemon juice, a tablespoon of starch and sour cream. | Mix gradually, adding ingredients one by one, and pour a glass of boiling water. Apply for ten days, fifteen minutes per defect. |
| Calendula, chamomile. | Mix, pour boiling water, leave for a day. Apply with compresses. |
| Chamomile, oak bark. | Brew with boiling water separately. Mix the decoctions and use them as baths. |
Cosmetic removal of stars for liver cirrhosis is a temporary solution to the problem. A progressive disease will again provoke the appearance of these signs. As your general condition improves, the stars will go away on their own.
The primary task is to fight the main disease, cirrhosis:
- Diet. Table number 5. Refusal of fatty, spicy, smoked, fried, salty foods. Alcohol ban. Moderate salt restriction. Meals are served six times a day, every three hours in small portions.
- Limiting physical activity.
- Drug therapy - hepatoprotectors, diuretics, beta blockers.
- Symptomatic therapy for the development of complications.
- Donor organ transplantation.
Primary biliary cirrhosis of the liver: causes, symptoms, diagnosis
Primary biliary cirrhosis is a chronic cholestatic progressive liver disease characterized by destruction of the intrahepatic bile ducts, portal inflammation and fibrosis, leading to the development of cirrhosis and liver failure. The formation of biliary cirrhosis is associated with intrahepatic cholestasis of bile acids, and not bilirubin in the bile capillaries of the portal tracts.
Among the causes of biliary cirrhosis of the liver are:
- the triggering mechanism is the destruction of hepatocytes and bile ducts by hepatotropic viruses, bacterial antigens (enterobacteria, Helicobacter);
- great importance is attached to genetic predisposition to this disease;
- the presence of pronounced hyper-γ-globulinemia, an increase in the concentration of IgM, IgG and circulating immunocomplexes indicates the autoimmune nature of biliary cirrhosis.
The leading symptom of the disease is jaundice (80% of cases), which either increases or decreases. Also, symptoms of biliary cirrhosis of the liver are changing skin color from yellow to dirty gray, diffuse skin itching is expressed, the liver is enlarged, but as cirrhosis progresses it decreases in size, the spleen is constantly enlarged. Disruption of calcium metabolism leads to damage to the tubular bones and spine, and constant pain occurs along the bones. Portal hypertension occurs quite late. The progression of biliary cirrhosis depends on the degree of cholestasis. The severity of the disease correlates with the level of hyperbilirubinemia and the severity of portal hypertension. In the later stages of the disease, liver dysfunction occurs: general intoxication, encephalopathy, ascites, blood clotting disorders, varicose veins of the esophagus and hemorrhoidal veins, severe polyavitaminosis, melanin deposition in the skin, bleeding is possible.
An effective combination of biochemical tests in the diagnosis of primary biliary cirrhosis is presented in the table:
| Biochemical test | Direction of change |
| Albumin in the blood | Decline |
| y-globulins in the blood | Promotion |
| Alkaline phosphatase in the blood | Promotion |
| Leucine aminopeptidase in the blood | Promotion |
| Fibrinogen in the blood | Decline |
| Prothrombin time | Decline |
| Bilirubin in the blood | Promotion |
| Ammonia in the blood | Promotion |
| Ammonia in urine | Promotion |
| Thymol test | (+) |
| Australian antigen | (-) |
| IgM | Promotion |
| Antibodies against mitochondrial membranes | (+) |
| Total blood lipids | Promotion |
Treatment of skin manifestations
There is practically no treatment for skin manifestations of liver disease, with the exception of symptomatic treatment of unbearable itching of the skin. If necessary, use the following drugs:
- "Cholestyramine";
- "Rifampicin"
- "Naltrexone";
- "Sertraline".
The listed drugs do not have a therapeutic effect, but only suppress itching, allowing the use of general treatment methods for the underlying disease. For cholestatic itching, antihistamines are not used due to their insignificant effectiveness and high likelihood of side effects.
After diagnosing and identifying the cause of dermatitis, treatment is prescribed for the disease that caused the appearance of skin manifestations - most often these are conservative methods, but, if necessary, surgical intervention is prescribed (for example, for blockage of the bile ducts).
Skin manifestations are a signal of the presence of pathologies in the body, and their intensity directly depends on the degree of dysfunction of the liver.
"Hepatic" cholestatic skin itch
Itching is the most common symptom of jaundice in cholestasis syndrome. Almost never occurs in other types of jaundice (parenchymal and hemolytic). Mainly affected areas of the body are the skin of the arms, legs and torso. The occurrence of this skin manifestation is associated with an increased content of bile acids in the blood. Scratching and xanthomatous rash are observed on the skin—subcutaneous yellowish, round-shaped plaques located on the face around the eyes and in the skin folds of the body. Itching of the skin can be paroxysmal and short-term, or, on the contrary, painfully persistent.
Diagnostics
Research at the cellular level will determine the nature of the pathology.
A dermatologist should rule out a fungal infection or skin cancer by performing a biopsy of the pigmented area. To clarify the diagnosis, a consultation with a hepatologist or gastroenterologist is scheduled. Vascular changes, in addition to liver disease, can be caused by congenital weakness in connective tissues, changes in hormonal levels, and cardiovascular pathologies, which also requires additional examination.
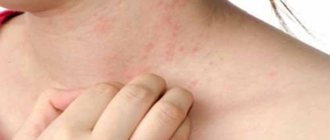
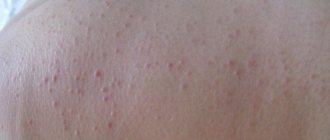
Spider veins on the body
Externally, spider veins resemble spiders, as can be seen from their photos. One such asterisk consists of a central arteriole and small vessels, clearly visible on the skin. The vessels extend from the arteriole in different directions. It may also resemble a sun drawn by a small child.
The size in diameter will range from very small, no larger than a pinhead, to 0.5 cm. Looking at enlarged photos on the Internet, you might think that they are much larger. If the size is large, upon palpation the doctor may notice its pulsation, which noticeably increases with pressure. And if you press on the very center of the arteriole, it will turn pale in appearance.
Most often they appear in the following diseases and conditions of the body:
- Viral hepatitis.
- Cirrhosis, including alcoholic.
- Pregnancy in women.
They can appear even in healthy people, but disappear very quickly. In a healthy person, such manifestations may go unnoticed, but with cirrhosis and other liver lesions they become quite numerous.
Cause of spider veins
Spider veins are a manifestation of vasodilation. And they expand with cirrhosis when the liver ceases to cope with its functions, and blood filtration becomes difficult. Stagnation occurs, due to which the vessels dilate, losing their elasticity.
If the treatment of the disease is successful, the elasticity of the vessels begins to return, and the venous “spiders” disappear from the skin. And they return when the disease progresses. Along with them appear:
- Other dilated vessels, appearing as red stripes and dots on the skin, are located in a chaotic manner.
- The appearance of white spots on the arms and buttocks, noticeable when the skin cools. In these places, new dilated arterioles with vascular rays are formed.
- Other external symptoms observed in cirrhosis.
By the appearance of dilated vessels in combination with other characteristic symptoms, the disease can be diagnosed. If a lot of venous stars appear on the skin, and the skin itself begins to turn yellow and dry out, it’s time to promptly consult a doctor and check your liver. If you don't know exactly what they look like, look at the photo and compare.
Where venous stars appear
In cirrhosis, venous stars can be found in the area of the superior vena cava, which runs to the heart from the head. Below the nipple area they are rarely observed. Usually located in the décolleté area, along the forearms and on the face. They can be found on the back of the hands, and in rare cases, on the mucous membrane of the nose or mouth.
Accompanied by other dilated vessels, this is especially noticeable on the face and décolleté. This symptom is called "money bill syndrome" because the appearance is similar to the random arrangement of hairs on dollar bills.
Types of the disease and their external manifestations
The disease is distinguished by the nature of the disease.
There are several types of classification of cirrhosis. According to the etiological factor, they are divided into those whose causes have been established, those with questionable or unknown origin. According to the clinical course, biliary, portal, hypertrophic and mixed types are distinguished. All of them are manifested by general and local symptoms.
In liver cirrhosis, the nervous system is the first to be affected, so initial symptoms such as fatigue, drowsiness, irritability, forgetfulness, and others are nonspecific. Specific symptoms increase and appear gradually
When examining a patient, the doctor pays attention to small signs of the disease, including:
- The tongue and mucous membrane of the mouth are bright red, swollen and shiny.
- Redness of the palms, hands, or entire arm.
- Angiomas on the face.
- Spider veins. Localized on the stomach, above the navel.
- Atrophy of the genital organs.
- Gynecomastia and erectile dysfunction in men, menstrual irregularities in women.
- Swelling of the lower extremities and muscle atrophy.
- General malaise, fatigue, weakness.
- Nosebleeds.
Minor signs of the disease do not differentiate its type and do not indicate the etiological factor that provoked the development of the disease. They cannot determine the stage of the disease. Signs only indicate the presence of a problem, and laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods, as well as specific symptoms, make it possible to more accurately determine the type of cirrhosis.
Biliary type of disease
The skin and eyes take on a yellowish tint.
This type of disease is caused by stagnation of bile. Externally it manifests itself as dark yellowness of the skin, severe itching and the formation of yellow plaques on the eyelids, chest and face, pain and hardening of the organ, darkening of urine and discoloration of feces. Swelling, which is not relieved by antihistamines, is explained by an excess of bile acids in the blood, which enter the subcutaneous tissue and irritate the nerve endings.
Alcoholic cirrhosis
The pathology develops after prolonged liver poisoning with alcohol-containing substances. The signs of such cirrhosis are especially significant in the last stages of organ destruction. Among them:
- lack of appetite;
- nausea;
- bloating;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- dry jaundiced skin with stars;
- itching;
- yellowness of the sclera;
- weight loss;
- hyperthermia.
Cirrhosis of viral etiology
The pathology is caused by a virus.
Its development is facilitated by viral hepatitis of various forms, the presence of which a person may not even know. Infection occurs mainly through the blood and leads to impaired liver function and inflammation. The development of cirrhosis of viral etiology is accompanied by a sharp increase in the size of the gland and abdomen, the skin and sclera become bright yellow. Complications such as bleeding into the abdominal cavity and peritonitis are common.
Photo of eyes with hepatitis C
“Wen” actively appears on the eyelids, which are signs of cholesterol accumulation. The photo shows a diseased eye surrounded by fatty plaques.
This is what eyes look like with hepatitis C. The photo may not reflect the true color of the whites; it also varies from a light yellowish tint to rich yellow.
In this case, yellowness is barely noticeable, but it also indicates the presence of a virus in the body.
Is cirrhosis curable at the last stage?
Therapy for stage 3 liver cirrhosis is aimed at correcting the pathology and preventing the development of concomitant diseases. The basis of treatment is the prevention of the development of viral hepatitis, the complete exclusion of alcohol and drugs that negatively affect liver function, and dietary nutrition.
What to do if cirrhosis is at the last stage? Qualified drug treatment in a hospital setting is required. Self-medication will lead to the rapid development of pathology and death.
Basic medications for the treatment of liver cirrhosis:
- vitamin complexes that contain all B vitamins, ascorbic and lipoic acid - they help improve metabolic processes;
- preparations based on milk thistle, oats, corn silk - slightly restore liver cells, they need to be taken for at least 1 month;
- Karsil, Legalon and other hepatoprotectors – help restore hepatocyte membranes;
- corticosteroids (Prednisolone) – prescribed for autoimmune liver cirrhosis;
- diuretics of different classes - used to eliminate ascites and swelling.
The only way to completely cure cirrhosis is a liver transplant.
Unconventional methods of treatment
Treatment with folk remedies at the last stage of liver cirrhosis is ineffective. Juice therapy can be used as maintenance therapy:
- add 45 ml of cucumber and beet juice to 150 ml of carrot juice;
- mix 100 ml of carrot juice with 60 ml of spinach juice;
- add 35 ml of black radish juice to 100 ml of carrot juice.
You can drink 0.6–4 liters of juice per day.
Turmeric will help reduce inflammatory processes - it has antioxidant properties, prevents the destruction of liver cells, and accelerates the outflow of bile. Dilute 5 g of turmeric powder in 200 ml of warm water; you can add honey to improve the taste. Drink 100 ml of the medicinal drink twice a day before meals.
Liver cirrhosis is a fatal pathology, which is characterized by constant progression and decline of liver function, which leads to the development of complications and death. Only timely diagnosis, proper treatment, and giving up bad habits can improve your condition and prolong your life.
Leather
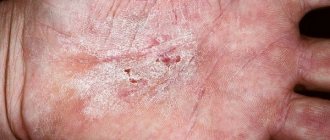
With cirrhosis of the liver, the skin suffers greatly. Numerous rashes of different types form on it, the color becomes jaundiced. The skin constantly dries out, so it itches, wrinkles and flakes. This sensation is associated with an excess of bile components in the blood due to obstructive liver damage. Antihistamines and a diet rich in unsaturated fatty acids and cholestyramine help reduce itching.
Along with a variety of rashes similar to hives, cirrhosis causes the appearance of “stars” on the skin in the upper part of the body, which is associated with dilation of blood vessels. The skin of the palms and soles undergoes a strong visual change, becoming unnaturally red. This symptom is called palmar erythema. Sometimes redness is observed on the bends of the phalanges of the fingers.
When the liver becomes inflamed, the skin loses its elasticity, itches, and turns yellow.
Pigment spots gradually appear on the body, which quickly fade when pressure is applied, but quickly return as the pressure stops. Purpura also develops, which is characterized by a small hemorrhagic rash. The symptom appears on the lower extremities and legs.
If the hepatobiliary system has been affected, dirty gray spots appear on large surfaces of the skin. With secondary hormonal disorders, atrophic stripes appear in the thighs, legs, buttocks and lower abdomen.
With cirrhosis, blisters, superficial scars and other age spots may appear on exposed skin.
Characteristic rash
The development of pathology can be signaled not only by changes in the skin. Many patients experience various rashes.
Sometimes the following symptoms occur:
- Pustular elements. There is a tendency to form furunculosis and folliculitis. The source of such rashes is an immune imbalance. It occurs as a result of decreased liver function. The organ is not able to synthesize immunoglobulin in sufficient quantities.
- Allergic manifestations. This pathology in most cases characterizes liver disease. Skin symptoms: spots and papules, occur as a result of a violation of the detoxification function of the organ. That is why a person is faced with the occurrence of allergic reactions to familiar conditions.
- Hemorrhagic rash. Minor hemorrhages are observed on the surface of the skin. They are called petechial eruptions. They characterize a decrease in the synthetic function of the organ. Initially, the protein contained in the blood suffers. As a result, patients have an increased tendency, even with the slightest damage, to form hematomas.
What should you be wary of?
Of course, the liver is extremely resistant to external influences. In addition, she has the ability to regenerate. But there are still factors that can cause diseases in the body’s laboratory.
Toxic substances. These include heavy metals and chemistry. With their constant intake into the body, various liver damage occurs. A single but sudden impact is also dangerous.
Viruses. Cause inflammatory processes in acute or chronic forms. Often the result of infection of the gland by viruses is hepatitis.
Alcohol. Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages has a detrimental effect on liver cells. Often, uncontrolled alcohol consumption causes cirrhosis, a life-threatening disease.
Medications. The use of hormones, antibiotics, and chemotherapy drugs negatively affects the functioning of the liver.
Poor nutrition. Fatty, fried, smoked foods in excess quantities lead to disruption of the outflow of bile. Excessive consumption of spices can also lead to it. The result is the formation of stones in the bile duct.
Parasites and infections. The most dangerous are roundworms, alveococcus, and echinococcus. They act as sources of pathological changes in the organ and can cause its cystic transformation.
Abdominal diseases. Suppuration processes can spread to the portal vein of the liver. Thrombosis often occurs as a result of such disorders.
Heredity. Often the cause of diseases in the “laboratory of the body” are genetic diseases. Ionizing radiation, chemical carcinogens that promote liver cancer. Abdominal injuries
It doesn't matter how long ago you suffered a serious stroke or abdominal injury. Cysts or fluid accumulations in the liver parenchyma can be detected even after several years.
Signs of pathologies
Diseases of one of the most important glands in our body are accompanied by skin symptoms. First of all, you can highlight the yellowish tint of the skin. Patients complain of nausea and heartburn. Sweating is increased, and the sweat has a pungent and extremely unpleasant odor. When visiting a medical facility based on these signs, the doctor can easily diagnose liver problems.
You should also think about visiting a doctor if the size of the gland is increased, pain and discomfort are felt in the area of the organ, weakness, swelling and headache are bothersome. Rash, itching, weight loss, unstable stool or changes in the characteristics of stool, bitter taste in the mouth, white or brown coating on the tongue, cracks on it are direct reasons for concern. A venous pattern on the abdomen, an enlarged abdomen, temperature, and acne also indicate the presence of diseases in the body.
How does your liver hurt?
Almost all pathologies of the gland are reflected on the human face and body. They are often accompanied by a feeling of pain. The nature of these sensations is very different:
- Minor pain in the right hypochondrium. As a rule, it has an aching or bursting character. It speaks of a sluggish inflammatory process. Discomfort is caused by stretching of the organ or enlargement of the liver capsule.
- Intense discomfort in the right hypochondrium. Quite a rare type of pain. Signals about a pronounced purulent-inflammatory process. In some cases, it appears with stones in the bile duct.
- Severe point pain in the liver area. Characteristic of pathology of the gallbladder or extrahepatic ducts.
However, with diseases of the “laboratory of the body” the patient does not always experience pain. As a rule, this is observed in the case of a sluggish disease that remains undetected for a long time. In the absence of pain, problems with the internal organ are indicated only by rashes on the skin.
Other types of hepatitis
In addition to the viral one, there are several other types of this disease with different etiologies:
- Toxic hepatitis. May be caused by exposure to external factors such as poisoning with chemically active substances (chloroform, acetic acid, arsenic, copper sulfate, industrial poisons), excessive consumption of alcohol or medications (Ibuprofen, Indomethacin, Azathioprine, Pyrazinamide, Paracetamol, anti-tuberculosis drugs and hormonal contraceptives ), the side effects of which affect the functioning of the digestive system. To treat this type of hepatitis, it is necessary to eliminate the source of its occurrence and limit the patient’s use of substances that negatively affect the condition of his liver.
— Infectious hepatitis. Occurs as complications in the development of diseases such as cytomegalovirus infection and Epstein-Barr virus infection, rubella, mumps, yellow fever and Lassa fever, herpes. Diagnosed in most people with AIDS or who are carriers of HIV infection.
- Bacterial hepatitis. A common disease that occurs in patients with leptospirosis or syphilis. It is difficult to transmit from person to person and has virtually no clinical manifestations.
— Autoimmune hepatitis. An inflammatory process of unknown origin, which results in slow and asymptomatic destruction of liver tissue. This disease mainly affects women over 40 years of age.
- Radiation hepatitis. It is a consequence of long-term influence on the human body of high doses of penetrating radiation. It practically never occurs in everyday life.
Liver cirrhosis: final stage
Any liver damage leads to early aging and even death.
The most common type of tissue damage is cirrhosis. Depending on the severity, there are several stages of disease progression. The most dangerous liver cirrhosis is in the last stage. During this period, the tissue structure is destroyed without the possibility of restoration. A person remains under the close supervision of doctors for the rest of his life.
The essence of the disease
Cirrhosis is the process of replacing the parenchymal tissue that makes up the liver with connective tissue. This is preceded by a number of serious diseases that affect the functioning of liver cells. In fact, cirrhosis is a consequence of the final stage of hepatitis.
The impetus for inhibition of the liver parenchyma can be:
- alcoholism;
- strong chemicals;
- infectious lesion;
- toxic drugs;
- content of complex genetically modified compounds in food
- entry of poisons into the blood;
- poor nutrition
The main cause remains alcoholism. Most often, people who abuse alcohol end up in a hospital bed with a diagnosis of cirrhosis. Late-stage liver cirrhosis is the most common diagnosis in this situation, and the patient is prescribed intensive therapy for the rest of his life.
Stages of cirrhosis
Changing the state of the body has several stages. The ongoing disease gradually covers the entire organ. Since the transformation of fabric quality is a lengthy process, this becomes an additional risk factor.
Often a person does not pay attention to the symptoms for a long time. Because in the early stages this disease has a blurred picture, inherent in most diseases such as hepatitis. It is possible to detect the disintegration process that has begun in a timely manner only by seeking medical help through a series of tests.
Photos of people with liver cirrhosis at the last stage demonstrate what severe morphological changes the body acquires:
- the skin takes on an unhealthy appearance;
- trophic damage to the integrity of the integument is formed;
- may change color to pale yellow;
- the whites of the eyes become cloudy;
- the abdominal cavity is swollen;
- varicose veins may form in areas of vascular damage;
- accumulations of vascular networks;
- the overall silhouette is deformed.
Diagnosis of cirrhosis
Photos of liver cirrhosis at the last stage very clearly illustrate external signs that may be symptoms of the disease. In the early stages, the disease is detected through tests and examination. You can seek medical help with a hint of a disease if you have the following symptoms:
- decreased body tone;
- fast fatiguability;
- nausea;
- foul belching;
- frequent vomiting;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- intolerance to fatty foods;
- acute reaction to alcohol.
In an outpatient clinic, tests are taken, in addition to which diagnostics are carried out through research:
- ultrasonic;
- radionuclide;
- X-ray.
One of the most promising methods is computed tomography.
Help with cirrhosis
Cirrhosis imposes special restrictions on the dynamics of the patient’s life. After a complete examination and determination of the extent of the lesion, a course of therapy is prescribed. These include many methods, including lifestyle changes.
The set of measures is aimed at relieving tension and possible additional external influence. Such measures include:
- decreased activity;
- reduction of loads;
- complete cessation of bad habits;
- stabilization of mental state;
- a number of therapeutic gymnastic exercises;
- normalization of the amount of substances taken;
- diet.
In severe stages, a person is constantly in a state of intensive therapy with medications and procedures. Along the way, he is prescribed the following measures:
- complete peace;
- limiting the amount of liquids;
- reducing the level of salt in food;
- hypothiazide;
- furosemide;
- hormonal complexes.
From active intervention, patients undergo bile pumping procedure (spironolactone).
What functions does the liver perform?
Directly or indirectly, the liver is involved in a huge number of biochemical reactions occurring in the body. It is called a chemical factory and a natural filter. The human liver is an active participant in metabolic processes.
Main functions:
- detoxification is a biological filter of the body that neutralizes and removes foreign toxins and excess metabolic products;
- secretory activity - secretion of bile;
- metabolic – regulates water, protein, lipid, amino acid metabolism;
- excretory – removes toxic compounds into the intestines;
- homeostatic – participant in antigenic self-regulation;
- depositing - accumulates proteins, carbohydrates, hormones, minerals and vitamins.
Spider veins on the body
This term refers to a condition in which the subcutaneous vessels greatly dilate, which is manifested by the appearance of a web of vessels or spider veins. The cobweb is an uncharacteristic cluster of veins that is localized on the skin of the torso, face, and arms.
Inflammation of the liver makes itself felt by the formation of blood “webs” on the skin.
When pressing on the angioma, a red “star” dot will pulsate in the center - the central arteriole. As the blood spreads through the capillaries, the point will turn pale.
Spider veins indicate serious liver damage. However, the symptom can appear not only during illness, but also during pregnancy, severe malnutrition, and also in healthy people.
Externally, spider veins resemble spiders, as can be seen from their photos. One such asterisk consists of a central arteriole and small vessels, clearly visible on the skin. The vessels extend from the arteriole in different directions. It may also resemble a sun drawn by a small child.
The size in diameter will range from very small, no larger than a pinhead, to 0.5 cm. Looking at enlarged photos on the Internet, you might think that they are much larger. If the size is large, upon palpation the doctor may notice its pulsation, which noticeably increases with pressure. And if you press on the very center of the arteriole, it will turn pale in appearance.
Most often they appear in the following diseases and conditions of the body:
- Viral hepatitis.
- Cirrhosis, including alcoholic.
- Pregnancy in women.
Spider veins are a manifestation of vasodilation. And they expand with cirrhosis when the liver ceases to cope with its functions, and blood filtration becomes difficult. Stagnation occurs, due to which the vessels dilate, losing their elasticity.
If the treatment of the disease is successful, the elasticity of the vessels begins to return, and the venous “spiders” disappear from the skin. And they return when the disease progresses. Along with them appear:
- Other dilated vessels, appearing as red stripes and dots on the skin, are located in a chaotic manner.
- The appearance of white spots on the arms and buttocks, noticeable when the skin cools. In these places, new dilated arterioles with vascular rays are formed.
- Other external symptoms observed in cirrhosis.
By the appearance of dilated vessels in combination with other characteristic symptoms, the disease can be diagnosed. If a lot of venous stars appear on the skin, and the skin itself begins to turn yellow and dry out, it’s time to promptly consult a doctor and check your liver. If you don't know exactly what they look like, look at the photo and compare.
In cirrhosis, venous stars can be found in the area of the superior vena cava, which runs to the heart from the head. Below the nipple area they are rarely observed. Usually located in the décolleté area, along the forearms and on the face. They can be found on the back of the hands, and in rare cases, on the mucous membrane of the nose or mouth.
Accompanied by other dilated vessels, this is especially noticeable on the face and décolleté. This symptom is called "money bill syndrome" because the appearance is similar to the random arrangement of hairs on dollar bills.
Other external signs of the disease
Along with general symptoms, such as pain in the right hypochondrium, colic, nausea with vomiting, decreased muscle tone and strength, itching, diarrhea and exhaustion, patients with cirrhosis change greatly in appearance. It is the visual signs that are specific for cirrhosis.
The most characteristic external manifestations of cirrhosis of the liver are as follows:
- jaundiced skin tone;
- drying of the dermis with severe peeling;
- xanthelasma - yellow-brown pigment spots around the eyes;
- thickening of the fingers on the upper extremities with swelling of the lower extremities and obvious swelling of the joints;
- spider veins and spider webs on the abdomen, limbs, joints;
- swelling of the tongue.
At the terminal, last stage, most cirrhotic patients develop ascites - excessive accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity. The main symptom of this complication is an enlarged abdomen with a pronounced network of blood vessels, similar to the “head of a jellyfish.” At the same time, the skin is smooth, mirror-like without hair growth.
Some of the signs indicate concomitant diseases that developed against the background of cirrhosis.
With cirrhosis, in addition to spider veins, other external signs are noted. It is impossible to make such a diagnosis based on one characteristic symptom: it may be temporary or relate to the clinical picture of some other disease. A large number of dilated vessels that are visible on the skin is a reason to consult a doctor. And you definitely can’t do without it if the following external symptoms were also noted:
- Bright red palms compared to the rest of the skin.
- Yellowish tint of the skin except for the palms.
- White nails, completely opaque.
- Darkened color of urine.
- A bitter taste in the mouth, which may come with hepatic halitosis.
- Bleeding gums.
- Swelling of the veins in the umbilical region and unhealthy rounding of the abdomen due to fluid accumulated in the abdomen.
Liver diseases - names
There are 10 groups of hepatological lesions, each of them unites diseases similar in symptoms and origin. Diseases of the gallbladder and its ducts are considered separately. What are the types of liver diseases?
- Primary purulent, inflammatory and functional damage to parenchyma cells.
This group includes viral and toxic hepatitis, steatohepatosis, tuberculosis and syphilitic infection, hepatomegaly, fatty hepatosis and abscess. - Injuries
- ruptures, stab wounds, crushing and gunshot damage to the liver. - Vascular pathologies.
These include arteriovenous fistulas and fistulas, pylephlebitis, Budd-Chiari syndrome, and portal hypertension. - Changes in the intrahepatic ducts
- cholestasis, Caroli's disease, cholelithiasis, acute and chronic cholangitis. - Tumors.
Cysts and hemangiomas, sarcomas, intraductal and cellular cancer, and metastases from other organs can develop in the liver. - Parasitic infestations
– ascariasis, alveo- and echinococcosis, leptospirosis, opisthorchiasis. - Hereditary problems.
Abnormalities include hemochromatosis, aplasia and hypoplasia, fermentopathy, pigmentary hepatosis and atresia. - Damage due to pathologies of neighboring organs.
Often, symptoms of liver disease develop against the background of diseases of other systems - cardiac cirrhosis (heart damage), amyloidosis (bone marrow diseases), hepatomegaly (leukemia). Additionally, this group includes renal and hepatic failure. - Systemic changes.
Unreasonable organ destruction occurs in primary biliary cirrhosis, sclerosing cholangitis, and autoimmune hepatitis. - Complications, structural and functional changes
- parenchymal jaundice, cirrhosis, coma, failure.
Symptoms and stages of development of cirrhosis
Additional manifestations of the disease
In the advanced stage of clinical manifestations, the symptoms of cirrhosis are composed, like a mosaic, of the following main disorders:
- Manifestations of liver failure (protein synthesis decreases, including for blood clotting);
- Portal hypertension syndrome (increased pressure in the portal vein, which absorbs all the blood flowing from the intestines with absorbed food). This blood goes to the liver for “checking” and neutralization, but with cirrhosis there is a problem with its normal flow through the liver.
These conditions progress and lead to a characteristic clinical picture. Symptoms of liver cirrhosis in women at an advanced stage are as follows:
- Hepatosplenomegaly (enlarged liver and spleen). In the later stages of cirrhosis, on the contrary, a decrease in liver size occurs;
- The appearance of telangiectasia, or “spider veins” on the skin;
- Palmar erythema, or severe redness of the palms;
- The appearance of jaundice - first transient, and then permanent;
- Pain and heaviness in the right hypochondrium;
- With increased activity and progression of cirrhosis, periods of increased temperature are possible, which are accompanied by jaundice and deterioration of health;
- A terrible symptom of portal hypertension is varicose veins of internal organs (stomach, intestines, esophagus) - wherever the “watersheds” of the portal system and the vena cava meet. Increased pressure in the portal vein system forces it to shunt, or dump blood into other pools, and this leads to bleeding.
For example, bleeding from esophageal varices in patients with cirrhosis often leads to death, since it occurs against the background of anemia and a pronounced decrease in blood clotting ability.
Ascites, or accumulation of free fluid in the abdominal cavity. This is a common symptom of decompensated, advanced cirrhosis.
The belly is large, tense like a ball, its skin is stretched, like a drum, and shiny: the umbilical depression is not visible, it has disappeared. When tapping on the side of the abdomen, if you place your palm on the other side, you can feel a wave of liquid reaching it. Often ascites is accompanied by varicose veins of the anterior abdominal wall, which resemble snakes on the head of Medusa the Gorgon.
This happens because increased pressure in the portal vein system leads to sweating of the liquid part of the blood plasma, which “drains” into the abdominal cavity. Newly diagnosed ascites is always an indication for hospitalization.
Laboratory symptoms of cirrhosis are characterized by a decrease in all red bone marrow sprouts (anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia). After all, a shrinking healthy liver synthesizes little protein, and there is simply nothing to build blood cells from. As a result of leukopenia, purulent processes occur, and due to a decrease in the synthesis of antibodies, the woman begins to develop infectious diseases. Since there is “no means” for the synthesis of platelets, a characteristic sign of low protein-synthesizing function of the liver in cirrhosis is the appearance of bleeding (uterine, nasal from the gums), prolonged blooming of bruises and their appearance as a result of any, even the most minor injuries.
In a biochemical blood test, the level of ALT and AST increases. Normally, these enzymes are located inside liver cells, but when they rapidly decompose, they enter the blood, forming the syndromes of cytolysis and necrosis.
Symptoms of hepatitis
The main symptoms of the development of the disease, which occur no earlier than 2 weeks from the moment of infection (depending on the type of hepatitis, the incubation period can range from 2 weeks to six months), include:
- increase in general body temperature;
- aches in muscles and joints;
- nausea, vomiting, complete loss of appetite, bloating;
- a feeling of discomfort and pain in the stomach and intestines, mainly on the right side;
- noticeable yellowish-orange tint to the skin and eyeballs;
- weakness, drowsiness, increased fatigue.