» Signs » The meaning of a pimple above the lip
0
6839
Article rating
It is hardly possible to find at least one person who has never encountered such a scourge as a pimple above the lip. Cosmetic problems and a feeling of discomfort are what this nuisance guarantees for each of its “lucky” owners. However, the appearance of a pimple above the lip is not always to be considered solely from a medical point of view. The experience of many generations shows that such misfortunes often arise due to completely different reasons, which will be discussed in this material.
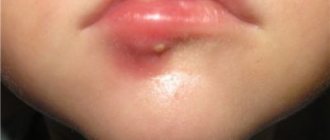
Pimple above lip
Causes of lip rash
Under no circumstances should skin rashes be ignored, because in this way the body tries to warn about a possible pathological process.
The causes of rashes can be:
- Hypothermia, as a result of which the body begins to develop a protective reaction
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract or endocrine system.
- Frequent stress.
- Poor nutrition and lack of vitamins. Due to the consumption of large amounts of fatty foods, the functioning of the sebaceous glands is disrupted.
- Allergy.
- Herpes virus.
In women, acne above the lip may appear due to:
- Excessive use of decorative cosmetics, which clog pores.
- The use of steroid drugs, which include hydrocortisone and prednisolone.
- The use of daily care products, which include petroleum jelly, paraffin, etc.
- Abrupt climate change.
- Bacteria and fungi that are found on the scalp.
- Taking contraceptives.
Common causes of cheilitis
The number of patients with the pathology in question among doctors at dermatological dispensaries, dentists and cosmetologists has increased significantly in recent years. This is due to an increase in the frequency of allergic conditions, secondary immunodeficiency, pathology of the endocrine glands, deterioration of the environmental situation and many other provoking and causative factors.
The most common cause of the development of cheilitis are certain dermatoses, for example, erythematosis (lupus erythematosus), lichen planus, psoriasis, syphilitic lesions and skin tuberculosis. They can also develop against the background of neurodermatitis, eczema, unfavorable climatic conditions (hot or cold climate), excessive or frequent and prolonged exposure to physical, chemical or mechanical factors, prolonged incomplete closure of the lips, in the presence of an allergic predisposition of the body, hypovitaminosis (hypovitaminous cheilitis), metabolic disorders.
The disease can develop when a viral (herpes simplex virus), bacterial or fungal infection is activated, for example, herpetic or angular cheilitis (“zaeda”), in which streptococcal or candidal cheilitis is distinguished.
Angular cheilitis
The cause is often a decrease in local immunity or the use of certain medications (medicinal cheilitis). One of these are antibiotics, which in some cases lead to dysbiosis. An example is damage to the lips due to dysbacteriosis (the same candidal cheilitis).
Fungal infection of the lip mucosa
Causes may also include pathology of the endocrine glands, especially the thyroid gland, diseases of the digestive organs, liver and biliary tract, cardiovascular system, pathology of the dental system, dysfunction of the respiratory organs, bad habits, psychosomatic disorders, genetic predisposition and others.
The main protective factors listed above are fully expressed in healthy adults, while in children and adolescents they are still just being formed. However, the constant nature of the influence of the negative external environment, participation in the act of eating, applying lipstick that closes the excretory ducts of the glands, childhood or adolescence, etc. lead to the loss of natural lip color, peeling of the epithelium, the formation of cracks, and the addition of infection in the presence of other favorable conditions. factors - to various forms of inflammatory diseases.
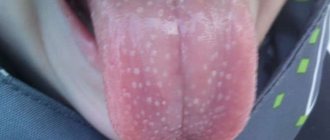
White rash above lip
White pimples above the lip look like ordinary ulcers. They are a reaction to an infectious lesion of the body, but often do not pose a great danger. The causes of sores can be clogging of the sebaceous glands with excess sebum and dead cells of the epidermis.
Another reason for their formation may be hyperkeratosis. This is a disease in which the stratum corneum of the skin quickly forms in a person, and the cells do not have time to be removed from the surface of the glands. Therefore, they accumulate and appear in the form of rashes. If a person does not follow the rules of personal hygiene, the ulcers may turn black.
If white pimples above the lip do not pose a great danger, then their formation on the lip itself can harm the body. In this case, you should definitely visit a doctor, because this may indicate serious violations.
If such rashes appear on the inner surface of the lips, tongue or cheeks, it may be stomatitis. It is treated with specially selected medications.
Blocked or inflamed pores
Poor-quality or expired hygienic lipstick can cause pimples. Damaged wax gets into the pore and clogs it. A plug forms inside. It's time to stop breathing and begin to swell. In principle, any cosmetic product with dye and wax can cause blockage. Even regular baby cream with glycerin, which is considered hypoallergenic.
To clean the pore and get rid of inflammation, you need to disinfect the skin with an alcohol-containing product, and with clean hands, carefully squeeze out the contents of the pimple - pus or plug. If it doesn’t squeeze out, don’t touch it. The pores need to be restored, so give up lip pencils, lipsticks, glosses and foundations for a few days. If the rash occurs constantly, and you guess that the problem is in cosmetics, reconsider your views and give preference to mineral, natural products.
Pimples on the upper lip can pop out due to toothpaste. The paste itself has nothing to do with it; most likely, you brushed your teeth after washing your face with deep cleansing. The skin steamed, the pores opened, the paste penetrated inside and caused an inflammatory process. Another cause of a rash above the lip and in the triangle under the nose can be an abrasive scrub with seeds. It injures the skin, the pores become inflamed.
Most often, girls who get rid of mustaches are strewn with acne. When using paraffin strips, you get the effect described just above with cosmetics. The wax penetrates the pore and clogs it. If a razor is used, the stratum corneum of the skin is removed along with the hairs, and bacteria from the surface of the blade or the hairs themselves enter the open pores. It is necessary to better disinfect the razor and skin, use an antibacterial and moisturizer. If you have rashes from waxing and razors, try sugar, cream depilation, or plucking hairs with an electric depilator or manually with tweezers.
Can problems with the gastrointestinal tract affect the skin?
Our body is cleansed in all possible ways, including through the skin. Therefore, rashes on the face may indicate poor functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, which is caused by slagging, gastritis or ulcers. With gastritis, not only rashes are observed. In general, the entire facial skin is dry and sometimes peels.
Food particles and intestinal juice with microorganisms are absorbed into the bloodstream, thus polluting it. “Dirty” blood affects the immune system and the condition of the facial skin. To avoid acne, you need to cleanse the gastrointestinal tract with enterosorbents, the lymph with beet juice, and then review your diet, excluding fatty foods and smoked foods. You should drink more clean water so that the body can easily remove accumulated toxins.
If you have problems with excess weight, you need to lose it with a diet of fruits and vegetables, adding green apples to your snacks. They are an excellent “broom” for the gastrointestinal tract; they will cleanse the body of toxins and saturate them with iron. Human fat is formed from what we eat, so it contains harmful substances that affect the appearance of acne and pimples. You need to get rid of ballast.
If you have problems such as abdominal pain and a burning sensation in the stomach, and pimples constantly appear above the upper lip, consult a gastroenterologist. Only by identifying the cause and eliminating it can you forget about the unpleasant consequences forever.
How does hormonal imbalance affect your appearance?
Problems with the endocrine system can affect the face. Guys encounter them during adolescence, when hormones are raging, and in girls this phenomenon is observed 12 times a year, during periods of PMS (premenstrual syndrome). These are natural processes of the body, so you should not interfere with their work.
Acne due to hormonal imbalance can also be observed in athletes who use growth hormones. Rashes above the lip and throughout the body are the most harmless reaction, which signals that it’s time to stop. When the body stops coping and removing substances it does not need through the skin, consequences worse than acne will occur.
If rashes occur in girls as a result of taking birth control pills, you need to try switching to others or abandoning them completely.
Purulent acne
The rashes are acne vulgaris, which can appear both on the lip itself and under it. The causes of such acne are clogging of the sebaceous ducts with fat and dead epithelial cells. If this is accompanied by a bacterial infection, the wound may begin to fester.
At the very beginning of the disease, the pimple above the lip is red, then its head becomes white. This means that the pus will soon come out and the surface of the lip will become crusty.
The causes of purulent rashes can be:
- Infection.
- Hormonal disorders as a result of pregnancy, menstruation and other things.
- Decreased immunity.
- Bad habits.
Important! Do not squeeze purulent pimples, as this can lead to infectious diseases.
The main symptoms of the rash are:
- pain in the lip area;
- inflammatory process;
- Possible throbbing pain at the site of the pimple.
What reasons can “strew” your face with acne?
The problem lies either in cosmetics, or in health, or in both. The main reasons include the following:
- clogged or inflamed pores;
- improper functioning of the endocrine system;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- herpes viruses and other infectious diseases;
- decreased immunity;
- poor nutrition;
- taking antibiotics.
Herpetic rashes
This is the most common cause of lip rashes. At the beginning of the disease, a water pimple appears, containing a clear liquid inside. In most cases, the virus affects the delicate parts of the skin near the lip.
After time, the bubble bursts, and in its place an ulcer forms, which then dries up. The disease can be cured with the help of specially selected therapy prescribed by the doctor.
Almost every person is a carrier of the herpes virus, but it does not always manifest itself. This requires a decrease in immunity or infection in the body. Sometimes herpes can appear as a result of mechanical damage to the lip.
Important! If herpes is not treated, it can negatively affect the meninges and lead to cancer.
Folk signs about pimples under the lips
A rash below the mouth can predict an event that will soon occur. To decipher the sign, you need to take into account the location of the pimple:
- Under the lip on the left - a kiss with your soulmate. If you are not in a love relationship, the meaning of a kiss can be interpreted as friendly, related.
- Pimple under the lower lip on the right - quarrels with close relatives and friends.
- In the middle. Promises positive changes in life: career advancement, an unforgettable trip, moving, receiving a bonus or a generous gift.
How is acne related to intestinal problems?
If rashes in the lip area indicate the development of gastrointestinal diseases, then you need to consult a gastroenterologist. Sometimes, to get rid of an illness, you will need to cleanse the intestines with an enema, medical lavage and proper nutrition.
Important! Colon lavage is done in medical institutions.
You can also try using herbal infusions, they will help rid the intestines of toxins. Plantain, fennel, and flax seed are suitable for this.
General recommendations for treating rashes
For treatment to be effective, you must follow the following rules:
- Do not squeeze, as this may cause infection.
Squeezing a pimple can make the situation worse
- It is acceptable to use drying agents that contain alcohol. This will help acne heal faster and stop the infection from spreading.
- Before using any cosmetic product, you should test it on the back of your hand.
- To keep your skin clean and healthy, you need to eat right and give up bad habits.
- Avoid stressful situations.
- Take vitamins.
Acne treatment
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor conducts a comprehensive examination to establish a diagnosis. Only after this are medications prescribed.
If it is a herpes virus, then preference should be given to:
- antiviral drugs: Acyclovir, Zovirax, Gerpevir;
- multivitamins;
- alcohol solutions of propolis or calendula.
To help get rid of stomatitis:
- Furacilin solution, which is used to rinse the mouth. To prepare it you will need half a Furacilin tablet and 1 glass of water. You need to repeat the procedure 3 times a day until the rash goes away.
- The oral cavity should be treated with water and hydrogen peroxide (1:5). A bandage is moistened in this solution and used to wipe the affected areas.
- You can also prepare the following mouthwash: 1 glass of water and 5 drops of calendula. You can use propolis instead.
- The pharmaceutical product Cholisal or Solcoseryl also helps. They relieve inflammation and heal wounds.
During treatment, you must stop using decorative cosmetics. To dry and quickly get rid of acne, you can use Vishnevsky ointment, ichthyol ointment or Levomekol.
Antibiotics are also prescribed. For infectious forms of lip lesions, drugs from the Tetracycline group are prescribed. If the lips are mildly affected, antibiotics in the form of a gel or ointment will be effective.
Viral infections
Most often, acne on the upper lip is a consequence of the presence of type 1-2 herpesvirus in the body. This is a global disease that affects at least 90% of people on the planet. You can become infected at birth. It is virtually useless to treat, since it will still not be possible to completely get rid of it.
Modern antibiotics can kill 98% of viral particles, but 2% will remain deep in the cells. At the same time, antibiotics do not bring anything good to the body: they kill the good microflora of the gastrointestinal tract, weaken the immune system to a critical state, from which the remaining 2% of herpes virus particles acquire resistance to the drug and easily make up for their losses in comfortable conditions. In trying to get rid of acne by curing 98% of the herpes virus with antibiotics, we will get a portion of new serious problems and get bogged down in lifelong treatment of first one, then another, then another.
It's better not to swing the pendulum. It is much more effective to solve the problem by boosting immunity. The stronger it is, the better it suppresses all harmful bacteria and viruses, so there will be no acne on the face.
Initially, you need to understand the relationship between the herpes virus in the body and its manifestation near the mouth. This happens for two reasons:
- hypothermia;
- weakening of the immune system.
Recurrence of herpes due to hypothermia occurs at the end of winter, when vitamin reserves are at zero and the immune system is weakened. There is only one way out: eat as many vitamins and minerals as possible.
In case of obvious hypovitaminosis, when in addition to herpes you feel general physical weakness, you can take a course of Supradin. If you take 2 effervescent tablets per day, lost reserves will be returned within a week. The virus will be suppressed by the immune system, acne will disappear until the next weakening.
Another argument in favor of boosting immunity instead of treating with antibiotics is the variety of herpes viruses. Officially, today 8 types have been studied, and there are about 90 more unstudied, but identified. It is not a fact that type 1-2 herpes appears in the mouth, for which modern antibiotics have been developed.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine will also help you cope with unpleasant symptoms and help you quickly get rid of the disease.
The following recipes have worked well:
- Chamomile decoction that cleanses the skin and relieves inflammation. To prepare it you will need 1 tablespoon of dried chamomile flowers and 1 cup of boiling water. Pour water over the flowers and steam them for 25 minutes, then strain it and add 1 tablespoon of propolis. Then take a cotton pad, moisten it well and apply to the affected area. Repeat the procedure every hour. This decoction can be taken orally, 1 tablespoon 3 times a day.
- Decoction of celandine. To prepare, you will need 1 tablespoon of crushed celandine and a glass of boiling water. It is brewed in the same way as chamomile, but only infused for an hour. Lotions should be applied every 3 hours until the pain on the lip goes away.
- Aloe. You will need to cut a small piece from an aloe leaf, remove the skin from it and apply it to the sore spot for 30 minutes, maybe more.
- Fresh aspen leaves. To do this, juice is squeezed out of them, a cotton pad is soaked in it and applied to the affected area for 15 minutes. You need to repeat this procedure 3 times a day.
- Laundry soap. Generously lubricate your finger with soap foam and apply it to the pimples. Wash off after 25-30 minutes. The procedure must be repeated every 3 hours.
- A film from the inside of the egg, which is applied to the sore spot. You can wear it for several hours, then remove it with warm water.
You should not wait for the rash to go away on its own; it is better to seek help from a doctor. After all, such an ailment may indicate a more serious disease in the body.
Clinical signs and treatment principles
Primary cheilitis
Glandular cheilitis
Chronic inflammation caused by pathological structural and functional changes in the salivary glands and their excretory ducts in the area of the red border and Klein's zone, congenital or acquired, which is accompanied by almost constant secretion of saliva. It occurs 2 times more often in the lower lip area than in the upper lip, and in men it is 2 times more common than in women.
The disease, depending on the cause, can be primary or secondary. Primary pathology develops as a result of a congenital anomaly of the mucosalivary glands and/or their excretory ducts in the specified area, an increased number of glands, their hypertrophy and hyperfunction, expansion of the excretory ducts and their mouth. The anomaly in the development of glandular structures consists in a displacement of their localization, in congenital atypical localization (heterotopia).
Glandular cheilitis is diagnosed, as a rule, in people over 40-50 years old, much less often in age groups under 20 years old, when serous or purulent inflammation develops. Provoking factors are infection, emotional and mental disorders, smoking, poor oral health (tartar, periodontitis, sharp edges of teeth, etc.), which contribute to an increase in the production of the salivary glands and the development of inflammation.
The cause of secondary glandular cheilitis is a chronic inflammatory process in the red border area, which develops in the presence of lupus erythematosus, leukoplakia, lichen planus and other dermatological diseases.
The inflammatory process can be:
- Serous.
- Fibrous, which in the area of the mouths of the excretory ducts is accompanied by keratinization.
- Purulent - with the addition of a pyogenic infection.
Serous inflammation
It is characterized by persistent redness and swelling of the lip, the surface of which has a bumpy appearance due to the enlarged salivary glands protruding above it. A “dew” or “drop” symptom is noted, caused by the release of droplets of clear serous fluid from the dilated ducts. Constant wetting with saliva and its evaporation leads to dryness and peeling of the red border, the appearance of cracks and erosions.
Fibrous form
Chronic long-term course of the serous form can cause fibrosis of the connective tissue of the lip. Fibrous tissue reduces the diameter of the mouths of the ducts or completely closes them, which leads to disruption of the outflow of secretions, its accumulation, stretching of the ducts and the formation of cysts. This is manifested by pronounced congestive redness of the red border, a significant increase in the size of the lip, tuberosity of its surface and a rim of opacification in the area of the mouths of the ducts due to keratinization of epithelial cells.
Purulent form
It is the result of free penetration of a pyogenic infection into the dilated ducts of the glands. The purulent inflammatory process is sometimes limited to one or two glands, but, as a rule, the damage is diffuse. Clinical manifestations of this form are enlargement, swelling and soreness of the lip (usually the lower one). The red border of the lip is covered with yellowish-green or brownish-black crusts, which are tightly fixed to the surface.
Excretory ducts take on the appearance of cones rising above the surface and surrounded by cracks and erosions. When pressure is applied to them, thick cloudy (serous-purulent) contents are released. If the lumen of the duct is blocked by purulent exudate, an abscess may form.
Treatment principle
Treatment consists of eliminating erosions, cracks and crusts, followed by surgical removal of the Klein zone, in the area of which the displaced glands are contained, or electrocoagulation of the latter.
Exfoliative cheilitis
It is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects only that half of the red border of the lips, which is adjacent to the mucous membrane, and is accompanied by peeling of epithelial cells. Mostly women between 20 and 40 years of age are affected. There are descriptions of cases of familial disease in the literature.
The main link in pathogenesis is a violation of the process of keratinization of the epithelium. The main reasons in recent years have been given to immunoallergic and genetic factors, and the influence of psychogenic factors and thyroid dysfunction cannot be ruled out.
According to clinical signs, 2 forms are distinguished:
- Dry.
- Exudative.
As a rule, they are considered as different stages of the development of one disease, since the first can transform into the second and vice versa.
Dry form of exfoliative cheilitis
It is characterized by the formation at the border of the mucous membrane with the red border of a strip consisting of thin translucent scales of yellowish and grayish color. These scales resemble plates, tightly attached in the central part and lagging behind the surface with their peripheral sections. After about one week, they are easily removed, revealing a bright red surface without erosion. However, after a few days, new ones appear in place of the removed scales. The duration of the dry form, which is not prone to self-healing, is sometimes tens of years (in the absence of treatment).
Exudative form
It occurs with the formation of massive yellow-brown or gray-yellow crusts on the hyperemic and swollen red border of the lower (mainly) lip, less often on both lips. The crusts are layered on top of each other, sometimes forming layers of considerable size, hanging from the lips like an apron. They periodically separate and then form again. After their removal, a bright red surface is exposed, which is covered with a whitish exudate. A characteristic feature of this form is that neither the skin nor the mucous membrane of the lips are affected. The process does not affect the corners of the mouth and the strip of red border bordering the skin. The course of the exudative form is more favorable compared to the dry form.
Treatment principle
For the dry form, indifferent ointments, creams and hygienic lipsticks, keratoplasty applications, sedatives and tranquilizers are prescribed. In case of exudative form, complex therapy is carried out with drugs that increase the body's resistance, applications of corticosteroids and keratoplasties, irradiation sessions with a helium-neon laser, ultraviolet radiation, and boundary Bucca rays (ultrasoft X-rays) are used.
Actinic cheilitis
A chronic inflammatory process caused by increased sensitivity of the red border area to ultraviolet radiation. A feature of the disease is its seasonality - the first occurrence and exacerbation in spring and summer.
There are 2 clinical forms:
- dry, in which the red border of the lower (usually) lip is bright red, dry, covered with silver-white scales. Areas of hyperkeratosis are often observed. With a long course, transformation into cancer is possible, especially in smokers;
- exudative - characterized by a bright red color of the red border, its swelling and quickly opening bubbles on its surface with the formation of weeping erosions and crusts; the patient is concerned about soreness, itching and burning of the lips.
Treatment
The essence of the treatment is protection from sunlight, including creams with ultraviolet filters. An ointment or cream with corticosteroids, hygienic lipstick, and oral vitamins, mainly “B2”, “B6”, “B12”, and nicotinic acid are prescribed.
Meteorological cheilitis
The inflammatory process is caused by unfavorable meteorological factors - excessive dryness or humidity, wind, solar radiation, cold, etc. It is more often observed in men and people with delicate skin, as well as in the presence of dermatoses such as neurodermatitis, seborrheic eczema, ichthyosis and some others. The treatment is chronic and not related to the season. Over a long period of time, a precancerous condition may develop.
The pathology is manifested by peeling and dryness, moderate hyperemia and swelling of the red border throughout, small scales, and complaints of a feeling of “tightening.” Cracks and erosions may appear.
The principles of treatment are the same as in the previous case.
Allergic cheilitis
This is a manifestation of a delayed type allergic reaction in response to contact of sensitized tissues with an allergen. Allergens can be chemical components of toothpastes, chewing gum or lipsticks, denture plastic, cigarette smoke, the mouthpiece of a wind instrument, etc.
The patient is concerned about swelling of the lips, itching and burning sensation. Upon examination, swelling and redness of the red border are revealed, against which fine lamellar peeling of the epithelium and cracks can be seen. In the case of a more severe course, the appearance of bubbles and erosions is noted. Sometimes the process can spread to the skin and mucous membrane of the lips.
Treatment
It is necessary to identify and eliminate the allergen. Antihistamines are prescribed orally (Zyrtec, Tavegil, Claritin, etc.), and ointment or cream with corticosteroids is prescribed locally.
Abrasive cheilitis Manganotti
Many authors include it in the classification of cheilitis. It occurs on the lower lip, mainly in older men. The disease develops as a result (as is assumed) of impaired blood circulation in altered vessels under the influence of meteorological, physical, chemical and other factors, as well as infectious pathogens of the oral cavity.
Characteristic are deep red erosions on a moderately pronounced inflammatory background, having a smooth surface and sometimes covered with crusts. This pathology is a precancerous disease and its inclusion in the classification of cheilitis is considered incorrect.
Secondary cheilitis
Atopic
It most often occurs in childhood and adolescence (from 6 to 17 years) and is one (and sometimes the only) of the symptoms of neurodermatitis or atopic dermatitis. A genetic predisposition to the formation of atopic allergy plays a significant role in its development.
This form is manifested by damage to the red border and, of course, the skin of the lips. The most intense damage affects the area of the corners of the mouth. The mucous membrane and the adjacent red border strip remain intact.
Initially, there is itching, then slight swelling and redness of the red border area occurs, with the simultaneous transition of the inflammatory process to the adjacent skin of the face and corners of the mouth. Infiltration appears in the affected areas (the corners of the mouth take on the appearance of a “folded accordion”), dryness and cracks, and after scratching - crusts. The subsidence of acute inflammation is accompanied by peeling and lichenification of the lips, which are combined with dryness of the affected areas of the facial skin and its peeling.
A long course (years) is possible with remission in spring and summer and relapses in autumn and winter.
Treatment
Therapy is carried out with desensitizing and sedative drugs, vitamins, and for a long period, corticosteroids are added internally. Topical application of ointment or cream with corticosteroids and Bucca rays is quite effective.
Eczematous
It can represent either an isolated pathology or be a sign of an eczematous process of the face. Even in cases where the process is isolated, it at least slightly spreads to areas of the skin adjacent to the red border.
Possible acute, subacute and chronic course. Persons aged 20–40 years are mainly affected. The main role in the etiology belongs to allergens, which can be food products, dentures, toothpastes, microorganisms, medications, etc.
The acute process is characterized by the sequential appearance of redness, then small bubbles (vesicles) with yellowish serous contents, after the merging and opening of which, “serous wells” and a weeping surface characteristic of eczema are formed. Straw-yellow crusts (sometimes massive) and scales form on it. This whole process, which is accompanied by swelling of the lips, quickly spreads to the skin of the corners of the mouth and areas of skin adjacent to the red border. It becomes difficult for the patient to open his mouth and speak, and he is bothered by burning and itching.
In the chronic course, the tissues are constantly swollen (but much less than in the acute period), they have a yellowish-red color, the affected surface is dry with peeling, cracks and bloody crusts.
The principles of treatment are the same as for skin eczema.
Plasma cell
Considered as an immunological reaction with the formation of an infiltrate of plasma cells. The reason has not been studied, but it is assumed that the main pathogenetic role is played by the factor of chronic irritation, especially from sunlight, microtrauma, etc.
Clinical manifestations are varied. The most common location is the lower lip, which develops dark red erythema with a varnish-like surface. Sometimes erosions form on it and petechial rashes appear. In some cases, the red border is partially covered with a massive crust (up to 1 cm thick) of a whitish-yellow or brownish color, which hangs with its edges from the lip like an apron. After its removal, a painful erosive surface or soft tumor-like plaque is exposed.
The course is chronic, long-term. The disease is not prone to self-healing or remission.
Treatment
Treatment is carried out using desensitizing drugs and external agents with corticosteroids. In case of ineffectiveness, surgical excision of the affected area is used with mandatory histological examination. Subsequently, lip plastic surgery is performed.
Lymphoedematous macrocheilitis
Refers to a group of pathological conditions that are caused by impaired lymph flow. The latter is due to increased sensitivity, mainly to infectious pathogens located in foci of chronic infection of the body. The main symptom is significant lip enlargement and soreness.
During the course of the disease, which occurs chronically with relapses, 3 stages are distinguished. The basis for this division is the histological picture of the depth of the lesion. At the early and advanced stages, significant swelling is observed, accompanied by disintegration of connective tissue structures, and the formation of lymphectasias, that is, dilation of lymph vessels in the form of cysts. Impaired lymph circulation at a late stage is manifested by deep degenerative changes in the lip tissue.
Treatment
Treatment at an early stage - thermal procedures, special massages and sclerotherapy, ingestion of potassium iodide. At an advanced stage, surgical excision of tissue affected by the process is effective. In addition, desensitizing therapy and sanitation of foci of chronic infection in the body are necessary.