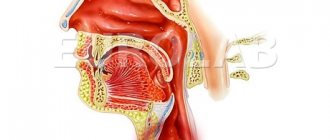
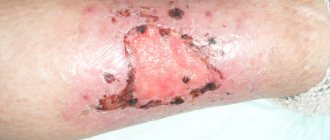
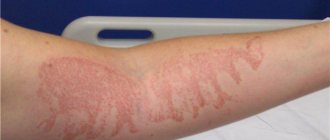
Facial burns are one of the most common types of injuries. Their appearance is a consequence of exposure to high temperatures or chemicals on the skin. In rare cases, burns on the face may occur due to an electrical charge.
Medicine divides facial burns into many classes according to different criteria, but they are often divided according to the type of injury:
- Thermal - damage to tissue on the face as a result of exposure to high temperature. Burns can be caused by: fire, hot liquid, steam or hot objects.
- Chemical – burns that are caused by poor-quality personal hygiene products or from the use of household hygiene products. These can be various elements: alkalis, acids, salts of heavy metals.
- Electrical burns are the least common type of facial burn and are caused by a short circuit. Unlike other types of burns, it leaves quite deep marks at the site of tissue damage.
- Radiation - can be caused by excessive exposure to direct sunlight or when using a laser in cosmetic medicine.
They can also be divided according to symptoms into 4 degrees: 1st is the least dangerous, and 4th – life-threatening burns. For first-degree burns, the most striking example is a sunburn on the face.
Classification of burns on the face
Due to lack of protection, facial injuries occur quite often, approximately 2% of them are burns.
A burn is a superficial or deep tissue injury that occurs under the influence of air, high-temperature liquids, chemical compounds and other external factors.
In medicine, several classifications of burns are used; the most common ones are based on the cause of damage and the depth of the affected tissue. The clinical picture, treatment methods, recovery time and prognosis depend on this.
Provoking factor
According to the reason that caused the burn, they distinguish:
- thermal;
- radial;
- chemical;
- electric.
Thermal burns
One of the most common and dangerous burns is thermal; under the influence of high temperatures, proteins that form tissues are destroyed. Thermal damage to the face can be caused by several factors, and the clinical picture of the burn is somewhat different:
- Hot steam.
Under its influence, a fairly large area of the face is affected, but the tissues are affected shallowly. The danger of steam burns lies in the high probability of damage to the mucous membranes, organs of vision and breathing.
- Liquids.
Such burns are small in area, but tissue damage can be deep, especially if hot oil comes into contact with the face.
- Fire.
Tissue damage caused by open flames is usually extensive and deep, with a high likelihood of complete or partial loss of vision and serious respiratory damage.
- Hot items.
They leave a burn with clear boundaries, which is often accompanied by detachment of part of the epidermis (when trying to remove the object). Very often, after such an injury, noticeable marks remain.
The prognosis for heat victims depends on the depth of the damage, but most often leaves scars.
Chemical
The second most common cause of facial burns is the action of chemicals. Today this can happen in the workplace (in a medical laboratory, at an industrial enterprise), at home (household chemicals, improper use of cosmetics) and even in beauty salons if the cosmetologist is insufficiently qualified.
Burns can be caused by acids, alkalis or salts of certain metals.
Alkaline burns are the most complex; when a chemical gets on the face, it literally eats away soft tissue, and sometimes even bone.
Damage to the face with various acids does not cause such deep damage, although the extent of the damage can be quite large. Under the influence of acid, scabs form on the skin, which prevent the substance from penetrating further. Deep tissue damage can occur when concentrated acids come into contact with the skin, while superficial damage occurs accidentally.
Today, peelings with fruit and synthetic acids are widely used in cosmetology. Liquids dissolve the upper layer of the epidermis, causing a minor burn, after which the formation of renewed skin begins. If the concentration of the composition is incorrectly selected, burns can be much deeper.
The same thing can happen at home: when using low-quality or inappropriate cream, face mask, when cauterizing acne, insect bites, and damage from antiseptics. For example, iodine burns the edges of the wound; healing will take longer and leaves an unattractive mark.
Damage to the facial skin by salts of heavy metals (bismuth, gold, antimony, iron, mercury, copper, lead) occurs relatively rarely. They occur upon contact with medications, pest control products for plants, and fertilizers. In appearance, such burns are similar to acid burns.
All types of chemical burns are dangerous due to general intoxication of the body.
Electrical
Electrical shock to facial tissues is extremely rare. In appearance it resembles a thermal burn, has a small area, but tissues can be damaged to a great depth.
Ray and solar
Complaints of radiation burns are very common. They arise under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, laser rays and other radiation. There are several varieties:
- Light.
The most common burns in this category are light or sunburns. They occur during prolonged exposure to the street during sun exposure, without the use of creams with a UV filter, and in solariums. The affected area is extensive, but the damage is superficial.
Typically, light burns are relatively mild and almost never leave marks.
- Ionizing burns.
They occur during intense laser exposure during cosmetic procedures. In this type, the outer integument is slightly injured; the danger comes from damage to the deep layers by rays. Treatment is complicated by impaired cell regeneration ability and capillary fragility.
Radiation burns can occur as a complication of therapy for malignant tumors.
In addition to the main types of facial burns, there are combined ones - injuries combined with other injuries.
Basic general information
Burn injuries to the face account for about two percent of the total amount of all types of tissue damage in the jaw and facial area. To decide what to do in case of a facial burn, it is necessary to clarify the cause of origin:
- thermal burn;
- chemical burn;
- radiation burn or electrical injury.
A significant part of facial burns is caused by factors of thermal origin, represented by open flames, hot liquids and objects, vapors and gaseous substances. In second place in terms of prevalence are facial burns of chemical origin and electrical trauma.
The radiation type of damage to facial tissue is an exceptional case. Such a burn on the face can be the result of radiation therapy in the treatment of tumors of various origins, as well as violations during modern cosmetic procedures. Often this type of burn is combined with damage to the scalp and cervical region, as well as the oral cavity and mucous membranes.
Thermal damage
To understand how to remove the effects of thermal damage from the skin, it is necessary to take into account the degree of such a burn:
- superficial first-degree burns are accompanied by hyperemia and irritation on the skin;
- superficial second-degree burns are accompanied by the formation of characteristic blisters and peeling of the skin;
- superficial third-degree burns are accompanied by the formation of partial necrosis of the skin and epithelization;
- deep third-degree burns “B” are accompanied by necrosis of all skin layers;
- deep fourth-degree burns are accompanied by the formation of necrotic changes not only in the skin, but also in the deep tissues.
It is possible to quickly cure a burn classified as superficial, even at home.
Chemical damage
The main danger of this type of injury is a fairly high risk of chemical or toxic poisoning of the body. First and second degree lesions, accompanied by allergic manifestations, very often result from exposure to cosmetics or household chemicals.
More severe lesions, as a rule, are a consequence of the traumatic effects of alkalis and acids. In this case, it will not be possible to quickly get rid of the burn, since even removing the irritating factor from the skin is not able to completely stop tissue destruction.
Electrical and radiation injuries
A fairly noticeable burn mark is a common result of electrical and radiation damage to the skin. Of course, the second type of damage is relatively rare, and in accordance with the medical classification can be presented:
- light damage or sunburn of the face caused by prolonged exposure to direct sunlight. Even when using folk remedies at home, questions about how to remove sunburn usually do not arise;
- ionizing lesions caused by laser during cosmetic and therapeutic procedures. Despite the shallow damage, the treatment process is often complicated by injured tissues and organs. There is fragility and bleeding of blood vessels, as well as a characteristic decrease in regenerative functions at the cellular level.
Combined and combined types of burns should be considered separately. In the first case, the lesion is the result of simultaneous exposure to several traumatic factors. The diagnosis of the combined variant is noted when a burn is combined with any type of other injury.
Damage level
When a face is burned, different layers of skin and muscle tissue can be damaged. On this basis they distinguish:
- First degree burns.
It is diagnosed when only the superficial layer of the epidermis is affected by any aggressive factors. Clinical picture: slight swelling, redness of the skin, pain when touched.
During the healing process, peeling begins, which disappears without a trace after a few days.
- Second degree burns.
They differ from the milder form by the formation of fluid-filled skin bubbles (blisters) on the surface. The healing of such an injury lasted 1-2 weeks, the restored tissues did not differ from undamaged ones. On the face, such burns often occur after cosmetic procedures.
- Third degree burns.
They are differentiated into 2 types: A and B. With tissue damage of grade A, huge blisters filled with serous fluid form on the surface of the skin. The epidermis partially dies, brown or black scabs appear. Degree B is diagnosed when all parts of the skin are completely affected.
- Fourth degree burns.
The most difficult and dangerous. The destruction of the epidermis, fatty tissue, part of the muscle tissue, and sometimes bones occurs.
Burns of the 1st, 2nd, 3rd (A) degrees are classified as superficial; the skin can recover on its own. With proper treatment, they do not leave scars, or they can be easily eliminated with special ointments and procedures. Treatment of such facial injuries can be carried out at home.
Deep burns (third (B), fourth degree) can be accompanied by complications; they leave deep scars that are difficult to correct. Treatment of a deep burn is carried out in a hospital and can last several weeks or months; without professional help, infection can occur.
First aid for burns
1. Break contact with the traumatic surface
Cool the affected area
It is strictly forbidden to apply ice to a burn. This will not alleviate the patient’s condition, but can provoke another injury – frostbite.
Provide comfort and convenience
- First degree - slight redness and minimal swelling of the skin, the presence of small blisters is acceptable.
- Second degree - severe redness and swelling, swollen or already burst blisters.
- Third degree - necrosis (death) of tissue, characterized by the formation of a scab (dry crust), damage affecting muscle tissue.
- Fourth degree - charring of the damaged area, tendons, muscles and bones are injured.
In the first or second degree, it is possible to treat the patient at home. But at the slightest suspicion of a more severe degree, even if it is a small burn on the hand, an urgent visit to a medical facility and prompt assistance from a traumatologist is necessary.
Determine the degree of burn
If first or second degree burns are detected with an area of no more than 1% of the body (the size of the palm), you can begin treatment - apply a special product to the affected area - gel, cream or pharmaceutical anti-burn bandage. If more serious and extensive skin damage is recorded or a burn to the face, genitals, foot or hand is obtained, you need to call an ambulance.
Do not allow the patient to make unnecessary movements - he may be in a state of shock. If you complain of pain, give an anesthetic drug - any analgesic or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug: Ibuprofen, Acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin), Diclofenac, Ketoprofen or Ketonal.
What to do first: emergency care
If a burn occurs on the face, first aid must be provided to the victim. This will prevent damage to deep tissue layers and reduce the likelihood of complications.
What to do in these cases? Actions depend on the cause of the burn and can vary significantly:
- In case of thermal burns caused by an open flame, you must first extinguish the flame (cover your face with a thick cloth).
- The next step is to cool the skin. You can place your face (if the integrity of the epidermis is preserved) under a stream of cool water, or wash the skin manually or irrigate it with a spray bottle.
- For chemical burns, it is important to know what exactly caused the tissue damage. Contact of some products (containing aluminum) with water is unacceptable, as the reaction intensifies. If the skin is damaged by acid, it is neutralized within a quarter of an hour with a solution of soap or soda, alkali, table vinegar.
- Examine the victim to ensure the absence or presence of other injuries.
- In case of electric shock, remove the source from your face and check your pulse. If necessary, perform artificial respiration.
- If the burn is small and the person feels relatively well, you should go to the burn department of the nearest hospital as soon as possible. In all other cases, it is necessary to call an ambulance, explain the situation and strictly follow their recommendations.
Deep burns often cause painful shock, when the victim does not experience discomfort, but performs chaotic actions. In this case, he needs to be calmed to prevent mechanical damage to the burned tissues and infection.
During transport to a medical facility, it is recommended to cover the damaged skin with a thin cloth, such as 2-layer gauze.
Thermal burn
Damage is provoked by high temperatures. Most often it occurs when the skin comes into contact with boiling water, steam, hot oil, or fire.
When exposed to negative influences, a person reflexively closes his eyelids to protect his eyes. This feature in some cases protects the organ of vision from irreversible damage, but causes severe injury to the eyelids, which is difficult to treat. Having received a burn to the face, you must definitely call an ambulance. Only a doctor is able to assess the depth of the lesion and prescribe the correct treatment. For 1st and 2nd degree burns, it is allowed to treat the injured area of the house, following all the recommendations of a specialist. Deeper injuries require inpatient treatment in a burn department.
First aid
First of all, it is necessary to neutralize the thermal effect. Put out the fire, push the person away from the steam or hot object.
If the integrity of the skin is not compromised, you should place your face under running water and cool for at least 10 minutes. Then rinse the dermis with an antiseptic. Can be used:
- Chlorhexidine,
- Furacilin solution,
- hydrogen peroxide.
After washing the skin, you need to treat the damaged area with an anti-burn ointment or aerosol, for example, Panthenol or Olazol. Cover it with sterile gauze and wait for the doctor to arrive. To relieve acute pain, you need to take analgesics.
Treatment
To treat 1st and 2nd degree burns, wound healing external ointments are used. As prescribed by a doctor, use:
- Bepanten,
- Levomekol,
- furacilin ointment,
- Vishnevsky liniment,
- Dexpanthenol,
- balm Rescuer,
- Solcoseryl.
Before applying the product, the epidermis is disinfected with peroxide. Treatment is carried out 2-3 times a day. If blisters have formed, it is advisable to apply an occlusive dressing.
Severe burns require powerful medications and inpatient therapy. The doctor prescribes treatment on an individual basis based on the patient’s condition. To relieve swelling, antihistamines are used, and antibiotics are used to relieve infection. If necessary, plastic surgery is performed by excising the burned layers of the dermis and transplanting healthy skin to this place.
Features of treatment
Treatment for facial burns differs from treatment for other injuries. Such injuries are considered the most complex.
Firstly, the skin and subcutaneous tissue layer are much thinner here, so the damage can be deep. Secondly, healing occurs faster if the tissues are at rest, which is almost impossible to do with the face: facial, chewing movements lead to permanent damage to the healing areas.
The most severe burns are the forehead, lips and eyelids. Here the tissues are very thin, often become necrotic, are very difficult to restore and cause serious complications: damage to the cornea, mucous membranes, speech impairment.
After visiting the burn department, the patient is examined, the severity of damage to facial tissues and treatment tactics are determined. First aid consists of several stages:
- Anesthesia (local or general). The type of anesthesia used depends on the depth of the injury. Local anesthesia is carried out through applications with Novocaine or Lidocaine. Several types of medications are taken orally: Paracetamol, Analgin, Baralgin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ketoprofen), strong narcotic painkillers (Morphine, Promedol).
- Patients in a state of shock (after electric shock or very deep burns) undergo antishock therapy - intramuscular injection of a solution of analgesics and antihistamines.
- Removal of affected tissue, drainage, antiseptic treatment (Chlorhexidine, isotonic solution, hydrogen peroxide).
- In some cases, additional antibacterial treatment and tetanus vaccination are required.
After antiseptic treatment and receiving treatment recommendations, patients with superficial burns are treated at home, while those with deep burns remain in the hospital. Treatment for severe burns is as follows:
- treatment several times a day with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory agents;
- applying bandages with medications that accelerate healing;
- removal of infected or dead tissue.
After healing, physiotherapeutic procedures or plastic surgery may be prescribed to restore facial tissues after deep burns.
How to treat with medications and creams
Several groups of drugs are used to treat burns:
- anesthetics;
- antiseptics;
- means to eliminate swelling and hyperemia (redness) in 1st and 2nd degree burns;
- antibiotics if there is a threat of infection;
- drugs that accelerate tissue regeneration.
Each group includes a large number of medications; it is not recommended to use them without a doctor’s prescription.
Pain of varying intensity may be felt until the facial tissues have completely healed. To relieve pain, you can use the well-known Nurofen, Ketanov, Analgin, but more often they use products for external use in the form of gels and ointments. Mephenate and Dioxyzol ointments have proven themselves well. In addition to pain relief, they have a pronounced antiseptic and wound healing effect.
The affected area must be treated daily with antiseptics to avoid infection: alcohol, Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, hydrogen peroxide. The use of Chlorhexidine and Miramistin is tolerated very well by patients - no discomfort occurs when applied to tissue.
To soothe the skin for superficial burns, use external remedies:
- Panthenol;
- ointment "Rescuer";
- Actovegin;
- Bepanten;
- furatsilin ointment;
- Levomekol;
- ointments of plant origin (sea buckthorn, with calendula).
Panthenol has proven itself well; it not only removes the feeling of tightness, but also accelerates regeneration and reduces the intensity of pain. In some cases, antihistamines are prescribed: Claritin, Diazolin, Loratadine.
Actovegin can be used in the treatment of burns of various types. The drug activates blood circulation and accelerates metabolic processes, which will help get rid of the consequences faster.
When a burn suppurates, antimicrobial agents are used: Levomekol, syntomycin ointment, streptocide (in the form of powder or ointment), Methyluracil, Baneocin, preparations with silver (Dermazin, for example). It is better not to use fat-containing products; they interfere with the outflow of fluid.
How to get rid of it using folk remedies
When treating superficial burns without complications, it is permissible to use traditional methods; they reduce discomfort, moisturize and accelerate tissue regeneration.
Proven means:
- dairy products;
- vegetable juices: cabbage, potatoes;
- applesauce;
- lotions with decoctions of oak bark, chamomile, elm;
- juice from lingonberries or chokeberries;
- a squeeze of boiled and then fried egg yolk;
- mumiyo dissolved in water;
- lotions with aloe leaf;
- dusting the wound with powder obtained from charcoal;
- a mixture of whipped egg whites and refined vegetable oil;
- lotions from burdock juice;
- sea buckthorn oil in pure form or mixed with fir oil in equal quantities.
Folk remedies can be used as an addition to the main treatment of minor burns, without damaging the skin, after consultation with a surgeon or therapist. If during their use the temperature rises, swelling or suppuration appears, you must seek professional help as soon as possible.
Treatment of burns at home
Outpatient treatment is acceptable:
- in mild form (1st and 2nd degree) for all types of burns;
- for a small area - less than 1% of the entire surface of the skin (visually no more than the palm of a person);
- no high fever or signs of tissue infection.
The treatment tactics in each case are determined by the doctor, in general terms it looks like this:
- antiseptic treatment 1-2 times a day;
- applying bandages with epidermis-restoring agents;
- taking painkillers.
If the face is damaged by chemicals, even to a minor extent, regular monitoring of the tissue condition during home treatment is necessary.
In case of a radiation burn of the face, it is enough to periodically apply softening and soothing substances to the skin: sour cream or kefir, cucumber juice, Panthenol, cooling gels with menthol, Indomethacin to eliminate swelling and pain.
A prerequisite for a facial burn is daily intake of fluid in large quantities (more than 2 liters) and consumption of food enriched with light protein, vitamins A and E: carrots, fresh vegetables and fruits, turkey and chicken meat in liquid or puree form.
How to treat?
Treating burns is a complex, lengthy and patient process.
You must immediately call an ambulance, regardless of the severity of the injury. Treatment of any burn should take place after consultation and under the further supervision of a physician.
What to do first?
Before the arrival of doctors, it is necessary to stop contact of the facial skin with the damaging factor. You can wash the burn with cold water or apply ice to the damaged area.
It won’t hurt to treat the skin area with peroxide or chlorhexidine. These remedies will not relieve pain, but at least prevent infection. However, you can do something yourself only if the area of the burns is small.
In the hospital, doctors prescribe antibacterial agents (for example, Levomycetin or Erythromycin) to destroy possible pathogenic microorganisms in the wound. This is the main goal of burn treatment. Under no circumstances should you use these medications on your own. Antibiotic bandages are applied to the burn site.
Specific treatment when exposed to chemistry
If you know which chemical caused the burn, it can be neutralized. This means that the destructive effect of the acid will stop after it comes into contact with the alkali and vice versa. However, this must be done in the first seconds of the burn. Unfortunately, this is very dangerous, especially if you overdose on the antidote in a stressful situation.
Further treatment of chemical burns involves the use of water-based products, because the fatty ointment acts as a kind of film for the wound. Namely, in this type of damage, it is important to ensure proper peeling of the scab and not interfere with the recovery process by using oil-based products.
How to remove pain?
Painkillers will help relieve severe pain. For not too extensive burns and in the absence of painful shock, you can use drugs such as Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, Analgin, Diclofenac, Imet, Dexalgin, Nimesulide, and in some cases Ketanov (according to indications and a doctor’s prescription).
In hospital settings, for extensive injuries, narcotic analgesics (Promedol, Fentanyl, Morphine) are used.
Using them on your own is strictly prohibited.
How to heal the skin?
For further healing of burns, such products as Panthenol, Bepanten, Levomekol, Syntomycin ointment, Olazol, Dioxyzol, Radevit, sea buckthorn oil, calendula ointment, Solcoseryl (at the same time prevents the formation of scars), furacilin ointment, Actovegin are used.
Cautions: how to avoid unpleasant consequences?
The result of burn healing depends on the treatment tactics and behavior of the victims. The face is a sensitive place; any mistake can leave a mark for life, which can worsen the quality of life and cause complexes.
Mistakes to avoid:
- Smearing the burned area with oil is perhaps the most common and dangerous misconception. Oil, even sterile, forms a dense film that will reduce the access of oxygen to the wound and block the outflow of physiological fluid. In the worst case (if you do not use an unrefined product), infection may occur.
- When trying to cool the damaged area during a thermal or radiation burn, blot it with cotton swabs or apply ice and cooled objects. Intense pressure will lead to mechanical damage to tissues, disrupt blood circulation and complicate treatment.
- In case of thermal burns from hot objects, molten metals or plastic, you should never remove them. This action further injures the tissue and can cause bleeding.
- Treating a fresh burn with alcohol-containing substances.
- Cover the burn with a thick cloth, and even more so with an adhesive plaster. The wound must “breathe.”
- Open the resulting blisters yourself. At home, it is impossible to make the process sterile; this will only increase the risk of infection.
- In case of a chemical burn, on the first day, any external actions are prohibited, except for washing with water or special solutions.
Self-medication for deep or extensive burns is strictly prohibited. For chemical burns, this is unacceptable, even if the affected area is small.
Why does the face swell after sunbathing?
It's easy to get sunburned skin. It is enough to sunbathe during the hours of increased sun activity, fall asleep on a sun lounger or forget about the clock, immersed in an interesting book.
If the face is burned and swollen, this is the third stage of the burn. Ultraviolet rays received by the skin in large dosages disrupt microcirculation of capillaries.
Swelling of the forehead and bridge of the nose after sunbathing is more common; these areas are the first to suffer. Swollen face - reasons:
- allergic reaction;
- prolonged exposure to scorching rays;
- drinking alcohol;
- dermatological diseases (when exposed to the sun, the pathology worsens).
An allergic reaction occurs unexpectedly. Ultraviolet rays lead to the accumulation in the body of substances that cause photodermatosis. These include cosmetics, perfumes and local medicinal products that increase skin sensitivity to the sun. Manifested by swelling, burning, itching, redness. The skin becomes covered with a small rash.
Prolonged stay in open areas is harmful. Ultraviolet rays cause sunburn, overheating and heatstroke. Thermal damage to tissue leads to fluid accumulation. The flow of lymph and blood is disrupted, the capillaries become permeable. The result is that the liquid penetrates into the intercellular space. It accumulates in the subcutaneous tissue.
Drinking alcohol in hot weather slows down your metabolism. With simultaneous exposure to ultraviolet radiation, the inflow and outflow of fluid is disrupted, the result is a swollen face after sunbathing.
Recommendations for the recovery period
Complete healing and tissue regeneration for facial burns can take several months. To ensure recovery without consequences, you must follow the following recommendations:
- strictly adhere to the prescribed treatment;
- do not apply decorative cosmetics to damaged skin;
- if possible, reduce facial movements;
- solarium, sauna, beach and swimming pool are strictly prohibited;
- postpone cosmetic procedures in the salon and at home;
- monitor the healing process with a dermatologist.
What to do if your face is swollen after sunbathing
Go indoors to prevent sun exposure. If it is not possible to go to a nearby store or cafe, and the house is far away, move under the shade. The sunburn will stop developing. If your face is swollen due to sunburn, the swelling will slowly subside and the skin will calm down.
The swelling may be associated with an allergic reaction; you need to take an antihistamine (Cetrin, Diazolin, Loratadine). Further actions:
- wipe the affected areas with a handkerchief dipped in water;
- drink more fluids;
- use pharmaceutical products.
Attention! If such a reaction to the sun causes difficulty breathing, call an ambulance immediately. When the face becomes swollen as a result of allergies, the swelling can spread to the upper respiratory tract, including the larynx.
Possible consequences
Due to anatomy and physiology, burns on the face often provoke various complications:
- loss of sensation;
- damage to the facial nerve;
- impaired visual acuity;
- damage to the respiratory system and, as a result, pneumonia;
- dysfunction of the speech apparatus;
- skin suppuration;
- blood poisoning.
If they occur during therapy, you should contact your doctor.
Deep facial burns may leave scars. If the burned area is small, ointments (Contractubex) and cosmetic procedures (laser resurfacing) will help cope with the problem. If the damage is large-scale and deep, only plastic surgery or skin grafting will help correct the situation.
Neither an adult nor a child is insured against burns. If the face is damaged by any of the aggressive factors, the victim must be immediately assisted. Even minor redness at first can cause serious complications and subsequently leave a scar.
Treatment and care during the recovery period
Superficial injuries are treated at home with anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, regenerating ointments. To treat wounds on the face the following are used:
- antimicrobial agents (Levomycetin, Baneocin, Streptocide) – destroy fungi and bacteria, preventing purulent inflammation;
- regenerating ointments and gels (Solcoseryl, Actovegin, Radevit) - stimulate metabolism in the affected areas, heal wounds on the face;
- antiseptics (Nitazol, Dioxidin, Furacilin) - eliminate pathogenic flora on the surface of the wound, prevent infectious inflammation of the skin.
For bacterial complications, systemic antibiotics from the group of fluoroquinolones, penicillins, cephalosporins are prescribed - Ceclor, Amoxicillin, Cefotaxime, Ofloxacin, etc.
To treat 3B and 4th degree burns, the patient is sent to a burn center. Therapy is carried out in two ways:
- closed - antiseptic treatment of the face followed by covering the burns with sterile bandages;
- open - wiping wounds with drying and disinfecting agents in aseptic (sterile) rooms without using dressings.
If necessary, surgical treatment is prescribed. If a scab forms on the face, it is excised down to the viable layer of skin. To correct cosmetic defects in the form of scars, dermatoplasty is used.
How long does it take for facial swelling to go away after sunbathing?
You can reduce the pain and minimize symptoms, but the swelling will not completely disappear by the next morning. The skin needs time to recover.
Even with the use of pharmaceutical products and frequent use of masks to eliminate swelling of the face after a sunburn, it will not subside before 5–7 days after it occurs. A noticeable improvement occurs on the third day from the start of using pharmaceutical products.
If your face is swollen after sunbathing due to an allergic reaction, it will remain swollen for 2-3 days. Sometimes symptoms last longer, depending on the duration of sun exposure.
Prevention of facial swelling after sunbathing
The best way to prevent post-sun swelling is prevention. Sunscreen SPF 30 or higher will help with this. It is recommended to use La Roche-Posay Anthelios Sport Activewear Sunscreen Lotion Broad Spectrum SPF 60 or Supergoop Super Power Sunscreen Mousse Broad Spectrum SPF 50, as the creams have a high level of protection and are resistant to water and sweat.
Advice! To prevent your face from becoming swollen, apply the cream 15 minutes before going outside, and re-treat your face every 2 hours.
If a person is more prone to getting damaged—they have fair skin or are taking medications that make their skin sensitive to the sun—the risk of getting a sunburn is higher. The use of cream is mandatory.
Other preventive measures:
- Avoid exposure to the sun between 10 and 16 hours to avoid swelling of the face. The optimal hours for obtaining an even tan are 8–10, 16–18.
- Wear sunglasses and a hat.
- During the holidays, stop taking medications that increase skin sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation.
- Before tanning, treat your face with sunflower or olive oil. The skin will become bronze, the face will not be swollen by the end of the evening.
- Increase the amount of liquid you drink to 2 liters. per day.
- Sunbathe under an umbrella, especially for people with white skin.
Placing the head on a slight elevation helps prevent swelling. Until the swelling subsides, you cannot sleep without a pillow.
Additionally, you will need to make adjustments to your diet. It is recommended to drink more water and eat protein-based foods. Such nutrition accelerates metabolism and restoration of tissues damaged by sunlight.