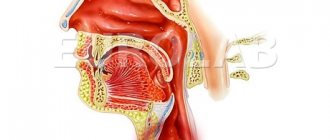
Burns to the oral mucosa occur quite often. Damage to the mucous membrane is caused by exposure to high temperatures (hot coffee, tea, etc.) or chemicals. Therefore, there are two types of burns (thermal and chemical), the treatment of which is carried out using different methods. Regardless of the type of burn to the oral mucosa, treatment should begin immediately after the injury is discovered.
Therapy
Traumatization of the oral epithelium can occur due to exposure to high temperatures and contact with a number of chemicals. Taking into account the causes of trauma to the epithelium in the mouth, thermal and chemical burns are distinguished.
Thermal
Thermal injury occurs as a result of exposure of the oral epithelial tissue to high or low temperatures. Trauma can occur due to contact with heated objects, boiling water, hot steam, frostbite, cryotherapy.
The choice of treatment method for thermal burns depends on the stage of the pathology and the reasons for its formation.
- At the initial stage, you need to relieve inflammation and pain by applying cold compresses for the first 2-3 hours.
- In the second stage, water bubbles form on the skin. In their place, erosion occurs and tissue necrosis is observed. Therapy for thermal damage to the skin in the mouth consists of cold compresses, painkillers, ointments, and emulsions to speed up wound healing.
- The third stage is characterized by the formation of ulcers and the death of areas of the mucosa. The manifestations of the disease can be eliminated in a hospital under the supervision of a specialist.
Chemical
Chemical damage occurs under the influence of an aggressive substance. Traumatization of the shell occurs after contact with acids, alkalis, silver nitrite, and incorrect dental prosthetics.
The pathology manifests itself in the form of severe pain, discoloration of the damaged area, characteristic odor, and death of tissue cells.
Treatment of the pathology consists of surgical removal of the affected area of the membrane.
When the oral cavity is burned by acid, you need to neutralize it with a soap solution, 0.1% ammonia, 1% lime water. 0.5% vinegar, citric acid, 0.1% hydrochloric acid solution will help localize the alkaline defect. Antiseptics, vitamin complexes, and painkillers are used.
First measures for burns of the oral cavity
The first actions for burns depend on their type:
In case of thermal damage it is necessary:
- rinse your mouth with cold water for several minutes;
- treat the oral cavity with an antiseptic solution: 3% liquid hydrogen peroxide, chlorhexidine, miramistin;
- periodically apply ice compresses;
- lubricate the affected area with lidocaine-based anesthetics or products like “Rescuer”;
- if the injury is caused by exposure to low temperatures, it is necessary to use anti-frostbite medications, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic agents.
Elimination of the consequences of chemical injuries is based on the type of reagent that caused the damage:
alkaline elements are neutralized by acids: acetic, malic, citric, oxalic.
- to eliminate acids, alkali is used: soap or soda solutions;
- if a burn in the oral cavity is caused by phenol, it can be eliminated with diluted ethyl alcohol or castor oil.
If you have a thermal burn, first rinse your mouth with clean water.
If chemical elements of another group are ingested, the oral cavity is also rinsed several times with cool water. Further actions are similar to those used for thermal injuries.
Important! In severe cases, hospitalization is required. Treatment should be carried out in a hospital setting. The patient is prescribed painkillers, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. For grades 3 and 4, surgical intervention is performed according to indications.
Ammonia
Ammonia is a colorless gas that is actively used in various production processes. Failure to comply with safety rules is a cause of injury to the oral epithelium by ammonia. It is able to penetrate into the deep layers of the skin and affect muscle and bone tissue.
Symptoms of the pathology are:
- Pain syndrome;
- Puffiness, swelling;
- Formation of watery blisters;
- Intoxication is observed;
- Heat.
It is important to provide first aid promptly after a burn injury occurs. The injured area should be thoroughly washed with running water and neutralizing solutions.
Pathology must be treated under the supervision of a specialist. A burn to the palate and oral mucosa can cause the development of ulcerative processes and laryngeal spasm.
Painkillers, non-narcotic analgesics and sedatives will help neutralize pain. Oxygen therapy is used in hospital settings.
Untimely treatment of a burn of the oral mucosa can cause the development of undesirable consequences: mental disorders, erosive and ulcerative processes, dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract or visual organs, tissue necrosis, anaphylactic shock.
For prevention when working with ammonia, personal protective equipment should be used: goggles, mask, overalls.
Chemical burn
Occurs as a result of exposure to high concentrations of drugs. Treatment of such burns should begin as soon as possible. An effective method of pre-medical treatment is prolonged rinsing with cold water (about an hour). But you should be careful, since not all chemical burns can be “treated” in this way. Some drugs react chemically when in contact with water. These include quicklime, as well as organic aluminum compounds.
After washing the oral mucosa, it is necessary to carry out special antidote therapy. Further treatment of such a burn consists of pain relief and enzyme therapy. At the final stage of treatment, surgical treatment of the oral cavity is performed using vitamin keratoplasty substances.
Factors of tissue damage
A chemical agent has a negative effect on oral tissues until it is tissue inactivated, neutralized, or diluted.
There are 5 factors that influence the degree of damage.
- Agent power. The main quality that is inherent in all chemicals.
- Number of agent. Directly depends on the volume and concentration of the chemical.
- Duration and method of contact. The longer the substance affects the mucous membrane, the stronger the damage will be.
- Degree of penetration. Depends on the possibility of neutralization in the mouth.
- Mechanism of action. Allows you to determine the necessary treatment measures.
Causes of chemical burns
Damage occurs when concentrated chemicals come into contact with the mucous membranes of the mouth. Often, this happens by accident (at home or at work), during a suicide attempt, and also during an appointment with a dentist. Although dentists no longer use many cauterizing agents, some medications can cause burns in the mouth.
Damage can occur as a result of contact with alkalis (ammonia, ammonia, bleach), acids, silver nitrite, formaldehyde, arsenic paste, or when wearing dentures whose plastics have not sufficiently polymerized.
Symptoms
In acute lesions, pain occurs immediately. The clinical picture directly depends on the nature of the chemical, its concentration and duration of exposure. Usually, the affected area is clearly visible in the mouth. The color of the affected area depends on the damaging agent.
When burned with sulfuric acid, a white scab forms, gradually acquiring dark shades of brown or black. When burned with hydrochloric acid, the scab becomes yellow. When burned with phenol, a white scab can be observed, with a gradual transition to a copper color. Sometimes the scab may have a distinct odor from the chemical that caused the burn.
The effect of alkalis is longer and more painful than with acid burns. This is due to the fact that acids convert tissue proteins into hard structures that form a dry scab. It becomes a kind of shield through which the acid no longer penetrates deep into the tissues of the oral cavity.
Alkalies form wet necrosis, the friability of which promotes deeper penetration of the chemical agent into the tissue. As a result, scars after alkali burns are deeper and more serious.
Severity
Burn injuries are divided according to severity, the level of damage depends on the complexity, depth of damage, intensity of pain, and the well-being of the victim:
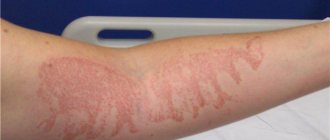
- First degree. Traumatization of the membrane is localized in the epithelial layer, the lower layers of the mucosa are not damaged. There is slight redness and slight swelling may occur. There is a burning sensation in the affected area and slight discomfort when eating food. Signs of burn injury disappear after 5 days. A pigment spot appears in the area of damage.
- Second degree. It is characterized by damage to most of the membrane in the mouth, the injury extends to the deeper layers. It is accompanied by redness and swelling. Blisters and plaque form in the oral cavity, and the affected areas bleed. The second degree is accompanied by high fever, chills, active salivation, and pain. Damaged areas heal within 2 weeks.
- Third degree. The upper layers of the membrane and the tissues underneath are affected. Characteristic symptoms are: high temperature, fever, intoxication. Watery blisters with thick walls appear, and a scab appears. An erosive-ulcerative process develops, which is accompanied by bleeding. Wet tissue necrosis develops, purulent foci appear, and during healing, scar formation is observed (replacement of mucous or other connective tissue). Intensive treatment will help eliminate the consequences of the injury. Full recovery occurs after 2.5 months.
Regardless of the type of injury, 2nd - 3rd degree burns can be accompanied by dysfunction of the esophagus, bronchi, and trachea. If the integrity of the epithelium is damaged, you must consult a doctor. He will tell you what to do based on the severity of the injury.
Acid, alkali, hot water
In case of grass burns, it is important to provide first aid in a timely manner, taking into account the symptoms and nature of the lesion.
First aid depends on the nature of the defect:
- The algorithm of action in case of chemical damage depends on the nature of the active substance:
- In case of a burn with alcohol, rinsing with plenty of water and saline will help.
- Low-concentrated citric, acetic, and malic acid will help localize the effect of alkali.
- If acid gets in, use soap, soda solution, milk, a mixture of ammonia and water.
- Treatment with vegetable oil can eliminate damage to the epithelium in the mouth with aluminum compounds.
- You can relieve inflammation and pain by taking anti-inflammatory or painkillers.
- To eliminate anaphylactic shock, an injection of antihistamines is used.
First aid for a thermal defect consists of several stages:
- Eliminate the source of high temperature;
- Rinse the area of thermal damage with cold water for 20 minutes;
- Take a pain reliever;
- Call the doctor.
In the process of eliminating damage to epithelial tissue in the child’s mouth, follow the dosage of medications and avoid the use of possible allergens.
Burn treatment
Treatment methods are chosen directly by the ENT doctor. At the same time, he is based on the results of the inspection and the severity of the injuries received.
Treatment of thermal burns
For the first degree of thermal burn, the use of medications is not required. The victim carries out simple recovery measures on his own at home. It is necessary to systematically rinse the nasal cavity with cool water, saline solution or its analogues (Marimer, Salin, Physiomer).
The second degree of thermal burn requires an integrated approach. In addition to rinsing, painkillers (Lidocaine) and restorative ointments (Propolis) are used.
The third degree is treated exclusively in an inpatient hospital setting. Rehabilitation therapy includes antibiotic drugs and various specialized ointments (Actovegin).
Treatment of a chemical burn
Most often, with a fairly serious degree of damage to the nasal membrane, all therapeutic and therapeutic measures are carried out in a hospital setting.
Specific medications and treatment methods are prescribed exclusively by the attending physician.
During the treatment course, painkillers and antiseptic drugs can be used. Regular hygiene procedures are carried out to remove crusts from the affected nasal cavity.
Folk remedies
Types of burns differ in the nature of their occurrence. Folk remedies can localize a burn in the mouth. They contain components that differ in septic, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and healing properties.
These include:
- You can eliminate the characteristic symptoms using a chamomile-based tincture. Boil 50g of dry leaves of the plant in 1l of water for about 10 minutes. The container with the medicine is infused for at least 2 hours. You need to rinse your mouth with the prepared infusion about 3 times a day.
- Aloe has anti-inflammatory and healing properties. 2 medium leaves of the plant need to be crushed to a mushy state. The plant mixture is combined with 100 g of honey. The resulting product is applied to the damaged areas of the tongue and palate for a quarter of an hour.
- Calendula is characterized by high efficiency. A teaspoon of the plant is added to 0.5 cups of water. The mixture is left for 2 hours. The oral cavity is treated with the prepared medicine.
- Plantain will help eliminate inflammation. 2 tablespoons of plant seeds must be crushed. The resulting powder is added to a glass of boiling water. The mixture must be shaken until a slimy consistency is obtained.
If characteristic symptoms of burn damage to the mucous membrane occur, you should consult a specialist. He will tell you how to treat injured areas depending on the nature, causes of its occurrence, and the characteristics of the patient’s individual reaction.
Ammonia burn to the oral mucosa (ammonia): what to do and how to treat?
Burns are a very unpleasant type of injury, most often resulting from unsuccessful interaction with heat sources.
However, in addition to such burns, there are others - when such an injury occurs under the influence of various chemicals. You have to interact with them in everyday life; in addition, they are often used for medical purposes.
For example, for some diseases of the oral cavity, it is necessary to treat the mucous membranes with ammonia.
If safety rules are not followed, tissues can be injured by this substance, resulting in an ammonia burn. Such an injury is very unpleasant and quite dangerous in its consequences.
Any chemical can seriously damage the mucous membranes and skin; in addition, such burns are often accompanied by poisoning. Therefore, it is necessary to know how to eliminate their consequences.
To do this, you need to find out what features they are characterized by and what can provoke their appearance.
Degrees and causes of injury
Ammonia burns to the oral mucosa occur for the same reasons as all other chemical burns - they are provoked by the effect of a chemical on the mucous membrane. In this case, this substance is ammonia.
This substance is used for disinfection purposes, but if used incorrectly it can cause adverse effects.
Since the mucous membranes are overly sensitive to external influences (they lack a layer of epidermal protective cells), aggressive substances contained in medications can cause severe irritation.
Depending on how strong the impact of ammonia was, the following degrees of damage differ:
- In the first degree of ammonia burn, the area affected by the substance becomes inflamed. A swelling forms on it, and slight swelling may occur. There is almost no pain; the patient may complain of minor discomfort, which ceases to be felt after a few days. Typically, such injuries do not lead to serious consequences, so they can be treated at home.
- With a second degree burn, more severe symptoms occur and you should definitely consult a doctor to eliminate them. Plaque may form on the mucous membrane, and the damaged area often bleeds. Severe pain is also observed. Sometimes the temperature may rise. All these signs can persist for two weeks.
- This degree of burn caused by ammonia is the most severe. In this case, you cannot do without the help of a specialist. The affected areas are covered with deep scabs, blisters and ulcers are found on the mucous membrane, which bleed heavily. If the oral mucosa is exposed, symptoms of poisoning may join the listed signs.
If you suspect a burn with ammonia, you should consult a doctor to minimize the negative consequences. Independent actions can provoke complications, so self-medication can only be done if you have the necessary knowledge about such injuries.
Features of therapy
The fight against such injuries is due to many circumstances. The most important thing to consider is the degree of their development. Individual characteristics, correct adherence to recommendations, etc. may also influence.
Traditionally, treatment of such injuries involves the following:
- When providing first aid to a victim, you must first neutralize the effects of the traumatic substance. The best way to do this is with acids - citric or acetic. Therefore, the patient should rinse the rod with one of these substances.
- After this, treatment of the oral cavity with analgesics (for example, Lidocaine or Pyromecaine ointment) is necessary. It is advisable that a doctor do this, since only he can choose the appropriate remedy and carry out the treatment correctly. In some cases, these actions are ineffective, and the patient is prescribed surgical intervention.
- During the recovery period, it is necessary to treat damaged surfaces with healing ointments (Metrogil, Solcoseryl).
- It is also necessary to take precautions so as not to injure the oral mucosa even more. These measures include following a diet (eating soft foods), as well as avoiding irritation of the respiratory tract with toxic substances and strong odors.
- During the recovery stage, it is permissible to use traditional medicines, for example, rinsing the mouth with decoctions of calendula or violet, but this can only be done with the permission of a specialist.
In case of severe damage, scars may form on the mucous membrane, to eliminate which it makes sense to perform an operation. But there are also less traumatic situations when there is no need to take such measures, and treatment is carried out at home.
The danger of burns resulting from improper use of ammonia is associated not only with damage to the mucous membranes.
Important! Such injuries are dangerous due to impaired respiratory function, since when this substance is inhaled, a reflex cessation of breathing occurs.
If ammonia enters the gastrointestinal tract, it can lead to a stomach burn, which is very risky. Therefore, no matter how severe the symptoms are, it makes sense to seek help from a doctor. This will ensure that there is no threat to health.
Burns of mucous membranes with ammonia, like any other chemical burns, are a serious injury that requires medical attention. Sensitive mucous membranes react very acutely to the aggressive effects of this substance; in addition, a reaction may occur from the respiratory tract and gastrointestinal tract.
Therefore, you need to be careful when using ammonia and take all precautions so as not to accidentally cause such an injury. And when the first signs appear, you need to consult a specialist, otherwise complications may arise.
If left untreated and severely damaged, the outcome may be negative.
Loading…
Source: //doloypsoriaz.ru/ozhogi/vidy-04/chto-delat-pri-ozhoge-nashatyrnym-spirtom.html