Radiation burns (radiation) are damage to the skin by light or ion irradiation, reminiscent in structure of burns received from the sun. Such injuries can be caused by radiation treatments, nuclear accidents, X-ray diagnostics and radioactive fallout. A radiation burn differs from a sunburn, first of all, in its delayed manifestation. This means that a person will not be able to immediately detect the consequences of a procedure or incident.
What are radiation burns
If thermal burns occur when tissue comes into direct contact with a source of high temperature, then direct contact with radiation sources is not required for the development of radiation burns . The physical factor of ultraviolet and radioactive radiation acts, as a rule, over a relatively long period of time, gradually causing burn injuries.
Note! Human skin is gradually exposed to ultraviolet radiation or ionizing rays, as a result of which cell destruction occurs. At the same time, the external resemblance to thermal burns of reactions and pathological processes occurring in the epithelium served as the basis for calling such injuries radiation burns.
What is the peculiarity of the pathology
Radiation injuries are caused by the following radiation:
- ultraviolet,
- alpha, beta and neural influence,
- X-rays.
The most dangerous are x-ray, neural and gamma particles that get on the skin. They can penetrate as deep as possible into the epidermis and cause serious destruction. Exposure to radioactive rays is dangerous for everyone, but people with fair, sensitive skin are more prone to negative effects. Burns appear faster on it.
Radiation damage causes a general deterioration in health. In severe cases, disruption of the functioning of internal organs is observed. The function of the nervous and cardiovascular systems decreases, radiation dermatitis develops, and radiation tumors form.
To reduce the risk of complications, if you are exposed to any dangerous radiation, you should immediately go to the hospital. The doctor will be able to determine the extent of the damage and prescribe the correct course of treatment.
Causes of radiation burns
Human skin is daily exposed to ultraviolet radiation and natural radiation, however, the strength of these factors is so insignificant that they cannot lead to any damage.
Burn damage develops in cases where the exposure and strength of radiation exceeds natural norms .
Ultraviolet, also known as solar burn, is familiar to absolutely everyone. The most common example is sunburn after trying to tan on the first day of rest. When the skin is completely unadapted to massive ultraviolet exposure, exposed to aggressive sun rays for 30 minutes or more, it eventually gets a sunburn.
Radioactive burns occur much less frequently in everyday life. A burn can occur with local exposure to ionizing radiation of sufficient duration and strength.
Similar reactions can occur during radiation therapy in oncology patients, poor X-ray technique, or direct contact with isotopes or radiation sources.
This is interesting! The first radiation burns after contact with radioactive isotopes were described by the Curies and V. Roentgen. Pierre Curie always carried a piece of uranium in his jacket pocket and a week later he noticed redness on his skin. V. X-ray took pictures of his friend’s hands, after which the latter also developed burn symptoms. In both cases, exposure to radiation led to the appearance of malignant tumors at the burn site.
Radiation burn and radiation sickness should not be confused . The latter develops due to the general effect of radiation on the body, which leads to serious consequences.
Stages of development of radiation burns
The distribution into stages is used in the case of burns by ionizing radiation. At the same time, local reactions will always be accompanied by the manifestation of radiation sickness to a greater or lesser extent due to the spread of toxins and radioactive isotopes throughout the body through the bloodstream.
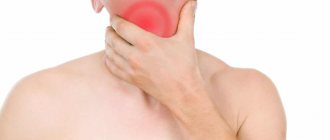
Photo 2. Dizziness and weakness are signs of a radiation burn. Source: Flickr (Niklas Nordlund).
Early reaction
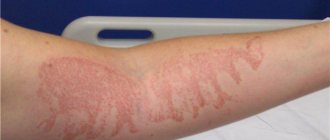
Lasts up to 5 days . Characterized by general symptoms of intoxication (weakness, fever, headache, dizziness, vomiting). Locally, redness of the skin will be detected, which can vary from a slight blush to severe hyperemia with peeling of the stratum corneum and the formation of ulcers.
Hidden stage
During the phase of apparent well-being, general symptoms are completely absent , local skin changes may partially or completely disappear. Blood parameters undergo pronounced changes. This period lasts from several days to a week .
Acute inflammation
The duration of the period is from one to three weeks. Depending on the severity of radiation sickness, either recovery or death can occur . It is characterized by a pronounced decrease in blood counts, anemia, diarrhea, hepatitis, weight loss, and the development of acute infectious and cardiovascular complications.
Recovery
Occurs with mild or moderate radiation sickness . Some residual effects may persist due to complications suffered. In the long term, the risk of developing tumors is extremely high.
How are thermal burns treated?
All treatment of thermal burns is aimed at restoring the functioning of burned tissues in the body. At the initial stage, it is important to carry out anti-shock therapy, which, based on the degree of the burn, the condition of the victim and other criteria, may consist of:
- eliminating pain syndrome;
- replenishment of blood deficiency;
- preventive procedures aimed at preventing or eliminating signs of hypoxia;
- adjustments of protein metabolism and acid-base balance in the victim’s blood;
- detoxification procedures;
- compensation measures for energy costs;
- treatment and prevention of cardiovascular and hepatic-renal diseases.
In hospitals and burn centers, the affected areas are first gently washed and treated with antiseptic.
This can also be done under anesthesia if the degree of burn is very high. Dirt from the burnt area is removed with hydrogen peroxide, particles of epidermis from superficially burnt skin are removed with tweezers, small blisters are not opened, and large ones are emptied using a special surgical technique so that they do not become infected.
If an open method of treatment is used in burn therapy, the surface of the burned skin is lubricated with special anti-burn ointments, and if it is a closed method, a sterile bandage impregnated with special preparations (often with Vishnevsky’s oil-balsamic emulsion) is applied to the site of the lesion. Such dressings do not aggravate pain, do not cause discomfort during replacement, and effectively protect the skin from infection. They are applied for 7-9 days until tissue epithelization.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: COVID-19
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
A large area of burns on the extremities requires their immobilization or immobilization. At the same time, in order not to disrupt the functionality of the joints, it is important to break immobilization every 2-3 days and then resume again. Blisters from burns are treated differently in different cases, sometimes they are opened, sometimes they are punctured, sometimes they are left in their original state until they resolve on their own. If a person has received a 4th degree burn, he needs immediate medical attention and often a skin graft.
Degree of injury
The degree of damage from radiation burns is different for sunburn and radioactive burns.
Degrees of sunburn
The severity of a sunburn is determined according to the generally accepted degrees of burn damage:
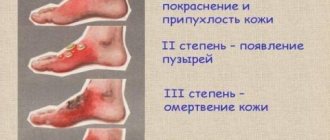
- I degree is characterized by the appearance of redness of the skin and its soreness;
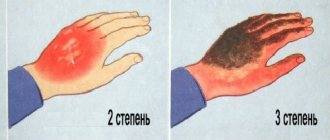
- In grade II , blisters filled with clear liquid appear on the skin;
- At stage III, the lesion affects the deep layers of the skin, the fluid in the blisters may turn red or brown;
- IV degree is characterized by deep tissue damage, charring of muscles and bones.
Note! Specifically, ultraviolet burns are characterized by the development of the first two degrees of severity. III degree develops extremely rarely and, as a rule, is observed in persons who have fallen asleep in direct sunlight while intoxicated. IV degree for solar skin damage is impossible due to the fact that UV rays do not penetrate deep into the tissue.
Degrees of radioactive burns
The degrees of burns from ionizing radiation are expressed somewhat differently; they are based on its local manifestations and are distributed as follows:
- An early (mild) reaction, which consists of the appearance of slight redness of the skin. Characteristic for irradiation at a dose of up to 3 Gy;
- Alopecia (hair loss). Observed 10–14 days after receiving a dose of 3–4 Gy;
- Acute dermatitis . A purplish-bluish color, itching, and pain appear locally on the skin. Continues for up to 8 weeks after receiving a radiation dose of 8 to 12 Gy;
- Bullous dermatitis . One or several large blisters (bullas) appear at the site of irradiation, after opening which painful, long-healing erosions remain. There are general reactions in the form of manifestations of radiation intoxication. Observed with irradiation of 12 – 20 Gy;
- Necrotizing dermatitis . The skin is swollen, covered with bullae, and painful. After opening the bullae, multiple non-healing ulcers remain. General intoxication is severe. Necrotizing dermatitis develops when receiving 25 Gy or more.
Symptoms and signs
The main symptoms of an ultraviolet or radiation burn depend on its severity. So, it is characterized by the following signs:
- Redness;
- The appearance of blisters;
- Increased body temperature;
- Local soreness, itching.
After 5–14 days, the local reaction will begin to subside. First, the formation of scales on the epithelium and their gradual exfoliation will be observed. In place of the blisters, minor scars may form, which are then replaced by normal skin of a lighter tone.
Note! In the absence of infection, radiation burns go away completely without a trace, unlike thermal burns, the third and fourth degrees of which, as a rule, lead to the formation of rough scars.
First aid for radiation burns
If you get a sunburn, rinse your skin as soon as possible , and, if possible, treat with special sprays like Rescuer or Panthenol. In case of severe pain or increased body temperature, it is necessary to take aspirin .
It is important! Do not lubricate burns, especially if there are blisters, with oil, kefir, etc. This may contribute to the development of infection.
Care for radiation burns of any degree should always be provided in specialized medical institutions . Such patients should receive powerful detoxification, antioxidant and immunostimulating therapy from the first hours after the injury.
At the prehospital stage, it is necessary to administer unithiol, ascorbic acid and activated carbon .
Operation
The patient is subjected to general anesthesia (the person is unconscious) and areas of scar tissue and foci of necrosis are removed. Surgical intervention is planned in advance. Before treating a patient, sensitivity to medications is clarified, tests are performed, and a general clinical picture is collected.
Treatment of radiation burns
The specificity of radiation burns is that they are superficial and, in the absence of complications, do not require surgical interventions.
Conservative therapy
Hospitalization for sunburn is carried out in the case of concomitant heat stroke or severe symptoms of general intoxication. For drug treatment, a glucose solution with ascorbic acid and Asparkam, Aspirin or Paracetamol is used. Local application of Solcoseryl, Levomekol, Panthenol is possible.
When radiation sickness develops, powerful detoxification therapy is used, preventing dehydration and combating the main symptoms (anemia, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, etc.). Antibacterial therapy begins from 2–3 days of treatment.
Surgical intervention
For sunburn, surgery is performed in exceptional cases . As a rule, this is required by the development of infectious complications. The inflamed areas of the skin are removed, followed by tensioning or transplantation.
During treatment for radiation sickness you may need:
- Massive blood transfusion;
- Hemodialysis and plasmapheresis to detoxify the body;
- Bone marrow transplantation.
Medicinal method
In addition to dressings with antiseptic solutions, antibiotics and sulfonamide are prescribed (provided there is normal blood circulation) if the affected area is infected. Swelling is relieved by taking antihistamines (local and general). Additionally, the patient undergoes a course of vitamin therapy. If therapeutic and medicinal treatment does not bring the expected result, surgical intervention is prescribed.
Rehabilitation period
After ultraviolet burns, complete healing occurs within 7–14 days, even in the absence of treatment. After 1 - 1.5 months, areas of hypopigmentation completely disappear.
Note! Recovery from burns associated with ionizing injury can take anywhere from one week to four months. At the same time, delayed consequences in the form of malignant skin tumors can develop over the next 10–15 years or more.
Possible complications
Complications can be caused not only by the radiation burn, but by the radiation therapy itself. After a burn of this type, a person may feel a deterioration in their general condition, and the most dangerous consequences are infection of the injured areas and possible bleeding. If severe damage has been sustained, the condition of the entire human body deteriorates significantly, and the greatest amount of damage goes to the organ that was closest to the site of irradiation.
You should not self-medicate. As soon as you notice similar symptoms, contact a specialist. If the therapist makes the correct diagnosis and prescribes effective treatment, the recovery period will be much shorter than with self-medication, and the risk of complications will be significantly reduced.
Prevention
To avoid ultraviolet burns you must:
- The first sessions of sun exposure should not exceed 10 minutes at a time and 30 minutes throughout the day;
- When tanning, it is necessary to use special creams that reduce the intensity of exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- If the skin already has any manifestations of damage, exposure to the sun should be stopped for 1 - 2 days.
In order to prevent radiation burns, it is necessary to use personal protective equipment and minimize the time spent working with a source of ionizing radiation.
When conducting radiation diagnostics or therapy, you must strictly adhere to the rules of work and behavior.