Moles can be divided into two types according to their shape: flat and convex. Flat formations do not cause discomfort and look quite aesthetically pleasing. Convex moles on the body, that is, moles that protrude above the skin, can bring daily inconvenience to a person and affect the psychological state due to their unpleasant appearance. From a medical point of view, a convex mole is the most dangerous for health, since any minor injury can provoke metastasis.
Convex moles are more dangerous than flat ones
What are nevi
Dermatologists call skin growths nevi. Their structure comes in two types:
- melanocytic;
- vascular.
The accumulation of melanocytes in a certain place provokes the appearance of a thickening on the skin. The formation has a dark color due to melanin, which is synthesized in cells under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. The more a person is exposed to sunlight, the more pigment is produced, causing the formation of new moles. In some cases, ultraviolet radiation causes changes in skin cells and the mole becomes raised.
Vascular moles are angiomas formed due to the proliferation of blood vessels. They are not prone to degeneration and only cause a cosmetic defect.
It is believed that the appearance of moles is inherent in a person at the genetic level. After birth, the baby's skin is absolutely clean except for birthmarks. But after 6 months, dark spots begin to appear on it, often in the same places as those of the parents.
Precautions and possible complications
If there are moles on the body, the recommendations of experts are as follows:
- The patient must monitor his skin, keep a record of old and new nevi, write down their sizes, and, if possible, record their shape and size by photographing.
- See a doctor once every six months or annually (depending on the number of pigmented dots).
- Remove moles that are subject to injury, friction, sun exposure, located in places inaccessible for self-examination, and that spoil the appearance.
- Dispose of only in medical institutions.
- Use sunscreen when exposed to the sun.
The most dangerous complication that can arise from moles is melanoma. The disease can begin not only from a nevus, but also on intact skin, so if any birthmarks appear on the skin, you should make an appointment with a specialist.
Reasons for appearance
Moles appear throughout life. Often the cause is hormonal imbalances in the human body. A sharp increase in pigmentation is observed during puberty and in women during pregnancy. When the hormonal changes end, the formations disappear on their own, leaving no consequences.
Doctors believe that the appearance of moles is caused by dysfunction of the endocrine and digestive systems. People suffering from:
- diabetes mellitus;
- diseases of the thyroid gland, stomach, liver;
- pathology of the adrenal glands.
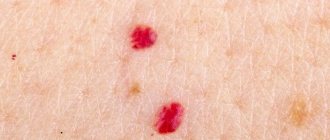
These formations have nothing to do with pigmentation. They are created from capillaries, so they have a red tint. Similar nevi occur in older people against the background of pathological vascular changes, lack of elastin and collagen.
Convex moles in children are observed in isolated cases from birth. More often, growths begin to form from the age of 5, have a round shape and are colored light brown. If they are not prone to rapid growth, changing color and outline, then it is better not to touch them. It is enough to avoid sunlight and regularly examine the tumor with a dermatologist. The exception is an excessive accumulation of moles on the body. The method of getting rid of growths in a child is determined by the doctor, based on the individual characteristics of the patient. For children, laser removal is usually used.
Injuries and infections
Sometimes a convex formation on the skin appears as a result of injury to the epidermis. This could be mechanical damage or an insect bite. This exposure leads to infection and inflammation, causing abnormal cell proliferation.
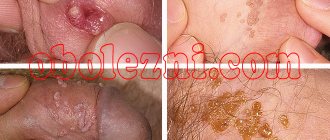
Often, growths on the skin are a consequence of the penetration of the virus. They qualify as papillomas and do not belong to nevi.
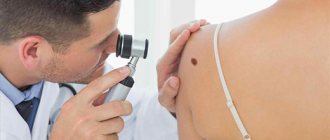
Many moles are fraught with danger and require regular examination by a dermatologist. This is the only way to notice in time the degeneration of cells into a malignant tumor.
Types of dangerous voluminous moles
Convex-shaped pigment formations come in several types. Not all of them are prone to degeneration. The most dangerous moles with a high oncogenic risk are:
- Blue nevus. The dimensions of the blue growth, which has the shape of a hemisphere, reach no more than 10 mm. It is diagnosed on the skin in the first months after birth, but sometimes appears later under the influence of hormonal disorders. Doctors note that cell degeneration often occurs with incomplete cosmetic removal of the growth and as a result of mechanical trauma.
- Borderline nevus. It is located in the basal layer of the epidermis and is noticeable already in childhood. Its characteristic feature is the ability to grow as a person grows older and reach a diameter of about 8–15 mm, and sometimes more. A slightly convex growth of bright brown color, which becomes more saturated closer to the center. A borderline mole can form anywhere. It is easy to notice on the back and chest, on the arms and soles of the legs.
- Giant mole. This is a congenital, grayish or brown formation protruding above the skin. It gradually increases in size and can expand up to 20 cm. It is believed that the reason for the development of the growth in children is infections and hormonal disorders in the body of a pregnant woman, but this is not known for certain. An unaesthetic large growth requires constant monitoring by a dermatologist, careful treatment and timely removal from the skin.
Most often, convex dangerous moles are localized on the back, face or neck. They cause significant discomfort, rub against clothing and become damaged. To avoid injury and the development of an infectious process, it is advisable to eliminate them as early as possible.
How to determine whether a mole is malignant or not
You can determine whether a mole is malignant or not using a simple “home” AKORD test:
- A – asymmetry of the formation, which is revealed by mentally drawing the axis along the center;
- K – the edges of the nevus are uneven and can be in the form of small/large denticles;
- O – the color of the surface of the formation changes and acquires a darker shade;
- P – the size of the mole increases quickly;
- D – general dynamics of nevus development (cracks and crusts appear on the surface).
If at least one of the signs is present, then you need to contact an oncodermatologist with the problem - the diagnosis of cancer will take place at the initial stage of development, which guarantees the success of treatment.
Harmless raised moles
One of the most common skin growths considered melanoma-free are fibroepithelial moles. These are small nodes consisting of skin cells and supported by a wide stalk. The delicate hemisphere of white, flesh or pink color slowly increases and rarely reaches 1–2 cm. Hair sometimes grows on the surface of the mole, and a vascular network appears. The growth is removed for aesthetic reasons and to prevent damage.
Another relatively safe formation is intradermal nevus. According to statistics, only 10% of such moles transform into melanoma under the influence of infection and injury. Outwardly, they resemble a uniform, round, dark-colored wart and grow from 2–3 mm to several centimeters.
There are two types of intradermal moles:
- pigmented;
- papillomatous.
In isolated cases, cell degeneration occurs, so the condition of the nevus should be monitored.
Papillomatous growths are similar in appearance to papilloma and are localized mainly on the head in the area of hair growth and neck. Hair often grows from a soft, nodular structure that is light, cream, or brown in color. During combing and washing your hair, raised moles become damaged and begin to bleed and become inflamed. The risk of the formation of malignant cells is almost zero, so papillomatous moles are considered safe.
Angiomas are another type of safe formation on the skin.
- Angiomas consist of deformed vessels.
- They grow on the back, face and bring aesthetic discomfort to their owners, as they noticeably rise above the surface of the skin and have a bright shade.
- They are not prone to pathological changes, so they are removed only for cosmetic purposes.
Setton's pigmented nevus has a weak tendency to degenerate. It is a small, dark, slightly raised formation surrounded by a halo of discolored skin. It often appears in children and adolescents with autoimmune diseases, but can develop in anyone in response to severe sunburn.
Despite the fact that the above moles rarely change pathologically, their condition should be closely monitored and go to the hospital if there are alarming symptoms.
Why is a convex nevus dangerous and its types?
Convex nevi can be classified according to the method of their formation into the following types:
- pigment,
- vascular.
The first type of spots is formed as a result of the accumulation of melanocytes, the color of which depends on the type of melanin they contain. Black nevi will be saturated with eumelanin, moles with a predominance of pheomelanin have a brown color.
Pigmented nevi are divided into three types:
- Fibroepithelial nevus - has a flesh color, its size changes slowly, is often covered with hairs, and has a high risk of degeneration into melanoma. Occurs on the back, chest or limbs.
- Intradermal nevus - has a brown color, round shape, no hair, and forms on the mucous membranes.
- Pappilomatous nevus - characterized by an uneven, rough surface and localization exclusively on the part of the head covered with hair.
- Vascular nevi are benign tumors made up of blood vessels called angiomas. Their color varies from pale pink to dark red. Red moles are of the vascular type. A convex agioma is not dangerous to health.
If a large number of red moles have formed on the skin, this may indicate that a person has the following health problems:
- liver diseases,
- vitamin K deficiency,
- weakening of the immune system,
- oncological diseases,
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or pancreas,
- changes in hormone levels,
- cardiovascular diseases.
A convex mole has the largest size of all types of similar formations, so the area of exposure to harmful sunlight is much larger. It is quite easy to injure such a nevus.
According to statistics, as a result of injuries to nevi, 40% of melanomas are formed. At particular risk are those who are constantly damaged by clothing, combing their hair or while shaving.
There is no need to worry if the convex nevus has a clearly defined color, round shape, or small size, since it is not dangerous to health.
Fibroepithelial nevus is light, flesh-colored
When to worry
Many people have raised moles on their bodies and live quietly with them all their lives, without feeling the slightest inconvenience. But sometimes a nevus is a harbinger of cancer, so any discomfort caused by its presence is a cause for concern.
A voluminous skin formation can be localized on any part of the body and have a variety of colors. The main features of its benign structure are:
- Symmetry. If the mole is visually divided into two parts and compared, you should get identical pieces.
- Size. A healthy mole is rarely larger than 6 mm.
- Smooth edges and dense surface.
- Uniform shade.
Even minor changes in the structure of a raised mole should not be ignored. Signs of melanoma-dangerous degeneration are:
- sharp increase in compaction;
- blurry edges, asymmetrical shape;
- inclusions of brighter colors in the color of the mole;
- cracks and peeling on the surface of the formation;
- itching, feeling of fullness, inflamed skin around the nevus.
If the appearance of a mole causes concern, there is no need to stress yourself out and panic . It is better to immediately go to an oncodermatologist. At an early stage of the disease, it is possible to remove the formation and maintain health. It is also recommended to eliminate benign convex nevi with a tendency to degenerate in order to prevent pathological changes.
Which mole needs to be removed
Having an idea of the number of your own nevi and their appearance, it is easy to monitor their condition. Signs of the onset of pathological processes in a pigmented area of the body are as follows:
- lack of symmetry around at least one axis;
- jagged, uneven boundaries of pigmentation;
- bleeding or other discharge from the formation;
- uneven coloring of the mole, dark inclusions, the appearance of a rim or edging;
- dimensions exceeding 6 mm in diameter;
- progressive growth, the nevus may hurt and itch.
Even if one of these signs is present, it is necessary to visit a dermatologist, who, if necessary, will refer the patient to an oncologist. The doctor will recommend how to remove the formation and do its histological analysis.
Even if the mole does not show signs of the presence of cancer cells, but is located in an open area of the body, where it is constantly exposed to ultraviolet radiation, in places where clothing rubs (on the neck, arms, lower back, armpits, under the breasts, on the nipples, in the genital area), it is constantly exposed mechanical damage from razors, combs, watches, such formations must be removed.
The following formations are considered signs of benign pigmentation:
- pedunculated, width less than 2-3 mm;
- long-term existence without any changes;
- surface hair growth;
- the skin pattern is preserved on the pigmentation;
- pale color;
- the structure is softer than the skin.
- smooth edges, axis symmetry.
These signs do not guarantee the absence of pathology, but the occurrence of cancer cells in such nevi is unlikely.
Tumors should be removed in medical, not cosmetology clinics or at home, since in a specialized institution it is possible to examine the material and, if necessary, prescribe treatment, which means not to waste time in the fight against oncology.
The following hardware techniques quickly and reliably remove skin defects:
- laser;
- a liquid nitrogen;
- radio waves.
Moles can be removed surgically under local anesthesia. This mainly occurs when a malignancy is suspected. Laser removal and cryodestruction do not allow testing the material for the presence of cancer cells. These methods are used to eliminate only good moles that have been examined by a doctor, that is, the method of removing the defect is always determined by a specialist.
Pharmacies offer many drugs for skin treatment, most of them require long-term exposure, which can trigger the development of tumors. This is why you should not self-medicate.
Diagnostics
First of all, the doctor conducts a visual examination and interviews the patient, finding out whether there are additional factors that contribute to the degeneration of the mole. These include:
- frequent exposure to the sun;
- work at chemical plants;
- chronic diseases of the endocrine system;
- weakened immune system;
- hormonal disorders;
- the presence of melanoma in close relatives.
Using special equipment, the surface of the tumor is examined (under high magnification), and the smallest details become visible. Then the temperature of the mole and healthy skin is measured, and urine and blood samples are taken. At the end a biopsy is performed. To study, nevus cells are scraped off. Based on the test results, a diagnosis is established and treatment is prescribed.
There is no point in getting rid of a raised mole with drug therapy. To cleanse the skin, it is necessary to remove the growth faster.
Principles of treatment
Modern medicine offers many advanced effective therapies.
Removal methods
If the examination reveals pathological changes in the tumor, surgical intervention is required. Along with the nevus, the surrounding tissue is removed, so a scar is formed on the skin. The operation is performed under local or general anesthesia.
- Small benign growths can be easily eliminated by treating them with liquid nitrogen (cryodestruction). During the procedure, skin cells freeze and die. The method eliminates the appearance of scars, but individual nevus cells may remain, and then the formation can form again.
- Laser removal is the most common way to get rid of moles on the back, face and other parts of the body. It destroys raised nevi and birthmarks by evaporating fluid from tissues. The technology eliminates bleeding, infection and reduces the likelihood of scar formation.
- Electrocoagulation works well with benign processes. The method involves exposing tissue to inactive and active electrodes, which cause coagulation, that is, the coagulation of proteins. As a result, the mole dies and a wound forms in its place. It quickly crusts over and heals.
- The radio wave method is highly effective and is suitable for eliminating growths of any size. The procedure lasts about 20 minutes, does not affect healthy skin and ensures complete sterility during the operation.
Based on the tests, the shape and location of the mole, the doctor determines the optimal method of removal.
Description of the mole and its main properties
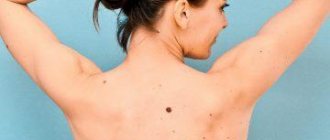
In general, the location of the mole is random. The neoplasm can appear almost anywhere (even cases of moles appearing on the surface of the eyeballs have been recorded). And yet, the hands, face and torso of a person are most susceptible to the appearance of nevi.
Sometimes, a certain external influence can provoke the formation of a mole
- Bites of some types of insects . Insects can introduce a virus under the skin, which stimulates the growth of pigment cells.
- Exposure to radiation.
- Ultra-violet rays . Exposure to solar radiation promotes the active production of melanin, a coloring pigment. When it is concentrated in excess, it can appear on human skin in the form of various moles.
- Injuries to existing tumors. Damage to a nevus can easily activate its growth. It can grow on its own, or give rise to smaller, daughter neoplasms nearby.
Photo 1. The location of moles is completely random. They can even appear on the eyeball. Source: Flickr (Lindsey Turner)
Prevention
To minimize the risk of pathological changes in skin cells, competent prevention is necessary.
- Excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation should be avoided.
- In summer, use sunscreen and moisturizing skin creams.
- Avoid injury to neoplasms.
- Contact the clinic if you experience any discomfort in the area of the growth.
- Have a routine examination with a dermatologist twice a year.
You need to be attentive to your health, give up bad habits and strengthen your immune system. It is important to monitor any features of your skin so as not to miss the moment of the onset of the pathological process and take care of its elimination in time.