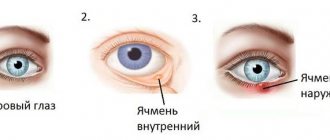
What diseases cause eye pain?
Many people have eye pain due to ophthalmological and systemic diseases. The reason may be in the organs of vision or in other disorders. The choice of specialist and treatment depends on the cause of the pain; in order to identify it, laboratory and instrumental examination methods are prescribed.
There are a number of ophthalmological diseases and conditions that can affect soft tissues, blood vessels, and nerves located in the organs of vision.
They cause acute and chronic pain:
- Increased eye strain. It occurs in people who spend a long time in front of a computer, phone, TV, or tablet. Pain occurs when reading books frequently in poor conditions, for example, in low light.
- Entry of a foreign body. It can penetrate the cornea due to strong winds, sparks from a welding machine, or for other reasons. Acute pain, redness, photophobia, increased sensitivity, and spasm of the eyelids occur.
- Conjunctivitis. It can be of an allergic, bacterial, viral nature. This is a disease in which the conjunctiva of the eye becomes inflamed. Redness, swelling, pain, and photophobia appear. With bacterial conjunctivitis, purulent exudate is released.
- Blepharitis is inflammation of the eyelids. It can develop due to the proliferation of fungi, viruses, bacteria, parasites (eyelash mites). The eyelids swell and an abscess filled with fluid may form under the skin.
- Keratitis is inflammation of the cornea. The inflammatory process begins as a result of mechanical damage, burns, and the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. If the disease lasts a long time, the cornea becomes cloudy and visual acuity decreases.
- Glaucoma is an increase in intraocular pressure due to impaired outflow of secreted fluid. There are anterior and posterior chambers in the eyeball, and fluid constantly circulates inside them. If it accumulates but does not come out, the pressure increases. This can lead to damage to the optic nerve, retinal detachment, and blindness.
- Retinal diseases. They develop due to burns, mechanical damage, and malnutrition through blood vessels. If the retina detaches, the person goes blind.
- Diseases of the optic nerve. Light streams pass through the eyes, hitting the rods and cones of the retina. From them, information in the form of nerve impulses passes through the nerve, entering the brain. The nerve is damaged due to malnutrition through blood vessels, mechanical damage, and infectious and inflammatory processes.
- Strabismus, amblyopia. If both eyes see the picture in front of them incorrectly, this leads to increased strain. As a result, not only your eyes hurt, but also your head.
There are diseases that develop not in the eyes, but in peripheral organs; with their prolonged development, complications arise from the organs of vision, this also leads to pain:
- Diabetes. A large amount of glucose accumulates in the patient’s blood, which is not distributed to the tissues, but binds to cholesterol and forms plaques. They are transported through large and small vessels, including the microcirculation of the eyes. This leads to blockage, severe pain, decreased or complete absence of vision.
- Atherosclerosis. Cholesterol accumulates in the patient’s blood, which spreads through the vessels, clogging their lumen. The mechanism of the disease is the same as for diabetes mellitus.
- Arterial hypertension. Increased pressure puts stress on the endothelium. This leads to rupture of the vessel wall and hemorrhage inside the eyeball. With chronic hypertension, the function of the visual organs decreases, and constant headaches and eye pain occur.
- Ischemic disease. A person experiences spasm of peripheral vessels. If this happens in the eyes, nutrition is disrupted. Gradually, the organs of vision will fail to function. Severe spasm causes severe pain.
- Vasculitis, increased fragility of blood vessels. If the endothelium is fragile, this leads to hemorrhage in any part of the body. Painful sensations appear during spasms, which causes a decrease in vision function.
- Neuropathy. The inflammatory disease can spread to the optic nerve, this is dangerous because it connects to the brain. This causes a decrease in its functionality and constant pain.
For each disease, a separate treatment is determined. Therefore, diagnostics are initially carried out, identifying the nature of pain, decreased vision function and other symptoms.
Pathologies of the eye in which redness occurs
Non-inflammatory eye pathologies
- Keratopathies (diseases of the cornea associated with impaired nutrition, blood supply and innervation of tissues). Keratopathy can be bullous, neurotrophic, filamentous, or superficial punctate. Redness of the eye accompanies any type of keratopathy;
- Keratoconus (dropsy of the cornea);
- Peripheral thinning and ulceration of the cornea;
- Corneal ulcer;
- Pterygium is a fold of the mucous membrane that has a triangular shape and is located at the inner edge of the eye. This fold gradually grows and spreads to the entire cornea of the eye;
- Pseudopterygium (scar pterygium) is a connective tissue fold that forms after healing of ulcers and burns of the cornea or conjunctiva of the eye;
- Hemorrhage in the tissue of the eye;
- Pinguecula of the eye (a benign neoplasm in the tissues of the eye, not prone to degeneration into cancer);
- Conjunctival pemphigus (formation of blisters on the non-inflamed mucous membrane of the eye);
- Tumors of the lacrimal gland;
- “Floppy” eyelid syndrome (the eyelid turns outward, rubs against the pillow and other surrounding objects, exposing the eye, which is injured and red);
- Trichiasis (improper eyelash growth, when hairs curl into the eye, irritate it and cause redness);
- Detachment of the choroid;
- Glaucoma (acute or incipient).
Inflammatory diseases of the eye
- Vaccination is an inflammatory reaction of the cornea to the recent administration of smallpox vaccine;
- Chickenpox of the eye (inflammation of the cornea against the background of active chickenpox, associated with the penetration of the virus into the chambers of the eye);
- Herpes zoster of the eyes;
- Eye herpes (herpetic keratitis, conjunctivitis, eyelid herpes) – inflammation caused by a virus from the herpes family that has entered the eye tissue;
- Keratitis (inflammation of the cornea of the eye) caused by various pathogenic microorganisms, for example, viruses, fungi, bacteria or protozoa;
- Dacryoadenitis (inflammation of the lacrimal gland);
- Dacryocystitis (inflammation of the lacrimal sac);
- Canaliculitis (inflammation of the tear ducts);
- Superior limbic keratoconjunctivitis (inflammation of the cornea and mucous membrane of the eye);
- All types of conjunctivitis (allergic, viral, bacterial, fungal, chlamydial, chronic, angular, etc.);
- Morax-Axenfeld blepharoconjunctivitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane and inner moist part of the eyelids);
- All types of keratitis (inflammation of the cornea of the eye);
- Inflammation of the eyelids;
- Stye on the eye;
- Uveitis (inflammation of the choroid of the eye of any etiology);
- Chorioretinal inflammation (inflammation of parts of the uvea);
- Iridocyclitis (inflammation of the iris and ciliary body);
- Traumatic injury to the eye (secondary glaucoma, hyphema, recession of the anterior chamber angle, displacement or damage to the lens of the eye);
- Panophthalmitis (inflammation of all structures and tissues of the eye);
- Episcleritis (inflammation of the connective tissue separating the mucous membrane of the eye from the sclera);
- Orbital abscess (an abscess in the area of bones and soft tissues that form the orbit of the eye);
- Optic neuritis;
- Idiopathic hypertension of the episcleral veins (extremely rare, etiology has not been established).
diagnosis of conjunctivitis
blindness
- Nausea or vomiting;
- Headache;
- Decreased visual acuity;
- Pain in the eyes;
- Discharge from the eye of any nature;
- Photophobia.
What can a doctor determine?
As soon as you describe your complaints at the doctor’s appointment, the doctor will begin to examine the eye.
If his left eye hurts, he will probably pay attention to the right one, because the eyes are nearby, and we sleep on the same pillow. This means that if an infection is detected in one eye and personal hygiene rules are not followed, it can spread to the other
As for bacteria, the healthcare worker always takes into account the likelihood of bacteria entering both from the external environment and from inside the body.
So, experts identify a number of diseases that cause the eye to hurt when blinking:
- Conjunctivitis. Young children with not yet formed immunity are especially susceptible to this disease. A child falls ill with ARVI - which ultimately manifests itself not only in the form of a cough and runny nose, but also entails unpleasant sensations in the eye area. Often, conjunctivitis occurs when the patient uses someone else's towels or wipes the eye with dirty hands. Conjunctivitis manifests itself as painful redness, swelling, tearing, irritation of the eye, from which discharge in the form of pus and large volumes of nitrous oxide is visible after sleep.
- Disease of the blood vessels. In this case, more often than not one eye hurts, but two at once. Also worrying is the sudden darkening of the image and glare, which is caused by insufficient blood supply.
- Myositis. The eye hurts when the pupil moves and when blinking.
- Glaucoma. It is characterized not only by unpleasant sensations in the eyes, but is also accompanied by nausea, migraines, and circles in the form of a colored rainbow.
- Dry eye syndrome. Office workers who are forced to sit for a long time near a computer with an air conditioner running nearby complain about this illness. As a result, the retina turns red, tears flow from the eyes, and they hurt a lot.
- Barley. It can affect both the lower and upper eyelids and the outer corner of the eye. The eyelid swells noticeably, redness is observed, every blink causes pain, the patient's mood drops, he is tormented by headaches and weakness. Several styes may occur in one eye at once, causing the eye to become so swollen that it closes completely.
- Obstruction of the lacrimal canals (partial or complete). Painful sensations appear in the corners of the eyes; treatment is represented only by surgical intervention.
- Herpes. Indeed, herpes is possible not only in the lip area, but can also spread to the eyes. The eye swells, in a bright room there is a desire to cover the eye, redness and pain when blinking first affects the inner corner, and then spreads to the entire eye.
How to get rid of dry skin around the eyes with moisturizer
The best treatment is to eliminate the cause of dry skin.
Some causes, such as eczema, have no cure. However, it makes sense to do everything you can to reduce the symptoms of dry skin around the eyes and skin of the eyelids. If the cause of your skin condition is a more serious condition such as blepharitis, you should consult your doctor. One way to treat itchy dry skin around the eyes is to use a moisturizer after washing your face with a mild cleanser. A moisturizer will provide quick relief from dry skin symptoms.
It is important to remember that you need to moisturize your skin immediately after washing to “lock in” the moisture.
Before using any moisturizer, you should perform a small test to make sure there is no allergic reaction.
Aloe Vera is better than drugstore cream for dry skin around the eyes
Aloe vera acts as a gentle moisturizer that can help repair the damage done to dry skin around the eyes. Its antimicrobial properties may help speed up wound healing. Additionally, aloe vera can help treat medical causes of dry skin around the eyes and eyelids, such as psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis.
You can apply aloe vera directly to the dry and flaky skin around your eyes, being careful not to get the product into your eyes. Use “pure” aloe vera gel for the most effective treatment. Simply apply a small amount of aloe vera to the skin around your eyes as well as your eyelid and let it absorb into your skin. You don't need to rinse it. Do this daily to soften your skin and speed up the healing process for dry skin.
Extra Virgin Coconut Oil for Dry Eyes
Extra Virgin Coconut Oil is another effective natural moisturizer for dry skin around the eyes. It can also soften the skin and reduce flaking. Coconut oil is able to penetrate the skin and provides deep hydration to the skin while maintaining a protective layer on the epidermis.
How to Get Rid of Dry Eye Skin with Coconut Oil
Apply coconut oil to the affected areas of skin near your eyes several times a day, and before going to bed. You can also use coconut oil to moisturize dry skin on your eyelids. This will help reduce itching and flaking of the eyelids. You can also slowly massage the oil into your skin. In small quantities, coconut oil is almost completely absorbed into the skin, leaving no greasy residue.
Another way to use coconut oil for dry skin is to mix coconut oil with aloe vera to create a natural lotion for healing ear infections and flaky skin. This mixture may also help treat causes of dry skin such as eczema.
Cocoa butter for dry skin around the eyes
Cocoa butter is another natural soothing and moisturizing agent that can relieve dry skin, preventing complications such as skin chapping. A study published in the International Journal of Cosmetic Science found that cocoa butter improved the appearance and tone of the skin.
To use cocoa butter on the delicate skin around the eyes, mix it with other beneficial products like castor oil or jojoba oil. Apply the mixture daily to hydrate the skin and treat dry and flaky skin.
You can also make this home remedy for dry eyes: 1 teaspoon coconut oil (melt first), 2 teaspoons cocoa butter, 1 teaspoon sweet almond oil. The oil mixture should then thicken. Apply to dry skin around the eyes to quickly get rid of flaky skin.
Natural oils to moisturize your skin
You can also use a solution of natural oils such as jojoba oil, sweet almond oil and avocado oil to treat dry skin. They provide a protective layer on the skin that retains moisture and prevents dry skin.
You only need a few drops of any of the above oils to keep the skin around your eyes soft and supple.
You can also mix natural oils with a drop of essential oil, such as lavender or chamomile. The soothing aroma of the essential oil will help reduce stress and can manage other skin conditions like eczema.
When using essential oils, care must be taken to ensure that the oil does not get into the eyes and cause irritation.
Reducing stress reduces dry skin around the eyes
Stress can cause flare-ups of eczema, which can cause dry and flaky skin around the eyes. Essential oils, relaxation and just a good night's sleep reduce stress and the risk of developing dry skin.
Prevention
There is no prevention of pain syndrome. It occurs with the development of external factors or certain ophthalmological diseases. Therefore, preventive measures are aimed at reducing the risk of developing such pathologies. The basic rules consist of the following recommendations:
- Timely visit to the ophthalmologist. Inspection must be done 1-2 times a year. This will help to detect the presence of pathological processes in a timely manner. In severe form, they can be irreversible.
- Healthy lifestyle. For healthy eyes and the whole body, you should adhere to a proper, balanced diet. Every day you need to eat a large amount of fruits, vegetables, and herbs. Carrots and blueberries are especially beneficial for the eyes. Getting enough sleep will help relieve tired eyes and give them a chance to rest.
- Quitting smoking, excessive consumption of alcohol and drugs.
- Use safety glasses when working with small objects, chemicals, and household chemicals.
- Wear sunglasses at appropriate times.
- Follow good hygiene rules when caring for your eyes and when using ophthalmic medications.
- During the period of drug therapy, strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations and do not exceed the prescribed dosage.
The main prevention consists of timely consultation with a doctor. In this way, you can avoid the development of severe complications. If necessary, consultation with several specialists may be necessary.
Why does the inner corner of the eye hurt?
Before starting therapy, it is necessary to find out why the inner corner of the eye hurts. This problem is not always of an ophthalmological nature. Some diagnoses can be very surprising to the patient. The merit of a quick and correct diagnosis largely lies in the professionalism of the diagnostician.
Migraine
For most people, migraine is a very severe headache that is extremely difficult to treat with medications or any other means. It is caused by a violation of the tone of intracranial vessels, which means that the problem is located much deeper than a standard headache. In addition to headaches, a person complains of photophobia, nausea and vomiting, spasms and increased sensitivity in the eye area. By the way, during a migraine attack, the outer corner of the eye usually hurts, closer to the temples.
This attack can last for several days. The condition is sometimes so severe that a person is unable to carry out ordinary household activities, and even eating food brings enormous difficulties. Any provoking factors can intensify the unpleasant sensations - strong light, noise, strong smell. This causes irritability and nervousness, as well as increased symptoms.
Glaucoma
Increased intraocular pressure (glaucoma) is caused by an increase in fluid levels in the organ of vision. This can happen for a variety of reasons. Untimely treatment leads to rapid visual impairment, loss of visual acuity and even blindness.
This is a very insidious disease, since in the initial stages it is almost asymptomatic. Few people turn to a specialist with pain in the corners of the eyes, but this step on the way to a specialist can save a person’s vision.
Sinusitis
This diagnosis can rival migraine in its popularity. Sinusitis is an inflammation of the sinuses; often, when the infection spreads, it turns into sinusitis. Radiating pain is very typical for this diagnosis. Discomfort may appear in various parts of the face, in particular, the patient may feel pain in the upper jaw and think that his teeth hurt. Since the eyes are located in close proximity, discomfort can easily move to their area. This is facilitated by swelling and increased pressure inherent in the active development of the inflammatory process.
This process is almost always accompanied by an increased temperature of the whole body, and the sinuses in particular. The patient feels the pain more in the corner of the eye closer to the nose. On the outside of the eye, almost no discomfort may be felt.
Neurology
Neuralgia of the facial nerve is a very scary diagnosis. In addition to severe pain, the patient is concerned about damage to the facial muscles, which are noticed by everyone around him. The symptoms here are very variable. In some patients, the clinical picture affects only the eyes (dryness, pain, spasms or lack of sensation in this area). In other patients, disturbances affect parts of the oral cavity, in particular changes in the taste of the front of the tongue.
The disease is complicated by constant relapses, and not always even the most modern treatment gives a good effect.
Ciliary knot syndrome
The inflammatory process in the area of the ciliary ganglion is also called neuralgia of the nasociliary nerve. This disease is also called Charlin's syndrome. This diagnosis is usually secondary, that is, the inflammatory process develops as a result of an existing active infection in adjacent areas. Ciliary ganglion syndrome can develop as a result of sinusitis, caries, stomatitis, trauma, as well as any other bacterial or viral infection in the body (cold).
With this disease, in addition to the traditional lacrimation, redness, and burning in the eye area, the patient also complains of the inability to fully open the eyelids. The eye seems to be constantly squinting. Corneal and conjunctival reflexes are reduced or completely absent. When trying to touch the eye, the patient experiences severe pain because the inflammation has affected the nerve - the most painful tissue of the body.
Lumps formed after blepharoplasty: why do lumps appear on the eyelids?
The recovery period after aesthetic surgery does not always go well. The process of tissue regeneration has its own characteristics and individual speed for each person.
Lumps after blepharoplasty form under or near surgical sutures, most often during correction of the lower eyelids. Typically, patients describe this problem using the words bump, pea, roller.
In fact, these can be various formations:
- Scar tissue that forms is the most common complication after blepharoplasty, but in many situations it is not a problem. Over time, it will resolve on its own.
- local swelling in the area where sutures are applied is also a non-dangerous consequence of plastic surgery.
- cyst - appears due to improper closing of the incision.
- bulging of the eyelid due to disruption of the connection of the cartilage of the ciliary edge of the eyelid with the muscle.
- lumps of fat at the site of lipofilling, which complements blepharoplasty.
- pyogenic granuloma.
Thus, we can talk about both a normal phenomenon and a developing complication. Let's talk together about the causes of each of the above-mentioned lumps and how to treat them.
Disturbance of scarring processes: the main causes and consequences of their influence
The formation of scars in the area of surgical incisions is a natural and inevitable process.
The occurrence of swelling in the first week after blepharoplasty and the presence of excess connective tissue for 2-3 months after surgery are inevitable side effects for which you must first mentally prepare and not panic. However, these processes may have individual characteristics:
- in some patients, after 10-14 days, no traces of the intervention remain on the eyelids, while in others, even after a couple of months, bumps along the seam can be clearly felt under the skin, and sometimes can be noticeable;
- the rate of resorption of seals can be different from different sides. Moreover, the scar itself is often uneven in length - the ends of the incisions, which are located in the corners of the eyes, retain their volume the longest;
- Due to natural swelling and active proliferation of connective tissue, scars can look for a long time as if they are on the outer areas of the eyelids. This is not a doctor’s mistake, but a feature of tissue healing. As the excess collagen is absorbed, the marks on the incision areas will turn into thin strips, hide in the natural folds of the skin and will not become an eyesore.
In many situations, such scar lumps occur after lower blepharoplasty. Normally, they should resolve after 12 weeks - in addition to the individual characteristics of the body, the technique of making incisions and suturing, as well as the overall scope of the operation, plays a big role. The following have negative effects on tissue regeneration processes:
- chemical and thermal burns: the influence of laser radiation, as well as irritating, drying solutions. This is why you need to forget about peeling the area around the eyes after blepharoplasty for a while;
- suppuration: the presence of an inflammatory process in the wound leads to hyperactive growth of connective tissue;
- incorrect comparison of the edges of the incision, strong skin tension and other surgeon errors when applying sutures;
- disruption of the immune system;
- genetic predisposition to hyperactive proliferation of connective tissue in response to skin injury.
We recommend: How to remove seals on the lower eyelid after blepharoplasty?
Moreover, excessive physical impact on deformed areas of the skin leads to tightening of the sutures - in particular, the habit of rubbing the eyes after sleep and active massage of the operated area. The collagen fibers of a young scar are in a chaotic order and cannot fight the stretching of the edges of the wound.
To prevent these complications, doctors apply special plasters over the sutures and strongly recommend not touching your eyelids with your hands in the first weeks after blepharoplasty: any physical impact promotes blood flow, increases the rate of collagen formation, and blocks the resorption of excess connective tissue - as a result, instead of thin threads on centuries, rough scars may remain.
If large fibrous cords begin to appear at the site of the incisions, you should contact the surgeon who performed the operation, a dermatologist or another specialist.
Don't self-medicate! The simplest advice, which often becomes difficult to implement: follow the recommendations of your surgeon and give your body time.
Usually, in the first few weeks, the doctor prescribes healing medications, then adds anti-scar ointments or hardware procedures - microcurrent therapy, lymphatic drainage.
The process is complemented by systematic examinations, and if something goes wrong, the doctor writes another prescription.
A few weeks after surgery, the doctor may decide to speed up the process of resorption of connective tissue by injecting hormonal drugs - glucocorticosteroids. In some situations, you can get by with their local application, but only after the incisions have been completely tightened.
If lumps form after blepharoplasty and do not go away 2-3 months after the operation, then the treatment method can be revised - even excision. But sometimes you need to wait a little: the natural displacement of the sutures into the folds of the skin can take a very long time due to the fact that swelling after blepharoplasty sometimes persists for up to 6 months.
Knots at the site of resorption of suture material
To connect the edges of the surgical incision in the eyelid area, safe thin threads with a round cross-section are usually used, which completely dissolve within 10-14 days. This process is impossible without the participation of the body’s immune system, which accelerates circulation at the site of the foreign body.
We recommend: What to do if ptosis appears after blepharoplasty?
The intense flow of blood and tissue fluid to the area of the suture causes local swelling, which, upon external examination and palpation, can be characterized as lumps, peas or nodes. As the threads dissolve, all these seals go away on their own. This process can be hindered by:
- slow blood circulation at the site of the surgical wound, when due to large swelling the outflow of blood through the venules and veins is complicated. Stagnation of tissue fluid occurs;
- malfunction of the immune system;
- too superficial arrangement of threads in the skin.
The last option is observed very often. In such a situation, only individual pieces of threads will dissolve, while other fragments will cut through to the surface. This situation is not a complication, since excess suture material is easily removed, and damaged skin is quickly restored. If the problem is swelling, then this is exactly the situation when a good massage will help.
It just needs to be carried out using the correct method - so as to increase the outflow of lymph and venous blood, stabilize the influx of arterial blood rich in oxygen and nutrients, and tone the tissues. The surgeon will tell you what movements should be and how long the sessions should last. In general, the threads will dissolve within 2-2.5 months.
If during this time the seals they provoke do not go away, the surgeon can make small incisions or punctures of the skin and remove the suture material, or prescribe a course of special absorbable drugs in injections.
Fat lumps
If blepharoplasty was performed together with lipofilling, then seals of various sizes may form due to the uneven distribution of transplanted fat cells, as well as if the transplant was poorly processed and lumps remain in it.
This complication is clearly visible on the lower eyelids, since the skin here is very thin and any nodule, even the smallest one, immediately comes to the surface. Over time, the lumps may resolve on their own, but may remain unchanged. There are several working methods to treat this condition:
- massage, which at an early stage of engraftment will make the seals flat and even out the surface of the skin;
- the use of fillers based on hyaluronic acid - they smooth out the boundaries of the fatty lump and temporarily make it less visible;
- repeated lipofilling to correct the poor result of the first procedure - acts in the same way as contouring with fillers;
- liposuction of excess, bulging fat cells.
In each individual case, the most appropriate option for correcting the defect that appears is identified by a plastic surgeon.
Cyst on eyelids after blepharoplasty
This seal usually forms near surgical incisions and looks like a yellow or white ball. By its design, it implies a cavity filled with liquid.
We recommend: How do scars heal after blepharoplasty?
The reason for the appearance of a cyst is improper treatment of the edges of the wound, when the skin areas are immersed into the tissue when sutures are applied.
The contents gradually accumulate, which leads to a constant increase in formation - as a result, it can grow up to 0.5 cm. The defect persists for 1 to 3 months.
At this time, you need to watch him and do nothing for now. If after 12 months the cyst does not disappear on its own, it is removed with a scalpel.
Pyogenic granuloma
This vascular neoplasm is benign in nature and develops on the mucous membrane of the eyelid in response to tissue injury. For the vessels to begin to grow abnormally, minimal microtrauma is enough, not to mention full-fledged incisions that are made at the time of blepharoplasty.
Pyogenic granuloma is round or lobular in appearance, dark red or burgundy in color, up to 2 cm in size.
Increasing in size, it can lift the skin of the eyelid and can be felt when pressed.
The time of appearance of botryomycoma is different: in some situations, the neoplasm appears a couple of days after the operation and grows quickly, in others, its growth can begin after 2-3 months.
If there is a dark red lump on the mucous membrane of the operated eyelids, there is no need to try to disguise it, apply ointments or irritate it in any other way. All efforts aimed at resolving the pea can have the opposite effect: the tumor may bleed and begin to increase in size. Eliminating such a granuloma is as easy as shelling pears.
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, it is removed surgically or with a laser. Moreover, there is no urgency in this procedure, so the surgeon will determine the time for its implementation, taking into account the condition of the operated eyelid tissues.
As you can see, there is no common cause and no universal procedures for eliminating seals on the eyelids after blepharoplasty.
It is extremely important that from an external description, even with a photo, it is not possible to identify the cause of the appearance of a nodule or lump.
Therefore, to accurately determine the problem and receive effective recommendations, you need to consult a doctor, or better yet, your surgeon who performed the operation.
responded with an error: Access Not Configured. Data API has not been used in project 268921522881 before or it is disabled. Enable it by visiting https://console.developers.google.com/apis/api/.googleapis.com/overview?project=268921522881 then retry. If you enabled this API recently, wait a few minutes for the action to propagate to our systems and retry.
Source: https://drplas.ru/blefaroplastika/oslozhneniya/pochemu-posle-blefaroplastiki-obrazovalis-shishki.html
Causes
The factors that provoke such symptoms are varied. The main ones include:
- Fatigue. In this case, the pain goes away on its own after rest. In this case, the patient does not take medications. There should also be no development of other symptoms.
- Barley. This disease is accompanied by inflammation that affects the eyelids. You can often observe that the corner of the eye becomes inflamed.
- Optical products that are not suitable for the patient. Incorrect optics lead to rapid eye fatigue, which is accompanied by pain. If you wear the wrong glasses, the edge of your eye can become very painful due to tension. In this case, you will need the help of an ophthalmologist. He must prescribe the correct optics.
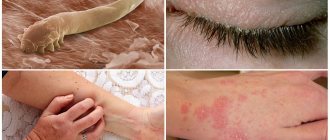
- Demodecosis. Accompanied by eye damage from pathogenic microbes (parasitic mites). If the immune system performs its functions normally, then the risk of such damage is insignificant.
- Allergic reactions. This is accompanied by redness, burning, itching of the mucous membrane. Against this background, inflammation and pain appear.
- Dacryocystitis. The pathology is associated with impaired lacrimal function. This causes inflammation and pain.
- Canaliculitis. Complication of infectious lesions of the conjunctiva. In addition, purulent discharge and sensitivity to light appear.
How to relieve inflammation at home
You can get rid of discomfort, remove swelling and other manifestations of the disease at home yourself. For conjunctivitis of an infectious nature, compresses from a decoction of elderberry or cornflower are used. If the eyelids are affected, it is enough to apply almond oil or calendula tincture to the affected area.
Chamomile decoction
For any pathological processes, chamomile decoction will be useful. It soothes delicate skin and inhibits bacterial activity.
To prepare the infusion, you need to brew 2 teaspoons of dried chamomile flowers with one glass of boiling water and let it brew.
Mint decoction
To prepare, you need to brew 2 tablespoons of dry herbs in half a liter of boiling water. It is important to boil the broth for no more than 10–15 minutes and let it cool. They moisten cotton swabs and apply to the eyes before going to bed.
Any pathological changes cannot be self-medicated, so when the first symptoms appear, it is important to seek help from a specialist.
provospalenie.ru
Redness in the corners of the eyes can not only spoil the appearance, but also cause significant discomfort, and in some cases, reduce vision.
The main causes of redness in the corners of the eyes:
— The most common cause is related to external irritants. This could be cigarette smoke, pollen, cosmetics, wind;
— Another reason may be excessive eye strain while working at a computer, watching TV for a long time or reading in poor lighting;
— Intracranial pressure also affects the condition of the eyes;
— If you use contact lenses, do not forget to take them off at night. Otherwise, you are guaranteed red corners.
How to get rid of redness in the corners of the eyes:
1. Rule out a disease that could cause the redness. If the redness of the corners has become chronic, then you need to consult an ophthalmologist. Self-medication in this case is strictly prohibited;
2. Moisturize the mucous membrane of the eyes. Periodically ventilate the room you are in, and also take moisturizing eye drops, which can be easily purchased at the pharmacy;
3. Apply cold to your eyes. Apply a handkerchief soaked in cold water or ice to your closed eye. Water will serve as an additional source of hydration, and cold will contribute to the constriction of blood vessels;
4. Do not get carried away with vasoconstrictor drugs. Frequent use of such drugs leads to chronic redness in the corners of the eyes;
5. Apply compresses. The easiest way is to brew green or black tea bags, which should be periodically applied to the eyes. Compresses made from linden, chamomile, mint or parsley are also distinguished by their effectiveness;
6. Take vitamins. The corners of the eyes may turn red due to a lack of vitamins B2 and A in the body. If you have been using vasoconstrictor drugs for a large amount of time, then you should take a course of vitamin A;
7. Normalize your rest schedule. One of the most important points. The eyes, like the entire body, should rest at least 8 hours a day during sleep. If your work involves eye strain, then take breaks for 5 minutes every 60 minutes to give your eyes a chance to relax.
Articles from this section:
nashi-glaza.ru
Redness of the outer or inner corners of the eyes in children indicates the development of inflammatory processes that are observed in various diseases.
This is a serious symptom that does not go away without timely treatment, and it is necessary to strive not only to eliminate the redness, but also to determine the disease that caused such a disorder.
Prevention
Prevention of pain in the corners of the eyes itself is impossible: the patient is required to prevent the development of the pathology that causes such a symptom.
To do this, you need to protect yourself from infectious diseases by maintaining personal hygiene (do not use other people’s cosmetics and cleansers, as well as towels, contact lenses and even eye drops).
To reduce the risk of activation of pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic microflora that causes ophthalmic diseases, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system by taking regular walks in the fresh air, maintaining an active lifestyle and eating as much healthy food as possible (fruits, vegetables, natural juices).
Redness of the inner and outer corners
The outer and inner corners of the eyes can become red for various reasons.
The outer corners most often turn red due to mechanical stress and rubbing , and symptoms such as pain and peeling of the skin may additionally appear.
In some cases, the outer corners of the eyes may become red due to exposure to allergens . Also, these areas may turn red due to certain diseases:
- ocular herpes;
- angular conjunctivitis;
- marginal blepharitis.
Note! The inner corners may turn red for the above reasons, as well as due to the development of the following diseases:
- dacryocystitis;
- canaliculitis;
- eyelashes that have grown into the skin (can only be corrected surgically).
Treatment options
There is no clear way to eliminate pain in the corners of the eyes: it all depends on the nature and severity of the lesion. In any case, the main method of treatment is conservative drug therapy.
For bacterial and viral infections, ophthalmic solutions or ointments (or a combination thereof) are used for this purpose.
This may be sofradex, ciprofloxacin, poludanum (if the disease was caused by a virus) or antibacterial drugs tobrex, gentamicin, oftadec, albucid.
Allergies that manifest themselves in this way are treated by instilling or ingesting antihistamines:
- Telfast;
- allergodil;
- erius;
- olopatadine;
- suprastin;
- azelastine.
Important! Canaculitis requires symptomatic and immediate treatment. To eliminate inflammation, use the same antibacterial and painkillers as for other eye infections.
In case of complications such as blockage of the canals, surgical intervention is required to widen them.
After such a procedure, it is also necessary to apply medications directly to the internal walls of the canals to combat bacterial and fungal pathogens and prevent their further spread.
If a patient is diagnosed with demodicosis, the disease is eliminated by applying bactericidal ointments to the edges of the eyelids and instilling antiparasitic solutions (one of them is carbachol).
The Demodex mite, which causes this pathology, mainly lives in the eyelash follicles.
Therefore, it is important to distribute the ointment along the entire eyelash line to cleanse all follicles of the pathogen. With barley, pain is a consequence of inflammatory processes, in turn they come from a granular purulent formation (or accumulations of such formations)
With barley, pain is a consequence of inflammatory processes, in turn they come from a granular purulent formation (or accumulations of such formations).
For your information! Usually, such abscesses open on their own over time, and as a treatment it is enough to instill antibacterial solutions in order to prevent and exclude damage to the conjunctiva when purulent contents get on it.
In rare cases of complications of barley, the abscess is opened by a surgeon.
There is a bubble on the white of the eye - what is it and how to treat the symptom that has arisen
Sometimes a bubble appears on the white of the eye, what it is is not entirely clear, and they are in no hurry to go to the hospital for advice on treatment for such a small thing.
Meanwhile, such growths are fairly common neoplasms, the origin of which occurs on the mucous membrane of the visual organ.
The appearance of bubbles or other foreign formations in the area of the visual organs is a reason to visit an ophthalmologist. Self-treatment can harm the condition of the eyes.
Bubble formations
Tiny blisters may appear on the mucous membrane of the eye or on the skin of the eyelid. When they are placed on the mucous membrane, serious discomfort can occur; a person experiences quite unpleasant sensations with such formations. The reasons for their occurrence vary and depend on the species.
What are the reasons for the appearance of bubbles on the organs of vision?
Problems with the eyes, expressed in the appearance of formations on their surface, can be caused by a variety of reasons, including:
- A person spends a long time outdoors, exposing his eyes to the rays of the sun;
- Respectable age. In older people, defense mechanisms weaken and processes occurring in the body slow down. The metabolism and absorption of nutrients deteriorates, which provokes an increased susceptibility to disease;
- Features of the profession when people are forced to experience the harmful influence of negative environments for a long time. The risk is considered increased for women and men who spend a lot of time in workshops, in contact with toxic fumes or small particles in the air that can cause mechanical injury;
- Hereditary factor. Such diseases are very difficult to treat; if surgically removed, their recurrence is possible;
- Living in a specific climate, where the constant air temperature is characterized as high, sandstorms often occur.
Adenoviral conjunctivitis
When the mucous membrane of the eyes becomes inflamed during pharyngitis, adenoviral conjunctivitis can occur. It is often accompanied by a significant increase in temperature. One of the manifestations of this kind of disease is the follicular appearance, in which small bubbles with transparent contents grow on the mucous membrane of the eyes.
Conjunctival cysts
Transparent, translucent formations that appear on the eyeballs or on the mucous membrane are conjunctival cysts. They can be either acquired or congenital.
Often such formations occur after eye injury, as well as due to various inflammatory diseases. If they are small in size, cysts may not cause any particular inconvenience.
Symptoms may appear subtle - for example, a feeling of sand in the eyes or excessive flow of tears.
When formed cysts grow in the eyes, pain and a feeling of fullness may appear. Vision may become less sharp. This disease must be treated surgically.
Ophthalmoherpes
In this disease, the pathogen becomes active when immunity declines. Signs of ophthalmoherpes are blisters that may appear on the cornea or on the skin of the eyelids. They are filled with a transparent secret.
If a blister bursts, it can infect healthy tissue with its contents. In this case, the disease is aggravated - photophobia, lacrimation and hyperemia of the eyeballs may appear.
If the disease develops to severe forms, blepharospasm appears, characterized by convulsive closure of the eyelids.
Delayed treatment can lead to glaucoma and cataracts. Sometimes blindness occurs.
Allergic phenomena
Cosmetics, various household products and even food can cause the appearance and development of allergies.
This often causes rashes of various types, including sometimes a blister appearing on the white of the eye, causing discomfort. Signs of allergies disappear after the cause of the unpleasant symptoms is identified and eliminated.
If the disease is neglected and treated incorrectly or not treated at all, it can become chronic. This course of eye damage is characterized by severe itching, nettle fever, and manifestations of discomfort.
Moll cyst
The cause of the disease is problems with the drainage of secretions formed in the sebaceous glands. This can happen if they are clogged. Allergies, herpes, and papillomavirus can provoke the appearance of cysts. The cyst does not pose a danger to the body, but if left untreated, its size can seriously increase. Then surgery will be required.
Cysts may resolve on their own. But they do not completely disappear, and the next time they appear again, the symptoms will be more serious.
Papillomas
Infection can occur through contact with carriers of the papilloma virus.
Viruses can be caused by a decrease in human immunity, various stresses, if a person has used antibiotic drugs for a long time, this can also cause the activation of the virus.
To cure papillomas, treatment may be prescribed using medications in the form of complex therapy and surgery.
It is not allowed to remove papillomas on the mucous membranes and eyelids on your own.
What should you do if you notice blisters on your eye?
If strange formations appear on the surface of the eyes, you should act as follows:
- First of all, visit an ophthalmologist. The earlier the diagnosis is made, the better the treatment provided;
- Strict adherence to hygiene standards is required. When washing, you should treat your visual organs as carefully as possible. To wipe your face, the towel must be individual;
- To avoid damage, do not rub your eyes too hard; you cannot remove the formations yourself. This may increase the development of the disease;
- The use of low-quality cosmetics should be avoided;
- If the presence of allergies is noted, it is necessary to exclude the effect of allergens on the body. It will be necessary to work out the food system and, if necessary, eliminate contact with pets.
Which side does it hurt on?
Pain in the corner of the eye can have a different meaning depending on which side it is concentrated on. Let's look at how the symptom manifests itself in both cases:
- Pain in the outer corner of the eye is usually only noticeable upon physical contact. That is, when you press or blink quickly, the pain will be felt significantly and sharply. Often the affected area becomes red and itchy.
- Pain in the corner of the eye near the bridge of the nose often spreads to the eyebrow, sometimes floating. Intensifies upon contact with a damaged area.
In both cases, painful sensations indicate either excessive stress or eye diseases. Prolonged pain that does not stop for several days should worry the patient. Such symptoms require a mandatory visit to an ophthalmologist.
Folk recipes
You can get rid of swelling and discomfort using traditional medicine recipes. One effective method is to use a chamomile-based decoction. To prepare, you need to take two spoons of dried flowers of this plant and brew them with 250 ml of boiling water. When the product has infused, wipe your eyes with the resulting solution.
You can also use mint infusion. To prepare it, take two tablespoons of dry mint and pour 500 ml of boiling water over them. The broth is boiled over a fire for a quarter of an hour. When it cools down, cotton pads are soaked in it and applied to the eyes before going to bed.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that when the first signs of eye inflammation appear, in particular, redness of the corners, you should seek help from an ophthalmologist. If this is not done, various complications may arise, including blindness.
Pain in the inner corners of the eyes closer to the nose
If the pain is localized closer to the nose, then this may be a sign of the following diseases:
- blepharitis;
- conjunctivitis;
- demodicosis;
- dacryocystitis;
- increased intraocular pressure.
With bacterial infection of the lacrimal canal, such symptoms develop. Herpes can affect the mucous membranes of the nose, eyes, and lips. The rash tends to cause pain. In an allergic reaction, the inner corner is initially inflamed, and then the outer corner
It is important to consider that infection can be spread into the eyes with dirty hands. Therefore, you should strictly observe the rules of personal hygiene
Treatment options
There is no clear way to eliminate pain in the corners of the eyes: it all depends on the nature and severity of the lesion. In any case, the main method of treatment is conservative drug therapy.
For bacterial and viral infections, ophthalmic solutions or ointments (or a combination thereof) are used for this purpose.
This may be sofradex, ciprofloxacin, poludanum (if the disease was caused by a virus) or antibacterial drugs tobrex, gentamicin, oftadec, albucid.
Allergies that manifest themselves in this way are treated by instilling or ingesting antihistamines:
- Telfast;
- allergodil;
- erius;
- olopatadine;
- suprastin;
- azelastine.
Important! Canaculitis requires symptomatic and immediate treatment. To eliminate inflammation, use the same antibacterial and painkillers as for other eye infections.
In case of complications such as blockage of the canals, surgical intervention is required to widen them.
After such a procedure, it is also necessary to apply medications directly to the internal walls of the canals to combat bacterial and fungal pathogens and prevent their further spread.
If a patient is diagnosed with demodicosis, the disease is eliminated by applying bactericidal ointments to the edges of the eyelids and instilling antiparasitic solutions (one of them is carbachol).
The Demodex mite, which causes this pathology, mainly lives in the eyelash follicles.
Therefore, it is important to distribute the ointment along the entire eyelash line to cleanse all follicles of the pathogen. With barley, pain is a consequence of inflammatory processes, in turn they come from a granular purulent formation (or accumulations of such formations)
With barley, pain is a consequence of inflammatory processes, in turn they come from a granular purulent formation (or accumulations of such formations).
For your information! Usually, such abscesses open on their own over time, and as a treatment it is enough to instill antibacterial solutions in order to prevent and exclude damage to the conjunctiva when purulent contents get on it.
In rare cases of complications of barley, the abscess is opened by a surgeon.
Symptoms of various diseases
Demodicosis is a disease that occurs quite often. It is a parasitic pathology, the causative agent of which is considered to be the iron mite.
Most often, this type of disease occurs in older and elderly people. It is extremely rare in children.
- redness of the skin around the eyelid;
- dryness, peeling of the skin;
- rashes in the form of a cluster of blisters or of an inflammatory nature.
Allergies are another type of disease that often causes serious harm to the skin. When an allergic reaction occurs, symptoms such as:
- redness of the skin around and in the corners of the eyes;
- peeling of the skin;
- increased lacrimation;
- itching and burning.
Hyperthyroidism is a serious disorder of the human endocrine system associated with excessive production of the hormones triiodothyronine and thyroxine. The main symptoms of this disease and differences from other diseases are the following:
- emotional tension (fear, nervousness, trembling hands);
- persistent, difficult to treat sinus tachycardia;
- limited mobility of the eyeball with possible protrusion forward;
- dry skin around the eyelids, frequent pain in the eyes, corneal erosion (there is a high probability of partial or complete loss of vision);
- frequent shortness of breath.
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism are eye irritation, dryness. They are quite pronounced and require urgent consultation with a doctor.
Main causes of irritation
Irritation under the eyes is a fairly common symptom that affects many people. There are many reasons for the appearance of irritation, let’s highlight the main ones.
- Allergic reaction.
- Dermatitis.
- Infectious diseases.
- Negative environmental impact.
- Improper skin care.
- Vitamin deficiency, dysbiosis or malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract.
Reddened and inflamed eyelid skin requires immediate treatment, as such irritation can cause quite serious discomfort.
Treatment methods for the problem
First of all, you need to consult with a specialist to determine the true cause of irritation. To do this, you need to seek advice from doctors such as an allergist, dermatologist, endocrinologist, or therapist.
After identifying the cause of irritation on the eyelids, treatment will be selected by a specialist, which will bring the best and fastest results.
Sometimes for treatment it is enough to take a course of antiallergic drugs or simply use drops for eye irritation. But sometimes itching and flaking are caused by serious disorders of the internal system of human organs, which require serious treatment.
You should never neglect such signals from our body, because they often help to quickly determine the type of disease, as well as choose the right treatment.
Below is a list of the most commonly prescribed medications when a patient presents with the above symptoms.
| Name | Description | Price |
| Bepanthen cream | Promotes active moisturizing and restoration of dry and damaged skin. | From 600 rub. |
| Cetirizine | Antiallergic drug, take 1 tablet 1 time per day. Allows you to quickly cope with an allergic reaction expressed in redness and itching in the eyelid area. | From 110 rub. |
| Loriden | Antihistamine in the form of an ointment. Relieves symptoms of itching and irritation in 30–60 minutes, effective for 24 hours. | From 330 rub. |
Help from traditional medicine
If the irritation is caused by negative environmental influences or is a consequence of the influence of household factors, you can fight the redness of the eyelids yourself using traditional medicine recipes.
There are several ways to relieve irritation; we will name the most effective of them.
A very effective way to combat fatigue, redness and irritation under the eyes are ice cubes with frozen infusions of medicinal herbs, which can always be found at your nearest pharmacy. Chamomile most effectively combats unpleasant symptoms.
For the compress you need:
- disposable bag of chamomile flowers;
- boiled water.
- Brew chamomile tea and fill an ice tray with the infusion.
- We take out an ice cube, wrap it in a disposable napkin, and apply it to the inflamed area of skin.
Non-pathological causes of redness in the corner of the eye in an adult
| There are many reasons for the development of the disease, from ordinary lack of sleep to serious illness. Inflammation can be eliminated only after the root cause of its occurrence has been determined. |
Redness of the corners of the eyes is also caused by physiological factors: stress, heavy lifting, lack of sleep, etc. If purulent discharge is observed, antibacterial treatment is prescribed. In some cases, antibiotics are prescribed. To relieve redness, use Prednisolone and Erythromycin eye drops.
Traditional medicine recipes will help eliminate inflammation:
- Prepare an infusion of chamomile; it copes well with pathogenic microorganisms. Pour boiling water over two tablespoons of dried flowers and let it brew;
- Pour water (500 milliliters) into a couple of tablespoons of dry mint and boil for fifteen minutes. Use for compresses.
In addition to diseases, an unpleasant problem can be caused by an incorrect lifestyle. Modern people cannot imagine themselves without computers; we often sit at them until the very night, straining our eyes. As a result, it is possible to develop dry eye syndrome or computer vision syndrome, which cause redness and burning of the corner of the eye, pain and other unpleasant manifestations, for example, intolerance to sunlight.
There are several types of reasons why this symptom appears:
- Mechanical irritation, for example, from dust, dirt, aerosols, smoke, foreign substances, strong winds, exposure to excessively bright light (for example, welding), prolonged eye strain, injuries;
- Physiological reasons - expansion of the blood vessels of the eye, but without any disruption of its functioning; this can happen with fatigue, drinking alcohol, severe sneezing, physical exertion, eye irritation with contact lenses or glasses if they are incorrectly selected;
- Eye pathologies - can be inflammatory or non-inflammatory in nature;
- Pathological changes in the functioning of other organs - for example, allergic diseases, diabetes mellitus, intoxication with toxic substances, hypertension, etc.
First aid before visiting a doctor
If the corners of the eyes are red , the first thing you need to do is eliminate the possible causes: stop overexertion, get rid of foreign bodies, rinse your eyes if necessary. If the redness is caused by another disease , for example, ARVI or hypertension, then you need to treat it first.
In some cases, compresses with cool water and decoctions of chamomile, mint, linden, or just a bag of green or black tea help. You can use eye drops that have a moisturizing effect, or vasoconstrictors, however, you should not get carried away with them.
In any case, it is necessary to consult a doctor for a diagnosis and properly selected treatment, since self-diagnosis may be incorrect, and many diseases have similar symptoms and can appear simultaneously.
Other reasons
List of possible causes of pain when blinking:
- Incorrectly performed vision correction. Pain in the eyeball when blinking can be caused by incorrectly selected glasses or contact lenses. With a large diopter difference between the eyes, as a rule, very severe discomfort develops. After some time, it develops into pain, which is localized in the eyeball and intensifies when blinking. And in most cases, a headache also develops. To get rid of such sensations, you should visit an ophthalmologist who will help correct the situation.
- Eye fatigue. Painful sensations when blinking are a sign of visual fatigue. This symptom especially often appears in people who spend a long time at the computer or work with papers. Visual stress is very harmful to the eyes. Dry eye syndrome is a pathology characterized by rapid drying of the mucous membranes of the eyeball. Occurs due to overwork of the visual apparatus. Complications: keratoconjunctivitis; ulcer, perforation, corneal keratinization, cataract, inflammation, blindness. To prevent the development of various eye pathologies, you should definitely take breaks and use special glasses and drops.
- Foreign bodies in the eye. When grains of sand, small debris, dust, or insects get in, a person feels not only pain when blinking, but also severe pain. It is not recommended to remove foreign bodies yourself, as you can damage the mucous membrane. It is better to immediately contact an ophthalmologist. It is imperative to visit a doctor if metal shavings or other hard objects get into your eye. The doctor will remove the object and prescribe treatment with Levomycetin, Albucid.
- Barley. This pathology is a purulent inflammation that is localized in the sebaceous gland in the lower or upper eyelid. The reason is a harmful bacterial infection. Swelling, redness, increased body temperature, and pain when blinking appear. Treatment involves the use of ointments and drops that have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties.
- Chalazion. Benign tumor on the lower and upper eyelids. Develops as a consequence of chronic inflammation of the eyelid cartilage gland. In most cases, it can only be treated surgically. The main symptom is pain when blinking, redness of the eyelid, swelling.
- Inflammation of the tissues that surround the eye. The inflammatory process that develops in the paranasal sinuses (with sinusitis, sinusitis) is also accompanied by pain when blinking. This is explained by the location of the sinuses of the nose too close to the eyes. But in this case, you should contact not an ophthalmologist, but an ENT specialist.
- Neuritis. Inflammation of the optic nerve. There are no changes in the area of the eyeball, but there is severe pain when the person blinks. It is fraught with a significant decrease in visual acuity. Requires immediate treatment.
- Canaliculitis. Inflammatory process in the area of the tear ducts. The corner of the eye hurts. Therapy involves the use of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drops.
- Furuncle. The eyelid hurts and there is redness. The eyelid is compacted, the boil looks like a cone with a purulent tip. Treatment is carried out with antibacterial drugs and ointments.
- Abscess of the century. The eyelid becomes thicker and hurts. Painful sensations can radiate to the corner of the eye, lower and upper eyelids. Swelling, redness and drooping of the upper eyelid appear. An abscess most often develops on the upper eyelid. It hurts to blink.
- Partial, complete obstruction of the lacrimal ducts. At the same time, it’s not only painful to blink. Active lacrimation and discomfort appear in the corner of the eye. It is treated surgically.
- Dacryocystitis. Inflammation of the lacrimal sac. It hurts to blink, and the pain radiates to the corner of the eye. It is treated with conservative and surgical methods.
As you can see, a symptom such as pain during blinking can be a sign of many pathologies. It is for this reason that self-medication is not necessary.
Many people begin to wash their eyes with herbal tinctures and tea. It is not prohibited. But it is better to consult a specialist to prevent the development of complications and blindness.
Many people experience pain in the corners of their eyes. Sometimes it appears when pressing or blinking. But it often takes on a permanent character. What is the cause of these unpleasant sensations? Is it possible to get rid of them?
Discomfort in the eyes
Diagnosis of pathology
First of all, the doctor conducts an external examination, which allows you to identify pustules and other pathological formations on the outside and inside of the eye. The patient must take a microflora test.
The doctor should also rule out the presence of chlamydial conjunctivitis, because it can also cause itching and plaque. For these purposes, a scraping is made and sent to the laboratory. To exclude the development of demodicosis, an examination of the eyelash and its bulb is carried out.
Treatment of eye diseases
The main directions of therapy are preventing the inflammatory process and suppressing infection. The doctor may prescribe antibiotics and combine them with anti-inflammatory drugs.
If the plaque is caused by excessive stress and fatigue, special drops are used, for example, Visin, Normax, Maxitrol, Levomycetin.
In some cases, massage of the eyelids and rinsing of the tear ducts are necessary.
If white plaque appears due to meibomite, install a solution of dicaine (0.5%) or trimecaine (3-5%) into the conjunctival sac.
Traditional methods of treatment
Such remedies cannot be used as primary therapy, but complement it well. For example, it is useful to drink a course of decoctions of plantain, St. John's wort, nettle, chamomile and elderflower.
Causes of irritation, redness and bruising in the corners of the eyes
Discomfort and unpleasant phenomena do not always indicate the presence of pathology. Both plaque and bruising, redness, and itching can occur due to external irritants. Poor-quality allergenic cosmetics, certain eye drops, prolonged wearing of contact lenses, foreign bodies, overexertion and ordinary fatigue are the main external causes.
In these cases, as a rule, no treatment is required; it is enough to take the following measures:
- eliminate the source of irritation;
- good rest;
- change the brand of cosmetics, etc.
But if there is deterioration in vision or a person has allergies, you need to consult a specialist to conduct a diagnosis, identify the exact cause and prescribe adequate treatment.
It is worth noting such a phenomenon as a crack in the corner of one eye or both. The wound may occur due to allergies due to frequent rubbing of the skin, or due to conjunctivitis.
At first glance, the crack does not pose a danger, but this is far from true, because a secondary infection can penetrate through the damage. So you need to quickly seek help from a doctor to prevent complications.
Itching, as already mentioned, can also be a symptom of conjunctivitis, but it is also characteristic of allergies. Usually it is accompanied by a runny nose, sneezing, and tearfulness. Demodectic mange should not be ruled out, although it usually occurs in people with weakened immune systems.
Those who work at a computer for a long time suffer from “dry eye syndrome”, so the appearance of irritation, itching and cracks in the corners indicate that you need to do special exercises and regularly be distracted by other activities. People who wear contact lenses and glasses should also remember that their eyes need to rest periodically.
Drooping, swollen corners of the eyes, bags and bruises
Such defects may indicate overwork, stress, or serious health problems. First, it is recommended to rest well, get enough sleep, you can take sedatives, if necessary, and take a walk.
When the work and rest schedule is normalized, but unpleasant phenomena do not go away, you need to contact a specialist. In this case, only he will be able to make a diagnosis, find out the cause and prescribe appropriate measures.
It is worth noting that drooping corners, plaque and other phenomena may be associated with age-related changes. However, hormonal imbalances and vitamin deficiencies cannot be discounted. These two conditions provoke pigmentation of the skin and the appearance of bruises.
Appearance can also deteriorate due to sudden weight loss. Problems with the heart and kidneys, exhaustion of the body after a protracted illness can also be provoking factors.
When your eye hurts, there is a bruise in the corner or other unpleasant conditions, you need to consult a doctor to rule out chronic pathologies and active inflammatory processes.
What does a wen in the corner or on the eyelid mean?
This cosmetic defect is especially common among newborns and the elderly. If in the former it is associated with a change in environment, then in the older it is usually caused by hormonal imbalances.
103583
Why does it hurt in the corner of the eye closer to the temple or nose?
Ophthalmic diseases can cause pain not only in the eyeball itself, but also in the corners of the eyes.
The reason may lie in the influence of external factors or internal processes.
Patients make a mistake when they believe that pain is associated with overwork. Pain that is localized closer to the nose or temple is usually associated with diseases. The exact cause can only be determined after a full examination.
Symptom Description
It is important to consider that pain in the corners of the eyes is not an independent pathology. Therefore, accompanying symptoms arise:. The pain may be temporary or persistent
Irregular pain may occur as a result of overwork. Irritation occurs, which is accompanied by dryness and burning. You will definitely need to consult an ophthalmologist
The pain may be temporary or persistent. Irregular pain may occur as a result of overwork. Irritation occurs, which is accompanied by dryness and burning. You will definitely need to consult an ophthalmologist.
Pain in the outer corners of the eyes closer to the temple
Pain on the external side in most cases is not associated with pathological processes. In most cases, such signs appear as a result of injury, foreign body penetration, or after excessive stress. Sometimes symptoms may indicate increased intraocular pressure.
Only a doctor can determine the exact cause after diagnosis. The main factors include:
- Overwork. Minor pain may appear on the bridge of the nose. At the same time, the eyelids turn red and itching appears. The patient needs proper rest. Then the symptoms will disappear on their own without the use of medications. When tired, dry mucous membranes are observed. To eliminate it, it is recommended to use moisturizing drops.
- Inflammatory processes. Irritation and pain in the corners causes canaliculitis. The disease affects the tear ducts. Occurs against the background of a bacterial or fungal infection. In this case, swelling of the eyelids is observed. If you press on the corners, purulent discharge will appear. The risk of infection arises when hygiene rules are not followed. At an early stage of development, antibiotics are prescribed. Severe damage will require surgery.
- Decreased protective functions of the body. This leads to parasitic infestation. For example, demodicosis. The disease occurs due to the defeat of parasitic mites.
- Conjunctivitis. Inflammation is accompanied by pronounced symptoms. The skin turns red, the sclera takes on an unhealthy color. The pain intensifies when blinking. The patient experiences a sensation of a foreign body in the eye. The disease has a bacterial and allergic form. May occur due to injury. Associated symptoms are itching and burning. Antiseptic and antiallergic drugs are prescribed for treatment.
- Myositis. This disease causes inflammation of the eye muscles. This causes swelling and pain when blinking. Especially intensifies in the corners. Severe headaches also appear. Corticosteroids are used for treatment. Treatment of severe forms will require surgery. If treatment is not carried out on time, the tissue will acquire a fibrous form.
The outer corner of the eye can be affected by herpes. Initially, itching appears, and then redness and a characteristic rash.
Pain in the inner corners of the eyes closer to the nose
If the pain is localized closer to the nose, then this may be a sign of the following diseases:
- blepharitis;
- conjunctivitis;
- demodicosis;
- dacryocystitis;
- increased intraocular pressure.
With bacterial infection of the lacrimal canal, such symptoms develop. Herpes can affect the mucous membranes of the nose, eyes, and lips. The rash tends to cause pain. In an allergic reaction, the inner corner is initially inflamed, and then the outer corner
It is important to consider that infection can be spread into the eyes with dirty hands. Therefore, you should strictly observe the rules of personal hygiene
Diagnostics
In order to determine the cause of the pain, you will need to be examined by an ophthalmologist. The doctor listens to the patient’s complaints and studies his medical history. If a visual examination fails to determine the cause, then the following additional examinations will be needed:
After making a diagnosis, the doctor prescribes drug therapy. If surgical intervention is necessary, the patient requires hospitalization.
What to take orally to reduce dry skin around the eyes
Evening primrose oil for dry skin
A study published in the international journal Cosmetic Science found that consuming evening primrose oil increased skin moisture content over a 12-week period. Evening primrose oil contains high amounts of gamma-linolenic acid (a fatty acid called essential for human health), only milk is a natural alternative to evening primrose oil. This product may offer some relief if the underlying cause of very dry skin is eczema.
Fish oil relieves dry skin around the eyes
Fish oil can also improve the appearance of dry skin by softening it. A study published in the Journal of Dermatological Science found that fish oil significantly increased water loss, increased skin hydration, and reduced skin itching over 60 days. As with any dietary supplement, consult a physician before using primrose oil and fish oil, especially if you have any health problems or are taking medications.
Treatment options
There is no clear way to eliminate pain in the corners of the eyes: it all depends on the nature and severity of the lesion. In any case, the main method of treatment is conservative drug therapy.
For bacterial and viral infections, ophthalmic solutions or ointments (or a combination thereof) are used for this purpose.
This may be sofradex, ciprofloxacin, poludanum (if the disease was caused by a virus) or antibacterial drugs tobrex, gentamicin, oftadec, albucid.
Allergies that manifest themselves in this way are treated by instilling or ingesting antihistamines:
- Telfast;
- allergodil;
- erius;
- olopatadine;
- suprastin;
- azelastine.
Important! Canaculitis requires symptomatic and immediate treatment. To eliminate inflammation, use the same antibacterial and painkillers as for other eye infections.
In case of complications such as blockage of the canals, surgical intervention is required to widen them.
After such a procedure, it is also necessary to apply medications directly to the internal walls of the canals to combat bacterial and fungal pathogens and prevent their further spread.
If a patient is diagnosed with demodicosis, the disease is eliminated by applying bactericidal ointments to the edges of the eyelids and instilling antiparasitic solutions (one of them is carbachol).
The Demodex mite, which causes this pathology, mainly lives in the eyelash follicles.
Reviews
Natalia, 45 years old I started itching a month ago, after using expensive cosmetics. I never thought that this could happen. The dermatologist at the clinic explained why the eyelids were peeling, advised me to throw away the eyelid cream, and prescribed an emollient anti-allergenic ointment. The peeling became less, but the redness went away only after a week.
Elena, 28 years old When the skin under her eyes turned red, she at first decided that it was a reaction to the cold weather. I tried to fight it by applying moisturizing baby cream, but the irritation did not go away. I went to the clinic to see a dermatologist. They took a test that showed that I have eyelash mites. She treated with sulfur ointment with antibiotics.
Tatyana, 36 years old After my family and I moved to the north, I suffer from an allergy to the cold. Every winter, my eyes hurt, water, and the skin around them peels. I save myself by simple rubbing with chamomile, compresses and masks with sea buckthorn oil. I do it in the morning, it lasts all day. I consulted with the doctor, he advised me to add antihistamines.
Treatment
There is no universal way to eliminate pain in the corners of the eyes. Treatment will depend on the cause, nature and severity of the lesion. After visiting the eye clinic, conservative drug therapy is usually prescribed.
Bacterial and viral infections are treated with ophthalmic drops and ointments or combinations thereof:
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Phloxal;
- Sofradex;
- Levomycetin;
- Tobrex;
- Gentamicin;
- Albucid;
- Vitabact;
- Oftadek.
Allergies that manifest themselves as pain in the corners of the eyes are treated with drops and oral antihistamines:
- Erius;
- Suprastin;
- Allomide;
- Azelastine;
- Telfast;
- Olopatadine.
When treating canaliculitis, pus is removed from the lacrimal canaliculi by pressing, and they are washed with antiseptic agents. It is also possible to introduce a small amount of special ointments into the cavity of the tubules.
Some causes of pain in the corners of the eyes, such as blocked canals, require surgery. After the procedure, treatment continues with ointments and drops.
In each specific case, treatment will be individual and should only be prescribed by a doctor. A competent specialist will select the most effective and safe drugs, taking into account the cause of pain.
Reference. There is no prevention of pain in the corners of the eyes itself, but it is possible to prevent the development of the pathology that causes the syndrome. To do this, you need to strengthen your immune system, protect yourself from infectious diseases and not use other people’s hygiene products (cosmetics, contact lenses, towels and even eye drops).